Significance
Timing, extent, and impacts of preindustrial agricultural expansion are uncertain, yet crucial for understanding the role of humans in the Earth’s environmental history. The buildup of northern peatlands, initiated after ice-age conditions, was a major carbon sink and could have compensated large CO2 emissions from land use, given timing matches. We present observation- and model-based reconstructions of past peatland carbon and land-use CO2 emission estimates based on all published scenarios. Our analyses of the terrestrial carbon balance reveal a large nonpeatland land carbon source after the Mid-Holocene climate optimum, not explained by land use, and we find that previously suggested links between CO2 and population and land-use history are not supported.
Keywords: carbon cycle, Anthropocene, agriculture, peatland, ice core
Abstract
CO2 emissions from preindustrial land-use change (LUC) are subject to large uncertainties. Although atmospheric CO2 records suggest only a small land carbon (C) source since 5,000 y before present (5 kyBP), the concurrent C sink by peat buildup could mask large early LUC emissions. Here, we combine updated continuous peat C reconstructions with the land C balance inferred from double deconvolution analyses of atmospheric CO2 and C at different temporal scales to investigate the terrestrial C budget of the Holocene and the last millennium and constrain LUC emissions. LUC emissions are estimated with transient model simulations for diverging published scenarios of LU area change and shifting cultivation. Our results reveal a large terrestrial nonpeatland C source after the Mid-Holocene (66 25 PgC at 7–5 kyBP and 115 27 PgC at 5–3 kyBP). Despite high simulated per-capita CO2 emissions from LUC in early phases of agricultural development, humans emerge as a driver with dominant global C cycle impacts only in the most recent three millennia. Sole anthropogenic causes for particular variations in the CO2 record (20 ppm rise after 7 kyBP and 10 ppm fall between 1500 CE and 1600 CE) are not supported. This analysis puts a strong constraint on preindustrial vs. industrial-era LUC emissions and suggests that upper-end scenarios for the extent of agricultural expansion before 1850 CE are not compatible with the C budget thereafter.
The Earth’s functioning is now so significantly affected by human activities that their impacts will leave long-lasting fingerprints in environmental records. This has motivated the definition of a new, human-dominated geological epoch—the Anthropocene (1, 2). However, human impacts on the Earth’s environmental history throughout the preindustrial Holocene are less clear. Although a causal link between anthropogenic greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and the rapid rise in their concentrations since industrialization is unequivocal, CO2 and CH4 concentrations already exhibited a particular, albeit slow and not synchronous increase millennia earlier. This may give rise to the possibility of far-reaching global environmental change induced by early agriculture (3). Similarly, variations in atmospheric CO2 during the last millennium have been linked to agricultural expansion and collapse (2). However, any association between a particular change in the GHG records and a coincidental continental or global socio-economic change hinges on a causal relationship between the two and on the plausibility of bottom–up estimates to imply a sufficient impact on atmospheric GHG concentrations.
In all cases where such a connection has been claimed, causality is strongly debated (4–8). For example, the link between the particular CO2 increase after 7 kyBP and the Neolithic Revolution is motivated by a multitude of local-scale paleo-ecological and archaeological archives documenting an early onset of a human influence on the landscape with land clearance impacts on vegetation openness and thus CO2 emissions even at low population densities (3, 9). However, terrestrial carbon (C)-cycle modeling studies have in general not supported this hypothesis and simulated CO2 emissions from anthropogenic land-use change appear to be too late and insufficient in magnitude to explain the timing and magnitude of the 20-ppm CO2 increase after 7 kyBP (6, 7). In addition, the total terrestrial C balance, derived from the measured parallel evolution of atmospheric CO2 and its isotopic signature (C), suggests a small reduction of only 36 37 PgC since 5 kyBP (10). Further, an ocean C-cycle modeling study (11) shows that the Holocene (since 11.7 kyBP) CO2 and C evolutions are quantitatively explained by the combination of the reconstructed terrestrial C balance (10) and ocean C-cycle changes after the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) with delayed effects during the Holocene, associated with terrestrial carbon changes and the carbonate compensation mechanism (4, 11, 12), sea level rise, and coral reef buildup (13, 14).
However, two factors have rendered previous analyses of the terrestrial carbon budget and the quantification of its individual components inconclusive. First, differing assumptions regarding the per-capita land requirement for the back projection of agricultural areas based on population numbers and hence vastly diverging bottom–up reconstructions of agricultural areas since the Neolithic Revolution imply a particularly large range of published estimates for preindustrial CO2 emissions from land-use change (6–8). Second, although the total terrestrial C balance reveals only a relatively small change during the last 5 ky, a potentially large terrestrial C source from land-use change could have been masked by a simultaneous and equally large natural terrestrial C sink. Indeed, peatlands have accumulated 500–600 PgC since the last deglaciation (15) (Fig. 1). Anthropogenic CO2 emissions of this magnitude would support an early onset of the Anthropocene and could have had far-reaching consequences on climate by inhibiting an insolation-driven transition to glacial conditions (3, 16). However, the temporal resolution of the peat C record has so far hindered a more detailed analysis of other land C sinks and sources at the millennial and centennial timescales.
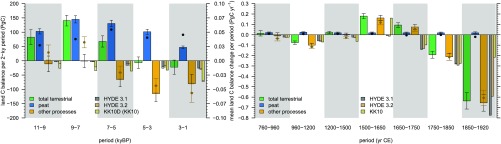
Fig. 1.
(Top row) Cumulative total terrestrial and peatland C storage change since 11 kyBP. Uncertainty ranges (shading) are given for and YML- and represent 1 SD around the mean (thick line). LPX- is the change in global total C stored in peat soils, represented by annual values (thin line) and their smoothing spline (thick line). Measured atmospheric CO2 is included at a separate y axis (Right) as gray and beige circles and their smoothing splines for records spanning the Holocene (“CO2 EPICA”, Left) (69) and the last millennium [“CO2 Law Dome” (70) and “CO2 WAIS” (40), Right]. (Bottom row) Cumulative budget residual (mean, 1 SD) based on the difference between YML- data and simulated cumulative land-use change emissions for each scenario. The pale-colored ranges for HYDE 3.1 and 3.2 represent the “HYDE 3.1 upper” and “HYDE 3.2 upper” scenarios, respectively. The gray band around 0 represents the interannual variability of land C storage as simulated by LPX. EPICA, European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica; WAIS, West Antarctic Ice Sheet.
Here, we synthesize and integrate existing and updated information to establish a budget of the global terrestrial C sources and sinks over the Holocene. We combine observation-based and model-based estimates for the global peatland C balance () with published reconstructions of terrestrial C stock changes () during the Holocene (10) and the last millennium (17). We quantify the terrestrial C budget residual as . is inferred from a double-deconvolution analysis of ice-core atmospheric CO2 and C measurements at the millennial Holocene timescale from ref. 10 and at the centennial-to-decadal timescale for the last millennium from ref. 17. is quantified by using (i) a continuous net C balance history throughout the Holocene as derived from a dataset of 64 dated peat cores and (ii) global model simulations with the LPX-Bern model hindcasting the transient dynamics of past peatland distribution and C balance (18). The budget residual is then contrasted with LPX-Bern results for CO2 emissions from land-use change (LUC), based on the full range of published scenarios for anthropogenic LUC covering the last 10 ky. These account for the declining per-capita land requirement and changing management practices through time and across space (Materials and Methods). The combination of bottom–up model estimates with top–down budget constraints narrows the range of past anthropogenic LUC emissions and their contribution to past C-cycle changes.
Results
Holocene.
