Abstract
Background
The aim of this study is to investigate whether body mass index (BMI) is a prognostic factor in gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination.
Methods
This is a retrospective study consisting of 518 patients with a histological diagnosis of gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination seen at the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University and Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center between January 2010 and April 2014. Patients were followed until December 2015. Chi-square test and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis were used to compare the clinicopathological variables and prognosis.
Results
Univariate analyses showed that significant prognostic factors included palliative gastrectomy (p < 0.001), tumor size (p < 0.001), tumor location (p = 0.011), peritoneal seeding grade (p < 0.001), ascites (p = 0.001), serum CEA level (p = 0.002), serum CA19-9 level (p = 0.033), palliative chemotherapy (p < 0.001), and BMI group (p < 0.001). For patients with palliative chemotherapy, univariate analysis revealed that palliative gastrectomy (p < 0.001), tumor size (p = 0.002), tumor location (p = 0.024), peritoneal seeding grade (p = 0.008), serum CEA level (p = 0.041), and BMI group (p < 0.001). Multivariate analysis revealed that BMI was an independent prognostic factor in gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination, especially in patients who received palliative chemotherapy.
Conclusions
BMI is a prognostic factor for patients who have gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination, especially in those who received palliative chemotherapy.
Keywords: BMI, Prognosis, Gastric cancer, Peritoneal dissemination, Palliative chemotherapy
Background
In China, gastric cancer is the third most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death [1]. And most patients with gastric cancer are diagnosed with an advanced stage of the disease in China, some even with metastatic disease [2, 3]. Peritoneal dissemination is the most common manifestation for late-stage gastric cancer [4]. The prognosis of patients who have gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination is very poor, even with the development of targeted therapy and chemotherapy [5, 6]. Palliative gastrectomy is still controversial for this group of patients. In clinic, we believed that the nutritional status is an important factor that impacts the treatment and prognosis of patients who have gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination.
Body mass index (BMI) is commonly used to assess nutritional status [7]. According to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) guidelines, BMI is divided into three groups with 18.5 and 25 as the cutoff values for a normal BMI level. However, in Asia, a BMI range of 18.5 to 23 is always used to classify people into the underweight group, normal range group, and overweight group [8]. BMI has always been used as an indicator of the status of patients. It had been reported that the BMI would infect the surgical outcomes in colorectal cancer, pancrea cancer, liver cancer, and so on. [9–13]. However, the controversy of the BMI on perioperative morbidity still remained [14–17]. In a report by Pawlik et al. about the BMI and gastric cancer, the overall survival of patients with underweight patients with a BMI <18.5 kg/m2 after gastrectomy for cancer was worse than those with BMI higher than 18.5 [18]. Hu et al. reported that a low BMI was associated with more severe postoperative complications and a poor prognosis, compared to patients with a normal BMI [19]. However, there are no reports in the current literature that have examined the relationship between BMI and the prognosis of patients who have gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination.
The aim of our study was to examine the relationship between BMI and the prognosis of gastric cancer patients who have peritoneal dissemination.
Methods
Ethics approval and consent
All patients provided written informed consent for their information to be stored in a hospital database. A separate consent was obtained for the use of this information for research purposes. Study approval was obtained from independent ethics committees at the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University. This study was undertaken in accordance with the ethical standards of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki.
Patients
Between January 2000 and April 2014, a total of 518 patients were histologically proven and diagnosed with gastric adenocarcinoma with peritoneal metastasis in surgery in The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University and Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. Patients were divided into three groups based on their BMI using 18.5 and 23 as the cutoff values. The clinicopathologic characteristics and clinical outcomes of all 518 patients were reviewed.
Patient inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) WHO performance status of 0 to 1; (2) the patient underwent surgery and had histologically proven gastric adenocarcinoma of the stomach with peritoneal dissemination; (3) no synchronous or metachronous cancers; (4) no history of previous radiotherapy or other treatments, including immunotherapy or traditional Chinese medicine; and (5) no prior gastric surgery.
