Abstract
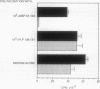
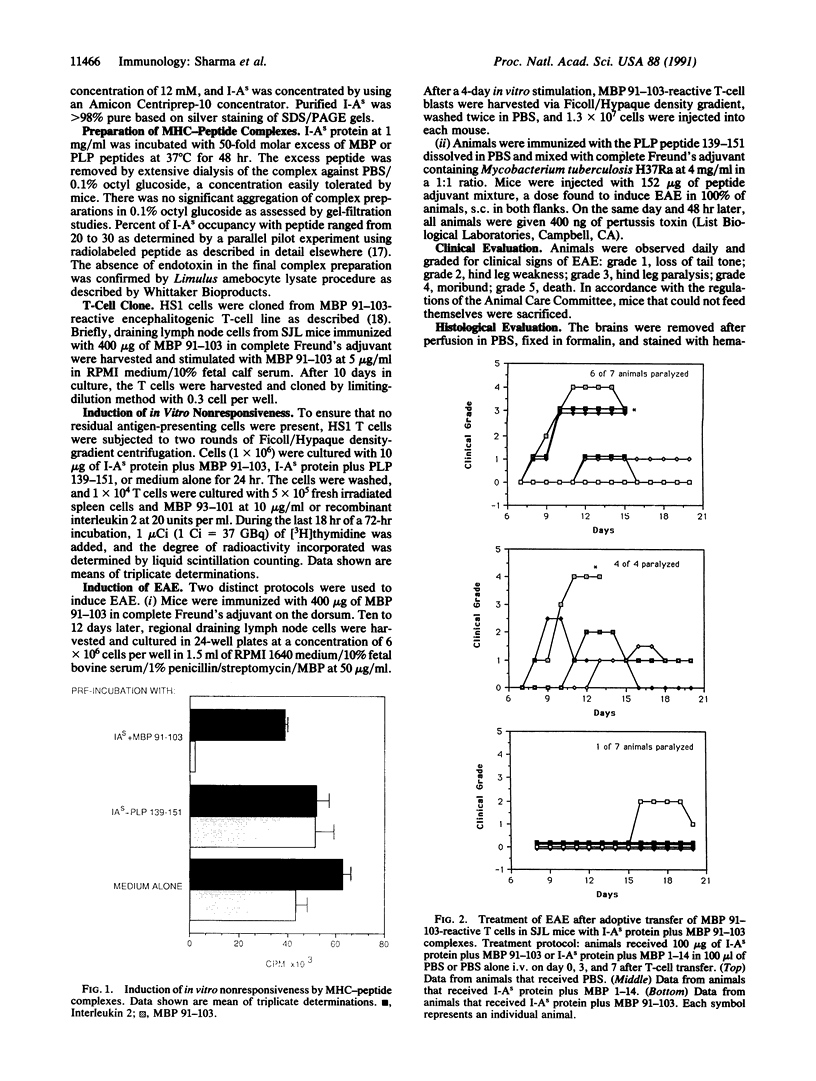
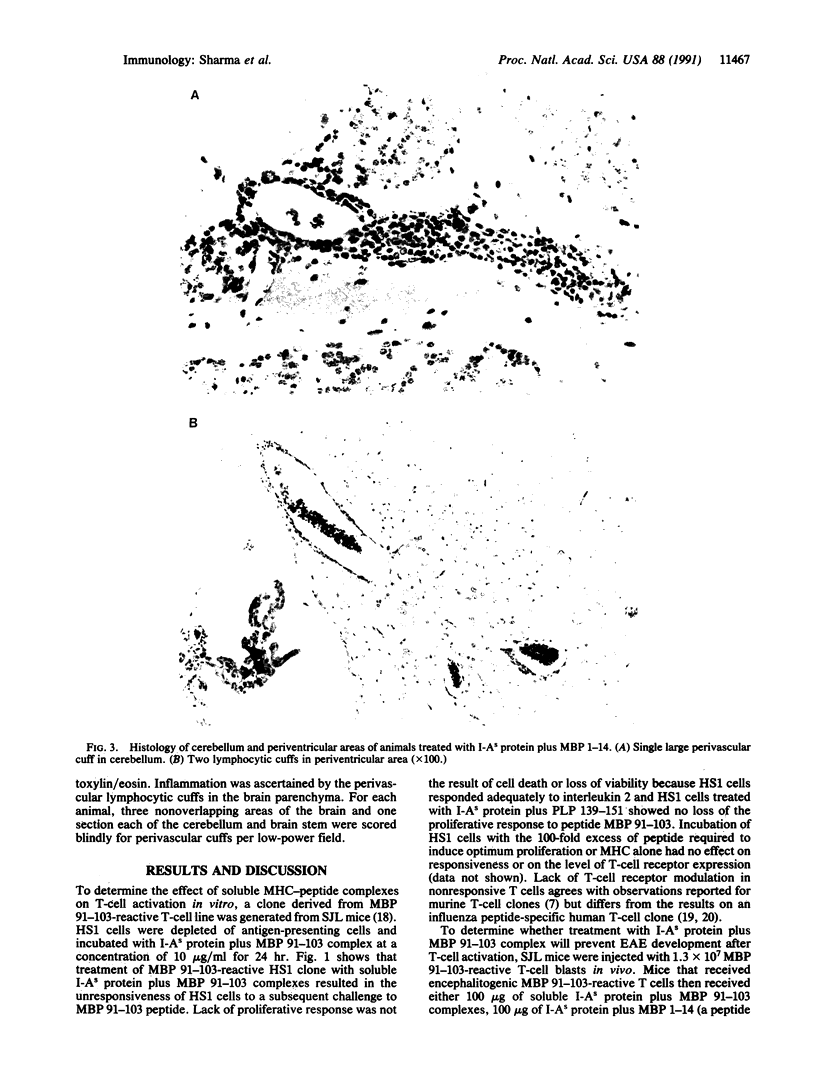
Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis is a T-cell-mediated, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II gene-linked autoimmune demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. To develop therapies that will specifically inactivate only the autoantigen-reactive T cells, mice were treated with soluble MHC class II molecules that had been complexed with encephalitogenic peptides. Intravenous injections of 300 micrograms of complexes consisting of encephalitogenic peptide 91-103 of myelin basic protein plus I-As protein on day 0, 4, and 7 were effective in preventing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Similarly, administration of 45 micrograms of I-As protein complexed to peptide 139-151 from proteolipoprotein on day 1, 4, and 7 prevented mortality and significantly reduced paralysis induced by immunization with the encephalitogenic proteolipoprotein peptide. Histological examination of sections of animal brains revealed that treatment with I-As protein plus myelin basic protein 91-103 peptide prevents the development of inflammatory lesions characteristic of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Thus, treatment with MHC-self-peptide complexes could serve as a highly specific therapeutic modality in treating autoimmune disease when the putative autoantigen and the MHC restricting elements are known.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., Mitchell D. J., Timmermann L., Wraith D. C., Tausch G. S., Waldor M. K., Zamvil S. S., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. Limited heterogeneity of T cell receptors from lymphocytes mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis allows specific immune intervention. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90558-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvord E. C., Jr, Shaw C. M., Hruby S. Myelin basic protein treatment of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in monkeys. Ann Neurol. 1979 Dec;6(6):469–473. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H., Alarcon B., Wileman T., Terhorst C. The T cell receptor/CD3 complex: a dynamic protein ensemble. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:629–662. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.003213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M. T cell receptor gene diversity and selection. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:475–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallis R. J., Raine C. S., McFarlin D. E. Chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in SJL mice following the adoptive transfer of an epitope-specific T cell line. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Apr;22(2):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz R. B., Chou C. H., McFarlin D. E. Relapsing murine experimental allergic encephalomyelitis induced by myelin basic protein. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1024–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn P., Linington C. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of autoimmune demyelination in the central nervous system. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1989;4(4):367–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Duby A. D., Lee S. J., Benjamin D., Seidman J. G., Weiner H. L. Oligoclonal T lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1313–1322. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell M. D., Winters S. T., Olee T., Powell H. C., Carlo D. J., Brostoff S. W. Vaccination against experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with T cell receptor peptides. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):668–670. doi: 10.1126/science.2814489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Antigen presentation by chemically modified splenocytes induces antigen-specific T cell unresponsiveness in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):302–319. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. K., Tan L. J., Dal Canto M. C., Tuohy V. K., Lu Z. J., Trotter J. L., Miller S. D. Inhibition of murine relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by immune tolerance to proteolipid protein and its encephalitogenic peptides. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):909–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Skidmore B. J., Green N., Chiller J. M., Feldmann M. Induction of tolerance in influenza virus-immune T lymphocyte clones with synthetic peptides of influenza hemagglutinin. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1434–1447. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse A. W., Mor F., Karin N., Cohen I. R. Control of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by T cells responding to activated T cells. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):820–822. doi: 10.1126/science.2471264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The T cell receptor. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1073–1079. doi: 10.1126/science.3317824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Howell M. D., Jaraquemada D., Flerlage M., Richert J., Brostoff S., Long E. O., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. A myelin basic protein peptide is recognized by cytotoxic T cells in the context of four HLA-DR types associated with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):19–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. D., Wetzig R. P., Claman H. N. The induction of cell-mediated immunity and tolerance with protein antigens coupled to syngeneic lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):758–773. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtarian F., McFarlin D. E., Raine C. S. Adoptive transfer of myelin basic protein-sensitized T cells produces chronic relapsing demyelinating disease in mice. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):356–358. doi: 10.1038/309356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller D. L., Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Clonal expansion versus functional clonal inactivation: a costimulatory signalling pathway determines the outcome of T cell antigen receptor occupancy. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:445–480. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag B., Deshpande S. V., Clark B. R. Novel methods to rapidly and sensitively analyze antigenic peptide binding to MHC class II molecules. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Aug 28;142(1):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90297-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quill H., Schwartz R. H. Stimulation of normal inducer T cell clones with antigen presented by purified Ia molecules in planar lipid membranes: specific induction of a long-lived state of proliferative nonresponsiveness. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3704–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Sinha A. A., Mitchell D. J., Zamvil S. S., Rothbard J. B., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. Involvement of distinct murine T-cell receptors in the autoimmune encephalitogenic response to nested epitopes of myelin basic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8608–8612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. A cell culture model for T lymphocyte clonal anergy. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1349–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.2113314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriram S., Schwartz G., Steinman L. Administration of myelin basic protein-coupled spleen cells prevents experimental allergic encephalitis. Cell Immunol. 1983 Feb 1;75(2):378–382. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriram S., Steinman L. Anti I-A antibody suppresses active encephalomyelitis: treatment model for diseases linked to IR genes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1362–1367. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J., Sriram S., Rassenti L., Chou C. H., Fritz R. B., Steinman L. Characterization of T cell lines and clones from SJL/J and (BALB/c x SJL/J)F1 mice specific for myelin basic protein. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2322–2327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuohy V. K., Lu Z., Sobel R. A., Laursen R. A., Lees M. B. Identification of an encephalitogenic determinant of myelin proteolipid protein for SJL mice. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1523–1527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbark A. A., Hashim G., Offner H. Immunization with a synthetic T-cell receptor V-region peptide protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):541–544. doi: 10.1038/341541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., Smilek D. E., Mitchell D. J., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. Antigen recognition in autoimmune encephalomyelitis and the potential for peptide-mediated immunotherapy. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Moore A. C., Kitamura K., Steinman L., Rothbard J. B. T-cell epitope of the autoantigen myelin basic protein that induces encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):258–260. doi: 10.1038/324258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Nelson P. A., Mitchell D. J., Knobler R. L., Fritz R. B., Steinman L. Encephalitogenic T cell clones specific for myelin basic protein. An unusual bias in antigen recognition. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2107–2124. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Steinman L. The T lymphocyte in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:579–621. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S., Nelson P., Trotter J., Mitchell D., Knobler R., Fritz R., Steinman L. T-cell clones specific for myelin basic protein induce chronic relapsing paralysis and demyelination. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):355–358. doi: 10.1038/317355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanders E. D., Lamb J. R., Feldmann M., Green N., Beverley P. C. Tolerance of T-cell clones is associated with membrane antigen changes. Nature. 1983 Jun 16;303(5918):625–627. doi: 10.1038/303625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]