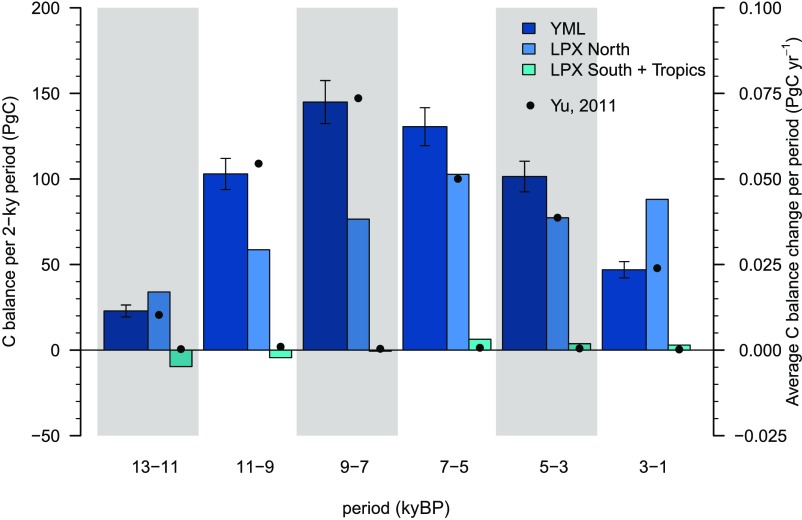
Terrestrial C storage increased by 83 26 PgC between 11 kyBP and 9 kyBP and by 141 19 PgC between 9 kyBP and 7 kyBP (10) (Figs. 1 and 2). C sequestration in peatlands alone is on the same order as the total land C sink. Whereas the data-based estimate (henceforth termed YML) suggests an increase of peatland C stocks of 103 9 PgC and 145 13 PgC in these respective periods, the model-based estimate (termed LPX) is lower in both periods (54 PgC and 76 PgC). The results for the model-based represent global totals, including C balance changes in northern, southern, and tropical peatlands. Results for observation-based are based on data from northern peatlands. While total C storage in southern and tropical peatlands was estimated by ref. 19 to be 10% of global peat C, their contribution to variations over time is smaller and negligible for global totals (Fig. S1). Our model results are consistent with these earlier observation-based estimates and suggest balance changes of less than 6 PgC in all 2-ky periods after 9 kyBP for peatlands south of 30∘N latitude. From 11 kyBP to 9 kyBP, a source of 4 (7) PgC from peatlands below 30∘ (45∘) N is simulated as a result of the continued disappearance of peatlands that formed under glacial conditions (Fig. S2)—an effect not captured by methods based on measurements of today’s existing peatlands and simulations with a prescribed and temporally fixed peatland distribution (20). Model results suggest that before the Holocene, disappearing peatlands affect the C budget even more with 10 (30) PgC loss below 30∘ (45∘) N between 13 kyBP and 11 kyBP. However, this shift in peatland distribution and C stocks is mostly completed by the beginning of the Holocene and does not affect the C budget in periods after 9 kyBP. The remaining difference between the YML and LPX estimates in the early Holocene may be due to an underestimation of peatland lateral expansion and vertical growth in early phases in LPX simulations, an overestimation of early lateral expansion, a bias of peatland site selection across space in YML, or uncertainties in peat decomposition rates used in both approaches.
Fig. 2.
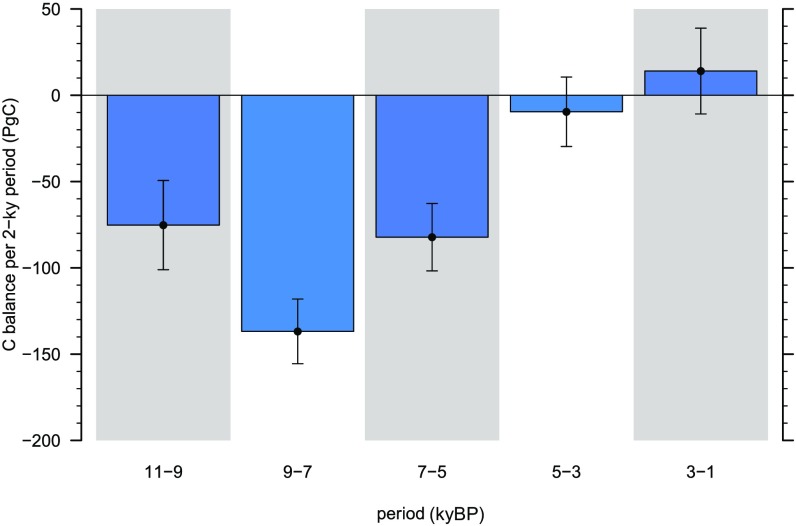
Land C budget in the Holocene for five 2-ky periods (Left) and the last millennium for seven periods of unequal length (Right), also shown as mean annual fluxes (Center). Positive values represent land C uptake. Shown is total global change in land C () as inferred from the CO2 and C ice-core records (green bars) (10, 17). Peatland C balance () is shown as derived from YML data (blue bars) and LPX simulations (black circles). “Other processes” show the budget residual , using YML-derived (brown bars and black whiskers for their uncertainty) and using LPX-derived (brown circles and whiskers). Cumulative emissions from LUC are given for each period and scenario (thin bars). Light-colored thin bars represent alternative scenarios where upper-end assumptions for population counts are used for HYDE 3.1 and 3.2. Light-colored bars behind KK10D represent the original KK10 scenario.
Fig. S1.
Holocene peatland carbon balance. YML estimates are from northern peatlands, but representative of global totals, whereas LPX estimates are given for northern and southern plus tropical peatlands, delineated at 30∘N/S. Earlier observation-based estimates from ref. 62 (black circles) are given for northern and tropical plus southern peatlands, separately, along with LPX simulation results for which the same latitudinal delineation at 30∘N is applied.
Fig. S2.
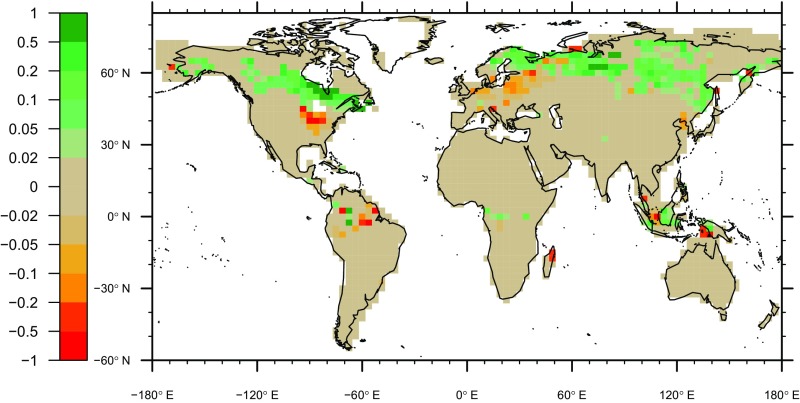
Change in the peatland area fraction between 13 kyBP and the present day, simulated by LPX under transiently changing environmental conditions, prescribed from CESM TraCE21k simulations (64). Note the irregular spacing of color levels. Negative values represent a larger peatland area fraction at 13 kyBP than at present.
