Abstract
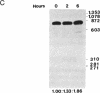
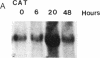
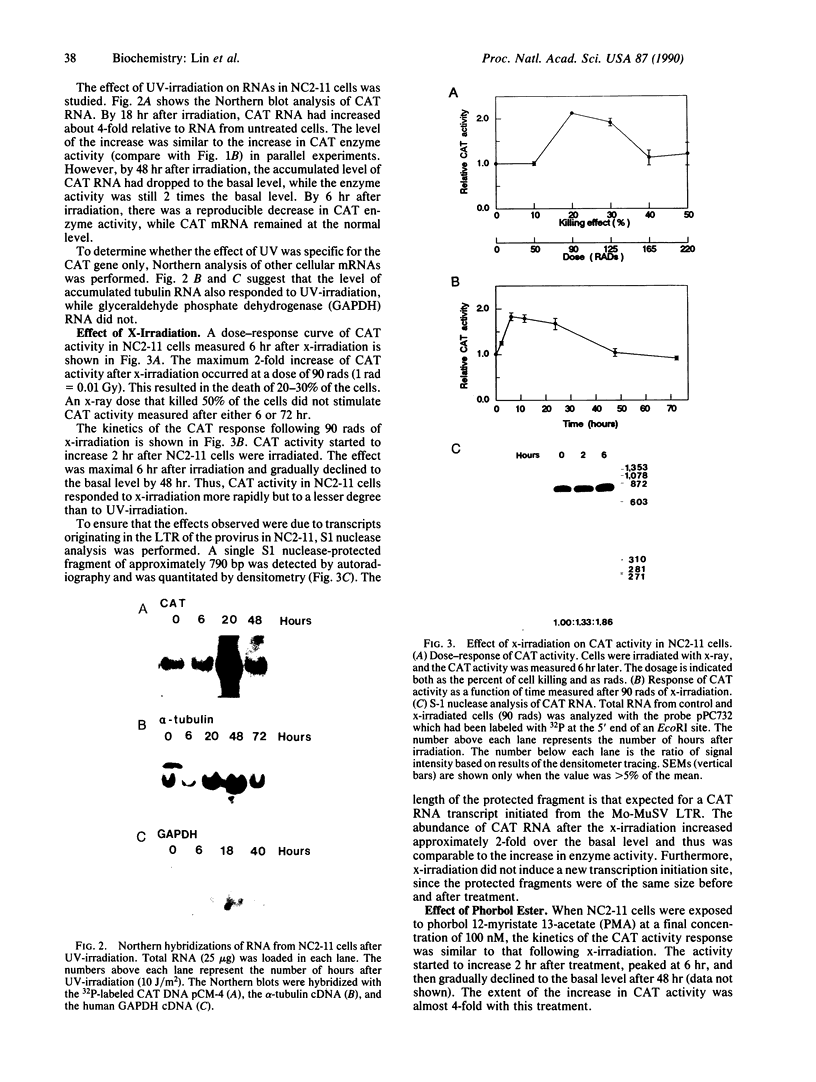
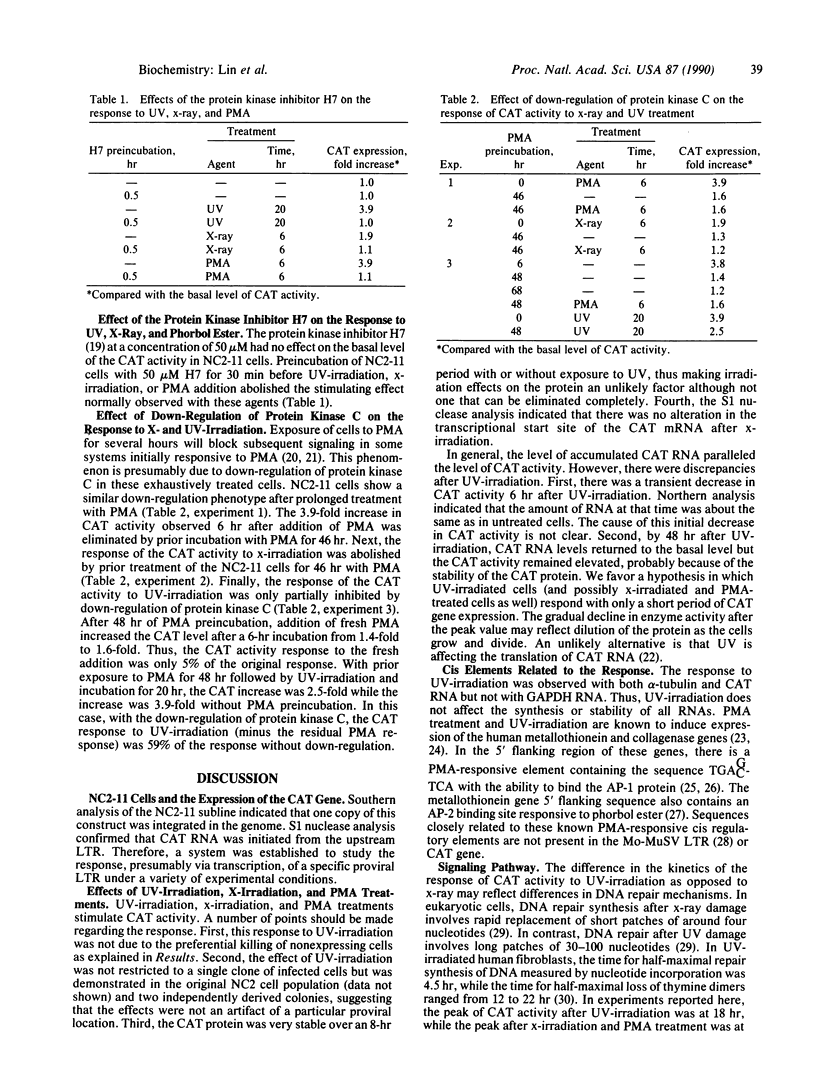
The long terminal repeat (LTR) of Moloney murine sarcoma virus (Mo-MuSV) was used as a model system to study the stress response of mammalian cells to physical carcinogens. The chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene was inserted between two Mo-MuSV LTRs, and the LTR-CAT-LTR construct was used for virus production and was integrated into the genome of NIH 3T3 cells in the proviral form. This construct was used to assure that the integrated CAT gene was driven by the promoter of the LTR. Expression of the CAT gene was stimulated 4-fold by UV irradiation, and the peak of activity was observed at 18 hr. In contrast, stimulation of the CAT expression after x-irradiation was 2-fold and occurred at 6 hr. Phorbol myristate acetate also stimulated CAT activity 4-fold with a peak at 6 hr. Down-regulation of protein kinase C blocked totally the response to x-irradiation but only partially the response to UV. The protein kinase inhibitor H7 blocked the response to treatment by UV, x-ray, and phorbol ester.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Pöting A., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Schorpp M., Herrlich P. Induction of metallothionein and other mRNA species by carcinogens and tumor promoters in primary human skin fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1760–1766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augenlicht L. H., Halsey H. Expression of a mouse long terminal repeat is cell cycle-linked. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1946–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borner C., Eppenberger U., Wyss R., Fabbro D. Continuous synthesis of two protein-kinase-C-related proteins after down-regulation by phorbol esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close T. J., Rodriguez R. L. Construction and characterization of the chloramphenicol-resistance gene cartridge: a new approach to the transcriptional mapping of extrachromosomal elements. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan N. J., Dobner P. R., Fuchs E. V., Cleveland D. W. Expression of human alpha-tubulin genes: interspecies conservation of 3' untranslated regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1738–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., McClements W. L., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequences of integrated Moloney sarcoma provirus long terminal repeats and their host and viral junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehmann U. K., Cook K. H., Friedberg E. C. The kinetics of thymine dimer excision in ultraviolet-irradiated human cells. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):249–264. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85487-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. I., Brewer J. M. The inactivation of yeast enolase by 2,3-butanedione. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giantini M., Shatkin A. J. Stimulation of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase mRNA translation by reovirus capsid polypeptide sigma 3 in cotransfected COS cells. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2415–2421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2415-2421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawalt P. C., Cooper P. K., Ganesan A. K., Smith C. A. DNA repair in bacteria and mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Mallick U., Pöting A., Hieber L., Lücke-Huhle C., Schorpp M. The mammalian genetic stress response. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1986;25:485–504. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(86)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. D., Valandra G., Roderiquez G., Bushar G., Giri C., Norcross M. A. Phorbol ester enhances human immunodeficiency virus-promoted gene expression and acts on a repeated 10-base-pair functional enhancer element. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3759–3766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschmeier P., Gattoni-Celli S., Dina D., Weinstein I. B. Carcinogen- and radiation-transformed C3H 10T1/2 cells contain RNAs homologous to the long terminal repeat sequence of a murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2773–2777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B., Cooper H. L., Sando J. J. Decrease in cytosolic calcium/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity following phorbol ester treatment of EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13193–13196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson M. N., Karchesy J. J., Deeney A. O., Deinzer M. L., Beaudreau G. S. Induction of endogenous avian tumor virus gene expression by pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Chem Biol Interact. 1984 May;49(3):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(84)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins A. S., Kirschmeier P. T., Gattoni-Celli S., Weinstein I. B. Design of a retrovirus-derived vector for expression and transduction of exogenous genes in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1123–1132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rascati R. J., McNeely M. Induction of retrovirus gene expression by aflatoxin B1 and 2-acetylaminofluorene. Mutat Res. 1983 Dec;122(3-4):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(83)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronai Z. A., Okin E., Weinstein I. B. Ultraviolet light induces the expression of oncogenes in rat fibroblast and human keratinocyte cells. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerie K., Delers A., Bruck C., Thiriart C., Rosenberg H., Debouck C., Rosenberg M. Activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by DNA damage in human cells. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):78–81. doi: 10.1038/333078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Friis R. R., Katz E., Vogt P. K. Induction of avian tumor viruses in normal cells by physical and chemical carcinogens. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):920–938. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]