Classification of peritoneal seeding
According to the first English edition of the Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma, the degree of peritoneal metastasis was classified as follows: P0, no peritoneal dissemination or seeding; P1, disseminating metastasis to the region directly adjacent to the peritoneum of the stomach (above the transverse colon including the greater omentum); P2, several scattered metastases to the distant peritoneum and ovarian metastasis alone; and P3, numerous metastases to the distant peritoneum [20].
Follow-up
Following treatment, patients were monitored every month for the first year, every 3 months for the second year, and every 6 months thereafter. Telephone calls and letters were used to follow-up patients who were unable to attend regular follow-up assessments. Complete data were collected for all 523 patients through December 2015.
Statistical methods
A chi-square test was used to compare the categorical variables between the palliative operative group and the other groups. Student’s t test was used to compare continuous variables. Univariate survival analyses were performed using Kaplan-Meier methods. Survival curves were compared using the log-rank test. Analyses were performed using SPSS software v.20.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL) for Windows. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
Results
Patient demographics
Among the 518 patients with gastric cancer and peritoneal dissemination, 330 underwent non-curative gastrectomy, while 188 patients did not. Their median age was 59 years (range, 18–83). Of these patients, 289 were male and 229 were female. The 1-year overall survival of the entire cohort was 26.0%, with a median survival of 13.2 months. Patients were separated into three groups based on their BMI with the cutoff values of 18.5 and 23. There were 167 patients with a BMI <18.5, 232 with a BMI 18.5–23, and 119 patients with a BMI >23. The patient clinicopathological characteristics are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Clinical pathological data for gastric cancer patients with different BMI groups
| Clinical pathological data | Fewer than 18.5 (n = 167 cases) | Between 18.5–23 (n = 232 cases) |
Greater than 23 (n = 119 cases) | p value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | % | Cases | % | Cases | % | |||
| Age (years) | Mean | 52.6 | 52.9 | 53.3 | – | |||
| Range | 20–85 | 19–85 | 29–84 | |||||
| Sex | Male | 95 | 56.9 | 122 | 52.6 | 72 | 60.5 | |
| Female | 72 | 43.1 | 110 | 47.4 | 47 | 39.5 | 0.347 | |
