Abstract
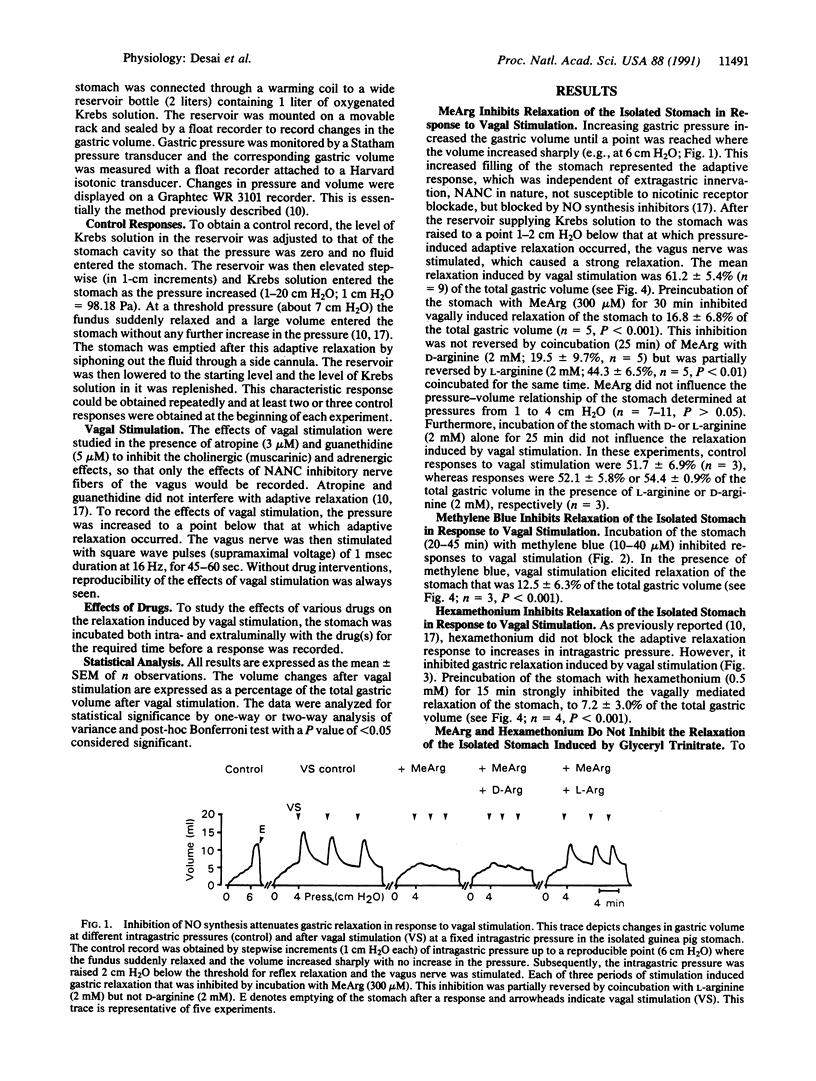
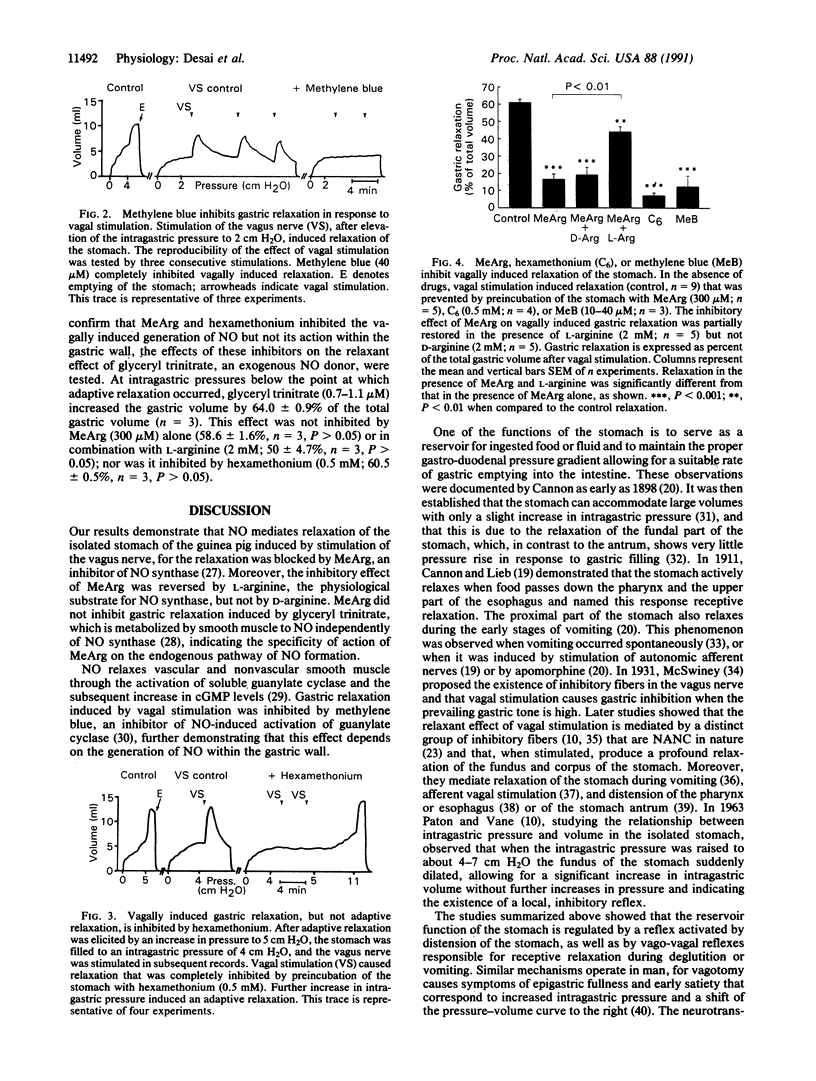
Here we show that the relaxation induced by stimulation of the vagus nerve in the presence of cholinergic (muscarinic) and adrenergic blockade in the isolated stomach of the guinea pig is mediated by nitric oxide (NO). This is substantiated by inhibition of vagal relaxation by NG-monomethyl-L-arginine, an inhibitor of NO synthesis. The effect of NG-monomethyl-L-arginine was partially reversed by coincubation with L-arginine but not with D-arginine. NO activates soluble guanylate cyclase, and relaxation of the stomach induced by vagal stimulation was prevented by an inhibitor of soluble guanylate cyclase, methylene blue, further supporting our conclusions. The relaxant effect of vagal stimulation was also ablated by hexamethonium, an inhibitor of ganglionic nicotinic receptors, thereby showing that ganglionic transmission did not rely on NO, through its release from preganglionic neurons. However, hexamethonium did not inhibit the gastric relaxation brought about by increasing the intragastric pressure, which is also mediated by NO as previously described by us. The selective inhibition by hexamethonium of only the vagally mediated relaxation but not of the pressure-induced relaxation of the stomach indicates the existence of at least two separate neuronal pathways able to generate NO and bring about gastric accommodation of food or fluid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamsson H., Jansson G. Elicitation of reflex vagal relaxation of the stomach from pharynx and esophagus in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Sep-Oct;77(1):172–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson H., Jansson G., Martinson J. Vagal relaxation of the stomach induced by apomorphine in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Jul;88(3):296–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson H., Jansson G. Vago-vagal gastro-gastric relaxation in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Jul;88(3):289–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson H. Non-adrenergic non-cholinergic nervous control of gastrointestinal motility patterns. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1986 Apr;280(2 Suppl):50–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson H. Studies on the inhibitory nervous control of gastric motility. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1973;390:1–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aune S. Intragastric pressure after vagotomy in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1969;4(5):447–452. doi: 10.3109/00365526909180631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K., Calamai F., Staderini G., Susini T. Gastric motor responses elicited by vagal stimulation and purine compounds in the atropine-treated rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1157–1166. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bogers J. J., Bult H., De Man J. G., Oosterbosch L., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Release of nitric oxide upon stimulation of nonadrenergic noncholinergic nerves in the rat gastric fundus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):441–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bult H., De Man J. G., Herman A. G., van Maercke Y. M. Evidence for nitric oxide as mediator of non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxations induced by ATP and GABA in the canine gut. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):434–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12191.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bult H., Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Jordaens F. H., Van Maercke Y. M., Herman A. G. Nitric oxide as an inhibitory non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmitter. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):346–347. doi: 10.1038/345346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Sep;24(3):509–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. J., Fung H. L. Identification of the subcellular site for nitroglycerin metabolism to nitric oxide in bovine coronary smooth muscle cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):614–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato M., De Beurme F. A., Lefebvre R. A. Comparison of the effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurone stimulation in the cat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 26;152(1-2):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90837-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beurme F. A., Lefebvre R. A. Influence of alpha-chymotrypsin and trypsin on the non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation in the rat gastric fundus. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 May;91(1):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai K. M., Sessa W. C., Vane J. R. Involvement of nitric oxide in the reflex relaxation of the stomach to accommodate food or fluid. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):477–479. doi: 10.1038/351477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrenkrug J., Haglund U., Jodal M., Lundgren O., Olbe L., de Muckadell O. B. Nervous release of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the gastrointestinal tract of cats: possible physiological implications. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:291–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A. Control of gastrointestinal motility by peptides: old peptides, new tricks--new peptides, old tricks. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1989 Jun;18(2):163–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Charles S. L., Chess-Williams R. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release on activation of NMDA receptors suggests role as intercellular messenger in the brain. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):385–388. doi: 10.1038/336385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Cable M. B., Said S. I., Makhlouf G. M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide as a neural mediator of gastric relaxation. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):G73–G78. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.1.G73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope B. T., Michael G. J., Knigge K. M., Vincent S. R. Neuronal NADPH diaphorase is a nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2811–2814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Heme-dependent activation of soluble guanylate cyclase by nitric oxide: regulation of enzyme activity by porphyrins and metalloporphyrins. Semin Hematol. 