Abstract
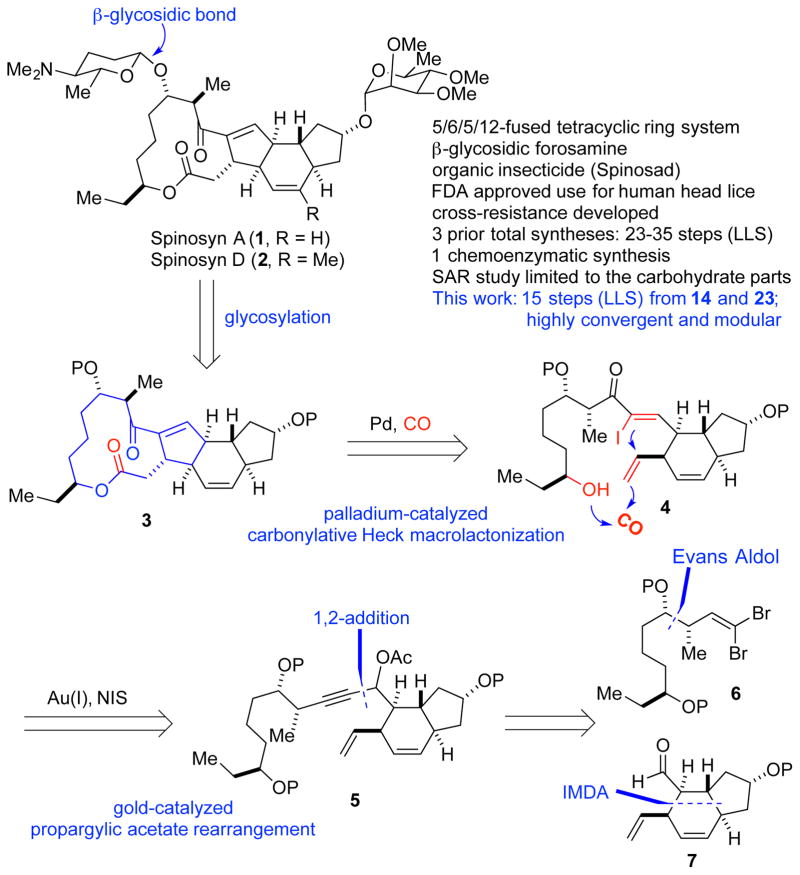
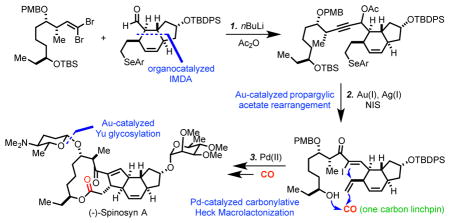
Spinosyn A (1), a complex natural product featuring a unique 5,6,5,12-fused tetracyclic core structure, is the major component of spinosad, an organic insecticide and an FDA-approved agent used worldwide. Herein, we report an efficient total synthesis of (−)-spinosyn A with 15 steps in the longest linear sequence and 23 steps total from readily available compounds 14 and 23. The synthetic approach features several important catalytic transformations including a chrial amine-catalyzed intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction to afford 22 in excellent diastereoselectivity, a one-step gold-catalyzed propargylic acetate rearrangement to convert 28 to α-iodoenone 31, an unprecedented palladium-catalyzed carbonylative Heck macrolactonization to form the 5,12-fused macrolactone in one step, and a gold-catalyzed Yu glycosylation to install the challenging β-forosamine. This total synthesis is highly convergent and modular, thus offering opportunities to synthesize spinosyn analogs to address the emerging cross-resistance problems.
