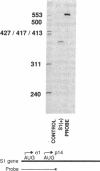
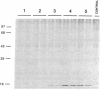
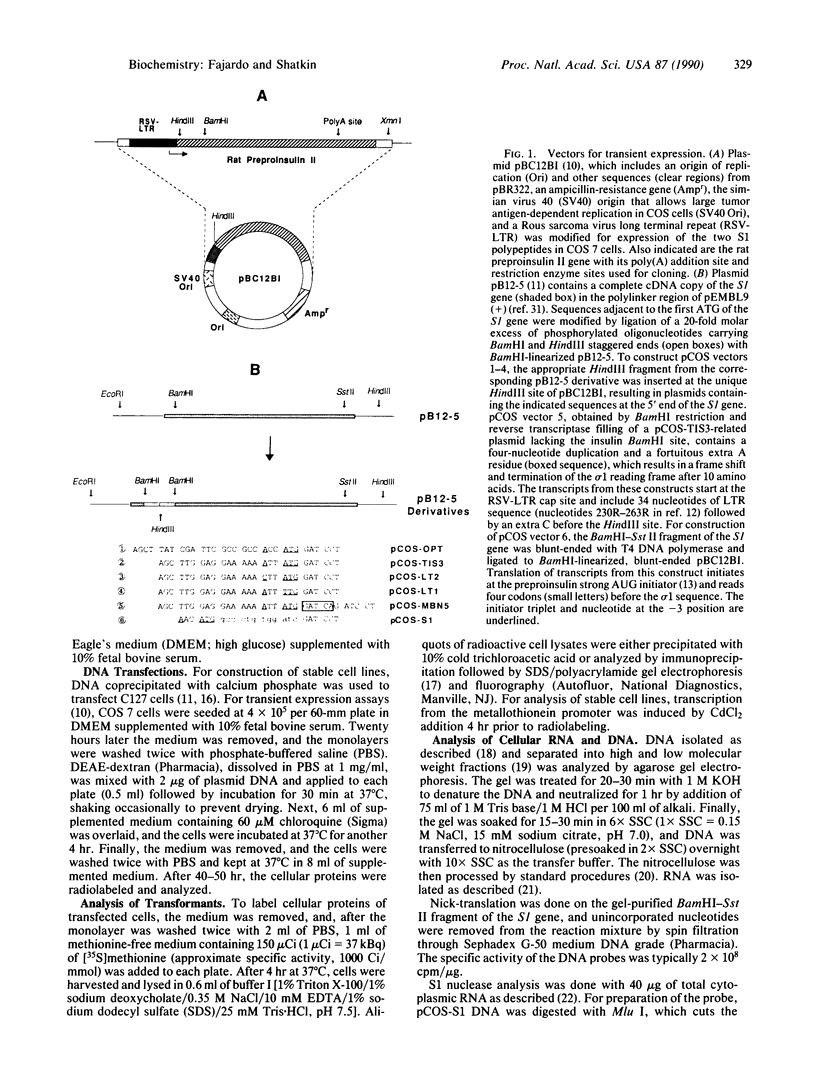
Abstract
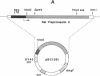
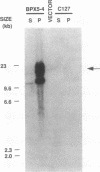
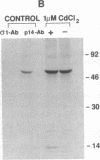
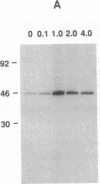
The S1 species of mammalian reovirus mRNA, like a number of other viral but not cellular mRNAs, codes for two dissimilar polypeptides by initiation of translation at two 5'-proximal, out-of-frame AUG codons. To determine if uninfected cells can utilize bicistronic genes, a bovine papilloma virus-based vector system was used to select mouse C127 cell lines containing multiple integrated copies of the reovirus S1 gene. These cell lines produced both reovirus polypeptides from a single mRNA. In addition, studies of COS cells transfected with the S1 gene containing small changes around the first AUG suggest that bicistronic mRNA translation is regulated at the level of elongation. A model is proposed in which ribosomes engaged in translation of one reading frame interfere with movement of ribosomes in the other frame because of differences in codon usage. Expression of bicistronic genes may be similarly regulated in virus-infected cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aota S., Ikemura T. Diversity in G + C content at the third position of codons in vertebrate genes and its cause. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6345–6355. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstin S. J., Spriggs D. R., Fields B. N. Evidence for functional domains on the reovirus type 3 hemagglutinin. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):146–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90514-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashdollar L. W., Chmelo R. A., Wiener J. R., Joklik W. K. Sequences of the S1 genes of the three serotypes of reovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):24–28. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceruzzi M., Shatkin A. J. Expression of reovirus p14 in bacteria and identification in the cytoplasm of infected mouse L cells. Virology. 1986 Aug;153(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst H., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus hemagglutinin mRNA codes for two polypeptides in overlapping reading frames. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):48–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Sarver N., Law M. F. Eukaryotic cloning vectors derived from bovine papillomavirus DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Effects of intercistronic length on the efficiency of reinitiation by eucaryotic ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3438–3445. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K. Eukaryotic protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1109–1149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides: effect of point mutation of the sequences flanking the 5'-proximal AUG initiator codons of the reovirus S1 and S4 genes on the efficiency of mRNA translation. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90309-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. mRNA cap binding proteins: essential factors for initiating translation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Bishop J. M. Alternative processing of RNA transcribed from NMYC. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4266–4272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubin M., Long E. O., Mach B. Two forms of the Ia antigen-associated invariant chain result from alternative initiations at two in-phase AUGs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90626-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., DeLorbe W. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of cloned unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: viral DNA contains direct and inverted repeats similar to those in transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):124–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Ribosome pausing and stacking during translation of a eukaryotic mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3559–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]