| Tumor location | Gastric cardia | 40 | 24.0 | 47 | 20.3 | 31 | 26.1 | |
| Middle | 26 | 15.6 | 47 | 20.3 | 32 | 26.9 | ||
| Antrum | 63 | 37.7 | 92 | 39.7 | 36 | 30.3 | ||
| Total stomach | 38 | 22.8 | 46 | 19.8 | 20 | 16.8 | 0.181 | |
| Surgery | Gastrectomy | 90 | 53.9 | 165 | 71.1 | 75 | 63.0 | |
| No gastrectomy | 77 | 46.1 | 67 | 28.9 | 44 | 37.0 | 0.002 | |
| Tumor size | <5 cm | 50 | 29.9 | 91 | 39.2 | 47 | 39.5 | |
| ≥5 and <10 cm | 83 | 49.7 | 104 | 44.8 | 56 | 47.1 | ||
| ≥10 cm | 34 | 20.4 | 37 | 15.9 | 16 | 13.4 | 0.249 | |
| Serum CEA level | <5 ng/ml | 104 | 67.5 | 165 | 73.7 | 80 | 70.8 | |
| ≥5 ng/ml | 50 | 32.5 | 59 | 26.3 | 33 | 29.2 | 0.433 | |
| CA19-9 level | <35 U/ml | 91 | 59.9 | 151 | 69.3 | 72 | 63.7 | |
| ≥35U/ml | 61 | 40.1 | 67 | 30.7 | 41 | 36.3 | 0.166 | |
| Seeding gradea | P1 | 28 | 16.8 | 66 | 28.4 | 42 | 35.3 | |
| P2 | 44 | 26.3 | 72 | 31.0 | 33 | 27.7 | ||
| P3 | 95 | 56.9 | 94 | 40.5 | 44 | 37.0 | 0.001 | |
| Multi-site metastasis | Without | 97 | 58.1 | 181 | 78.0 | 81 | 68.1 | |
| With | 70 | 41.9 | 51 | 22.0 | 38 | 31.9 | < 0.001 | |
| Chemotherapy | Without | 77 | 46.1 | 68 | 29.3 | 36 | 30.3 | |
| With | 90 | 53.9 | 164 | 70.7 | 83 | 69.7 | 0.001 | |
aPeritoneal dissemination grade was divided into P1, P2, and P3 groups under the standard of first English version of Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma
Univariate analyses of the prognosis of this group of gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination
Based on Kaplan-Meier analysis, palliative gastrectomy (p < 0.001), tumor size (p < 0.001), tumor location (p = 0.011), peritoneal seeding grade (p < 0.001), ascites (p = 0.001), serum CEA level (p = 0.002), serum CA19-9 level (p = 0.033), palliative chemotherapy (p < 0.001), and BMI group (p < 0.001) were significant prognostic factors in this cohort, and the results were shown in Fig. 1. As shown in Table 2, the median survival of patients based on BMI were 8.17 months in patients with a BMI less than 18.5, 18.67 months for those with a BMI between 18.5 and 23, and 11.87 months in patients with a BMI greater than 23.
Fig. 1.
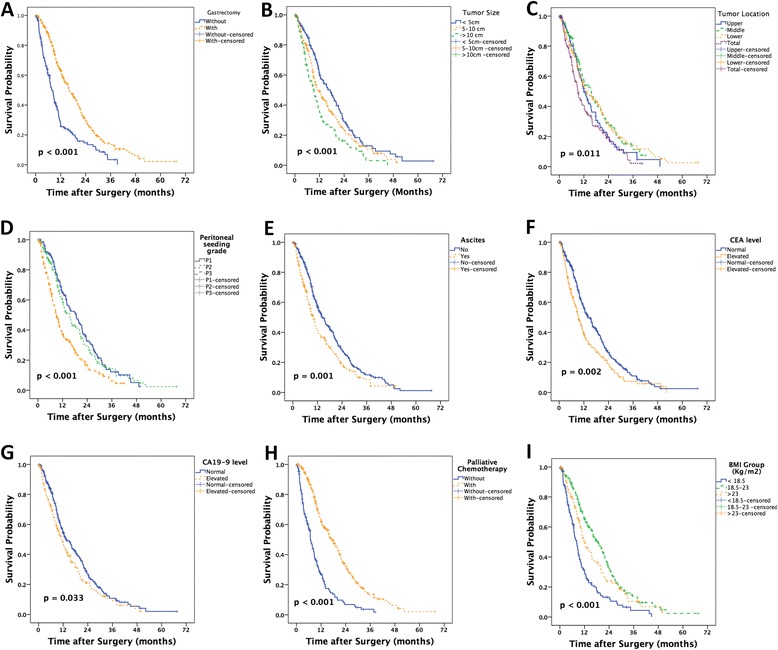
The Kaplan-Meier analysis of the prognosis of this group of gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination. Palliative gastrectomy (a), tumor size (b), tumor location (c), peritoneal seeding grade (d), ascites (e), serum CEA level (f), serum CA19-9 level (g), palliative chemotherapy (h), and BMI group (i) were significant prognostic factors in this cohort
Table 2.