1989 Jan;26(1):63–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. G., Rand M. J. Nitric oxide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mediate non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory transmission to smooth muscle of the rat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 4;191(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94162-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden K., Holden W. S. The act of vomiting in man. Gut. 1969 Mar;10(3):173–179. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.3.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINSON J. THE EFFECT OF GRADED STIMULATION OF EFFERENT VAGAL NERVE FIBRES ON GASTRIC MOTILITY. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Nov;62:256–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb03972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson J. Vagal relaxation of the stomach. Experimental re-investigation of the concept of the transmission mechanism. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Aug;64(4):453–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawe G. M., Schemann M., Wood J. D., Gershon M. D. Immunocytochemical analysis of potential neurotransmitters present in the myenteric plexus and muscular layers of the corpus of the guinea pig stomach. Anat Rec. 1989 Jul;224(3):431–442. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092240312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukawa K., Vincent S. R., McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G. Distribution of reduced-nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide-phosphate diaphorase-positive cells and fibers in the cat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jan 8;279(2):281–311. doi: 10.1002/cne.902790210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Hibbs J. B., Jr Role of nitric oxide synthesis in macrophage antimicrobial activity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90079-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohga A., Nakazato Y., Saito K. Considerations of the efferent nervous mechanism of the vago-vagal reflex relaxation of the stomach in the dog. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1970 Mar;20(1):116–130. doi: 10.1254/jjp.20.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D., VANE J. R. Analysis of he responses of the isolated stomach to electrical stimulation and to drugs. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165:10–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. A specific inhibitor of nitric oxide formation from L-arginine attenuates endothelium-dependent relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):418–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N., Baba H., Okamura T. Role of nitric oxide in non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic nerve-mediated relaxation in dog duodenal longitudinal muscle strips. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;53(2):281–284. doi: 10.1254/jjp.53.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R., Anggård E. E., Botting R. M. Regulatory functions of the vascular endothelium. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 5;323(1):27–36. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007053230106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Cyclic GMP synthesis and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Sep;39(3):163–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



