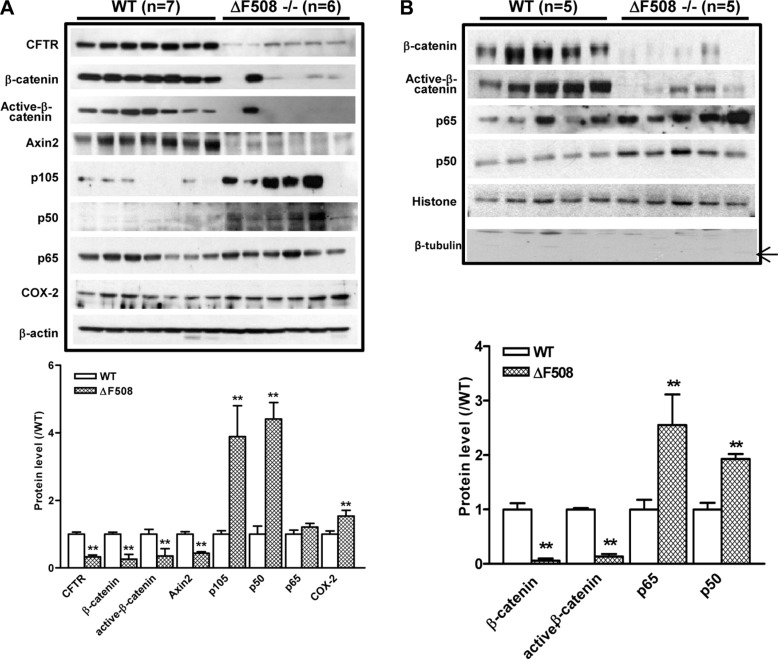
Figure 2. Aberrant activation of NF-κB and suppression of β-catenin pathways in ΔF508cftr−/− mouse small intestine.
(A) Western blot of total lysates of WT (n = 7) and ΔF508cftr−/− (n = 6) mouse small intestine shows reduced expression of β-catenin, active-β-catenin and Axin2; and upregulation of NF-κB p105, p50 as well as NF-κB downstream target COX-2 in ΔF508cftr−/− mice. (B) Western blot of the nuclear fraction of WT (n = 5) and ΔF508cftr−/− (n = 5) mouse small intestine shows significantly reduced nuclear β-catenin and active-β-catenin, whereas an increase of NF-κB p65 and p50 nuclear translocation in CF mice. The arrow indicates the expected band of tubulin. Image shown is the representative result from three independent experiments. (**p < 0.01, One-way ANOVA).