Univariate analysis of the overall survival in these group gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination
| Variables | n | 1-year survival rate (%) | Median survival (months) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All 518 gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination | ||||
| Palliative gastrectomy | <0.001 | |||
| With | 330 | 19 | 7.33 | |
| Without | 188 | 31 | 16.13 | |
| Tumor size | <0.001 | |||
| <5 cm | 188 | 31 | 17.30 | |
| 5 and <10 cm | 243 | 26 | 11.00 | |
| >10 cm | 87 | 18 | 9.30 | |
| Tumor location | 0.011 | |||
| Upper | 118 | 23 | 12.00 | |
| Middle | 105 | 30 | 15.60 | |
| Lower | 191 | 39 | 13.33 | |
| Total | 104 | 20 | 8.97 | |
| Peritoneal seeding grade | <0.001 | |||
| P1 | 136 | 34 | 18.67 | |
| P2 | 149 | 31 | 15.48 | |
| P3 | 233 | 19 | 8.97 | |
| Ascite | 0.001 | |||
| With | 207 | 20 | 9.87 | |
| Without | 311 | 31 | 14.27 | |
| Serum CEA level (ng/ml) | 0.002 | |||
| Normal | 349 | 29 | 14.03 | |
| Elevated | 142 | 20 | 9.33 | |
| Serum CA19-9 level (U/ml) | 0.033 | |||
| Normal | 314 | 29 | 13.53 | |
| Elevated | 169 | 22 | 11.27 | |
| Palliative chemotherapy | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 337 | 35 | 17.40 | |
| No | 181 | 9 | 6.90 | |
| BMI group (kg/m2) | <0.001 | |||
| <18.5 | 167 | 15 | 8.17 | |
| 18.5–23 | 232 | 35 | 18.67 | |
| >23 | 119 | 25 | 11.87 | |
BMI value was an independent prognostic factor of gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination by multivariate analyses
Cox regression model was used to identify the independent prognostic risk factors in patients with gastric cancer and peritoneal seeding. The results revealed that palliative gastrectomy, peritoneal seeding grade, serum CEA level, palliative chemotherapy, and BMI value were independent prognostic risk factors. All of these results are presented in Table 3.
Table 3.
Multivariate analyses of the overall survival in gastric cancer patients (Cox regression model)
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| OS in gastric cancer patients | |||
| Palliative gastrectomy (Gastrectomy vs. without gastrectomy)a |
0.689 | 0.540–0.879 | 0.003 |
| Tumor size (<5, ≥5, and <10 vs. ≥10 cm) |
1.176 | 0.999–1.383 | 0.051 |
| Tumor location (Upper, middle, and lower vs. total) |
1.080 | 0.962–1.213 | 0.192 |
| Ascite (With vs. without) |
1.026 | 0.817–1.288 | 0.827 |
| Peritoneal seeding grade (P1 and P2 vs. P3) |
1.298 | 1.124–1.500 | < 0.001 |
| Serum CEA Level (Normal vs. elevated) |
1.424 | 1.120–1.810 | 0.004 |
| Serum CA19-9 Level (Normal vs. elevated) |
1.133 | 0.900–1.424 | 0.287 |
| Palliative chemotherapy (With vs. without) |
0.399 | 0.314–0.506 | < 0.001 |
| BMI group (<18.5 and 18.5–23 vs. >23) |
0.812 | 0.686–0.962 | 0.016 |
Abbreviations: OS overall survival, HR hazard ratio, CI confidence interval
