Abstract
Objective
Mild Cognitive Impairments (MCI) is a transitional state in aging associated with increased risk of incident dementia. The current study investigated whether MCI status moderated the effect of time on word generation during verbal fluency tasks. Specifically, the objective was to determine whether MCI status had differential effects on initial automatic or latter more effortful retrieval processes of fluency tasks.
Method
Participants were community residing older adults enrolled in a longitudinal cohort study. Of the 408 participants, 353 were normal (age =76.06 ± 6.61; %female=57.8) and 55 were diagnosed with MCI (age =78.62 ± 7.00; %female=52.7). Phonemic and category fluency were each administered for 60s, but performance was recorded at three consecutive 20-second intervals (0–20s [T1], 21–40s [T2] 41–60s [T3]. Separate linear mixed effects models for each fluency task were used to determine the effects of group, time, and their interaction on word generation.
Results
In both fluency tasks, word generation declined as a function of time. Individuals with MCI generated fewer words compared to controls during the first 20s of phonemic (beta =−1.56, p<.001; d=0.28) and category fluency (beta =−1.85, p<.001; d=0.37). Group by time interactions revealed that individuals with MCI demonstrated attenuated declines in word generation from the first to the second and third time intervals of both phonemic ([T1vs. T2] beta=2.17, p=.001; d=0.41; [T1vs.T3]beta= 2.28, p=001; d=0.45) and category ([T1 vs. T2] beta= 2.22, p=.002; d=0.50; [T1 vs. T3]beta=3.16, p<.001; d= 0.71) fluency.
Conclusions
Early automatic retrieval processes in verbal fluency tasks are compromised in MCI.
Keywords: Aging, Dementia, Cognitive Decline, Preclinical, Word Retrieval, Time Trajectories
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), a transition state in aging that is associated with increased risk of incident dementia, requires the presence of subjective cognitive complaints and objective cognitive impairment (Petersen et al., 2014), with performances typically ranging from 1 to 1.5 standard deviations below the mean on neuropsychological test scores (Albert et al., 2011). Furthermore, although daily activities are persevered, instrumental activities are slightly impaired (Petersen et al., 2014; Winblad et al., 2004).
Individuals with MCI may demonstrate subtle cognitive impairments in episodic (Summers & Saunders, 2012) and semantic memory (Wilson, Leurgans, Boyle, & Bennett, 2011), processing speed, attention, working memory (Summers & Saunders, 2012), and executive functioning (Brandt et al., 2009; Summers & Saunders, 2012; Traykov et al., 2007). Different MCI subtypes capture this variability; amnestic MCI (aMCI) subtype manifests subtle deterioration in memory whereas the non-amnestic (naMCI) subtype refers to individuals who manifest cognitive decline in other cognitive domains (Winblad et al., 2004). These conditions are further distinguished as single or multiple domains (Petersen, 2004). Variability in the underlying brain pathology implicated in MCI has been documented, including reduced brain volume in the hippocampus (Erten-Lyons et al., 2006; Wolf et al., 2004), entorhinal cortex (Pennanen et al., 2004), and neurofibrillary tangles in the medial temporal lobe (Petersen et al., 2006). Additionally, white matter pathology has also been noted in individuals with MCI (Raz & Rodrigue, 2006; Sullivan & Pfefferbaum, 2006) in frontal (Grambaite et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2009) temporal, parietal areas, splenium of corpus callosum, and parahippocampal white matter (Chua, Wen, Slavin, & Sachdev, 2008).
Verbal fluency is often included in clinical and research batteries designed to identify cognitive impairments and dementia in older adults (Holtzer, Goldin, et al., 2008). It requires individuals to generate words beginning with a specific letter (phonemic fluency) or belonging to a category (Lezak, 2004). Category fluency draws from semantic associations, whereas phonemic fluency requires search and word retrieval based on lexical characteristics (Henry, Crawford, & Phillips, 2004; Teng et al., 2013). While both tasks draw on semantic memory (Henry et al., 2004) and, therefore, the integrity of temporal lobes, category fluency relies considerably on this brain region (Martin, Wiggs, Lalonde, & Mack, 1994; Murphy, Rich, & Troyer, 2006) when compared to phonemic fluency. Conversely, phonemic fluency poses more substantial demands on strategic search processes as it requires word identification based on the initial letter, which is not linked to existing semantic knowledge and organization (Martin et al., 1994). Distinct cognitive processes contribute to word production in verbal fluency such as semantic memory, verbal abilities (McDowd et al., 2011), and executive processes including initiation of word retrieval (Henry et al., 2004; Monsch, 1994), application of strategies to identify appropriate examples, monitoring of responses given, restraint of intrusions (Henry et al., 2004), and repetitive responses (Henry & Phillips, 2006). Verbal fluency is a multi-dimensional task that relies on sustained attention, working memory, cognitive flexibility (Diamond, 2013), and speed of processing (Bryan, Luszcz, & Crawford, 1997).
Findings concerning the effect of MCI on verbal fluency have been inconsistent. With respect to overall performance, research has mainly focused on individuals with aMCI, demonstrating reduced (Malek-Ahmadi, Small, & Raj, 2011; Murphy et al., 2006; Price et al., 2012), but also comparable (Traykov et al., 2007) performance compared to healthy older adults. Studies comparing performance between category and phonemic fluency reveal worse category fluency in individuals with aMCI (Murphy et al., 2006), but also evidence of comparably reduced performance on both fluency measures (Brandt & Manning, 2009; Nutter-Upham et al., 2008; Weakley, Schmitter-Edgecombe, & Anderson, 2013). It has also been reported that individuals with multiple cognitive impairments exhibit performance patterns similar to AD, with category worse than letter fluency (Brandt & Manning, 2009; Nutter-Upham et al., 2008). Research in naMCI indicates poor performane on letter fuency, but comparable performance to healthy older adults in category fluency (Weakley et al., 2013), whereas others noted reduced performance on both tasks (Brandt & Manning, 2009).
It is recognized, however, that differences in performance between individuals with MCI and healthy controls are relatively small, as the former often perform within normal limits (Malek-Ahmadi et al., 2011; Murphy et al., 2006). In light of the limited utility of total fluency scores in distinguishing MCI from normal aging (Radanovic et al., 2009) and the distinct cognitive processes that underlie fluency tasks, it is of interest to examine whether or not within task performance indices are sensitive to age-related disease and transition states. Different methods have been proposed to address this issue including qualitative evaluation of the words produced (i.e. “clustering” and “switching”), analysis of the time effect on performance by measuring inter-word intervals (Mayr & Kliegl, 2000), and examination of overall verbal output within smaller time units during one minute of administration (Fernaeus & Almkvist, 1998).
