Abstract
Numerous risk factors have been implicated in the development of a gastric ulcer. Common risk factors are Helicobacter pylori infection, chronic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory intake, and alcohol consumption. The aim of the current study was to identify environmental risk factors for a gastric ulcer in northern Ghana. The data for this retrospective study were obtained from 2035 patient records from the Minimal Access Therapy and Operative Endoscopy unit of the Tamale Teaching Hospital in Tamale, Ghana from 2010 to 2014. A separate questionnaire was administered to assess the environmental risk factors. The rapid urease test was used to determine the presence of H. pylori. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 20.0 was used to analyse the data. Univariate and bivariate analyses were performed, and the results were presented in tables provided. The Chi-square values of the bivariate analysis were considered statistically significant when P < 0.05. Bivariate analysis revealed a strong association between gastric ulcer and various risk factors such as smoking (P = 0.001, χ2 = 27.3), fasting (P = 0.001, χ2 = 42.6), H. pylori infection (P = 0.01, χ2 = 19.9), and alcohol consumption (P = 0.001, χ2 = 30.6). There was no association between the traditional herbal preparation usage (P = 0.251, χ2 = 1.8) and the gastric ulcer. Environmental risk factors responsible for the development of a gastric ulcer in people of the northern part of Ghana show a similar pattern to other geographical regions of the world.
Keywords: Gastric ulcer disease, dyspepsia, H. pylori infection, endoscopy
Introduction
Dyspepsia is a nonspecific term that denotes upper abdominal discomfort that is thought to arise from the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract. A gastric ulcer is a common cause of dyspepsia that encompasses a variety of more specific symptoms including epigastric discomfort or pain, bloating, anorexia, early satiety, belching or regurgitation, nausea, and heartburn. The gastric ulcer has been found in 4.3% of patients with dyspeptic symptoms in the central part of Ghana [1]. Numerous risk factors have been implicated in the development of a gastric ulcer. Common environmental risk factors attributed to the development of gastric ulcer include Helicobacter pylori infection, chronic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) intake, and alcohol consumption. Environmental factors play a vital role in the development of a gastric ulcer. The aim of this study was to identify environmental risk factors responsible for the development of a gastric ulcer in patients in northern Ghana undergoing endoscopic diagnosis.
Methods
The data for this retrospective study were obtained from patient records from the Minimal Access Therapy and Operative Endoscopy unit of the Tamale Teaching Hospital in Tamale, Ghana from 2010 to 2014. All of the patients who received an upper GI endoscopic diagnosis at the unit were included in the study. Patients were either referred to the hospital from other facilities or reported directly to the hospital. Those patients who underwent colonoscopy were excluded. The objectives of the study were explained to the patients on the appointed day, and a written consent form was obtained from each patient. The study was approved by the Tamale Teaching Hospital Ethical Review Committee (TTHERC/18/11/15/07. A separate questionnaire was administered to patients by an endoscopy nurse before the procedure to assess risk factors for a gastric ulcer (Figure 1). Information on the socio-demographic status, GI symptoms and clinical diagnosis were obtained from patients' folders. Gastric biopsies for rapid urease test were performed during endoscopy for detection of H. pylori. The endoscopic findings and the results of the rapid urease test were recorded. Data collected from patients' records included socio-demographic status, symptoms presented, and the results of clinical and endoscopy diagnoses. Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 20.0 was used to analyse the data. Univariate and bivariate analyses were performed to ascertain environmental risk factors for gastric ulcer. The Chi-square values of the bivariate analysis were considered statistically significant when P < 0.05.
Figure 1.