Other land C sinks and sources account for the budget residual , quantified at −11 27 PgC at 11–9 kyBP and −1 23 PgC at 9–7 kyBP (insignificant sources to atmosphere) based on YML. The LPX-based suggests substantial additional land C sinks of 29 26 PgC at 11–9 kyBP and 65 19 PgC at 9–7 kyBP to close the budget. Simulated LUC emissions are 3–7 PgC based on the different HYDE scenarios (31, 32) and 26 PgC based on KK10 (24) at 11–9 kyBP. We use an additional LUC scenario where the emergence of agriculture given by KK10 is constrained for each region by archaeological evidence as summarized in ref. 16. This leads to a delay of first significant LUC in all regions (Fig. S3). In this scenario, termed KK10D, emissions are reduced to 10 PgC at 11–9 kyBP and are 22 PgC at 9–7 kyBP. The airborne fraction of emissions occurring on a millennial timescale is 10–20% (7, 21), leaving a minor LUC effect of 1–2 ppm on atmospheric CO2 concentrations [assuming 2.12 ppm per PgC (22)]. Thus, substantial peat C sequestration is a dominant driver of the Early Holocene land C balance. An inferred residual land sink is due to natural causes, likely linked to vegetation and soil establishment in northern high latitudes during continuing ice-sheet retreat (23). Top–down and bottom–up estimates consistently show that the decrease in atmospheric CO2 between 11 kyBP and 7 kyBP is driven by natural processes and that the role of LUC is negligible.
Fig. S3.
Original total cropland area for each continent for KK10 (black curve) (24) and KK10D (blue curve). The timing of agriculture emergence used for delaying first land conversion in KK10D specifically for each continent (vertical red line) is from ref. 16. Vertical green lines represent the year after which land use areas are identical in KK10 and KK10D. This is done for each continent separately.
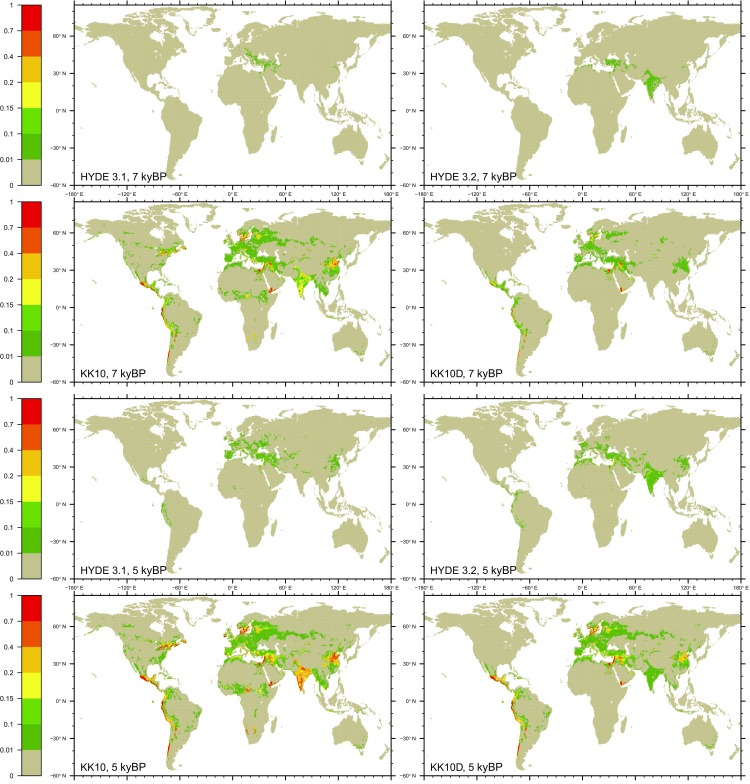
Atmospheric CO2 exhibits a trend reversal around 7 kyBP and increases by 7.8 ppm between 7 kyBP and 5 kyBP (based on the splined CO2 record shown in (Fig. 1). This coincides with the divergence of the and curves (Figs. 1 and 2). Ice-core CO2 and C records imply an increase in by 68 20 PgC and a net ocean outgassing of 82 20 PgC (Fig. S4), thus suggesting that the atmospheric CO2 increase is dominated by marine C-cycle changes, consistent with bottom–up ocean model analyses (11). However, , inferred from either YML (131 11 PgC) or LPX (109 PgC), is higher than for the period from 7 kyBP to 5 kyBP. This implies a residual land C source of 66 25 (41 22) PgC to close the budget. Is this an anthropogenic signal? In the same period, the KK10D scenario suggests substantial expansion of agricultural land in the Middle East, northeastern China, Meso-America, and along the Pacific Coast of South America (Fig. S5). LUC emissions of all scenarios (ranging from 11 PgC to 36 PgC) are within the uncertainty of the budget residual but likely explain less than half of the implied land C source. LUC emissions estimated for this period are substantially higher than previous estimates. Apart from including the KK10 and KK10D scenarios that assume higher per-capita land use under low population densities (27) and suggest a larger extent of early agricultural areas, this result is also due to important effects of shifting cultivation-type agriculture in early periods of agricultural expansion. Hypothetical LUC emissions corresponding to the full budget residual in this period (means) translate into an increase in CO2 concentration of 2–6 ppm, corresponding to 25–80% of the CO2 rise of 7.8 ppm. Taken together, both bottom–up and top–down information indicate that anthropogenic effects likely account for less than half of the CO2 rise between 7 kyBP and 5 kyBP, suggesting a substantial oceanic contribution for explaining the remainder, consistent with the double-deconvolution analysis.
Fig. S4.
Oceanic C balance change inferred from the same double-deconvolution analysis as used to quantify the total land C balance, and based on data from ref. 10. Positive values represent ocean C uptake. Uncertainty ranges are 1 SD, quantified from 2000 Monte Carlo simulations.
Fig. S5.
Cropland area for different scenarios [HYDE 3.1 (31), HYDE 3.2 (32), KK10 (24), and KK10D] at 7 kyBP (Top four panels) and 5 kyBP (Bottom four panels).
In the period 5–3 kyBP, remained small (− 7 20 PgC), whereas continued peat buildup sequestered 101 9 PgC following YML and 81 PgC following LPX. This implies a residual land source of 115 27 (87 25) PgC based on YML (LPX). Irrespective of the LUC scenario, anthropogenic emissions of 11–29 PgC clearly fall short of explaining this source, suggesting that natural nonpeatland processes had a dominant effect on the land C balance. This result may be related to declining northern hemisphere summer insolation and resulting climatic change and biome shifts after the Mid-Holocene (25–28). This includes neoglacial cooling at high latitudes and the retreat of the boreal treeline (29) and decreasing monsoon intensity at low latitudes (30), accompanied by the desertification of the Sahara (33) that alone may have contributed 30 PgC loss (25). However, large land-use C loss after the Mid-Holocene is not consistently found in available model simulations (34). Further research is required to improve the understanding of this natural land C source between 5 kyBP and 3 kyBP.
