Figure 4. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) on postoperative sleep apnea and breathing in the PACU.
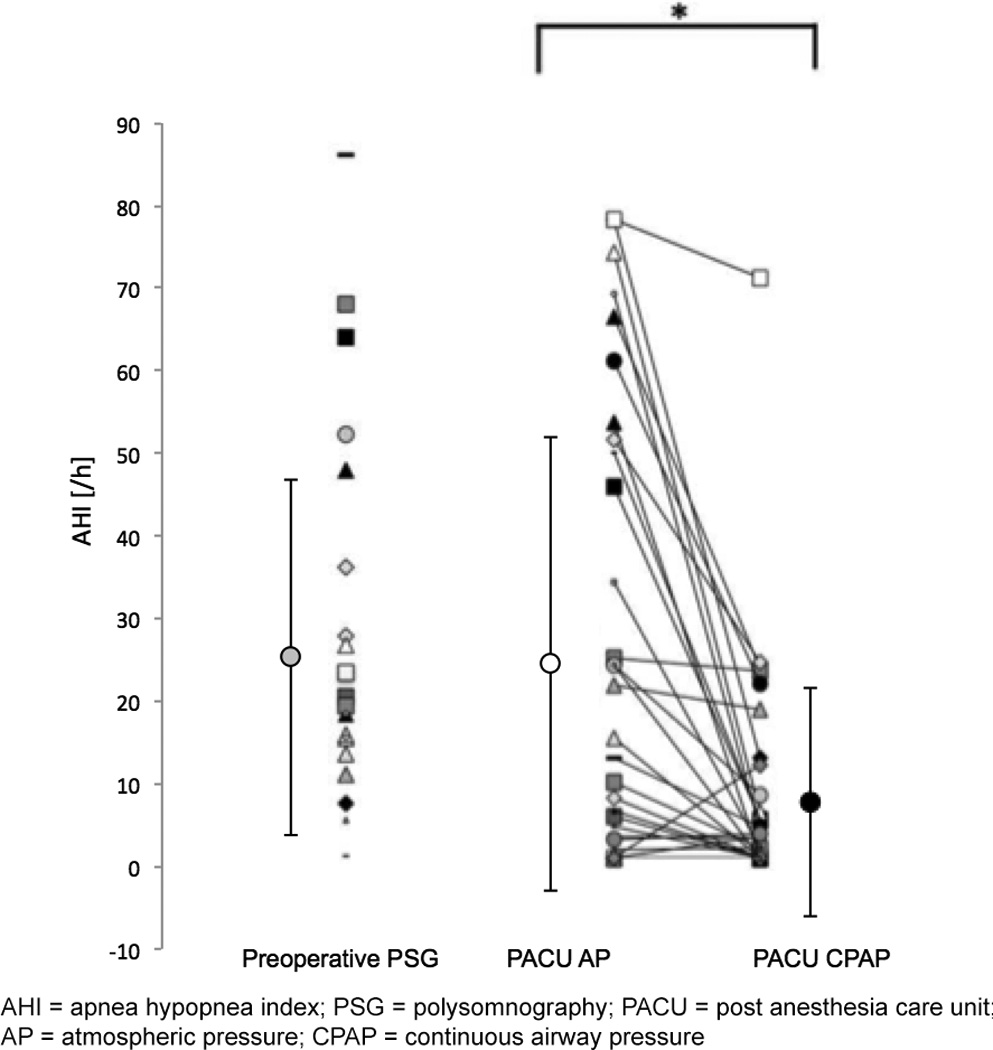
Apnea hypopnea index (AHI) during baseline preoperative evaluation visit (n=26) and in the Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) following surgery (n=33). Values for AHI during PACU stay are shown as mean ± standard deviation (circle with error bars on left) and individual values (right).
Severity of sleep apnea was unchanged from baseline at the start of study in the PACU (Baseline AHI vs. PACU AP AHI, p=0.927). During the study, CPAP treatment improved AHI (p<0.05), compared to standard of care (atmospheric pressure, AP). * denotes statistically significant difference.