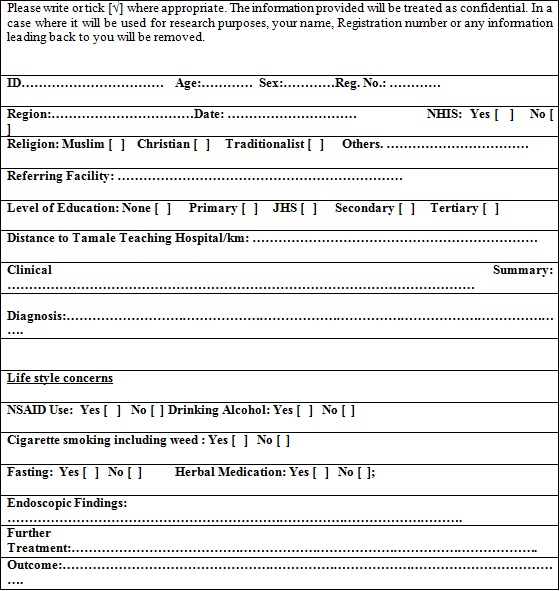
Questionnaires to identify risk factors of gastric ulcer
Results
Table 1: A total of 2035 patients were included in the study. Some patients had more than one endoscopy finding; therefore, the total number of endoscopy findings was 3176. The age range was 2-89 years, and a mean age was 40.2 ± 16.7 years (mean ± SD). A total of 1037 men (51.0%) and 998 women (49.0%) were included in the study. The largest number of patients was in the age group 31-40 years (680/2035, 34.4%. The least number of patients was in the age group 2-15 years (35/2035, 1.7%. The epigastric pain was the most frequent major symptom (1551/2035, 76.2%) followed by abdominal pain (1002/2035, 49.2%). Other significant symptoms such as heartburn, effortless vomiting, hematemesis, and dysphagia, were present in 13.4% (273/2035), 10.6% (215/2035), 7.5% (153/2035), and 6.5% (132/2035) patients, respectively. The peptic ulcer disease (PUD) clinical diagnosis was most common (1451/2035, 71.3%), followed by gastro-reflux disease (GORD) (184/2035, 9.0%), upper GI bleeding (144/2035, 7.1%), gastric cancer (136/2035, 6.7%), and oesophageal cancer (61/2035, 3.0%). A total of 1259/2053 (61.9%) patients tested positive for H. pylori infection.
Table 1.
Socio-demographic status, main symptoms, clinical diagnosis, endoscopy findings and Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with gastric ulcer
| Variable | Frequency | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sex (n = 2035) |
Male | 998 | 49.0 |
| Female | 1037 | 51.0 | |
|
Age in years (n = 2035) |
0-20 | 35 | 1.7 |
| 21-30 | 652 | 32.0 | |
| 31-40 | 680 | 34.4 | |
| 41-50 | 399 | 19.6 | |
| 51-60 | 199 | 9.8 | |
| >60 | 70 | 3.4 | |
|
Major symptoms (n = 3724) |
Epigastric pain | 1551 | 41.6 |
| Abdominal pain | 1002 | 26.9 | |
| Heartburn | 273 | 7.3 | |
| Persistent vomiting | 215 | 5.8 | |
| Hematemesis | 153 | 4.1 | |
| Dysphagia | 132 | 3.5 | |
| Others | 398 | 10.7 | |
|
Clinical diagnosis (n = 2092) |
PUD | 1505 | 71.9 |
| GORD | 184 | 9.0 | |
| Upper GI bleeding | 144 | 6.9 | |
| Gastric cancer | 136 | 6.5 | |
| Oesophageal cancer | 61 | 2.9 | |
| Others | 62 | 3.0 | |
|
Endoscopy diagnosis (n = 3176) |
Gastritis | 892 | 28.1 |
| Gastric ulcer | 615 | 19.4 | |
| GORD | 586 | 18.4 | |
| Gastric cancer | 263 | 8.3 | |
| Duodenal ulcer | 226 | 7.1 | |
| Oesophageal cancer | 191 | 6.0 | |
| Upper GI bleeding | 104 | 3.3 | |
| Normal | 112 | 3.5 | |
| Others | 187 | 5.9 | |
| H. pylori infection (n = 2035) | 1286 | 63.2 | |
PUD- Peptic ulcer disease; GORD - Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease; GI - Gastrointestinal
Of 2035 patients, 1344 (66.0%) marked NSAID on the questionnaire; 1812 (89.0%) patients admitted alcohol intake greater than 5 units/day. Herbal usage for medicinal purposes (traditional concoction) was used by 822 (40.4%) patients. Cigarettes and cannabis were used by 183 (8.9%) patients. Fasting or irregular eating was present in 1126 (55.3%) cases.