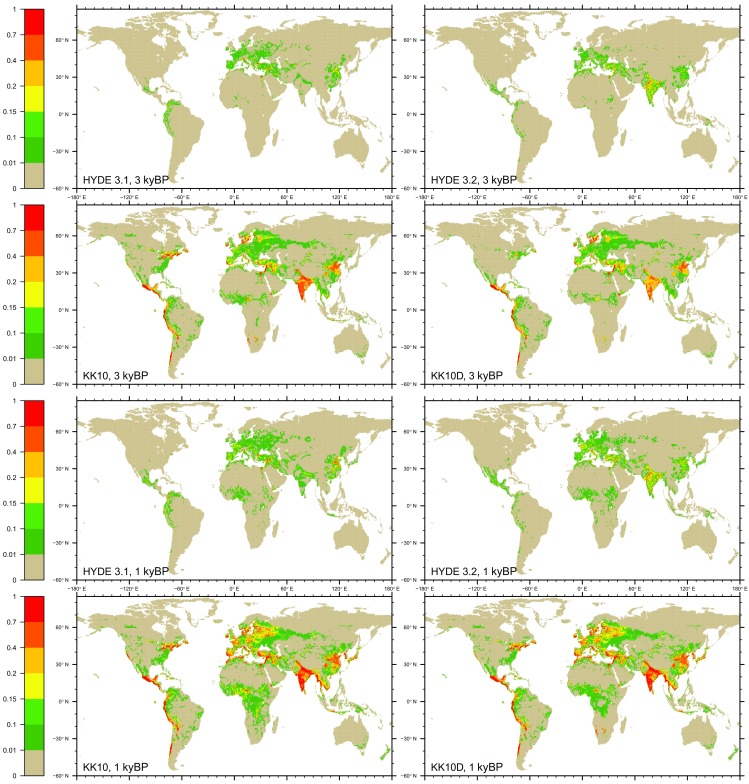
Whereas the YML estimate for suggests a decline in C sequestration for the period 3–1 kyBP, the LPX estimate is similar to the prior period. With a small overall negative land C balance (−22 25 PgC), the residual turns out to be −80 32 PgC and −113 32 PgC, using the two estimates. Increasing emissions from LUC follow from all scenarios. In this period, the KK10-based scenarios suggest emissions of the same order as the budget residual. This is the result of major cropland expansion, particularly in South Asia and western Eurasia (Fig. S6). Taken together, the C budget analysis at the Holocene timescale suggests that humans emerged as a driver with dominant global C-cycle impacts in the most recent three millennia. This result is in line with evidence from a wide range of paleo-ecological records documenting first significant landscape transformations in the Bronze Age in Europe (35–37). In China, archaeological evidence suggests major expansion of settlements already after 5 kyBP (38). Associated land conversion is captured by the KK10 and KK10D scenarios used here, but translates into limited C-cycle effects.
Fig. S6.
Cropland area for different scenarios [HYDE 3.1 (31), HYDE 3.2 (32), KK10 (24), and KK10D] at 3 kyBP (Top four panels) and 1 kyBP (Bottom four panels).
Last Millennium.
During the last millennium, the ice-core CO2 and C records suggest that sustained land C uptake over decades to centuries alternated with periods of C loss (17). However, measured preindustrial variations are often small and centennial-to-decadal–scale sink reconstructions may be affected by uncertainties associated with the ice-core paleo-archive. Inferred terrestrial C storage decreased during the early Medieval period (−18 4 PgC at 960–1200 CE) and after Industrialization (−19 3 PgC at 1750–1850 CE and −45 4 PgC at 1850–1920 CE), but increased between these periods and most substantially from 1500 CE to 1650 CE (27 4 PgC). Note that Fig. 2, Right shows average annual fluxes for comparability between periods of unequal length. LPX-simulated peatland C sequestration exhibits a declining trend throughout the last millennium, similar to results in ref. 39. Together, LPX and YML suggest that is of the same magnitude as in early periods (760–960 CE and 1200–1500 CE). Thereafter, peat C changes are minor in comparison with , and LUC emerges as a dominant control and appears to have overriding impacts over other natural drivers.
Atmospheric CO2 concentration exhibits a marked decline between 1500 CE and 1650 CE in several ice cores (40, 41) and inferred terrestrial C storage increased by 27 4 PgC (17). These changes occur at the time of the European arrival in the Americas and during the subsequent collapse of the native population by around 90% (42). The pre-Columbian population count in the Americas and the extent of human impacts on the landscape are controversial (9, 42–46). Forest regrowth on previously cultivated land has been suggested to sequester enough C to explain observed variations in atmospheric CO2 composition (43, 44), and the CO2 dip may therefore serve as a geological marker for the beginning of the Anthropocene (2). However, this link has been put into question on several grounds (45–48). Land-use reconstructions applied here cover the range of this uncertainty and simulated CO2 emissions bracket earlier non-model–based estimates (43, 44). Between 1500 CE and 1650 CE, LUC leads to a cumulative global uptake of 24 PgC in the KK10 scenario and to negligible emissions in HYDE 3.1 and HYDE 3.2. Concurrent agricultural expansion on other continents, largely consistent across scenarios, partly compensates C sequestration in the Americas.
Applied land-use scenarios rely on similar assumptions regarding the pre-Columbian population (60 million in 1500 CE) and their decline thereafter (70% reduction by 1600 CE), but make differing assumptions regarding the per-capita land use. This value is around 7 ha per capita in KK10 for all Americas combined, but varies from 2.6 ha per capita in Meso-America (at a population of 27 million) to 8 ha per capita in South America (29 million) and 34 ha per capita in North America (4 million), depending on population density following ref. 24. In contrast, this value is only around 0.5 ha per capita in HYDE 3.1 and HYDE 3.2 in all three regions, implying a much smaller reduction of American agricultural land in absolute terms. These numbers represent only land cultivated at any one point in time. An even wider impact by shifting cultivation and wood harvesting is accounted for in our simulations and inflates the area of recently disturbed forests. Other estimates for per-capita agricultural land use in pre-Columbian America are around 1–2 ha per capita (43, 44, 49) and suggest that the KK10 and HYDE scenarios cover more than a plausible range of uncertainty in the pre-Columbian extent of agricultural land in the Americas. We conclude that only extreme assumptions for per-capita land use in 1500 CE translate into land abandonment in the Americas large enough to explain the full reconstructed terrestrial CO2 sink. A likely remaining sink may be explained by natural causes, such as climate forcing by explosive volcanism (50), solar activity (51), and unforced internal climate variability and its impact on natural ecosystems (52).
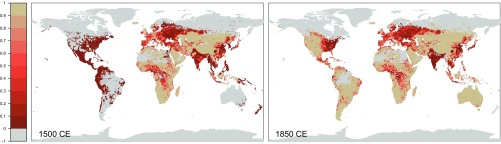
Terrestrial ecosystems continue sequestering C between 1650 CE and 1750 CE (9 2 PgC uptake), whereas all LUC scenarios suggest a resumption of related emissions with rates substantially higher than during the Medieval period (10–14 PgC emissions). The inconsistency between the budget residual (7 2 PgC uptake) and LUC emissions may be linked to inaccuracy of the LUC scenarios, climate–carbon-cycle feedbacks in a period with low northern hemisphere temperatures (53), or a combination of both. In all scenarios, global LUC emission rates increase substantially after 1750 CE. With 26–29 PgC emitted between 1750 CE and 1850 CE, LUC likely explains most of the observed decline of −19 3 PgC in land C storage. Land C loss further accelerated in the period thereafter. Between 1850 CE and 1920 CE, the land biosphere was a source of 45 5 PgC. This falls into a period characterized by slowly increasing temperatures in the northern hemisphere (53). However, the positive feedback between climate warming and land C loss cannot explain the magnitude of the observed C source and is likely attenuated by a small fertilization effect by concurrently increasing CO2 concentration. At a C-cycle–climate sensitivity of −50 PgC K−1 at a global scale (54, 55) and a temperature increase of up to 0.5 K this leads to a maximum C loss of 25 PgC, compensated by an uptake of 20 PgC, assuming 1 PgC per ppm CO2 (54) and an increase of 20 ppm between 1850 CE and 1920 CE. This result leads us to assume that the C source between 1850 CE and 1920 CE is largely an anthropogenic signal and thereby offers a constraint on bottom–up estimates of LUC emissions (56). As a result of the large extent of agricultural areas in KK10 in year 1850 CE (Fig. S7), subsequent expansion to the well-constrained present-day distribution is necessarily limited. This is reflected also by the convergence of total cumulative emissions until present day across scenarios (Fig. 1) and implies relatively small emissions (15 PgC) between 1850 CE and 1920 CE in KK10. These small emissions fall significantly short of explaining the land C source in the same period. Emissions based on the HYDE scenarios are 39–54 PgC and are of a similar magnitude to that of the budget residual. Furthermore, between 1850 CE and 2000 CE, our LUC emission estimates based on HYDE 3.1 (3.2) are 148 (126) PgC and are therefore consistent with a wide range of estimates (155 55 PgC) based on independent LUC scenarios (57, 58) and constrained by observed C density of converted land. Under the assumption of relatively small natural impacts on land C storage between 1850 CE and 1920 CE, the budget constraint on LUC emissions therefore suggests that total pre-1850 land conversion in KK10 may be overestimated.