Verbal fluency performance declines significantly over the standard one-minute test administration (Butters, Granholm, Salmon, Grant, & Wolfe, 1987; Crowe, 1998; Fernaeus & Almkvist, 1998; Ober, Dronkers, Koss, Delis, & Friedland, 1986; Raboutet et al., 2010). Fernaeous & Almkvist (1998) showed that phonemic fluency loads on two separate factors: semi-automatic and effortful retrieval. They further proposed that the distinction between these two retrieval processes is likely to extend beyond the specific testing conditions of phonemic fluency to word production in general. Consistent with the above notion, it has been suggested that a pool of readily available words exists during the initial stages of fluency tasks (Crowe, 1998). As time passes by and the initial pool of words is exhausted, word generation becomes more challenging requiring more effortful retrieval (Crowe, 1998; Raboutet et al., 2010). The above findings are consistent with Smith and Claxton’s lexical organization model (Smith & Claxton, 1972 cited in Crowe, 1998) proposing that initially individuals access the “topicon”, their long-term store, which contains commonly used and easily accessible words. When this stock is utilized, individuals try to retrieve words from the larger lexicon, which requires more strenuous effort (Crowe, 1998). This model of word production in verbal fluency has been examined in children (Hurks et al., 2004, 2010) and adult (Fernaeus & Almkvist, 1998) populations and, importantly, it has provided additional information about patterns of performance. Examining changes in word production during the standard one-minute test administration could provide incremental information and additional performance indices that may be sensitive to transition states such as MCI.
The current study examined the effect of time on Verbal fluency performance during the standard one-minute administration of the task in healthy older adults and in individuals with MCI. Consistent with previous research, we predicted that word generation would decrease during both fluency tasks and that MCI would be associated with reduced performance. Moreover, we aimed to determine whether MCI status moderated the time effect on verbal fluency performance. Specifically, we evaluated three possibilities. A greater effect of MCI on the initial and more automatic phase of verbal fluency would suggest that word retrieval is less efficient in this group, specifically in this early stage of the task. According to this scenario, because word generation in MCI is less efficient and more effortful in the initial phase of verbal fluency, the slope of decline compared to controls would be attenuated. Conversely, a greater effect of MCI on the latter and the more effortful process of verbal fluency (Fernaeus & Almkvist, 1998) would be associated with a steeper decline in word generation over time. If, however, MCI affects equally earlier and later phases of verbal fluency, the slope of decline would parallel that of normal controls.
Method
Participants
Participants were recruited from “Central Control of Mobility in Aging” (CCMA), a longitudinal cohort study, which is designed to identify cognitive and brain predictors of mobility decline and disability in older adults. Details concerning the study procedures have been previously described (Holtzer, Wang, & Verghese, 2014). Eligibility criteria for the study were determined through a structured telephone interview that included a medical history questionnaire, mobility assessment (Baker, Bodner, & Allman, 2003), and cognitive screens for dementia (Galvin et al., 2005; Lipton et al., 2003). Exclusion criteria included inability to speak English, inability to ambulate, history of neurological and/or psychiatric disorder, and the presence of dementia. Moreover, individuals currently receiving hemodialysis, or anticipated medical procedures that would affect mobility were also excluded. Eligible participants were at the age 65 or older without significant loss of vision and/or hearing. Participants were scheduled for 2 yearly study visits. On day 1, all participants underwent comprehensive neuropsychological evaluation that included the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS), as well as additional tests which assessed a range of domains including Wide Range Achievement Test-4 reading subtest (WRAT-4;Wilkinson & Robertson, 2006), American National Adult Reading Test (Gladsjo, Heaton, Palmer, Taylor, & Jeste, 1999), Wechsler Test of Adult Reading (WTAR; Wechsler, 2001), digit symbol substitution test (DSST;Wechsler, 1981), Trail Making Test (TMT), COWAT (Spreen & Benton,1977) and category fluency, Boston Naming Test (Kaplan, Goodglass, & Weintraub, 1983; Stern et al., 1992), and the Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test (Buschke, 1984). Symptoms of depression (Geriatric Depression Scale; Yesavage et al., 1982) and anxiety (Beck Anxiety Inventory; Beck & Steer 1990) were also assessed. Mobility and motoric evaluations were performed on day 1 as well. On day 2, participants received a structured neurological evaluation and additional mobility, psychological, and functional assessments. Cognitive status was determined at consensus clinical case conferences, attended by at least one clinical neuropsychologist and one neurologist, using procedures that have been previously described (Holtzer, Verghese, Wang, Hall, & Lipton, 2008). MCI status was determined based on published guidelines (Albert et al., 2011; Winblad et al., 2004) and included the following criteria: performance at 1.5 standard deviation below the mean for age and education in at least two tests in one or more cognitive domains, relatively persevered activities of daily living, and absence of dementia. Cognitive complaints were required and were assessed through structured interviews and questionnaires (Galvin et al., 2005; Katz, 1983). Written informed consent was obtained from participants in person according to study protocols approved by the institutional review board and in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki.
Measures
COWAT & category fluency
The Control Word Oral Associated Test (COWAT; Spreen & Benton,1977) was administered to all participants as part of the comprehensive neuropsychological evaluation. In category fluency, participants were required to name as many words as possible that belong to the categories of fruits, animals, and vegetables. Repetitions and perseverations were considered incorrect and were not included in the analyses. For the letter fluency test, participants were instructed to provide as many words that begin with a specified letter. The letters F, A and S were used in the present study. Participants were instructed to avoid giving responses consisting of proper nouns or responses with different suffixes. Proper nouns, words with different endings, repetitions, and perseverations were considered incorrect and were excluded from the analyses. Three trials were administered for phonemic (F/A/S) and category fluency (animals/vegetables/fruits). Participants were given 60s for each trial. Different time intervals have been used in the literature to examine performance patterns within the standard 60s administration of verbal fluency ranging from 10 to 30 seconds (Fernaeus & Almkvist, 1998; Hurks et al., 2010; Raboutet et al., 2010; Weakley et al., 2013). In the present study, responses were recorded separately at 0–20, 21–40 and 41–60 s without altering the standard administration of the tests. The number of words produced at 0–20 s [T1], 21–40 s [T2] and 41–60 s [T3] across the three trials of each fluency task was summed and used in the analyses. Phonemic fluency was administered first followed by category fluency.
RBANS
The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) was administered to all participants. The battery consists of measures of immediate and delayed memory, attention, language, and visuospatial skills. The participants’ overall cognitive performance score was used to characterize their cognitive status. The reliability and validity of RBANS have been well established (Duff et al., 2008; Randolph, 2012).
Demographic measures
Demographic and health information was assessed via structured interviews. In addition, a neurologist who served as the study clinician conducted structured neurological evaluations and medication use. Based on these data, a general health status (GHS) summary score was determined for each participant with possible scores ranging from 0–10 (Holtzer, Verghese, et al., 2008). Health conditions included: diabetes, chronic heart failure, arthritis, hypertension, depression, stroke, Parkinson disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, angina, and myocardial infarction (Holtzer, Verghese, et al., 2008). A dichotomous rating was used to indicate the presence or absence of each disease (absence-0 or presence -1).