Graphical Abstract
Spinosyn A (1, Figure 1) is the major component of spinosad, an important organic and natural insecticide that is widely used around the world in agriculture.1 Spinosad is also an FDA-approved agent for treating human head lice. Spinosyns A and D were produced by Saccharopolyspora spinosa in a roughly 17:3 ratio and were demonstrated to have novel mode of actions.2 They primarily target the insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) of the nervous system. They also function as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter agonists. The overall effects make the insect hyperexcited, which ultimately leads to death. More importantly, in addition to spinosad’s high efficacy and broad insect pest spectrum, it has very low mammalian toxicity as well as an excellent environment profile. Unfortunately, cross-resistance has been observed for spinosad recently, which puts the usage life of this important insecticide at risk.3 Thus, developing the next generation of spinosad insecticides becomes important and urgent. So far, the current biosynthesis approach is effective for producing spinosyns in large scale, but cannot be adapted to make a large number of analogs with structural variations at different sites to target the emerging cross-resistance.
Figure 1.
Spinosyn A and retrosynthetic analysis.
Structurally, spinosyn A and D consist of a unique 5,6,5,12-fused tetracyclic ring system attached with two carbohydrates: D-forosamine and tri-O-methyl-L-rhamnose. In addition to the synthetic challenges posed by the tetracyclic core, stereoselective installation of the β-D-forosamine, a 2-deoxy sugar, is nontrivial as well. So far, three total syntheses of spinosyn A have been reported from the groups of Evans (31 steps in the longest linear sequence (LLS), 37 steps total),4 Paquette (35 steps LLS, 44 steps total),5 and Roush (23 steps LLS, 29 steps total).6 One chemoenzymatic synthesis has been reported by Liu and co-workers.7 This chemoenzymatic synthesis requires 23 steps (LLS) and 35 total steps including one enzymatic step. Currently, most of the analog exploration relies on semi-synthesis and focuses on modifications of the tri-O-methyl-L-rhamnose moiety.8 Structural modification of the tetracyclic core is important but highly challenging and an efficient and modular synthetic approach toward spinosyns is needed for this purpose. Herein, we report such a total synthesis of (−)-spinosyn A with 15 steps in the longest linear sequence and 23 steps total from readily available compounds 14 and 23.
Our group9 has an ongoing interest in developing novel catalytic carbonylative reactions10 to streamline the synthesis of complex bioactive natural products with carbon monoxide as a one carbon linchpin. After carefully examining the structural features of the spinosyns, we envisioned the possibility of developing an unprecedented palladium-catalyzed carbonylative Heck macrolactonization to construct the spinosyn A aglycone (3) from (Z)-α-iodoenone 4. Such a carbonylative Heck macrolactonization, while challenging, would significantly improve the synthetic efficiency and enable unique bond scission of the carbocycle and macrolactone moieties. Stereoselective synthesis of α-iodoenone 4 is not a simple task. The commonly used Wittig-type olefination is not suitable because of low stereoselectivity and the issues associated with the accessibility and stability of the corresponding α-iodoylide reagent.11 Iodination of the corresponding acyclic enone is problematic as well.12 Inspired by the recent discoveries of Zhang13 and Shi14 for the stereoselective rearrangement of propargylic acetates to Z or E α-iodoenones by using different gold(I) catalysts, we envisioned propargylic acetate 5 as the precursor of 4. Compound 5 could be assembled by 1,2-addition of an acetylide derived from dibromide 6 to aldehyde 7 followed by in situ acetate formation. This bond disconnection is critical and strategic because it would cut compound 5 into two relatively simple pieces with about equal complexity. Compound 6 could be readily synthesized with an Evans aldol reaction to construct the two contiguous carbon centers. Compound 7 could be assembled with an intramolecular Diels-Alder (IMDA) reaction.