Fig. S7.
Cropland area for different scenarios [HYDE 3.1 (31), HYDE 3.2 (32), KK10 (24), and KK10D], 1850 CE.
Present-day cumulative C sinks and sources from peat buildup and LUC are relatively well known from large-scale peatland data syntheses (19, 59) and from the combination of remotely sensed land cover and biomass density maps. LUC-induced erosion, temporarily acting as a net C sink (60), and a LUC-induced CO2 fertilization feedback (6, 7) may have reduced cumulative historical LUC emissions. In contrast to cumulative total LUC emissions, their temporal course over the last 11 kyBP is subject to substantial remaining uncertainties. Nevertheless, by analyzing the land C budget within discrete periods and by using a budget constraint for the period 1850–1920 CE, we conclude that sole anthropogenic causes for the CO2 increase after 7 kyBP and decline after 1500 CE are not supported and that rates of LUC emissions markedly increased after the onset of Industrialization. Separating from reveals the magnitude of other land C changes. We identify a nonpeatland land C source of 100 PgC between 5 kyBP and 3 kyBP, likely related to land C loss from low-latitude aridification and high-latitude forest retreat and productivity decline after the Mid-Holocene (25–28). To improve reconstructions of past LUC, paleo-ecological records and archaeological evidence should be combined with a focus on better capturing the timing of emergence and expansion of agriculture at the regional-to-continental scales, on providing information on per-capita land use specifically for different agricultural systems, and on constraining landscape-scale vegetation with pollen-based reconstructions (35).
Materials and Methods
.
The total terrestrial C balance () was inferred from a double-deconvolution analysis (61) of the parallel evolution of atmospheric CO2 and its isotopic signature (C values), measured from ice-core records. We used time series from EPICA Dome C (10) for the millennial scale covering the Holocene and from WAIS Divide (17) for the centennial scale covering the last millennium. Uncertainties associated with measurements and the fractionation factors of air–sea gas exchange and photosynthesis are accounted for in Monte Carlo simulations of 2,000 (1,000) realizations of continuous time series for the Holocene (last millennium). of the last millennium, shown in Fig.1, is based on 5,000 combinations of individual reconstructions from refs. 10 and 17.
.
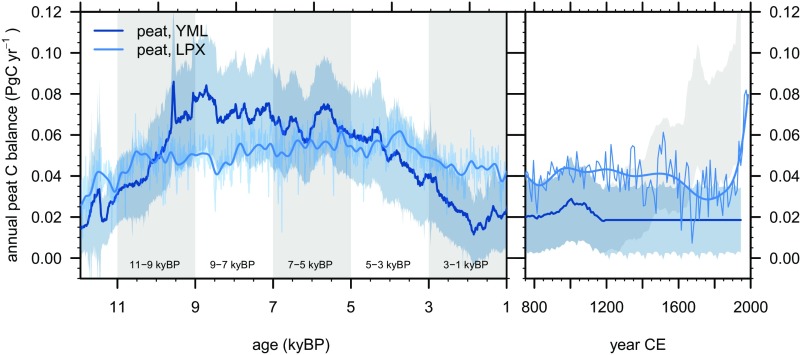
The C balance of global peatlands () was derived using an observation-based reconstruction (62) and global modeling (21). The former, termed YML, is based on C accumulation records from an updated dataset of 64 peat cores from northern peatlands from ref. 63 (Dataset S1 and SI Text, ), using the same methodology as in ref. 62 to calculate their net C balance (NCB ) through time. Uncertainty in global was obtained from a set of 1,000 Monte Carlo simulations, generated by varying input parameters used for the reconstruction (C accumulation measurements and peatland area for global upscaling) within an assumed Gaussian distribution. Our inability to systematically account for the higher decomposition rates in young peat limit data usability of the YML time series in the most recent centuries (Fig. S8). Therefore, we assume constant peatland C sequestration () in the YML time series after 1200 CE (repeated values from years 1110 CE to 1200 CE) (SI Text).
Fig. S8.
Annual peat C balance (PgCy−1). YML data represent the (62) derived from updated synthesis of peat core measurements. The uncertainty range represents the 10% and 90% quantiles, and the thick line is the median of individual time series for which uncertainty in C accumulation measurements and global peatland area is taken into account. LPX data represent the simulated net ecosystem productivity (NEP) of peatlands and are given for annual data (thin line) and a 30-y running mean (thick line). All budget analyses are based on modeled peat C stocks, not cumulative NEP, and thus reflect effects of disappeared peatlands. Periods used for the budget evaluation in main text Fig. 2 are illustrated by vertical gray bars. The dark blue line (YML, fixed after 1200 CE) represents the data used for the budget analysis of the last millennium, as shown in Fig. 2, Right. (Right) the light gray shaded area in the top right is the original data. Increasing annual Cpeat simulated by LPX after 1900 is due to rising CO2 and a warming climate, stimulating peatland net primary productivity at high latitudes.
The global peatland simulations were done using version 1.2 of the LPX-Bern dynamic global vegetation model that includes the DYPTOP module (Dynamical Peatland Model Based on TOPMODEL) to simulate peat and wetland extent (18). Peatland C dynamics are explicitly represented whereby decomposition rates are governed by the water table depth and soil temperature (20). Peatland inception and extent are dynamically simulated across space in response to the water balance, long-term C accumulation, and topographically constrained inundation persistency (18). Simulations were initialized and started under LGM conditions (22 kyBP) and account for transient peatland dynamics until the present in response to varying CO2 and climate, prescribed from TraCE21ka simulations (64) with the Community Earth System Model (CESM), and changing land–sea–ice distribution (23). Results are evaluated here only for the period after 13 kyBP.
Budget Residual.
The budget residual was quantified as , using a bootstrap method where 5,000 realizations of were drawn from the 2,000 (1,000) realizations of and 1,000 realizations of YML-derived reconstructions at the Holocene (last millennium) timescale. Alternatively, was quantified from the combination of all realizations and the single time series of LPX-derived . Results referred to in the text (also for and are means and standard deviations.
Land-Use Change Emissions.
CO2 emissions from anthropogenic land-use change were simulated using LPX-Bern version 1.2, accounting for gross land-use transitions arising from shifting cultivation and wood harvesting (65). This is the same global vegetation model as used to quantify model-derived , but applied for an independent set of simulations, where peatland C dynamics are not accounted for (no anthropogenic peatland drainage considered). CO2 is fixed at 287 ppm and climate was held constant [repeated 1901–1931 Climate Research Unit Time Series (CRU TS 3.22) data (66)]. Only land use was varied and CO2 emissions were quantified as the difference in the net land–atmosphere CO2 exchange flux from a simulation including LUC and a control simulation without LUC. Past LUC scenarios are based on published datasets HYDE 3.1 (31), HYDE 3.2 (32), KK10 (8), and KK10D (SI Text). Shifting cultivation is simulated in time-varying regions with permanent agriculture, following ref. 67 (Fig. S9). Wood harvest is prescribed based on maps for harvested area given by ref. 68 for the period 1960–2000 CE (area associated with biomass harvested from primary forested land) and is back projected following total cropland area per continent specifically for each land-use scenario. Additional steps necessary for implementation of available scenarios for our simulations are described in SI Text and Fig. S10. All data were processed in 0.5∘ × 0.5∘ resolution in longitude and latitude and then spatially aggregated for model simulations at 3.75∘ × 2.5∘ in longitude and latitude.