Statistical Analysis
Linear mixed effects models (LMEMs) were used to determine the effects of group, time and their interaction on phonemic and category fluency performance. Specifically, two separate linear mixed effects models were executed for phonemic and category fluencies. In each model, cognitive status (MCI vs. controls) served as the between group variable. Time served as the three level repeated measures variable (T1, T2 and T3). Performance was separated into three time intervals to optimize the distinction between early automatic and later effortful retrieval processes. The total number of correct words in each of the three time intervals served as the dependent measure using T1 as a reference against which we evaluated performance at T2 and T3. The moderating effect of MCI on the decline in word generation was tested via two-way interactions of group status and time. Cohen d (Cohen, 1988) was used to provide estimates of effect sizes for the main effects of group, time and their interactions. Age, gender, education, overall fluency performance, GDS total score, BAI total score, and global health status were used as covariates in each model. Additional exploratory analyses were performed for both phonemic and category fluency using MCI subgroups as the between group variable. These analyses were considered as exploratory due to the small sample size of each MCI subgroup. MCI group classification was based on the following criteria: individuals were classified as aMCI if they performed below expected levels on at leat two tests of memory, naMCI classification was assigned if neuropsychological performance was below expectation on at least two tests of any cognitive domain excluding memory. Mild cognitive impairment combined (MCIcom) was determined if individuals showed reduced perfromance on at least two cognitive domains including memory. All statistical analyses were performed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) 21.
Results
A total of 408 community-dwelling older adults were included in the study. The mean age (76.41±6.71ys), education (14.44±3.06ys) and percent female (57.1%) were broadly representative of the population age 65 years and older from this catchment area. Summary of demographic characteritics, levels of depression, anxiety and neuropsychological test performance stratified by MCI status is provided in Table 1. The distribution of data within each group and time intervals did not reveal evidence of restricted range or significant skewness.
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics and cognitive performance stratified by MCI group status.
| Variable | Normal (n=353)
|
MCI (n=55)
|
aMCI (n=13)
|
naMCI (n=18)
|
MCIcom (n=24)
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Age (years) | 76.06 | 6.61 | 78.62 | 7.00 | 82.38 | 6.46 | 73.50 | 4.71 | 80.42 | 6.69 |
| Education(years) | 14.63 | 3.03 | 13.20 | 2.94 | 13.69 | 2.84 | 14.06 | 3.21 | 12.29 | 2.69 |
| RBANS total | 93.49 | 11.11 | 78.20 | 10.04 | 82.46 | 8.03 | 74.83 | 10.17 | 78.42 | 10.36 |
| RBANS Indices | ||||||||||
| Immediate memory | 98.50 | 11.37 | 89.00 | 10.62 | 85.62 | 7.61 | 91.47 | 12.98 | 89.09 | 10.06 |
| Visuospatial/Const. | 93.23 | 13.11 | 85.14 | 14.08 | 91.15 | 14.18 | 77.61 | 9.92 | 88.16 | 14.85 |
| Attention | 101.83 | 14.03 | 91.50 | 14.26 | 96.46 | 17.26 | 86.00 | 12.84 | 92.52 | 12.62 |
| Language | 94.60 | 10.12 | 83.07 | 10.80 | 91.23 | 9.53 | 75.50 | 9.96 | 84.39 | 8.16 |
| Delayed Memory | 94.40 | 10.09 | 83.54 | 8.52 | 82.00 | 9.86 | 85.56 | 7.23 | 82.83 | 8.73 |
| GDS | 4.70 | 4.07 | 5.16 | 2.94 | 3.85 | 2.07 | 4.89 | 2.80 | 6.08 | 3.20 |
| BAI | 4.88 | 5.66 | 4.78 | 5.71 | 2.38 | 3.15 | 5.06 | 4.78 | 5.88 | 7.07 |
| Sex (%female) | 57.8 | 52.7 | 46.2 | 66.7 | 45.8 | |||||
| Race (%) | ||||||||||
| Caucasian | 88.1 | 65.5 | 76.9 | 44.4 | 75.0 | |||||
| Other | 11.9 | 34.5 | 23.1 | 55.6 | 25.0 | |||||
| Category Fluency | ||||||||||
| Seconds | ||||||||||
| 0–20 s | 24.28 | 5.11 | 18.35 | 4.46 | 17.62 | 6.02 | 18.33 | 4.38 | 18.75 | 3.64 |
| 21–40 s | 11.03 | 4.02 | 7.33 | 2.82 | 6.92 | 3.20 | 7.28 | 3.14 | 7.58 | 2.41 |
| 41–60 s | 7.31 | 3.96 | 4.55 | 2.78 | 3.85 | 2.03 | 5.44 | 3.53 | 4.25 | 2.40 |
| Total | 42.63 | 9.78 | 30.22 | 7.60 | 28.38 | 8.88 | 31.06 | 9.41 | 30.58 | 5.14 |
| z-score | 0.37 | −1.07 | −1.3 | −1.0 | −1.0 | |||||
| Phonemic Fluency | ||||||||||
| 0–20 s | 19.53 | 5.56 | 14.82 | 5.25 | 16.69 | 5.68 | 14.33 | 5.58 | 14.17 | 4.72 |
| 21–40 s | 11.68 | 5.01 | 9.15 | 4.68 | 9.62 | 5.00 | 9.56 | 5.21 | 8.58 | 4.21 |
| 41–60 s | 9.43 | 4.67 | 7.00 | 3.70 | 6.85 | 4.43 | 6.67 | 3.60 | 7.33 | 3.47 |
| Total | 40.64 | 13.30 | 30.96 | 11.83 | 33.15 | 12.54 | 30.56 | 12.99 | 30.08 | 10.86 |
| z-score | 0.24 | −0.43 | −0.26 | −0.60 | −0.39 | |||||
Note. MCI = mild cognitive impairment; aMCI= amnestic mild cognitive impairment; naMCI= non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment; MCIcom= mild cognitive impairment combined; RBANS= Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status; GDS= Geriatric Depression Scale; BAI= Beck Anxiety Inventory
Separate LMEMs for category and phonemic fluency were used to examine the main effect of time, group status and their interaction on verbal fluency performance. With respect to phonemic fluency, there was a significant main effect of time between T1 and T2 (beta = −7.84; p<.001; d= 1.48) as well as T1 and T3 (beta= −10.10, p<.001; d= 1.97) among healthy controls indicating that performance declined over the course of the task. The main effect of MCI status on the number of words produced at T1 was significant (beta = −1.56, p<.001; d= 0.28) indicating that individuals with MCI produced fewer words than healthy participants. As expected, the main effect of the total words produced was also significant (beta=3.61, p<. 001; d=0.74). There was a significant time by MCI status interaction indicating that healthy older adults showed greater decline in performance from T1 to T2 (Beta= 2.17, p=.001; d= 0.41), and from T1 to T3 (Beta= 2.28, p=.001; d= 0.45) when compared to individuals with MCI (see Table 2).
Table 2.
