Abstract
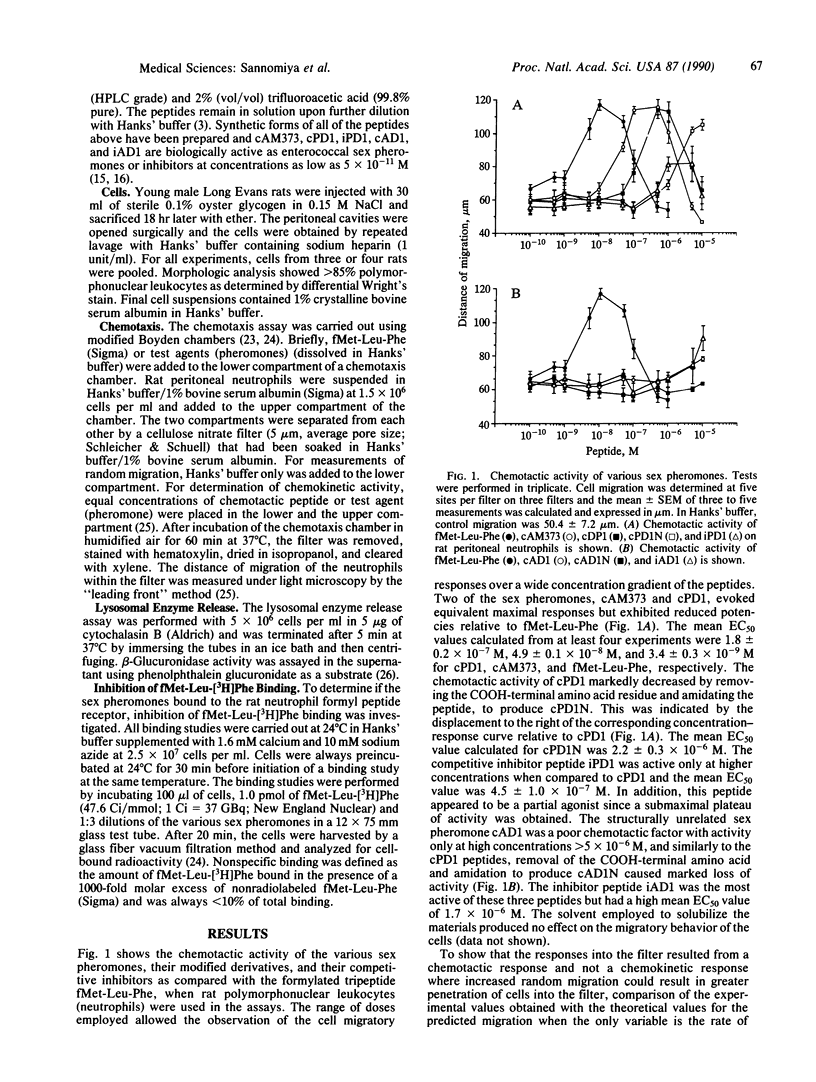
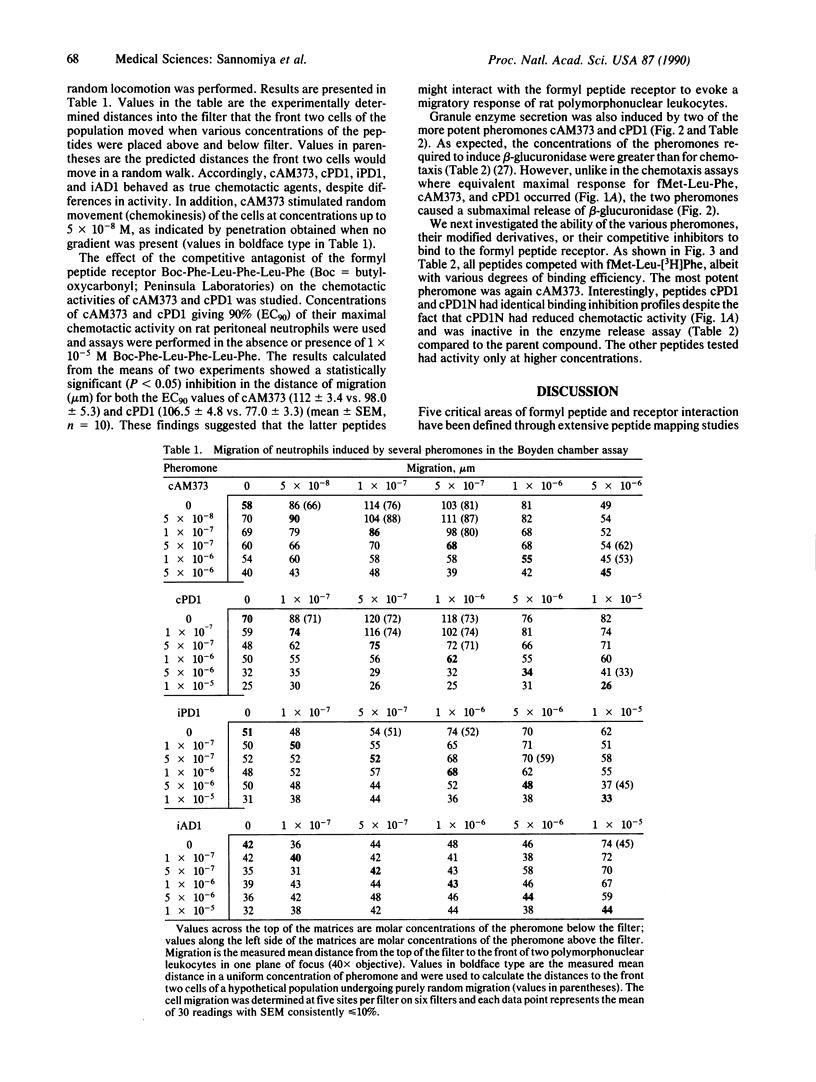
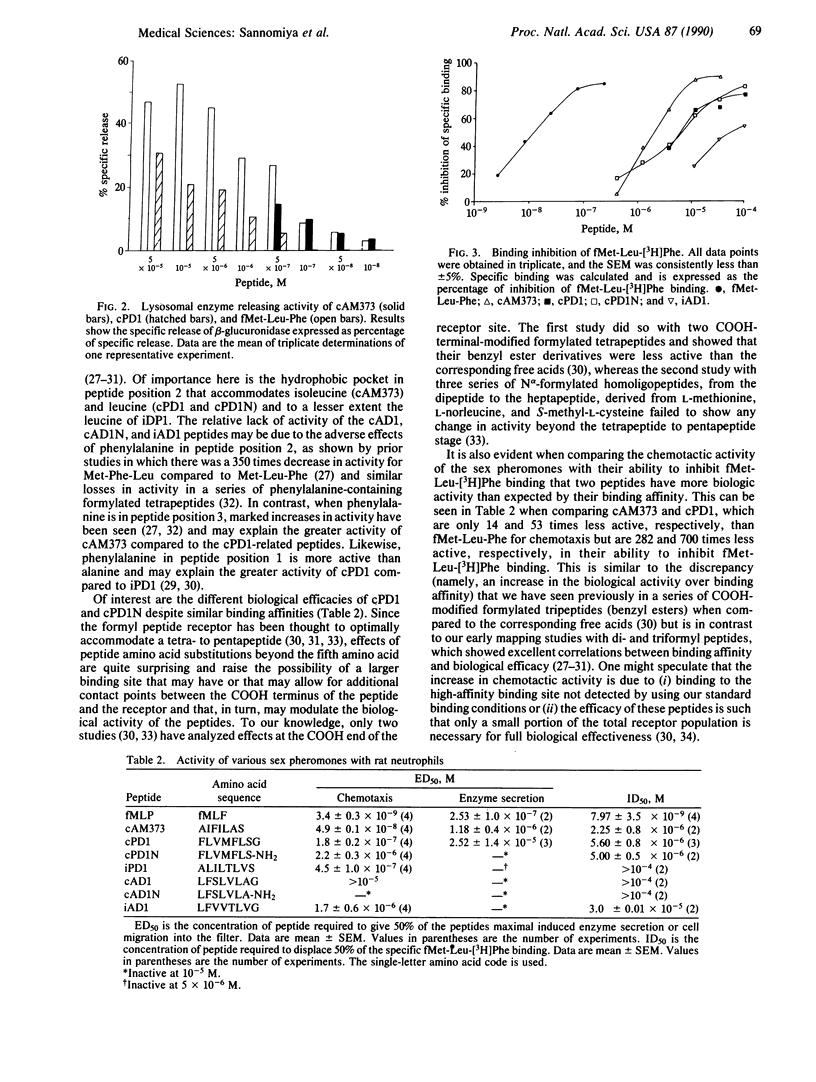
Bacteria produce a heterogeneous mixture of neutrophil chemotactic agents in culture filtrates. Formylmethionyl peptides have been shown to comprise a significant portion of the chemotactic activity in bacterial culture filtrates; however, not all of the chemotactic agents in bacterial culture filtrates are formylated peptides. To examine whether nonformylated peptides derived from bacteria could act as chemotactic agents, we studied several nonformylated hepta- and octapeptide Enterococcus faecalis-derived sex pheromones, their modified derivatives, and their competitive inhibitors for activation of rat peritoneal neutrophils. Several of these peptides, in particular cAM373 and cPD1, proved to be potent chemotactic agents in submicromolar concentrations as well as inducers of lysosomal granule enzyme secretion. Moreover, the more biologically active peptides were able to compete with fMet-Leu-[3H]Phe for binding to the formyl peptide receptor. These studies demonstrate that the formylmethionyl moiety may be an absolute requirement only for the binding of di- and tripeptides to the formyl peptide receptor. Larger peptides that may have or that may allow for additional contact points between the peptide and receptor may require N-formylation only relatively. Indeed, by removing this structural restraint, the formyl peptide receptor may interact with an unlimited number of peptide fragments of both infectious and host origins to then modulate neutrophil responses to infection and inflammation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker E. L. A multifunctional receptor on the neutrophil for synthetic chemotactic oligopeptides. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Dec;26(Suppl):701–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H. Mitochondrial N-formylmethionyl proteins as chemoattractants for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):264–275. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Weaver K. E. Sex pheromones and plasmid transfer in Enterococcus faecalis. Plasmid. 1989 May;21(3):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ember J. A., Hugli T. E. Characterization of the human neutrophil response to sex pheromones from Streptococcus faecalis. Am J Pathol. 1989 Apr;134(4):797–805. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltner D. E., Marasco W. A. Regulation of formyl peptide receptor binding to rabbit neutrophil plasma membranes. Use of monovalent cations, guanine nucleotides, and bacterial toxins to discriminate among different states of the receptor. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3963–3970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer R. J., Day A. R., Muthukumaraswamy N., Pinon D., Wu A., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Formyl peptide chemoattractants: a model of the receptor on rabbit neutrophils. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 19;21(2):257–263. doi: 10.1021/bi00531a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer R. J., Day A. R., Radding J. A., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Further studies on the structural requirements for synthetic peptide chemoattractants. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2404–2410. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janatova J. C3, C5 components and C3a, C4a, and C5a fragments of the complement system. Methods Enzymol. 1988;162:579–625. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)62104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Fantone J. C., Freer R. J., Ward P. A. Characterization of the rat neutrophil formyl peptide chemotaxis receptor. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jun;111(3):273–281. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Phan S. H., Krutzsch H., Showell H. J., Feltner D. E., Nairn R., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Purification and identification of formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine as the major peptide neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5430–5439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Substance P binds to the formylpeptide chemotaxis receptor on the rabbit neutrophil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1065–1072. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90727-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake Y., Yasuhara T., Fukui K., Suginaka H., Nakajima T., Moriyama T. Purification and characterization of neutrophil chemotactic factors of Streptococcus sanguis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 29;758(2):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Sakagami Y., Narita M., Isogai A., Fujino M., Kitada C., Craig R. A., Clewell D. B., Suzuki A. Isolation and structure of the bacterial sex pheromone, cAD1, that induces plasmid transfer in Streptococcus faecalis. FEBS Lett. 1984 Dec 3;178(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Tanaka H., Sakagami Y., Isogai A., Fujino M., Kitada C., Clewell D. B., Suzuki A. Isolation and structure of the sex pheromone inhibitor, iPD1, excreted by Streptococcus faecalis donor strains harboring plasmid pPD1. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1747–1749. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1747-1749.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Tanaka H., Sakagami Y., Isogai A., Fujino M., Kitada C., White B. A., An F. Y., Clewell D. B., Suzuki A. Isolation and structure of the Streptococcus faecalis sex pheromone, cAM373. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81342-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J., Wilkinson S., Cuatrecasas P. Receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of 125I-chemotactic peptide by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10700–10706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rot A., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Leonard E. J. A series of six ligands for the human formyl peptide receptor: tetrapeptides with high chemotactic potency and efficacy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7967–7971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rot A., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Leonard E. J. A series of six ligands for the human formyl peptide receptor: tetrapeptides with high chemotactic potency and efficacy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7967–7971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Showell H. V., Corcoran B. A., Ward P. A., Smith E., Becker E. L. The isolation and partial characterization of neutrophil chemotactic factors from Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1831–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solymossy M., Nagy Z., Antoni F., Szollár L. Ethanol-soluble substances isolated from Escherichia coli culture filtrate induce polymorphonuclear chemotaxis. Acta Microbiol Hung. 1984;31(4):345–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Mori M., Sakagami Y., Isogai A., Fujino M., Kitada C., Craig R. A., Clewell D. B. Isolation and structure of bacterial sex pheromone, cPD1. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):849–850. doi: 10.1126/science.6436978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. J. A simple multiple chamber apparatus for measuring chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes utilizing centrifugation of the chambers before incubation. J Immunol Methods. 1977;16(4):385–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(97)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Turner S. R., Lynn W. S. New aspects of chemotaxis. Specific target-cell attraction by lipid and lipoprotein fractions of Escherichia coli chemotactic factor. Am J Pathol. 1975 Nov;81(2):401–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo C., Bonora G. M., Showell H., Freer R. J., Becker E. L. Structural requirements for formyl homooligopeptide chemoattractants. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 14;23(4):698–704. doi: 10.1021/bi00299a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner S. R., Campbell J. A., Lynn W. S. Polymorphonulcear leukocyte chemotaxis toward oxidized lipid components of cell membranes. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1437–1441. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Lepow I. H., Newman L. J. Bacterial factors chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1968 Apr;52(4):725–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