Fig. S9.
Distribution of permanent agriculture (red) at different points in time based on refs. 67 and 68. For years before 1700, the distribution of permanent agriculture is taken from ref. 67. For years from 1700 onward, the distribution of permanent agriculture is a combination of data from ref. 67 and from ref. 68, taken as areas outside regions with shifting cultivation (data downloaded from luh.umd.edu/). Spatial patterns displayed here for a given year are held constant for all years thereafter until a new pattern is defined. No permanent agriculture is assumed before 4000 BC.
Fig. S10.
Pasture area as a fraction of total agricultural area (sum of pasture and cropland). This share, given by HYDE 3.1, is used to derive cropland and pasture area fraction for KK10 and KK10D scenarios, for which original data are provided only for total land use, representing the sum of pasture and croplands. This share is given specifically for each year where HYDE data are available, but shown here only for 1500 (Left) and 1850 (Right). This share changes little before 1500 and after 1850. Pasture area as a fraction of total agricultural area is zero in the Americas in 1500 CE and before, reflecting that pasture land use was minor or absent in agricultural systems of the pre-Columbian Americas.
Data Access.
Global time series for YML-, LPX-, and LUC emissions are available through the Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC; cdiac.ornl.gov) at dx.doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1374 and www.climate.unibe.ch/research/publications/datasets/index_eng.html.
SI Text
Cpeat
The observation-based peatland C balance reconstruction (Cpeat) is based on 64 well-dated high-resolution peat cores. This is a subset from ref. 63 and data were included here if records of direct measurements of bulk density and C content have at least one age determination per 2,500 y and cover at least the last 4,500 y. Global upscaling was done using the mean C accumulation rate across all peat cores and a time-varying global peatland area, estimated from the cumulative peat inception ages over time from ref. 71 and arriving at 3.7 0.3 million km2 for present-day peatland area (62). A single decomposition rate, derived from fitting the full combined set of available peat mass-age profiles (“megabog”), was used to calculate peat C release and the net C balance (62). The reconstructed Cpeat of the Holocene is illustrated in Fig. S1. This reconstruction shows an increasing trend of from its minimum around 2 kyBP to the highest value of about 0.1 PgCy−1 in the most recent decades. This high value in recent decades is similar to the value in the Mid- and Early Holocene but, unlike that millennial-scale feature, is not supported by the LPX simulation results. This apparent increase in in recent centuries (after around 1200 CE in the YML reconstruction) is due to the autogenic effect of varying peat decomposition rates along its depth profile (39). Due to relatively frequent aerobic conditions in the upper part of the peat profile (acrotelm), decomposition rates are generally higher than in the lower parts of the profile (catotelm) where anaerobic conditions prevail. This variation is not accounted for in the method applied to derive the YML reconstruction (62) and implies that the reconstructed peat input rates (accumulation) are overestimated for recent centuries when assuming low decomposition rates representing conditions in the catotelm being representative for the entire column. This affects the reconstruction only for the more recent periods during the last millennium. It is in general not possible to delineate the start of this autogenic effect in time series of reconstructions. Here, we chose to hold values constant after 1200 CE, i.e., around the time when the original YML starts diverging from the LPX data (Fig. 1 in main text). A declining trend of peatland productivity throughout the last millennium and until around 1800 CE is found in ref. 39. This finding is generally consistent with the LPX results. As evident from Fig. 2 in the main text, peatland C sequestration is quantitatively minor in comparison with other components of the C budget in the most recent periods investigated in the last millennium. Hence, the assumptions regarding the YML estimate made here do not affect our conclusions drawn from the budget. Model-simulated Cpeat (LPX) provides additional support for the robustness of our conclusions in view of uncertainty in peatland C balance reconstructions.
LUC Scenarios
Past LUC scenarios are based on published datasets HYDE 3.1 (31), HYDE 3.2 (32), KK10 (8), and KK10D, derived from KK10 (SI Text). Additional steps necessary for implementation of available scenarios for our simulations are described below.
Land-use transitions.
LUC, including gross land-use transitions arising from shifting cultivation and wood harvesting, is implemented following the Generated Transitions Method described in ref. 65, with the following changes. In areas of nonpermanent agriculture (see below), shifting cultivation with a cropland abandonment rate of 25%/y was simulated. New cropland area is first claimed from primary forest. Once limited by land suitability and accessibility as specified by a separate map of cropland suitability (72), new agricultural land is claimed from secondary nonagricultural land. In areas of permanent agriculture, the cropland area provided by the scenarios is assumed to represent only areas currently under cultivation and a fallow-to-cultivation ratio of 0.5:1 is assumed before 1850 CE, corresponding to a three-field rotation system, declining to 0:1 by 1960 CE. Shifting cultivation or fallow does not apply to pasture land.
Permanent vs. nonpermanent agriculture.
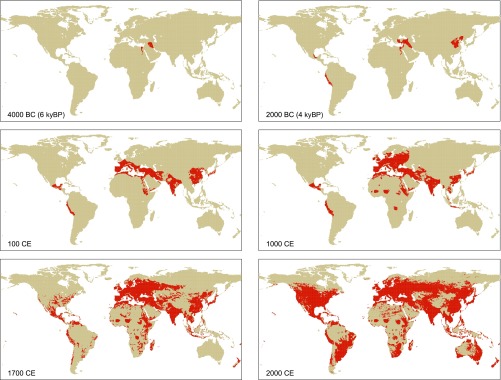
To account for changes in management practices and cultivation intensity in time and space, we used maps for temporally varying areas of nonpermanent and permanent agriculture from ref. 67 (below and Fig. S5). Permanent agriculture is limited to core areas of civilization, whereas shifting cultivation dominates in peripheral regions. We use maps delineating permanent vs. nonpermanent agriculture at five different points in time (4000 BC, 2000 BC, 1 CE, 1000 CE, 1700 CE) from ref. 67 (Fig. S5) and apply their spatial distribution for all subsequent years until the subsequent time slice. From 1700 CE onward the distribution is held constant and we merged the 1700 CE slice from ref. 67 with the shifting cultivation map by ref. 68, assuming that shifting cultivation is restricted to grid cells that are specified as nonpermanent in the 1700 AD slice by ref. 67 and specified as shifting cultivation area by ref. 68. All others are considered to be areas of permanent agriculture.
Land suitability.
We assume an inaccessible area fraction in each grid cell that is not affected by shifting cultivation or wood harvest during the entire simulation and remains primary land. The extent of this nonconvertible land fraction is determined here by the suitable land fraction for agriculture as defined by ref. 72 and excludes areas where climate or soil conditions limit agricultural production. If the fraction suitable for agriculture is smaller than or equal to the sum of cropland and pasture areas defined in the individual scenarios, this constraint is neglected.
Deforestation for pasture expansion.
Land conversion for pasture expansion is assumed to imply deforestation only if naturally open vegetation area, as simulated by LPX under preindustrial environmental conditions, is insufficient to meet the pasture area given by each scenario. To implement this, we first applied LPX under constant preindustrial environmental boundary conditions, derived the area covered by nonwoody plant functional types, and subtracted this from the pasture area given for each scenario. Negative values were set to zero. This substantially reduces “effective” land conversion for pasture in semiarid and cool climates. In contrast, cropland expansion is assumed to lead to proportional reduction in forested and nonforested land as simulated by LPX (potential natural vegetation).
KK10 scenario.