Linear mixed effects model examining the effects of time, MCI status and their interaction on phonemic fluency performance
| MCI
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Estimate | t | 95%CI | p-value |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | − 7.84 | −34.13 | [−8.29, −7.39] | <.001 |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | −10.10 | −42.18 | [−10.56, −9.63] | <.001 |
| Age | −0.01 | −0.82 | [−0.02, 0.01] | .42 |
| Education | 0.50 | 31.47 | [0.46, 0.53] | <.001 |
| Gender | −0.11 | −1.14 | [−0.30, 0.08] | .25 |
| GHS | 0.07 | 1.54 | [−0.02, 0.15] | .12 |
| GDS | 0.01 | 0.65 | [−0.02, 0.03] | .52 |
| BAI | −0.01 | −1.09 | [−0.03, 0.01] | .27 |
| Phonemic Fluency z-score | 3.61 | 87.67 | [3.53, 3.69] | <.001 |
| MCI | −1.56 | −3.62 | [−2.41, −0.71] | <.001 |
| MCI*Time | ||||
| (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | 2.17 | 3.47 | [0.94, 3.40] | .001 |
| (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | 2.28 | 3.49 | [0.99, 3.56] | .001 |
Note. Phonemic Fluency z-score was based on the total number of words generated and was calculated using age and education corrected published local norms.
MCI= mild cognitive impairment; GHS= General health status; GDS= Geriatric Depression Scale; BAI= Beck Anxiety Inventory.
With regard to category fluency, there was a significant main effect of time between T1 and T2 (beta= −13.24, p<.001; d= 2.88) as well as T1 and T3 (beta= −16.96, p<.001; d = 3.71) among healthy controls indicating that performance declined over the course of the task. MCI status was associated with worse performance at T1 (beta = −1.85, p<.001; d= 0.37). As expected, the main effect of total words produced was significant (beta=2.51, p<.001; d=1.30). There was a significant time by MCI status interaction indicating that, compared to individuals with MCI, healthy older adults showed greater decline in performance from T1 to T2 (Beta=2.22, p=.002; d= 0.50), as well as from T1 to T3 (Beta=3.16, p<.001; d= 0.71) (see Table 3).
Table 3.
Linear mixed effects model examining the effects of time, MCI status and their interaction on category fluency performance
| MCI
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Estimate | t | 95%CI | p-value |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | −13.24 | −50.86 | [−13.75, −12.73] | <.001 |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | −16.96 | −61.91 | [−17.50, −16.42] | <.001 |
| Age | −0.02 | −3.76 | [−0.03, −0.01] | <.001 |
| Education | 0.26 | 22.31 | [0.24, 0.29] | <.001 |
| Gender | −0.05 | −0.75 | [−0.20, 0.09] | .455 |
| GHS | 0.003 | −0.12 | [−0.07, 0.06] | .90 |
| GDS | − 0.01 | −0.96 | [−0.03, 0.01] | .34 |
| BAI | −0.002 | −0.37 | [−0.02, 0.01] | .71 |
| Categroy Flunecy z-score | 2.51 | 84.02 | [2.45, 2.57] | <.001 |
| MCI | −1.85 | −4.00 | [−2.76, −0.94] | <.001 |
| MCI*Time | ||||
| (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | 2.22 | 3.14 | [0.83 to 3.62] | .002 |
| (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | 3.16 | 4.24 | [1.70 to 4.63] | <.001 |
Note. Category Fluency z-score was based on the total number of words generated and was calculated using age and education corrected published local norms.
MCI= mild cognitive impairment; GHS= General Health Status; GDS= Geriatric Depression Scale; BAI= Beck Anxiety Inventory.
Exploratory Analyses
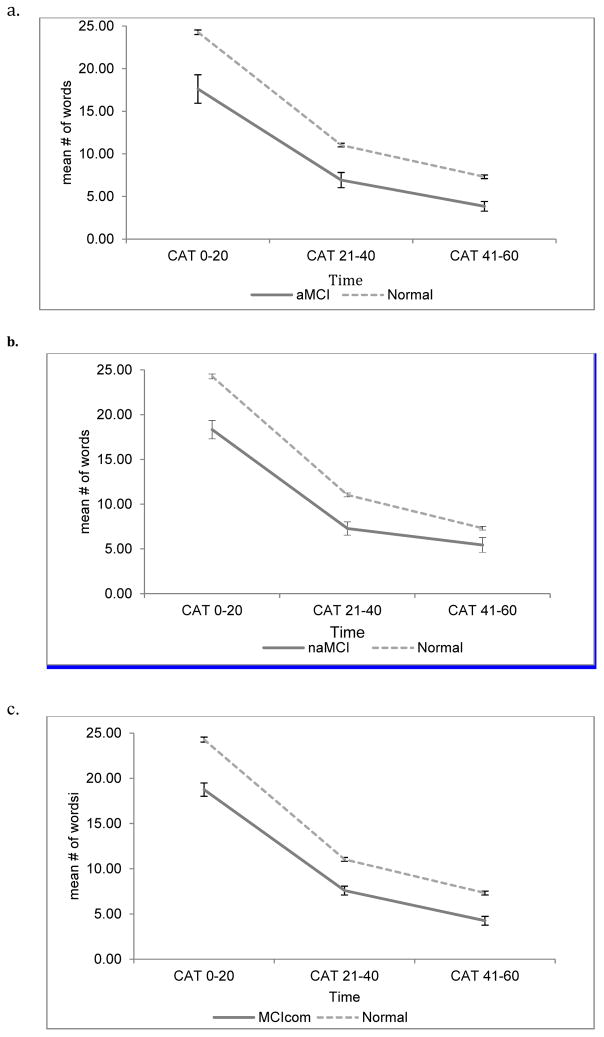
Separate LMEMs were performed with each MCI subgroup for both category and phonemic fluency. With regards to category fluency, there was a main effect of all MCI subtypes revealing that all MCI subgroups produced fewer words at T1 compared to controls (aMCI; Beta=−5.86, p<.001, naMCI; Beta=−6.10, p<.002, MCIcom; Beta= −4.53; p<.001). Time by MCI subtypes interactions revealed that there were significant effects between T1 and T3 for naMCI (Beta= 4.07, p=.002), MCIcom (Beta= 2.46, p=.03) as well as aMCI (Beta=3.19, p=.04; see Table 4) suggesting that, regardless of MCI subtype classification, normal controls showed greater decline in the number of words produced from T1 to T3 (see Figure 1).
Table 4.
