Abstract
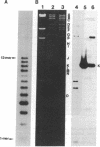
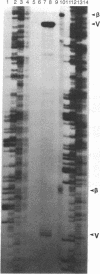
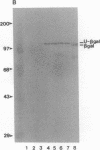
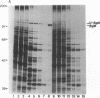
The baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV, which is representative of the MNPV subtype in which the virions may contain many nucleocapsids within a single viral envelope) encodes a protein, v-ubi, that has 76% identity with the eukaryotic protein ubiquitin. Transcriptional mapping indicated that the gene for v-ubi was transcribed during the late phase of viral infection. Two transcriptional start sites potentially encoding v-ubi were identified. Both sites were contained within a sequence motif common to baculovirus late genes. A recombinant virus, AcUbi-beta Gal, encoding a ubiquitin-beta-galactosidase fusion protein was constructed to monitor the temporal regulation of v-ubi gene during viral infection. The fusion protein was expressed maximally at 14-18 hr postinfection, consistent with its classification as a late protein. The amount of ubiquitin-beta-galactosidase fusion protein that accumulated in AcUbi-beta Gal-infected cells by 48 hr postinfection was approximately 14% of the level of beta-galactosidase that was synthesized under control of the polyhedrin promoter. Transcriptional analysis confirmed that synthesis of the fusion protein was directed by the v-ubi gene promoter. AcUbi-beta Gal also produced normal levels of authentic viral ubiquitin message. Southern blot analysis of AcUbi-beta Gal and 15 additional isolates revealed that the fusion sequences had not recombined at the ubiquitin locus. A polyubiquitin gene was isolated and sequenced from Spodoptera frugiperda, a lepidopteran host cell line for AcMNPV. The predicted amino acid sequence of the product of the host gene is identical to animal ubiquitin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball E., Karlik C. C., Beall C. J., Saville D. L., Sparrow J. C., Bullard B., Fyrberg E. A. Arthrin, a myofibrillar protein of insect flight muscle, is an actin-ubiquitin conjugate. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U., Schlesinger M. J. Ubiquitin is a heat shock protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):949–956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau V., Tobias J. W., Bachmair A., Marriott D., Ecker D. J., Gonda D. K., Varshavsky A. A multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1576–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.2538923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford A. M., Miller L. K. Characterization of an early gene accelerating expression of late genes of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2773–2781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2773-2781.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunigan D. D., Dietzgen R. G., Schoelz J. E., Zaitlin M. Tobacco mosaic virus particles contain ubiquitinated coat protein subunits. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):310–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90691-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of a trans-activating gene required for expression of a baculovirus delayed-early gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.563-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. L., Ahrens P., Bright P. M., Ankel H. Interferon induces a 15-kilodalton protein exhibiting marked homology to ubiquitin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11315–11323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Summers M. D. Glycosylation and secretion of human tissue plasminogen activator in recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):214–223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Miller L. K. Effects of serial passage of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus in cell culture. Virus Res. 1987 Jun;7(4):335–349. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. S., Simon J. A., Lis J. T. Structure and expression of ubiquitin genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4727–4735. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow V. A., Summers M. D. High level expression of nonfused foreign genes with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus expression vectors. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Finley D., Solomon M. J., Varshavsky A. The yeast ubiquitin genes: a family of natural gene fusions. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1429–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02384.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman K. L., Rechsteiner M. Identification of the long ubiquitin extension as ribosomal protein S27a. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):438–440. doi: 10.1038/338438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann G. F. Polyhedrin structure. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1499–1513. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T., Gallatin W. M., Siegelman M., Smith H. T., Fried V. A., Weissman I. L. Expression cloning of a lymphocyte homing receptor cDNA: ubiquitin is the reactive species. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):845–850. doi: 10.1126/science.3003914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., Persico M., Alcalay M. A "housekeeping" gene on the X chromosome encodes a protein similar to ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):851–855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]