aThe factor listed at the last was used as the control level in this Cox regression model
Univariate analyses and multivariate analysis of the prognosis of gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination without palliative chemotherapy
Patients were stratified based on having received palliative chemotherapy or not. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that palliative gastrectomy (p < 0.001), tumor size (p = 0.049), tumor location (p = 0.002), peritoneal seeding grade (p < 0.001), ascites (p = 0.017), serum CEA level (p = 0.024), serum CA19-9 level (p = 0.014), and BMI group (p = 0.008) were prognostic risk factors. All of these results are presented in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
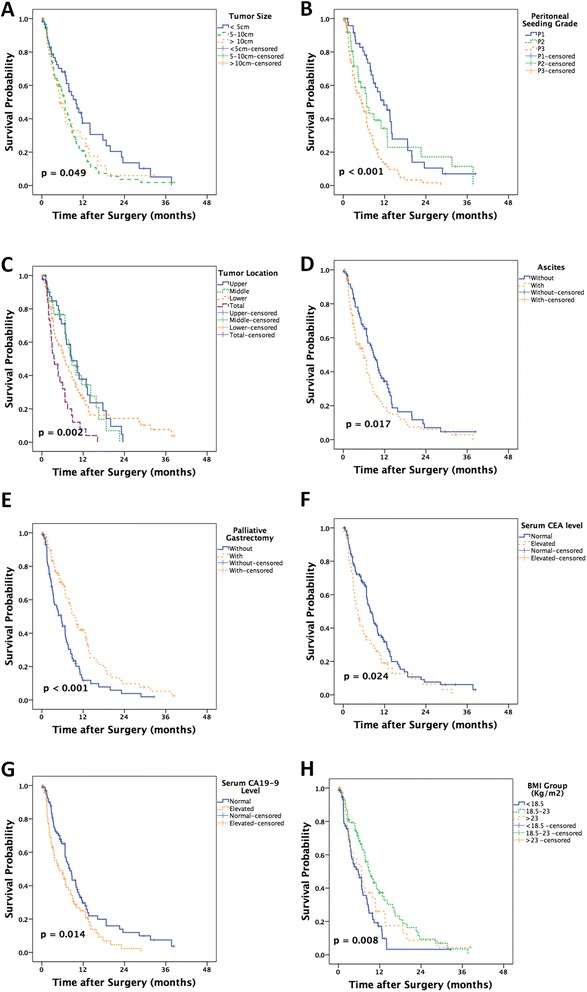
The Kaplan-Meier analysis of the prognosis of this group of gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination without palliative chemotherapy. Palliative gastrectomy (a), tumor size (b), tumor location (c), peritoneal seeding grade (d), ascites (e), serum CEA level (f), serum CA19-9 level (g), and BMI group (h) were prognostic risk factors
Only the tumor location and the peritoneal seeding grade remained independent prognostic factors upon Cox regression analysis, as shown in Table 4.
Table 4.
Multivariate analyses of the overall survival in these group gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination without palliative chemotherapy (Cox regression model)
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| OS in gastric cancer patients | |||
| Palliative gastrectomy (Gastrectomy vs. without gastrectomy)a |
0.772 | 0.516–1.154 | 0.207 |
| Tumor size (<5, ≥5, and <10 vs. ≥10 cm) |
1.016 | 0.771–1.339 | 0.910 |
| Tumor location (Upper, middle, and lower vs. total) |
1.314 | 1.070–1.614 | 0.009 |
| Ascite (With vs. without) |
0.969 | 0.653–1.438 | 0.877 |
| Peritoneal seeding grade (P1 and P2 vs. P3) |
1.507 | 1.178–1.928 | 0.001 |
| Serum CEA Level (Normal vs. elevated) |
1.356 | 0.915–2.011 | 0.129 |
| Serum CA19-9 Level (Normal vs. elevated) |
1.384 | 0.943–2.031 | 0.097 |
| BMI group (<18.5 and 18.5–23 vs. >23) |
0.871 | 0.654–1.161 | 0.346 |
Abbreviations: OS overall survival, HR hazard ratio, CI confidence interval
aThe factor listed at the last was used as the control level in this Cox regression model
Univariate analyses and multivariate analysis of the prognoses of gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination with palliative chemotherapy
As shown in Fig. 3, 337 patients received palliative chemotherapy in this cohort. Results from Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the palliative gastrectomy (p < 0.001), tumor size (p = 0.002), tumor location (p = 0.024), peritoneal seeding grade (p = 0.008), serum CEA level (p = 0.041), and BMI group (p < 0.001) were risk factors.
Fig. 3.