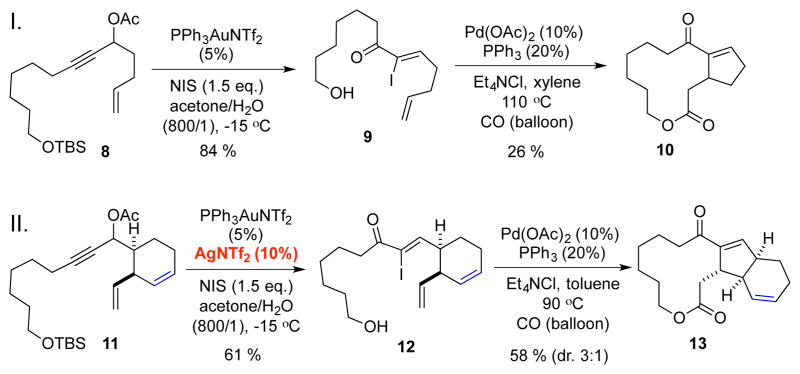
So far, there have been no reports of palladium-catalyzed carbonylative-Heck macrolactonization. Even for the sporadically reported intramolecular carbonylative Heck reactions,15 issues such as over cabonylation or no carbonylation are potential problems. In the proposed gold-catalyzed propargylic acetate rearrangement, there is a 1,6-enyne structural motif in substrate 5 and a potential enyne cycloisomerization16 may compete with the desired rearrangement. Under these circumstances, model studies were conducted (Scheme 1). We first prepared propargylic acetate 8 with a 1,6-enyne moiety. To our delight, using Zhang’s protocol,13 the gold-catalyzed rearrangement in the presence of NIS provided α-iodoenone 9 in excellent yield and stereoselectivity without any detection of the corresponding cycloisomerization byproduct. The TBS-protecting group was removed as a bonus. We then explored the feasibility of using carbonylative-Heck macrolactonization to build the 5,12-fused macrolide. After extensive investigations, we were able to obtain desired product 10 in 26% yield with a catalytic amount of Pd(OAc)2/PPh3 under balloon pressure of CO. While the yield was not yet optimal, this result demonstrates the feasibility and efficacy of using a carbonylative-Heck macrolactonization to build the 5,12-fused macrolide ring system. Encouraged by this simple model study, we prepared model substrate 11 to investigate four things. First, will the internal double bond of the six-membered carbocycle intercept the acyl-palladium species via a 5-exo-trig cyclization before it undergoes the macrolactonization with the tethered remote alcohol? Second, will the six-membered ring facilitate the carbonylative-Heck macrolactonization via a Thorpe-Ingold type effect to improve the reaction yield? Third, with the Thorpe-Ingold type effect, will 1,6-enyne cycloisomerization become a problem since the terminal olefin and the alkyne are getting closer in comparison to the case of 8? Fourth, what is the stereochemical outcome of the newly generated carbon center? With these questions in mind, substrate 11 was subjected to the gold-catalyzed rearrangement conditions. The reaction turned out to be quite complex and α-iodoenone 12 was produced in trace amount. We then found that addition of 10% of AgNTf2 to the reaction system is beneficial and 12 was obtained in 61% yield, indicating some silver effect in this transformation.17 More importantly, the carbonylative Heck-macrolactonization was much more effective and product 13 was produced in 58% yield with 3:1 diastere-oselectivity favoring the desired stereochemical outcome. About 10% of the regular Heck reaction product was obtained as well. These results indicate the critical role of the six-membered ring in facilitating the carbonylative Heck-macrolactonization process.
Scheme 1.
Model studies.