Table 2: Bivariate analysis revealed a strong association between gastric ulcer and the following risk factors: smoking of cigarette including weeds (P = 0.001, χ2 = 27.3), fasting (P = 0.001, χ2 = 42.6), H. pylori infection (P = 0.01, χ2 = 19.9), and alcohol consumption (P = 0.001, χ2 = 30.6). There was no association between herbal usage and gastric ulcer (P = 0.251, χ2 = 1.8).
Table 2.
environmental risks factors for development of gastric ulcer in patients in northern Ghana
| Variable (n = 2035) | Frequency | Percentage | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol consumption >5 units/day | 30.6 | 0.001* | ||
| Yes | 1812 | 89.0 | ||
| No | 223 | 11.0 | ||
| Smoking: | 27.3 | 0.001* | ||
| Yes | 183 | 9.0 | ||
| No | 1852 | 91.0 | ||
| Long fasting (irregular eating habit): | 42.6 | 0.001* | ||
| Yes | 1126 | 55.3 | ||
| No | 909 | 44.7 | ||
| NSAID: | 24.9 | 0.001* | ||
| Yes | 691 | 34.0 | ||
| No | 1344 | 66.0 | ||
| CLO test result: | 39.3 | 0.01 | ||
| Positive | 1286 | 63.2 | ||
| Negative | 749 | 36.8 | ||
| Traditional herbal preparation: | 1.8 | 0.251 | ||
| Yes | 822 | 40.4 | ||
| No | 1213 | 59.6 |
NSAID - Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory intake; CLO - Campylobacter-like organism
P < 0.05 statistically significant
Discussion
Dyspepsia is a common affliction with an estimated prevalence of up to 40% in the general population worldwide [2]. It accounts for 25-47% of patients refer for upper GI endoscopy in East Africa [3–5]. The patients included in the study were between 2 and 89 years old; the majority were 31-45 years old. These findings differ from Veldhuyzen et al. [6] who found dyspeptic symptoms predominantly in people <20 years. In our study, the dyspeptic symptoms were predominantly found in older patients. This could be attributed to lifestyle choices such as irregular eating habits, cigarette smoking, and chronic NSAID intake prevailing in the older group in Ghana. Ohene-Yeboah et al [7] found that NSAID, herbal medicines or concoctions are commonly abused by patients with gastric perforation [6, 7]. In the current study, the incidence of epigastric pain was 41.6% which is consistent with the previous report [8]. Clinical diagnosis of PUD was 71.9% in our series, similar to earlier findings [9].
Common causes of dyspepsia symptoms include gastric ulcer, GORD, functional disorders (non-ulcer dyspepsia), malignancy, and age <45 years [10–14]. According to Numans et al. [15], H. pylori infection plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of gastric ulcer. In patients suffering from gastric ulcers, 70% - 80% are H. pylori positive on rapid urease test of gastric biopsy at endoscopy [16, 17]. PUD has been associated with smoking, H. pylori infection, and chronic NSAID intake [18–20]. Numerous factors are implicated in the pathophysiology of gastric ulcer. These include smoking habits, alcohol consumption, coffee drinking, and familial occurrences of peptic ulcers in patients with a gastric or duodenal ulcer. Epidemiologic studies suggest that smokers are about twice as likely to develop gastric ulcers compare to non-smokers [21]. Bivariate analyses identified smoking, H. pylori infection, fasting, alcohol consumption, and chronic intake of NSAID as risk factors for gastric ulcer which is similar to the findings in other parts of the world.
Conclusion
Previously identified environmental risk factors for gastric ulcer development show a similar pattern in patients of the northern part of Ghana compared with other geographical regions of the world.
What is known about this topic
Risk factors of gastric ulcer in other population settings;
Causes of peptic ulcer disease in different population settings in Ghana.
What this study adds
Identification risk factors of gastric ulcer in Northern Ghana for the first time;
Describes association of the risk with endoscopy findings in this population;
Knowledge to the problem of gastric ulcer.
Acknowledgments
Our sincere thanks go to the Healing the Children Organization, Louisville, KY, USA, which donated the video-endoscopy system to the Tamale Teaching Hospital (TTH). We are grateful to Dr. Ken Segoe (former Chief Executive Officer of TTH) for his immense contribution towards the establishment of the Minimal Access Therapy and Operative Endoscopy unit at the TTH. We are grateful to Mr. Samuel Berko (Endoscopist nurse) for the collection of the data.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
Stephen Tabiri: provided concept and design of the paper, revised the draft critically for important intellectual content and final approval of the version to be published. Prosper Akanbong: interpreted data and drafted the article. Braimah Abubakari: was in charge of acquisition of data and analysis. All the authors read the final manuscript.