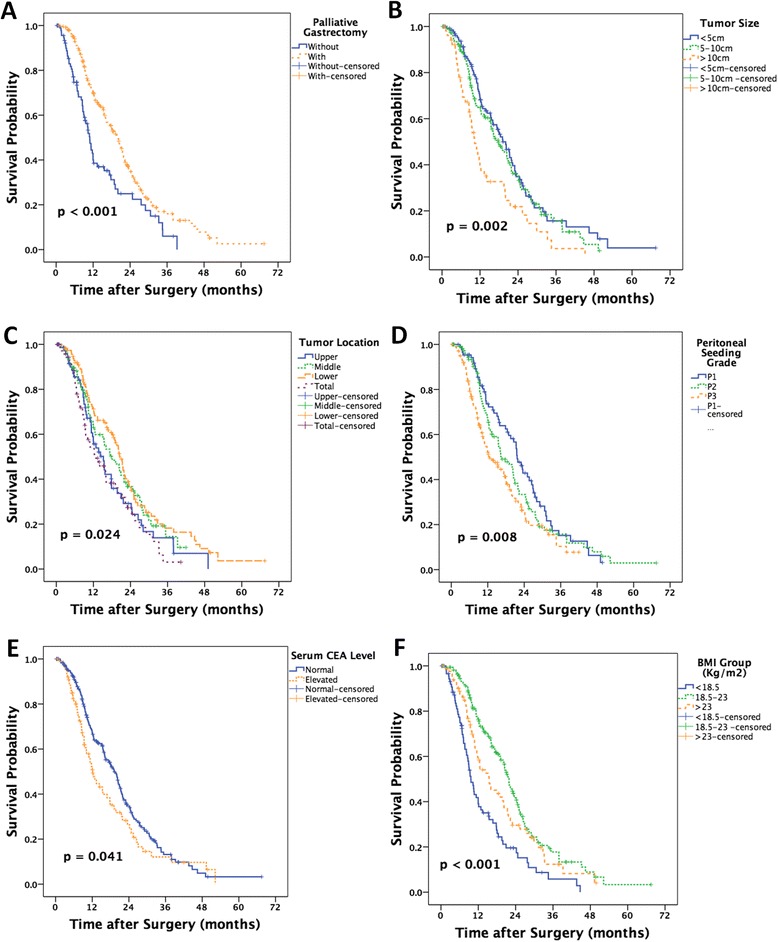
The Kaplan-Meier analysis of the prognosis of this group of gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination underwent palliative chemotherapy. Palliative gastrectomy (a), tumor size (b), tumor location (c), peritoneal seeding grade (d), serum CEA level (e), and BMI group (f) were risk factors
Multivariate analysis showed that palliative gastrectomy, serum CEA level, and BMI group were independent prognostic factors, as showed in Table 5.
Table 5.
Multivariate analyses of the overall survival in these group gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination with palliative chemotherapy (Cox regression model)
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| OS in gastric cancer patients | |||
| Palliative gastrectomy (Gastrectomy vs. without gastrectomy)a |
0.652 | 0.477–0.893 | 0.008 |
| Tumor size (<5, ≥5, and <10 vs. ≥10 cm) |
1.265 | 1.027–1.559 | 0.027 |
| Tumor location (Upper, middle, and lower vs. total) |
0.972 | 0.844–1.118 | 0.689 |
| Peritoneal seeding grade (P1 and P2 vs. P3) |
1.172 | 0.982–1.398 | 0.079 |
| Serum CEA level (Normal vs. elevated) |
1.413 | 1.045–1.912 | 0.025 |
| BMI group (<18.5 and 18.5–23 vs. >23) |
0.783 | 0.636–0.964 | 0.021 |
Abbreviations: OS overall survival, HR hazard ratio, CI confidence interval
aThe factor listed at the last was used as the control level in this Cox regression model
Discussion
With the increasing prevalence of obesity that occurred in China and worldwide [21], few recent reports have concluded that some classes of obesity can be considered “healthy.” Findings from our study show that BMI value was an independent prognostic factor for patients who have gastric carcinoma with peritoneal seeding. Patients with low BMI as well as a high BMI had a worse survival rate compared with patients who had a BMI within normal range. Previous studies have reported that patients with higher BMI would be at higher risk for perioperative morbidity after major abdominal cancer surgery [16, 22]. In the study from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, the results showed that higher BMI of the patients (higher than 25) would bring longer operative time, fewer lymph nodes, and higher complications [15]. In our study, a higher ratio of the patients with a normal BMI underwent palliative gastrectomy, which is an important independent prognostic factor, in addition to palliative chemotherapy.