Linear mixed effects model examining the effects of time, MCI subtypes and their interaction on category fluency performance
| Variable | Estimate | t | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aMCI | ||||
| Time (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | −13.24 | −46.34 | [−13.80, −12.68] | <.001 |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | −16.96 | 59.29 | [−17.52, −16.40] | <.001 |
| aMCI | −5.86 | −3.97 | [−8.77, −2.96] | <.001 |
| aMCI*Time | ||||
| (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | 2.55 | 1.68 | [−0.43, 5.51] | .09 |
| (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | 3.19 | 2.10 | [0.21 to 6.17] | .04 |
| naMCI | ||||
| Time (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | −13.24 | −47.07 | [−13.79, −12.69] | <.001 |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | −16.96 | −59.98 | [−17.52, −16.41] | <.001 |
| naMCI | −6.10 | −4.91 | [−8.55, −3.66] | <.002 |
| naMCI*Time | ||||
| (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | 2.19 | 1.71 | [−0.32, 4.70] | .09 |
| (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | 4.07 | 3.17 | [1.55, 6.60] | .002 |
| MCIcom | ||||
| Time (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | −13.24 | −46.98 | [−13.80, −12.69] | <.001 |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | −16.96 | −59.99 | [−17.52, −16.41] | <.001 |
| MCIcom | −4.53 | −4.16 | [−6.67, −2.39] | <.001 |
| MCIcom*Time | ||||
| (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | 2.08 | 1.86 | [−0.12, 4.27] | .06 |
| (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | 2.46 | 2.20 | [0.26, 4.66] | .03 |
Note. MCI= Mild Cognitive Impairment; naMCI= non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment; MCIcom= Mild cognitive impairment combined.
Figure 1.
Trajectory by time interval in category fluency for MCI subgroups and normals.
(a) Trajectory by time for amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal, (b) Trajectory by time for non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal; (c) Trajectory by time for mild cognitive impairment combined type and normal. CAT= category fluency. Error bars represent standard error of the mean
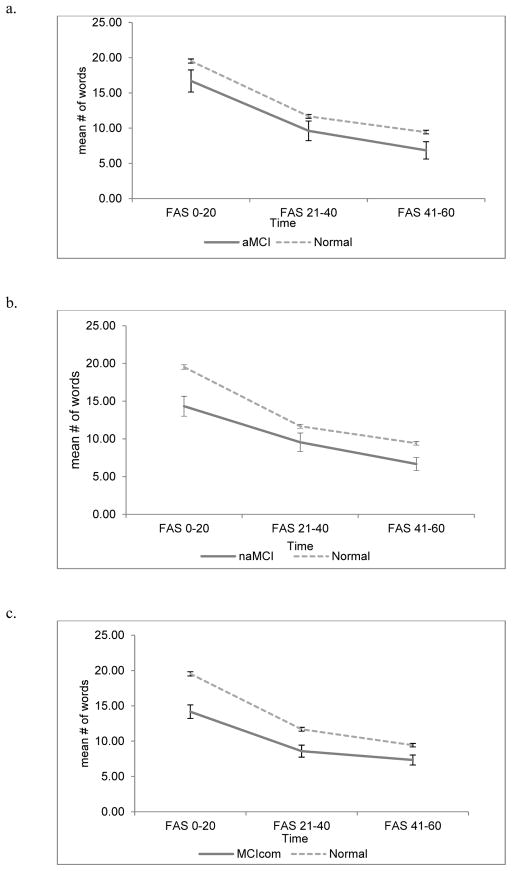
Phonemic fluency analyses revealed that there was a main effect of naMCI (Beta=−4.97, p<.001) and MCIcom status (Beta=−4.48, p<.001) but not aMCI (Beta= −2.69, p=.09), suggesting that compared to the other subtypes aMCI performed comparably to controls at T1. Time by MCI status interactions were significant only for individuals with naMCI and MCIcom both between T1 and T2 (naMCI; Beta= 3.06, p=.005, MCIcom; Beta= 2.26, p=.02) as well as between T1 and T3 (naMCI; Beta= 2.43, p=.02, MCIcom; Beta=3.26, p<.001; see Table 5) revealing that, compared to individuals with naMCI and MCIcom, healthy older adults showed greater decline in the number of words produced at T2 and T3 (see Figure 2).
Table 5.
Linear mixed effects model examining the effects of time, MCI subtypes and their interaction on phonemic fluency performance
| Variable | Estimate | t | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aMCI | ||||
| Time (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | −7.84 | −32.57 | [−8.32, −7.37] | <.001 |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | −10.10 | −42.54 | [−10.56, −9.63] | <.001 |
| aMCI | −2.69 | −1.71 | [−5.77, 0.40] | .09 |
| aMCI*Time | ||||
| (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | 0.77 | 0.60 | [−1.74, 3.28] | .55 |
| (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | 0.25 | 0.20 | [−2.22, 2.72] | .84 |
| naMCI | ||||
| Time (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | −7.84 | −32.84 | [−8.31, −7.37] | < .001 |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | −10.10 | −42.96 | [−10.56, −9.63] | <.001 |
| naMCI | −4.97 | −3.74 | [−7.58, −2.35] | <.001 |
| naMCI*Time | ||||
| (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | 3.06 | 2.83 | [0.94, 5.19] | .005 |
| (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | 2.43 | 2.28 | [0.34, 4.52] | .02 |
| MCIcom | ||||
| Time (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | −7.84 | −33.04 | [−8.31, −7.38] | <.001 |
| Time (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | −10.10 | −43.17 | [−10.55, −9.64] | <.001 |
| MCIcom | −4.48 | −3.81 | [−6.78, −2.17] | <.001 |
| MCIcom*Time | ||||
| (0–20 s vs. 21–40 s) | 2.26 | 2.40 | [0.41, 4.10] | .02 |
| (0–20 s vs. 41–60 s) | 3.26 | 3.52 | [1.44, 5.08] | <.001 |
Note. naMCI= non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment; MCIcom= Mild cognitive impairment combined.
Figure 2.
Trajectory by time interval in phonemic fluency for MCI subgroups and normals.
(a) Trajectory by time for amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal, (b) Trajectory by time for non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal; (c) Trajectory by time for mild cognitive impairment combined type and normal. FAS= phonemic fluency. Error bars represent standard error of the mean
Discussion
Consistent with the previous literature, performance of normal and MCI participants declined over time both in phonemic and category fluency. Significantly more words were generated during the first time interval compared to the second and third intervals. Decline in word generation during the task has been previously reported in healthy young (Crowe, 1998; Raboutet et al., 2010), individuals with MCI (Fernaeus & Almkvist, 1998) and diseased populations including older adults with dementia (Butters et al., 1987; Ober et al., 1986). As previously discussed (Fernaeus & Almkvist, 1998), this finding has been interpreted as evidence that two distinct processes underlie verbal fluency performance. These include a semi-automatic retrieval process, which is present in the initial stages of the task, and effortful retrieval in later stages. It has been suggested that production of words is maximal during the initial stages of the task (Crowe, 1998; Fernaeus & Almkvist, 1998) as individuals access their long-term store termed ‘topicon’, which consists of ordinary, easy to retrieve words (Smith & Claxton, 1972 cited in Crowe 1998). When this store is exhausted, the individual attempts to retrieve words from a larger pool of word store (Smith & Claxton, 1972 citen in Crowe, 1998); making the search process more time-consuming and more difficult (Crowe, 1998; Raboutet et al., 2010).