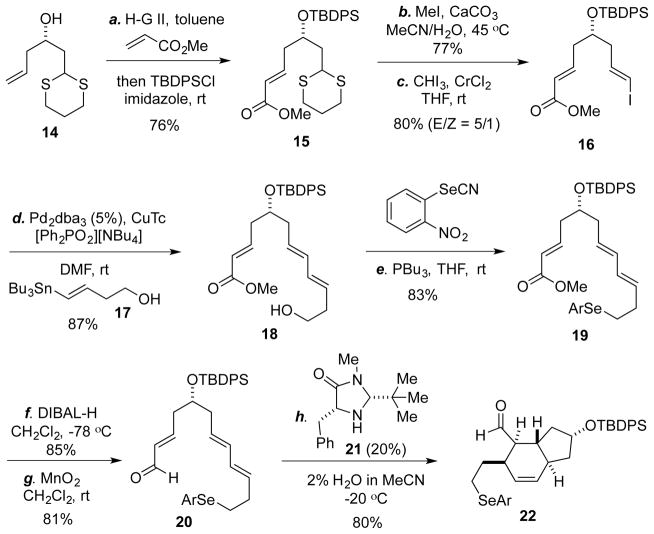
We then embarked on the total synthesis. We planned to use a chiral amine-catalyzed IMDA reaction developed by the MacMillan group to control the relative stereochemistry of the trans 5,6-fused ring system,18 since the substrate-controlled cases tend to give low stereoselectivity. Among the substrates reported in MacMillan’s work, a conjugated triene substrate was shown to be ineffective, therefore we decided to introduce the terminal olefin after the IMDA reaction and designed 20 as the IMDA precursor (Scheme 2). This choice also gives us an opportunity to release the double bond at later stage if it gets involved in the gold-catalyzed rearrangement process. The synthesis of 20 started with known compound 14,19 which can be prepared via a one-pot reaction from commercial starting materials (see the Supporting Information). Cross-metathesis with the Hoveyda-Grubbs second generation catalyst followed by TBDPS-protection gave 15 in 76% yield. Removal of the thioketal group followed by Takai olefination provided vinyl-iodide 16 with good E/Z selectivity. Stille cross-coupling20 of 16 with 17 afforded 18 in excellent yield, which was then advanced to the IMDA precursor 20 via a sequence of selenide formation, DIBAL-H reduction, and MnO2 oxidation. The IMDA reaction took place smoothly with a 20% loading of catalyst 21 and product 22 was produced in 80% yield as a single diastereomer. Notably, the IMDA reaction is sluggish and not selective in the absence of the chiral amine catalyst even at elevated temperatures.
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of 22.
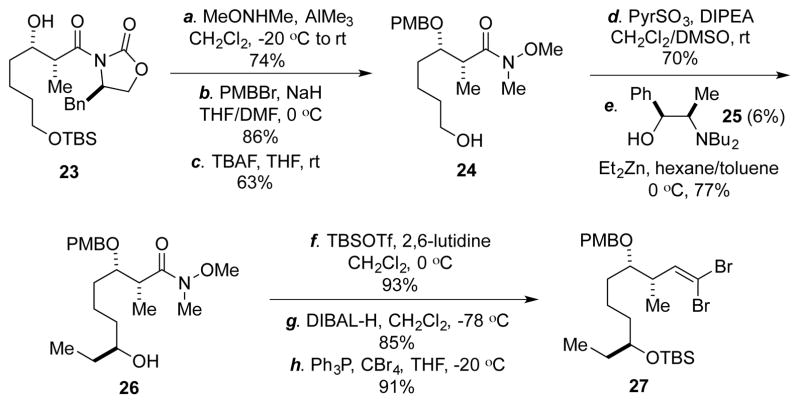
We then prepared dibromide 27 (Scheme 3). The synthesis is quite straightforward and started from known compound 23, which can be prepared in three steps from cheap 1,5-pentanediol or one step from the more expensive 5-OTBS pentanal via an Evans aldol reaction.21 After switching the Evans chiral auxiliary to a Weinreb amide and protecting the secondary alcohol as PMB-ether, the TBS group was removed to give 24. Oxidation of 24 to an aldehyde followed by an asymmetric 1,2-addition afforded 26, which was then converted to 27 via a sequence of TBS-protection, DIBAL-H reduction, and dibromide formation.
Scheme 3.
Synthesis of 27.