The KK10 LUC scenario (24) defines open vegetation fraction corresponding to the sum of cropland and pasture areas. To disaggregate, we assumed the same share of cropland vs. pasture over time in each grid cell as given in HYDE 3.1 (Fig. S6) and linearly interpolated to the few remaining grid cells where this share is not defined by HYDE 3.1 in respective time steps.
KK10D scenario.
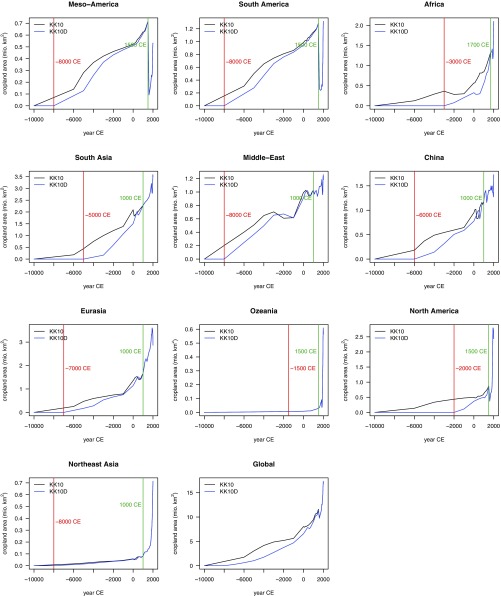
The KK10D scenario is derived here based on the original KK10 scenario by additionally accounting for archaeological evidence for the first emergence of agriculture in each continent. This information is taken from ref. 16 (their figure 6) and illustrated in Fig. S7. KK10D was compiled by setting all cropland and pasture areas to zero before the year given by the vertical red line in Fig. S7 () and scaling all values by a factor that increases from zero in to 1 in the “pivot year” (), given by the green vertical line in Fig. S7. and were chosen for each continent separately. For all years after , land-use areas in KK10 and KK10D are identical. Differences between simulated LUC emissions in the KK10 and KK10D scenarios are negligible for periods of the last millennium and scenarios were not evaluated separately for its C budget analysis (Fig. 2 of the main text).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Kaplan for sharing LUC scenario data and support, K. Klein Goldewijk and J. Olofsson for sharing land-use data, B. Otto-Bliesner for sharing TraCE21ka climate simulation data, R. Spahni for conducting peatland model simulations, J. Loisel and M. Blaauw for compiling and analyzing the peat-core data, and peat data contributors for sharing peat-core records. B.D.S. and F.J. were supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation. Z.Y. and C.M. were supported by the US National Science Foundation.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission. L.C.S. is a Guest Editor invited by the Editorial Board.
Data deposition: Global time series for YML- and LPX-, and LUC emissions are available through dx.doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1374 and www.climate.unibe.ch/research/publications/datasets/index_eng.html.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1613889114/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Crutzen PJ. Geology of mankind. Nature. 2002;415(6867):23. doi: 10.1038/415023a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lewis SL, Maslin MA. Defining the Anthropocene. Nature. 2015;519(7542):171–180. doi: 10.1038/nature14258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ruddiman WF. The anthropogenic greenhouse era began thousands of years ago. Clim Change. 2003;61:261–293. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Joos F, Gerber S, Prentice IC, Otto-Bliesner BL, Valdes PJ. Transient simulations of Holocene atmospheric carbon dioxide and terrestrial carbon since the Last Glacial Maximum. Global Biogeochem Cycles. 2004;18:1–18. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Broecker WS, Stocker TF. The Holocene CO2 rise: Anthropogenic or natural? Eos. 2006;87(3):27. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pongratz J, Reick CH, Raddatz T, Claussen M. Effects of anthropogenic land cover change on the carbon cycle of the last millennium. Global Biogeochem Cycles. 2009;23(4):GB4001+. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stocker BD, Strassmann K, Joos F. Sensitivity of Holocene atmospheric CO2 and the modern carbon budget to early human land use: Analyses with a process-based model. Biogeosciences. 2011;8(1):69–88. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kaplan JO, et al. Holocene carbon emissions as a result of anthropogenic land cover change. Holocene. 2011;21(5):775–791. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ellis EC, et al. Used planet: A global history. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(20):7978–7985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217241110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Elsig J, et al. Stable isotope constraints on Holocene carbon cycle changes from an Antarctic ice core. Nature. 2009;461(7263):507–510. doi: 10.1038/nature08393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Menviel L, Joos F. Toward explaining the Holocene carbon dioxide and carbon isotope records: Results from transient ocean carbon cycle-climate simulations. Paleoceanography. 2012;27 [Google Scholar]
- 12.Broecker WS, et al. Evidence for a reduction in the carbonate ion content of the deep sea during the course of the Holocene. Paleoceanography. 1999;14(6):744–752. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ridgwell AJ, Watson AJ, Maslin MA, Kaplan JO. Implications of coral reef buildup for the controls on atmospheric CO2 since the last glacial maximum. Paleoceanography. 2003;18(4):1083–1093. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kleinen T, Brovkin V, von Bloh W, Archer D, Munhoven G. Holocene carbon cycle dynamics. Geophys Res Lett. 2010;37:L02705. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yu ZC. Northern peatland carbon stocks and dynamics: A review. Biogeosciences. 2012;9(10):4071–4085. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ruddiman WF, et al. Late Holocene climate: Natural or anthropogenic? Rev Geophys. 2016;54(1):93–118. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bauska TK, et al. Links between atmospheric carbon dioxide, the land carbon reservoir and climate over the past millennium. Nat Geosci. 2015;8(5):383–387. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stocker BD, Spahni R, Joos F. DYPTOP: A cost-efficient TOPMODEL implementation to simulate sub-grid spatio-temporal dynamics of global wetlands and peatlands. Geosci Model Dev. 2014;7(6):3089–3110. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yu Z, Loisel J, Brosseau DP, Beilman DW, Hunt SJ. Global peatland dynamics since the Last Glacial Maximum. Geophys Res Lett. 2010;37(13):1–5. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Spahni R, Joos F, Stocker BD, Steinacher M, Yu ZC. Transient simulations of the carbon and nitrogen dynamics in northern peatlands: From the Last Glacial Maximum to the 21st century. Clim Past. 2013;9(3):1287–1308. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Archer D, et al. Atmospheric lifetime of fossil fuel carbon dioxide. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci. 2009;37(1):117–134. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Enting IG, Wigley TML, Heimann M. 1994. Future Emissions and Concentrations of Carbon dioxide: Key Ocean/Atmosphere/Land Analyses (CSIRO, Division of Atmospheric Research, Clayton South, VIC, Australia), Tech Rep.
- 23.Peltier W. Global glacial isostasy and the surface of the ice-age earth: The ice-5G (VM2) model and GRACE. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci. 2004;32:111–149. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kaplan JO, Krumhardt KM, Zimmermann N. The prehistoric and preindustrial deforestation of Europe. Quat Sci Rev. 2009;28(27-28):3016–3034. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Indermühle A, et al. Holocene carbon-cycle dynamics based on CO2 trapped in ice at Taylor Dome, Antarctica. Nature. 1999;398(6723):121–126. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Prentice IC, Jolly D, Participants B. Mid-Holocene and Glacial-Maximum vegetation geography of the northern continents and Africa. J Biogeogr. 2000;27(3):507–519. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang Y, Mysak LA, Roulet NT. Holocene climate and carbon cycle dynamics: Experiments with the “green” McGill Paleoclimate Model. Global Biogeochem Cycles. 2005;19(3):1–18. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wanner H, et al. Mid- to Late Holocene climate change: An overview. Quat Sci Rev. 2008;27(19-20):1791–1828. [Google Scholar]
- 29.MacDonald GM, Edwards TWD, Moser KA, Pienitz R, Smol JP. Rapid response of treeline vegetation and lakes to past climate warming. Nature. 1993;361(6409):243–246. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang Y, et al. The Holocene Asian monsoon: Links to solar changes and north Atlantic climate. Science. 2005;308(5723):854–857. doi: 10.1126/science.1106296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Goldewijk KK. Estimating global land use change over the past 300 years: The HYDE database. Global Biogeochem Cycles. 2001;15(2):417–433. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Klein Goldewijk K. 2016 A historical land use data set for the Holocene; HYDE 3.2. Available at https://doi.org/10.17026/dans-2ct-fmud. Accessed June 7, 2016.