While individuals with MCI performed within normal limits on phonemic and category fluency, examination of their performance over the course of these tasks revealed important distinctions. Specifically, individuals with MCI produced fewer words during the first time interval in both phonemic and category fluency compared to healthy controls. These findings suggest that word retrieval at earlier stages, although cognitively less demanding (Raboutet et al., 2010), is compromised and therefore more laborious in individuals with MCI. This effect may be attributed, in part, to slowing of speed of information processing and retrieval of words from mental lexicon in the MCI group. Indeed, processing speed is impacted early in MCI and has been suggested to play a role in the transition from normal aging to MCI status (Dixon, 2007).
Using the two-factor structure of Verbal Fluency performance as a conceptual framework, we examined the moderating effect of MCI status on word retrieval over time. Our results demonstrated that individuals with MCI showed attenuated decline in their performance over the one minute of administration in both fluencies compared to controls. This finding supports the notion that automatic search processes are compromised in MCI. Indeed, individuals with MCI were slower at initiating the search processes and retrieving words from memory even for easily accessible words. Hence, it appears that compared to controls, this process demanded more effort on the part of MCI participants necessitating recruitment of executive processes from the early stages of the task. In contrast, healthy older adults were faster and more efficient at initiating search processes and retrieving words from memory as evidenced by the larger number of words they produced in the first 20s of the task. Given the effect of MCI on semi-automatic processes, it is noted that the differences in decline between the two groups can be attributed, at least in part, to the fact that controls had more to lose due to greater efficiency in retrieving words at the initial stages of the task. Healthy older adults had to monitor and inhibit responses that had already been given from a larger number of words thus making the discrepancy between the first time interval and the subsequent two intervals greater compared to individuals with MCI. On the other hand, performance of individuals with MCI was already less efficient and more effortful during the early stages of the task and their decline in word production was less prominent. These findings suggest that MCI affects initial semi-automatic retrieval processes of word production. Further evidence in support to this notion is attributed to the fact that our analyses controlled for total fluency scores. We also note that if MCI had a comparable negative effect on later and more effortful retrieval processes during verbal fluency the moderation effect of MCI status on the change in word generation over time would not have been significant. It is evident, therefore, that important differences in word fluency generation that are sensitive to transition states in aging are not captured by a total score on standard phonemic and category fluency measures.
Since MCI is a heterogeneous transition state with different underlying brain pathologies, verbal fluency performance of MCI subtypes was also explored. Both naMCI and MCIcom generated fewer words in first 20s intervals of category and phonemic fluency relative to controls. Individuals with aMCI generated fewer words in the first 20s intervals in category but not phonemic fluency. The results are in accordance with previous reports suggesting that aMCI is the least impaired group on verbal fluency performance (Brandt & Manning, 2009). It has been proposed that individuals with multiple deficits in addition to memory have higher conversion to dementia of Alzheimer type (Alexopoulos, Grimmer, Perneczky, Domes, & Kurz, 2006; Roberts et al., 2014) and non-Alzheimer type (Roberts et al., 2014) than individuals with isolated memory deterioration (Alexopoulos et al., 2006; Roberts et al., 2014). Worse performance in category fluency in aMCI is consistent with documented neuropathology in temporal lobes and its structures, in individuls with aMCI (Du et al., 2001; Petersen et al., 2006) and in dementia of the Alzheimer’s type (Du et al., 2001). Poor performance in category fluency in individuals with AD is related to dysfunction of semantic network, which hampers an individual’s capacity to identify the characteristics of a concept and, consequently, the capacity to cite appropriate examples rapidly (Monsch et al., 1994). Similarly, subtle pathology in the semantic structure of aMCI individuals possibly affects the capabilty to retrieve exemplars rapidly. Phonemic fluency performance was comparable in individuals with aMCI individuals and controls. This finding maybe attributed to the fact that phonemic fluency relies more on the phonological features of words rather than on semantic networks. Given the small sample size of the MCI subtypes and exploratory nature of the analyses these findings should be interpreted with caution.
Literature proposes that, compared to phonemic fluency, category fluency is superior in identifying individuals who subsequently develop AD (Clark et al., 2009; Fernaeus, Ostberg, Hellstrom, & Wahlund, 2008). In addition, it has been suggested that performance at the initial 30s of category fluency may be adequate to distinguish MCI with memory related impairments and AD from healthy adults (Fernaeus et al., 2008). The present findings suggest that subtle impairments in phonemic fluency are also present, for at least a portion of MCI individuals who might subsequently develop AD or other dementias. In addition, distinct patterns of performance within phonemic fluency were identified among MCI subtypes when compared to healthy older adults. It is worthy of note that, on average, phonemic and category fluency was within one standard deviation in all subgroups suggesting a substantial overlap in performance as determined by normative total scores; Nonetheless, in this context, differences in the rate of word generation decline during the course of the task between healthy and MCI groups provided incremental and relevant clinical information.
It is important to consider the limitations of the current study. Recruitment of participants was restricted to relatively healthy, senior individuals who reside in the community and function relatively independently. Further research should consider the generalizability of the present findings to more diverse samples in terms of demographic and physical characteristics. Furthermore, longitudinal studies are necessary to determine whether differences in the slopes of word generation predict the incidence of transition states and dementia. Future research should further explore divergences in patterns of performance between different cognitive profiles within MCI subgroups using a larger sample. Older age is associated with increased number of errors (McDowd et al., 2011) and individuals with AD produce more errors than healthy older adults (Haugrud, Crossley, & Vrbancic, 2011). Future studies could explore types of errors in individuals with MCI and whether these can differentiate transitional states from normal cognition. It would also be of interest to consider the effect of relevant biological markers such as amyloid burden as well as the effect of use of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors on verbal fluency trajectories. Although symptoms of depression and anxiety did not affect verbal fluency performance in the present study, mood symptoms in our sample were relatively mild. Future research should explore verbal fluency performance in a population with more severe levels of depression and anxiety. Research can also use independent neuropsychological tests of speed of processing and executive functions to determine whether these influence the effect of MCI on verbal fluency time trajectories. Although validation for the two-factor structure of verbal fluency exists in the literature (Crowe, 1998; Fernaeus & Almkvist, 1998), independent confirmation in the current study is lacking. Furthermore, research on structural and functional brain substrates vis-à-vis the aformentioned two-factor structure is limited. One study examining white matter hypersensitivities and performance on phonemic fluency in individuals with a range of memory impairments showed that performance in the initial 30 seconds of the task correlated with white matter hypersensitivities in the frontal lobes, which likely impacted initiation of word retrieval (Fernaeus et al., 2001). Hence, future research should identify shared and distinct structural and functional brain correlates of the proposed semi-automatic and effortful processes of verbal fluency in healthy controls and individuals in transition states to dementia. In addition, it would be of interest to further explore whether compromised automatic processes in MCI is a phenomenon that impacts performance across neuropsychological measures.