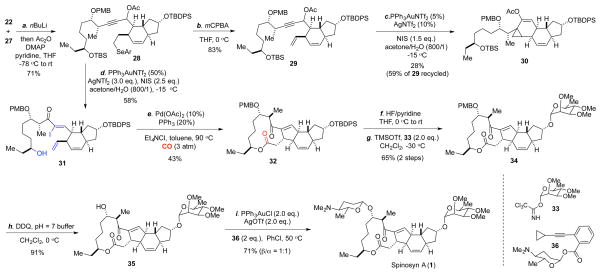
With both 22 and 27 in hand, we used the Corey-Fuchs protocol to unite them and the resulting alkoxide was converted to acetate 28 in situ (Scheme 4). Compound 28 was obtained as a mixture of diastereomers in 71% yield from a 1:1 ratio of 22 and 27. While this 1,2-addition was not stereoselective, the newly generated stereocenter will be eliminated at later stage, so the effect is not permanent. mCPBA oxidative elimination converted 28 to 29 with a terminal olefin. To our surprise, despite the success of the two model substrates, rearrangement of 29 to the corresponding α-iodoenone did not take place. Instead enyne cycloisomerization product 30 was produced in 28% yield with 59% of 29 recycled. The structure of 30 was tentatively assigned based on NMR studies. We then decided to explore the gold-catalyzed rearrangement with 28 directly and only a trace amount of desired product was obtained using the conditions established in the model studies. Notably, both the selenide and the secondary TBS-ether were found to be not stable under the rearrangement conditions, which further complicated the reaction process. However, we also saw an opportunity of realizing the rearrangement, oxidative selenide elimination, and TBS removal in just one step. After extensive reaction condition optimizations, we learned that the ratio of AgNTf2 and NIS is critical. When the amount of AgNTf2 is less than the amount of NIS, the reaction was in general complex and the desired product was produced in very low yield. The amount of water is critical as well.13a Eventually, desired product 31 was obtained in 58% yield with 3.0 equiv. of AgNTf2 and 2.5 equiv. of NIS. Carbonylative Heck macrolactonization of substrate 31 required 3 atm of carbon monoxide and higher pressure was not beneficial and even showed inhibitory effect. At last, product 32 was produced in 43% yield as a single diastereomer. The carbonylative Heck macrolactonization reaction built both the five-membered ring and the twelve-membered macrolactone in one step. Overall, a highly convergent and modular sequence was developed to convert 22 and 27 to tetracyclic intermediate 32 in only 3 steps!
Scheme 4.
Total synthesis of (−)-spinosyn A.
With the tetracyclic core structure assembled, the final stage was to install the two carbohydrate moieties. Installation of the α-tri-O-methyl-L-rhamnose proceeded smoothly. After removal of the TBDPS-protecting group with HF/pyridine, Schmidt glycosylation gave 34 in 65% yield in two steps. The spectra data of 34 matches with those reported in the Roush synthesis.6 Oxidative removal of the PMB-protecting group gave the pseudoaglycon 35 in 91% yield. The last hurdle in our synthesis was to introduce the β-D-forosamine. The difficulty involved in a direct glycosylation with a D-foroamine derived donor has been experienced by the previous pioneers and no methods have been reported to stereoselectively introduce the β-linkage. The Evans group used a silver zeolite catalyzed glycosylation of the pseudoaglycon 35 with a N-Fmoc protected glycosyl bromide donor to give a 69% yield of a 1:6 mixture of β/α-glycosides, but favoring the undesired α-isomer.4 The Paquette group used AgOTf-catalyzed glycosylation with a glycosyl sulfide donor to give the glycosylation product in 17% yield as a 2:3 mixture of β/α-glycosides, again favoring the undesired isomer.5 The Roush group used a 2-acetate glycosyl imidate donor to circumvent the stereoselectivity issue, but it requires 11 steps to synthesize this donor and another 5 steps to convert the glycosylated product to spinosyn A. Recently, Yu and co-workers reported a gold-catalyzed glycosylation, which favors β-selectivity.22 We decided to investigate the Yu glycosylation in our synthesis by using donor 36. To our delight, after finely tuning the reaction conditions, the glycosylation product was obtained in 71% yield along with 15% of recycled pseudoaglycon 35. While the β/α-selectivity is only 1:1, it is still so far the most effective way of direct glycosylation with a D-foroamine derived donor. The β/α-glycoside isomers were separated by preparative TLC to complete the total synthesis of (−)-spinosyn A, the spectra data of which match with the ones of the natural product.