- 33.Hoelzmann P, et al. Mid-Holocene land-surface conditions in northern Africa and the Arabian Peninsula: A data set for the analysis of biogeophysical feedbacks in the climate system. Global Biogeochem Cycles. 1998;12(1):35–51. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brovkin V, et al. Comparative carbon cycle dynamics of the present and last interglacial. Quat Sci Rev. 2016;137:15–32. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gaillard MJ, et al. Holocene land-cover reconstructions for studies on land cover-climate feedbacks. Clim Past. 2010;6(4):483–499. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Roberts N, Eastwood WJ, Kuzucuoglu C, Fiorentino G, Caracuta V. Climatic, vegetation and cultural change in the eastern Mediterranean during the mid-Holocene environmental transition. Holocene. 2011;21(1):147–162. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fyfe RM, Woodbridge J, Roberts N. From forest to farmland: Pollen-inferred land cover change across Europe using the pseudobiomization approach. Global Change Biol. 2015;21(3):1197–1212. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Li X, Dodson J, Zhou J, Zhou X. Increases of population and expansion of rice agriculture in Asia, and anthropogenic methane emissions since 5000 BP. Quat Int. 2009;202(1-2):41–50. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Charman DJ, et al. Climate-related changes in peatland carbon accumulation during the last millennium. Biogeosciences. 2013;10(2):929–944. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ahn J, et al. Atmospheric CO2 over the last 1000 years: A high-resolution record from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) Divide ice core. Global Biogeochem Cycles. 2012;26(2):GB2027. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rubino M, et al. A revised 1000 year atmospheric C CO2 record from law dome and south pole, Antarctica. J Geophys Res Atmos. 2013;118(15):8482–8499. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Denevan WM. The pristine myth: The landscape of the Americas in 1492. Ann Assoc Am Geogr. 1992;82(3):369–385. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nevle RJ, Bird DK. Effects of syn-pandenic fire reduction and reforestation in the tropical Americas on atmospheric CO2 during European conquest. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. 2008;264(1-2):25–38. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dull RA, et al. The Columbian encounter and the Little Ice Age: Abrupt land use change, fire, and greenhouse forcing. Ann Assoc Am Geogr. 2010;100(4):755–771. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Piperno DR, McMichael C, Bush MB. Amazonia and the Anthropocene: What was the spatial extent and intensity of human landscape modification in the Amazon Basin at the end of prehistory? Holocene. 2015;25(10):1588–1597. [Google Scholar]
- 46.McMichael CH, et al. Sparse pre-Columbian human habitation in western Amazonia. Science. 2012;336(6087):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.1219982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Power MJ, et al. Climatic control of the biomass-burning decline in the Americas after AD 1500. Holocene. 2012;23(1):3–13. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Liebmann MJ, et al. Native American depopulation, reforestation, and fire regimes in the Southwest United States, 1492–1900 CE. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(6):E696–E704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521744113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Klein Goldewijk K, Verburg PH. Uncertainties in global-scale reconstructions of historical land use: An illustration using the HYDE data set. Landsc Ecol. 2013;28(5):861–877. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Frölicher TL, Joos F, Raible CC. Sensitivity of atmospheric CO2 and climate to explosive volcanic eruptions. Biogeosciences. 2011;8(8):2317–2339. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vieira LEA, Solanki SK, Krivova NA, Usoskin I. Evolution of the solar irradiance during the Holocene. Astron Astrophys. 2011;531(A6):1–20. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schurer AP, Hegerl GC, Mann ME, Tett SFB, Phipps SJ. Separating forced from chaotic climate variability over the past millennium. J Clim. 2013;26(18):6954–6973. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Büntgen U, et al. Cooling and societal change during the Late Antique Little Ice Age from 536 to around 660 AD. Nat Geosci. 2016;9(3):231–236. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Arora VK, et al. Carbon-concentration and carbon-climate feedbacks in CMIP5 earth system models. J Clim. 2013;26(15):5289–5314. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Stocker BD, et al. Multiple greenhouse-gas feedbacks from the land biosphere under future climate change scenarios. Nat Clim Chang. 2013;3(7):666–672. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Brovkin V, et al. Role of land cover changes for atmospheric CO2 increase and climate change during the last 150 years. Glob Change Biol. 2004;10:1253–1266. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Le Quéré C, et al. Global carbon budget 2015. Earth Syst Sci Data. 2015;7(2):349–396. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Houghton RA. How well do we know the flux of CO2 from land-use change. Tellus B. 2010;62:337–351. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gorham E. Northern peatlands: Role in the carbon cycle and probable responses to climatic warming. Ecol Appl. 1991;1(2):182–195. doi: 10.2307/1941811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Van Oost K, et al. The impact of agricultural soil erosion on the global carbon cycle. Science. 2007;318(5850):626–629. doi: 10.1126/science.1145724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Joos F, Bruno M. Long-term variability of the terrestrial and oceanic carbon sinks and the budgets of the carbon isotopes 13C and 14C. Global Biogeochem Cycles. 1998;12:277–295. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yu Z. Holocene carbon flux histories of the world’s peatlands: Global carbon-cycle implications. Holocene. 2011;21(5):761–774. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Loisel J, et al. A database and synthesis of northern peatland soil properties and Holocene carbon and nitrogen accumulation. Holocene. 2014;24(9):1028–1042. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Liu Z, et al. Transient simulation of last deglaciation with a new mechanism for Bølling-Allerød warming. Science. 2009;325(5938):310–314. doi: 10.1126/science.1171041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Stocker BD, Feissli F, Strassmann K, Spahni R, Joos F. Past and future carbon fluxes from land use change, shifting cultivation and wood harvest. Tellus B. 2014;66(0) [Google Scholar]
- 66.Harris I, Jones P, Osborn T, Lister D. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations – the CRU TS3.10 Dataset. Int J Climatol. 2014;34(3):623–642. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Olofsson J, Hickler T. Effects of human land-use on the global carbon cycle during the last 6,000 years. Veg Hist Archaeobot. 2008;17:605–615. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hurtt GC, et al. The underpinnings of land-use history: Three centuries of global gridded land-use transitions, wood-harvest activity, and resulting secondary lands. Glob Change Biol. 2006;12(7):1208–1229. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Monnin E, et al. Evidence for substantial accumulation rate variability in Antarctica during the Holocene through synchronization of CO2 in the Taylor Dome, Dome C and DML ice cores. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 2004;224:45–54. [Google Scholar]
- 70.MacFarling Meure C, et al. Law Dome CO2, CH4 and N2O ice core records extended to 2000 years BP. Geophys Res Lett. 2006;33(14):L14810. [Google Scholar]
- 71.MacDonald GM, et al. Rapid early development of circumarctic peatlands and atmospheric CH4 and CO2 variations. Science. 2006;314(5797):285–288. doi: 10.1126/science.1131722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ramankutty N, Foley JA, Norman J, McSweeney K. The global distribution of cultivable lands: Current patterns and sensitivity to possible climate change. Global Ecol Biogeogr. 2002;11(5):377–392. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.