In conclusion, the present study suggests that MCI status uniquely affects early semi-automatic retrieval processes in phonemic and category fluency tasks. Consequently, the decline in word generation is attenuated in individuals with MCI compared to controls. These findings further support the notion that within task performance may provide incremental information that can be used to discriminate early neuropathological transition states such as MCI from normal aging.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Institutes on Aging (R01AG036921 and R01AG044007). The authors of the manuscript do not have any conflicts of interest that pertain to the reported work or conduct of the research.
References
- Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, … Phelps CH. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(3):270–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexopoulos P, Grimmer T, Perneczky R, Domes G, Kurz A. Progression to dementia in clinical subtypes of mild cognitive impairment. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders. 2006;22(1):27–34. doi: 10.1159/000093101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker PS, Bodner EV, Allman RM. Measuring life-space mobility in community-dwelling older adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2003;51(11):1610–1614. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck AT, Steer RA. Manual for the Beck Anxiety Inventory. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J, Aretouli E, Neijstrom E, Samek J, Manning K, Albert SM, Roche Bandeen K. Selectivity of executive function deficits in Mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychology. 2009;23(5) doi: 10.1037/a0015851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J, Manning KJ. Patterns of word-list generation in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical Neuropsychologist. 2009;23(5):870–879. doi: 10.1080/13854040802585063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J, Luszcz MA, Crawford JR. Verbal knowledge and speed of information processing as mediators of age differences in verbal fluency performance among older adults. Psychology and Aging. 1997;12(3):473–478. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.12.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschke H. Cued recall in amnesia. Journal of Clinical Neuropsychology. 1984;6(4):433–440. doi: 10.1080/01688638408401233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters N, Granholm E, Salmon DP, Grant I, Wolfe J. Episodic and semantic memory: a comparison of amnesic and demented patients. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 1987;9(5):479–497. doi: 10.1080/01688638708410764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua TC, Wen W, Slavin MJ, Sachdev PS. Diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Current Opinion in Neurology. 2008;21(1):83–92. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e3282f4594b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark LJ, Gatz M, Zheng L, Chen YL, McCleary C, Mack WJ. Longitudinal verbal fluency in normal aging, preclinical, and prevalent Alzheimer’s disease. American Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias. 2009;24(6):461–468. doi: 10.1177/1533317509345154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2. Hillsdale, NJ: L. Erlbaum Associates; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe SF. Decrease in performance on the verbal fluency test as a function of time: evaluation in a young healthy sample. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 1998;20(3):391–401. doi: 10.1076/jcen.20.3.391.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond A. Executive functions. Annual Review of Psychology. 2013;64:135–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon RA, Garrett DD, Lentz TL, MacDonald SW, Strauss E, Hultsch DF. Neurocognitive markers of cognitive impairment: exploring the roles of speed and inconsistency. Neuropsychology. 2007;21(3):381–399. doi: 10.1037/0894-4105.21.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du AT, Schuff N, Amend D, Laakso MP, Hsu YY, Jagust WJ, … Weiner MW. Magnetic resonance imaging of the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. 2001;71(4):441–447. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.71.4.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff K, Humphreys Clark JD, O’Bryant SE, Mold JW, Schiffer RB, Sutker PB. Utility of the RBANS in detecting cognitive impairment associated with Alzheimer’s disease: sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive powers. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 2008;23(5):603–612. doi: 10.1016/j.acn.2008.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erten-Lyons D, Howieson D, Moore MM, Quinn J, Sexton G, Silbert L, Kaye J. Brain volume loss in MCI predicts dementia. Neurology. 2006;66(2):233–235. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000194213.50222.1a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernaeus SE, Almkvist O. Word production: dissociation of two retrieval modes of semantic memory across time. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 1998;20(2):137–143. doi: 10.1076/jcen.20.2.137.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernaeus SE, Almkvist O, Bronge L, Ostberg PA, Winblad B, Wahlund LO. White matter lesions impair initiation of FAS flow. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders. 2001;12:52–56. doi: 10.1159/000051235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernaeus SE, Ostberg P, Hellstrom A, Wahlund LO. Cut the coda: early fluency intervals predict diagnoses. Cortex. 2008;44(2):161–169. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2006.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvin JE, Roe CM, Powlishta KK, Coats MA, Muich SJ, Grant E, … Morris JC. The AD8: a brief informant interview to detect dementia. Neurology. 2005;65(4):559–564. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000172958.95282.2a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladsjo JA, Heaton RK, Palmer BW, Taylor MJ, Jeste DV. Use of oral reading to estimate premorbid intellectual and neuropsychological functioning. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 1999;5(3):247–254. doi: 10.1017/s1355617799533079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grambaite R, Selnes P, Reinvang I, Aarsland D, Hessen E, Gjerstad L, Fladby T. Executive dysfunction in mild cognitive impairment is associated with changes in frontal and cingulate white matter tracts. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2011;27(2):453–462. doi: 10.3233/jad-2011-110290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugrud N, Crossley M, Vrbancic M. Clustering and switching strategies during verbal fluency performance differentiate Alzheimer’s disease and healthy aging. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 2011;17(6):1153–1157. doi: 10.1017/S1355617711001196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry JD, Crawford JR, Phillips LH. Verbal fluency performance in dementia of the Alzheimer’s type: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia. 2004;42(9):1212–1222. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2004.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry JD, Phillips LH. Covariates of production and perseveration on tests of phonemic, semantic and alternating fluency in normal aging. Neuropsychology, Development, and Cognition Section B: Aging, Neuropsychology and Cognition. 2006;13(3–4):529–551. doi: 10.1080/138255890969537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzer R, Goldin Y, Zimmerman M, Katz M, Buschke H, Lipton RB. Robust norms for selected neuropsychological tests in older adults. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 2008;23(5):531–541. doi: 10.1016/j.acn.2008.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzer R, Verghese J, Wang C, Hall CB, Lipton RB. Within-person across-neuropsychological test variability and incident dementia. JAMA. 2008;300(7):823–830. doi: 10.1001/jama.300.7.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzer R, Wang C, Verghese J. Performance variance on walking while talking tasks: theory, findings, and clinical implications. Age (Dordr) 2014;36(1):373–381. doi: 10.1007/s11357-013-9570-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurks PPM, Hendriksen JGM, Vles JSH, Kalff AC, Feron FJM, Kroes M, … Jolles J. Verbal fluency over time as a measure of automatic and controlled processing in children with ADHD. Brain and Cognition. 2004;55(3):535–544. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2004.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurks PP, Schrans D, Meijs C, Wassenberg R, Feron FJ, Jolles J. Developmental changes in semantic verbal fluency: analyses of word productivity as a function of time, clustering, and switching. Child Neuropsychology. 2010;16(4):366–387. doi: 10.1080/09297041003671184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan E, Goodglass H, Weintraub S. The Boston Naming Test. Philadelphia, PA: Lea & Fibiger; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. Assessing self-maintenance: activities of daily living, mobility, and instrumental activities of daily living. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 1983;31(12):721–727. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1983.tb03391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Loring DW, Hannay HJ, Fischer JS. Neuropsychological assessment. Oxford, NY: Oxford University Press; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lipton RB, Katz MJ, Kuslansky G, Sliwinski MJ, Stewart WF, Verghese J, … Buschke H. Screening for dementia by telephone using the memory impairment screen. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2003;51(10):1382–1390. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek-Ahmadi M, Small BJ, Raj A. The diagnostic value of controlled oral word association test-FAS and category fluency in single-domain amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders. 2011;32(4):235–240. doi: 10.1159/000334525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A, Wiggs CL, Lalonde F, Mack C. Word retrieval to letter and semantic cues: a double dissociation in normal subjects using interference tasks. Neuropsychologia. 1994;32(12):1487–1494. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(94)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr U, Kliegl R. Complex semantic processing in old age: does it stay or does it go? Psychology and Aging. 2000;15(1):29–43. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.15.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowd J, Hoffman L, Rozek E, Lyons KE, Pahwa R, Burns J, Kemper S. Understanding verbal fluency in healthy aging, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychology. 2011;25(2):210–225. doi: 10.1037/a0021531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsch AU, Bondi MW, Butters N, Paulsen JS, Salmon DP, Brugger P, Swenson MR. A comparison of category and letter fluency in Alzheimer;s disease and Huntington’s disease. Neuropsychology. 1994;8(1):25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy KJ, Rich JB, Troyer AK. Verbal fluency patterns in amnestic mild cognitive impairment are characteristic of Alzheimer’s type dementia. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 2006;12(4):570–574. doi: 10.1017/s1355617706060590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutter-Upham KE, Saykin AJ, Rabin LA, Roth RM, Wishart HA, Pare N, Flashman LA. Verbal fluency performance in amnestic MCI and older adults with cognitive complaints. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 2008;23(3):229–241. doi: 10.1016/j.acn.2008.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ober BA, Dronkers NF, Koss E, Delis DC, Friedland RP. Retrieval from semantic memory in Alzheimer-type dementia. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 1986;8(1):75–92. doi: 10.1080/01688638608401298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennanen C, Kivipelto M, Tuomainen S, Hartikainen P, Hanninen T, Laakso MP, … Soininen H. Hippocampus and entorhinal cortex in mild cognitive impairment and early AD. Neurobiology of Aging. 2004;25(3):303–310. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(03)00084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2004;256(3):183–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen RC, Caracciolo B, Brayne C, Gauthier S, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L. Mild cognitive impairment: a concept in evolution. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2014;275(3):214–228. doi: 10.1111/joim.12190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen RC, Parisi JE, Dickson DW, Johnson KA, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Jicha GA, Ivnik RJ, Smith GE, Tangalso EG, Braak B, Kokmen E. Neuropathologic features of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Archives of Neurology. 2006;63(5):665–672. doi: 10.1001/archneur.63.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price SE, Kinsella GJ, Ong B, Storey E, Mullaly E, Phillips M, … Perre D. Semantic verbal fluency strategies in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychology. 2012;26(4):490–497. doi: 10.1037/a0028567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raboutet C, Sauzeon H, Corsini MM, Rodrigues J, Langevin S, N’Kaoua B. Performance on a semantic verbal fluency task across time: dissociation between clustering, switching, and categorical exploitation processes. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 2010;32(3):268–280. doi: 10.1080/13803390902984464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radanovic M, Diniz BS, Mirandez RM, Novaretti TM, Flacks MK, Yassuda MS, Forlenza OV. Verbal fluency in the detection of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease among Brazilian Portuguese speakers: the influence of education. International Psychogeriatrics. 2009;21(6):1081–1087. doi: 10.1017/s1041610209990639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph C. Repeatable battery for the assessment of neuropsychological status update (RBANS Update) San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Raz N, Rodrigue KM. Differential aging of the brain: patterns, cognitive correlates and modifiers. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 2006;30(6):730–748. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2006.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts RO, Knopman DS, Mielke MM, Cha RH, Pankratz VS, Christianson TJ, … Petersen RC. Higher risk of progression to dementia in mild cognitive impairment cases who revert to normal. Neurology. 2014;82(4):317–325. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000000055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith PT, Claxton GL. Lexical search and phonemic organisation in memory. Paper presented to the Experimental Psychology Society; London. 1972. Apr, [Google Scholar]
- Spreen O, Benton AL. Neurosensory center comprehensive examination for aphasia: Manual of directions. Victoria, British Columbia: University of Victoria; 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Stern Y, Andrews H, Pittman J, Sano M, Tatemichi T, Lantigua R, Mayeux R. Diagnosis of dementia in a heterogeneous population. Development of a neuropsychological paradigm-based diagnosis of dementia and quantified correction for the effects of education. Archives of Neurology. 1992;49(5):453–460. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530290035009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan EV, Pfefferbaum A. Diffusion tensor imaging and aging. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 2006;30(6):749–761. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2006.06.002. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2006.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers MJ, Saunders NL. Neuropsychological measures predict decline to Alzheimer’s dementia from mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychology. 2012;26(4):498–508. doi: 10.1037/a0028576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng E, Leone-Friedman J, Lee GJ, Woo S, Apostolova LG, Harrell S, … Lu PH. Similar verbal fluency patterns in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 2013;28(5):400–410. doi: 10.1093/arclin/act039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traykov L, Raoux N, Latour F, Gallo L, Hanon O, Baudic S, … Rigaud A-S. Executive Functions Deficit in Mild Cognitive Impairment. Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology. 2007;20(4):219–224. doi: 10.1097/WNN.0b013e31815e6254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Goldstein FC, Veledar E, Levey AI, Lah JJ, Meltzer CC, … Mao H. Alterations in Cortical Thickness and White Matter Integrity in Mild Cognitive Impairment Measured by Whole Brain Cortical Thickness Mapping and Diffusion Tensor Imaging. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology. 2009;30(5):893–899. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weakley A, Schmitter-Edgecombe M, Anderson J. Analysis of verbal fluency ability in amnestic and non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 2013;28(7):721–731. doi: 10.1093/arclin/act058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised. New York: The Psychological Corporation; 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler D. Wechsler Test of Adult Reading. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson GS, Robertson GJ. Wide Range Achievement Test-4 (WRAT-4) Lutz, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson RS, Leurgans SE, Boyle PA, Bennett DA. Cognitive decline in prodromal Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Archives of Neurology. 2011;68(3):351–356. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, … Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment--beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2004;256(3):240–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H, Hensel A, Kruggel F, Riedel-Heller SG, Arendt T, Wahlund LO, Gertz HJ. Structural correlates of mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiology of Aging. 2004;25(7):913–924. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, Lum O, Huang V, Adey M, Leirer VO. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: a preliminary report. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 1982;17(1):37–49. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(82)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]