Overall, we have developed an efficient and modular total synthesis of (−)-spinosyn A with 15 steps in the longest linear sequence and 23 steps total from readily available compounds 14 and 23. The synthetic approach features an organocatalyzed IMDA reaction to build the trans 5,6-fused ring in excellent diastereoselectivity, a one-step gold-catalyzed23 propargylic acetate rearrangement, selenide elimination, and TBS-removal to convert 28 to α-iodoenone 31, an unprecedented palladium-catalyzed carbonylative Heck macrolactonization to form the 5,12-fused macrolactone, and a Yu glycosylation to install the challenging β-forosamine. This total synthesis is highly convergent and flexible, thus providing new avenues to access spinosyn analogs to address the cross-resistance problems.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank NSF (CAREER 1553820) and the ACS Petroleum Research Foundation (PRF# 54896-DNI1) for financial support and the NIH P30CA023168 for supporting shared NMR resources to Purdue Center for Cancer Research. We also thank Dow AgroSciences for sharing D-forosamine and natural sample of (−)-spinosyn A. This paper is dedicated to Professor Samuel J. Danishefsky and Professor Stuart Schreiber on the occasion of their 80th and 60th birthdays, respectively.
Footnotes
ASSOCIATED CONTENT
Experimental procedures and compound characterization. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.(a) Sparks TC, Crouse GD, Durst G. Pest Manag Sci. 2001;57:896. doi: 10.1002/ps.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Kirst HA. J Antibiot. 2010;63:101. doi: 10.1038/ja.2010.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kirst HA, Michel KH, Martin JW, Creemer LC, Chio EH, Yao RC, Nakatsukasa WM, Boeck LD, Occolowitz JL, Paschal JW, Deeter JB, Jones ND, Thompson GD. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991;32:4839. [Google Scholar]
- 3.(a) Su T, Cheng ML. J Med Entomol. 2014;51:428. doi: 10.1603/me13207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Rehan A, Freed S. Crop Prot. 2014;56:10. [Google Scholar]; (c) Khan HAA, Akram W, Shad SA. Acta Trop. 2014;130:148. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Sparks T, Dripps JE, Watson GB, Paroonagian D. Pestic Biochem Phys. 2012;102:1. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Evans DA, Black WC. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115:4497. [Google Scholar]
- 5.(a) Paquette LA, Gao Z, Ni Z, Smith GF. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;120:2543. [Google Scholar]; (b) Paquette LA, Collado I, Purdie M. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;120:2553. [Google Scholar]
- 6.(a) Mergott DJ, Frank SA, Roush WR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:11955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401247101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Winbush SM, Mergott DJ, Roush WR. J Org Chem. 2008;73:1818. doi: 10.1021/jo7024515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kim HJ, Choi SH, Jeon BS, Kim N, Pongdee R, Wu Q, Liu HW. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2014;53:13553. doi: 10.1002/anie.201407806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Oliver MP, Crouse GD, Demeter DA, Sparks TC. J Agric Food Chem. 2015;63:5571. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.(a) Davis DC, Walker KL, Hu C, Zare RN, Way-mouth RM, Dai MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b06573. just accepted manuscript. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Bai Y, Davis DC, Dai MJ. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2014;53:6519. doi: 10.1002/anie.201403006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Bai Y, Dai MJ. Curr Org Chem. 2015;19:871. doi: 10.2174/1385272819666150119225149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.For reviews, see: Gehrtz PH, Hirschbeck V, Ciszek B, Fleischer I. Synthesis. 2016;48:1573.Wu XF, Neumann H, Beller M. Chem Rev. 2013;113:1. doi: 10.1021/cr300100s.