However, the function of palliative gastrectomy remains controversial, especially for the patients with peritoneal dissemination. Some studies have suggested that palliative gastrectomy may improve survival without increasing morbidity and mortality [23, 24], while other reports have contradicted this suggestion [2, 25]. Selection of patients for palliative gastrectomy remains controversial for both surgeons and oncologists. In our studies, we stratified the 518 patients based on receipt of palliative chemotherapy to eliminate the influences of the palliative chemotherapy. Among the patients who did not receive palliative chemotherapy, neither palliative gastrectomy nor BMI was independent prognostic factors. Conversely, among patients who received palliative chemotherapy, both palliative gastrectomy and BMI were independent prognostic factors. This finding implies that patients with a normal BMI who receive palliative chemotherapy may benefit from gastrectomy.
As a retrospective study, there were confounding factors that may have influenced the statistical analyses and conclusions. BMI is an important factor that reflects the nutritional status and is correlated with postoperative complications and long-term survival of gastric cancer. Findings from this study suggest that gastric cancer patients with a normal BMI may benefit from palliative gastrectomy combined with chemotherapy. Additional experiments and clinical trials are needed to validate the important value of BMI on the prognosis of gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination.
Conclusions
BMI is a prognostic factor for patients who have gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination, especially in those who received palliative chemotherapy. BMI can be used to predict the effect of palliative chemotherapy on these patients.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20110171110075) and Guangdong Medical Research Foundation (No. A2015124).
Availability of data and materials
We do not wish to share our data, because all these data only can be used under the permission of the ethics committees at the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University.
Authors’ contributions
PJS and CYB designed this study. CS, NRC, and OLY checked the data, and CS did the statistical analysis. XJ, LYF, and ZZW modified the manuscript and made recommendations. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All patients provided written informed consent for their information to be stored in a hospital database. A separate consent was obtained for the use of this information for research purposes. Study approval was obtained from independent ethics committees at the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University.
Abbreviations
- BMI
Body mass index (BMI)
- OS
Overall survival
- WHO
World Health Organization
Contributor Information
Shi Chen, Email: cscp@163.com.
Run-Cong Nie, Email: nierc@sysucc.org.cn.
Li-Ying OuYang, Email: ouyly@sysucc.org.cn.
Yuan-Fang Li, Email: liyuanf@sysucc.org.cn.
Jun Xiang, Email: xxj007@126.com.
Zhi-Wei Zhou, Email: zhouzhw@sysucc.org.cn.
YingBo Chen, Phone: +86-20-87343625, Email: chenyb@sysucc.org.cn.
JunSheng Peng, Phone: +86-20-38254092, Email: pengjunsheng@tom.com.