References
- 1.Afihene MKY, Denyer M, Amuasi JH, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori and Endoscopic findings among dyspeptics in Kumasi, Ghana. Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2014;2(3):63–68. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vakil N, Moayyedi P, Fennerty MB. Limited value of alarm features in the diagnosis of upper gastrointestinal malignancy: systemic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:390–401. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.04.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ocama P, Kagimu MM, Odida M, Wabinga H, Opio CK, Colebunders B, et al. Factors associated with carcinoma of the oesophagus at Mulago Hospital, Uganda. Afr Health Sci. 2008 Jun;8(2):80–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mothes H, Chagaluka G, Chiwewe D, et al. Do patients in rural Malawi benefit from upper gastrointestinal endoscopy? Trop Doct. 2009 Apr;39(2):73–6. doi: 10.1258/td.2008.080142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wolf LL, Ibrahim R, Miao C, et al. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy in a public referral hospital in Lilongwe, Malawi: spectrum of disease and associated risk factors. World J Surg. 2012 May;36(5):1074–82. doi: 10.1007/s00268-012-1490-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJ, Chiba N, Armstrong D. A randomized trial comparing omeprazole, ranitidine, cisapride, or placebo in helicobacter pylori negative, primary care patients with dyspepsia: the CADET-HN Study. Am J Gastroentero. 2005;100(7):1477–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.40280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ohene-Yeboah M, Togbe B. Perforated gastric and duodenal ulcers in an urban African population. West Afr J Med. 2006 Jul-Sep;25(3):205–11. doi: 10.4314/wajm.v25i3.28279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ford AC, Qume M, Moayyedi P. Helicobacter pylori “test and treat” or endoscopy for managing dyspepsia: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2005;128(7):1838–44. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.American Medical Forensic Specialist Newsletter 12/03/2008. [Google Scholar]
- 10.El-Serag HB, Talley NJ. Systemic review: the prevalence and clinical course of functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Mar 15;19(6):643–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chey WD, Wong BCY. American College of Gastroenterology guideline on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Amer J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1808–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dehn TCB, Shepherd HA, Colin-Jones, et al. Double blind comparison of omeprazole (40mg od) versus cimetidine (400mg qd) in the treatment of symptomatic erosive reflux oesophagitis, assessed endoscopically, histologically and by 24 h pH monitoring. Gut. 1990;31:509–13. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fransen GA, Janssen MJ, Muris JW. Meta-analysis: the diagnostic value of alarm symptoms for upper gastrointestinal malignancy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20:1045–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rabeneck L, Nelda PW, Graham DY. Managing dyspepsia: what do we know and what do we need to know? Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;93:920–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.277_e.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Numans ME, van der GY, de Wit NJ. How useful is selection based on alarm symptoms in requesting gastroscopy? An evaluation of diagnostic determinants for gastro-oesophageal malignancy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2001;36(4):437–43. doi: 10.1080/003655201300051379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Holcombe C. Helicobacter pylori: the African enigma. Gut. 1992;33:429–31. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lastovica AJ, Newell DG, Lastovica EE, editors. Campylobacter, Helicobacter and Related Organisms. South Africa: Rustica Press; 1998. p. 565. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fashner J, Gitu AC. Diagnosis and treatment of peptic ulcer disease. Am Fam Physician. 2015 Feb 15;91(4):236–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Farhad B, Abbas Y, Farhad P, et al. Epidemiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Endoscopic Results of a Systematic Investigation in Iran, Middle East. J Dig Dis. 2012 Apr;4(2):90–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rosenstock SJ, Bonnevie T, et al. Risk factors for peptic ulcer disease: a population based prospective cohort study comprising 2416 Danish adults. Gut. 2003;52:186–93. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vergara M, Catalán M, Gisbert JP, et al. Meta-analysis: role of Helicobacter pylori eradication in the prevention of peptic ulcer in NSAID users. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Jun 15;21(12):1411–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