- 11.(a) Denney DB, Ross ST. J Org Chem. 1962;27:998. [Google Scholar]; (b) Speziale AJ, Ratts KW. J Org Chem. 1963;28:465. [Google Scholar]; (c) Kayser MM, Zhu J, Hooper DL. Can J Org. 1997;75:1315. [Google Scholar]
- 12.(a) Johnson CR, Adams JP, Braun MP, Senanayake PM, Wovkulich PM, Uskokovic MR. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992;33:917. [Google Scholar]; (b) Krafft ME, Cran JW. Synlett. 2005:1263. [Google Scholar]
- 13.(a) Yu M, Zhang G, Zhang L. Org Lett. 2007;9:2147. doi: 10.1021/ol070637o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Yu M, Zhang G, Zhang L. Tetrahedron. 2009;65:1846. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang D, Ye X, Shi X. Org Lett. 2010;12:2088. doi: 10.1021/ol100576m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.(a) Negishi E, Copéret C, Ma S, Mita T, Sugihara T, Tour JM. J Am Chem Soc. 1996;118:5904. [Google Scholar]; (b) Ma S, Negishi E. J Am Chem Soc. 1995;117:6345. [Google Scholar]; (c) Tour JM, Negishi E. J Am Chem Soc. 1985;107:8289. [Google Scholar]; (d) Aggarwal VK, Davies PW, Moss WO. Chem Commun. 2002:972. doi: 10.1039/b201311h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Liu C, Widenhoefer RA. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:10250. doi: 10.1021/ja046810i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Li S, Li F, Gong J, Yang Z. Org Lett. 2015;17:1240. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.For reviews: Zhang L, Sun J, Kozmin SA. Adv Synth Catal. 2006;348:2271.Jiménez-Núñez E, Echavarren AM. Chem Rev. 2008;108:3326. doi: 10.1021/cr0684319.
- 17.Wang D, Cai R, Sharma S, Jirak J, Thummanapelli SK, Akhmedov NG, Zhang H, Liu X, Petersen JL, Shi X. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:9012. doi: 10.1021/ja303862z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.(a) Wilson RM, Jen WS, MacMillan DWC. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:11616. doi: 10.1021/ja054008q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Lambert TH, Danishefsky SJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:426. doi: 10.1021/ja0574567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.(a) Jin M, Taylor RE. Org Lett. 2005;7:1303. doi: 10.1021/ol050070g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Trost BM, Amans D, Seganish WM, Chung CK. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:17087. doi: 10.1021/ja907924j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fürstner A, Funel J-A, Tremblay M, Bouchez LC, Nevado C, Waser M, Ackerstaff J, Stimson CC. Chem Commun. 2008;25:2873. doi: 10.1039/b805299a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang H, Negretti S, Knauff AR, Montgomery J. Org Lett. 2015;17:1493. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li Y, Yang Y, Yu B. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008;49:3604.Yang Y, Li Y, Yu B. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:12076. doi: 10.1021/ja9055245.Yu B, Sun J, Yang X. Acc Chem Res. 2012;45:1227. doi: 10.1021/ar200296m.Zhu Y, Yu B. Chem Eur J. 2015;21:8771. doi: 10.1002/chem.201500648.For selected applications in total synthesis: Zhang X, Zhou Y, Zuo J, Yu B. Nat Commun. 2015;6:5879. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6879.Nie S, Li W, Yu B. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:4157. doi: 10.1021/ja501460j.Nicolaou KC, Cai Q, Sun H, Qin B, Zhu S. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138:3118. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b12687.
- 23.For reviews of gold-catalysis in total synthesis Zhang Y, Luo T, Yang Z. Nat Prod Rep. 2014;31:489. doi: 10.1039/c3np70075e.Dorel R, Echavarren AM. Chem Rev. 2015;115:9028. doi: 10.1021/cr500691k.Pflästerer D, Hashmi ASK. Chem Soc Rev. 2016;45:1331. doi: 10.1039/c5cs00721f.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.