References
- 1.Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen S, Li YF, Feng XY, Zhou ZW, Yuan XH, Chen YB. Significance of palliative gastrectomy for late-stage gastric cancer patients. J Surg Oncol. 2012;106(7):862–71. doi: 10.1002/jso.23158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang XF, Huang CM, Lu HS, Wu XY, Wang C, Guang GX, et al. Surgical treatment and prognosis of gastric cancer in 2,613 patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10(23):3405–8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hioki M, Gotohda N, Konishi M, Nakagohri T, Takahashi S, Kinoshita T. Predictive factors improving survival after gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis. World J Surg. 2010;34(3):555–62. doi: 10.1007/s00268-010-0396-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9742):687–97. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61121-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T, Takagane A, Akiya T, Takagi M, et al. S-1 plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): a phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(3):215–21. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Janssen I, Heymsfield SB, Allison DB, Kotler DP, Ross R. Body mass index and waist circumference independently contribute to the prediction of nonabdominal, abdominal subcutaneous, and visceral fat. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;75(4):683–8. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/75.4.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.MacKay NJ. Scaling of human body mass with height: the body mass index revisited. J Biomech. 2010;43(4):764–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.10.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Amri R, Bordeianou LG, Sylla P, Berger DL. Obesity, outcomes and quality of care: body mass index increases the risk of wound-related complications in colon cancer surgery. Am J Surg. 2014;207(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Balentine CJ, Wilks J, Robinson C, Marshall C, Anaya D, Albo D, et al. Obesity increases wound complications in rectal cancer surgery. J Surg Res. 2010;163(1):35–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Santoso JT, Barton G, Riedley-Malone S, Wan JY. Obesity and perioperative outcomes in endometrial cancer surgery. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012;285(4):1139–44. doi: 10.1007/s00404-011-2116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tsai S, Choti MA, Assumpcao L, Cameron JL, Gleisner AL, Herman JM, et al. Impact of obesity on perioperative outcomes and survival following pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic cancer: a large single-institution study. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14(7):1143–50. doi: 10.1007/s11605-010-1201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bhayani NH, Hyder O, Frederick W, Schulick RD, Wolgang CL, Hirose K, et al. Effect of metabolic syndrome on perioperative outcomes after liver surgery: a National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) analysis. Surgery. 2012;152(2):218–26. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2012.05.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kodera Y, Ito S, Yamamura Y, Mochizuki Y, Fujiwara M, Hibi K, et al. Obesity and outcome of distal gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy for carcinoma. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2004;51(58):1225–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bickenbach KA, Denton B, Gonen M, Brennan MF, Coit DG, Strong VE. Impact of obesity on perioperative complications and long-term survival of patients with gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(3):780–7. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2653-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yasunaga H, Horiguchi H, Matsuda S, Fushimi K, Hashimoto H, Ayanian JZ. Body mass index and outcomes following gastrointestinal cancer surgery in Japan. Br J Surg. 2013;100(10):1335–43. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kulig J, Sierzega M, Kolodziejczyk P, Dadan J, Drews M, Fraczek M, et al. Implications of overweight in gastric cancer: a multicenter study in a Western patient population. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2010;36(10):969–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2010.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ejaz A, Spolverato G, Kim Y, Poultsides GA, Fields RC, Bloomston M, et al. Impact of body mass index on perioperative outcomes and survival after resection for gastric cancer. J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.12.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chen HN, Chen XZ, Zhang WH, Yang K, Chen XL, Zhang B, et al. The impact of body mass index on the surgical outcomes of patients with gastric cancer: a 10-year, single-institution cohort study. Medicine. 2015;94(42):e1769. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nishi MOY, Miwa K. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma. 1 English. Tokyo: Kanehara & Co; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yanovski SZ, Yanovski JA. Obesity prevalence in the United States—up, down, or sideways? N Engl J Med. 2011;364(11):987–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1009229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mullen JT, Davenport DL, Hutter MM, Hosokawa PW, Henderson WG, Khuri SF, et al. Impact of body mass index on perioperative outcomes in patients undergoing major intra-abdominal cancer surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(8):2164–72. doi: 10.1245/s10434-008-9990-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lasithiotakis K, Antoniou SA, Antoniou GA, Kaklamanos I, Zoras O. Gastrectomy for stage IV gastric cancer. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(5):2079–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yang K, Liu K, Zhang WH, Lu ZH, Chen XZ, Chen XL, et al. The value of palliative gastrectomy for gastric cancer patients with intraoperatively proven peritoneal seeding. Medicine. 2015;94(27):e1051. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kokkola A, Louhimo J, Puolakkainen P. Does non-curative gastrectomy improve survival in patients with metastatic gastric cancer? J Surg Oncol. 2012;106(2):193–6. doi: 10.1002/jso.23066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
We do not wish to share our data, because all these data only can be used under the permission of the ethics committees at the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University.


