Abstract
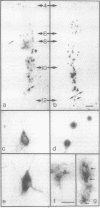
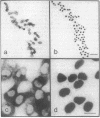
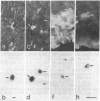
We used a recombinant retrovirus to study cell lineage in the chicken optic tectum. The virus inserts the Escherichia coli lacZ (beta-galactosidase) gene into the genome of an infected cell; a histochemical stain marks the progeny of infected cells with a blue precipitate. We had previously shown that individual clones frequently contain diverse neuronal types. Now we asked whether individual clones contain glia as well as neurons. To this end, we constructed a virus in which lacZ is fused to a nuclear localization signal sequence from the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Cells infected with this virus are marked with blue nuclei instead of blue somata. In embryos injected with a mixture of the two retroviruses, individual clusters contained cells with only one label type (nuclear or cytoplasmic), thus verifying that clusters of cells were clones. Furthermore, it was possible to immunostain the somata of cells that had blue nuclei, whereas the blue cytoplasmic precipitate hampered immunostaining. Together, these methods allowed us to show that some clones contained neurons (neurofilament-positive) and two types of glia (glutamine synthetase-positive and glial fibrillary acidic protein-positive). This result demonstrates the existence of a common progenitor for neurons and glia in optic tectum.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender M. A., Palmer T. D., Gelinas R. E., Miller A. D. Evidence that the packaging signal of Moloney murine leukemia virus extends into the gag region. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1639–1646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1639-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. S., DiLullo C. Transient expression of a neurofilament protein by replicating neuroepithelial cells of the embryonic chick brain. Dev Biol. 1985 Jan;107(1):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Rocancourt D., Briand P., Grimber G., Nicolas J. F. A beta-galactosidase hybrid protein targeted to nuclei as a marker for developmental studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6795–6799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Protein import into the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:367–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Genes with promoters in retrovirus vectors can be independently suppressed by an epigenetic mechanism. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):449–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. E., Glover J. C., Majors J., Sanes J. R. Radial arrangement of clonally related cells in the chicken optic tectum: lineage analysis with a recombinant retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7356–7360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt C. E., Bertsch T. W., Ellis H. M., Harris W. A. Cellular determination in the Xenopus retina is independent of lineage and birth date. Neuron. 1988 Mar;1(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang L. W., Schindler M. Nuclear transport in 3T3 fibroblasts: effects of growth factors, transformation, and cell shape. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):13–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt P., Cooper M. L., Rakic P. Coexistence of neuronal and glial precursor cells in the cerebral ventricular zone of the fetal monkey: an ultrastructural immunoperoxidase analysis. J Neurosci. 1981 Jan;1(1):27–39. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-01-00027.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P. J. Multiple marker analysis in the avian optic tectum reveals three classes of neuroglia and carbonic anhydrase-containing neurons. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2388–2396. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02388.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P. J., Perkins M. S., Fitch F. W., Moscona A. A. Comparative characterization of monoclonal antibodies to carbonic anhydrase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):690–697. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90594-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P. J., Perkins M. Gliogenesis in the embryonic avian optic tectum: neuronal-glial interactions influence astroglial phenotype maturation. Brain Res. 1987 Feb;428(2):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luskin M. B., Pearlman A. L., Sanes J. R. Cell lineage in the cerebral cortex of the mouse studied in vivo and in vitro with a recombinant retrovirus. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Buttimore C. Redesign of retrovirus packaging cell lines to avoid recombination leading to helper virus production. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Thurlow L. Cell lineage in the rat cerebral cortex: a study using retroviral-mediated gene transfer. Development. 1988 Nov;104(3):473–482. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Turner D., Cepko C. Lineage analysis in the vertebrate nervous system by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugatsch T., Stacey D. W. Identification of a sequence likely to be required for avian retroviral packaging. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):505–511. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. The effect of protein context on nuclear location signal function. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R. Analysing cell lineage with a recombinant retrovirus. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Jan;12(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. L., Cepko C. L. A common progenitor for neurons and glia persists in rat retina late in development. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):131–136. doi: 10.1038/328131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C., Cepko C. L. Clonally related cortical cells show several migration patterns. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1342–1345. doi: 10.1126/science.3137660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetts R., Fraser S. E. Multipotent precursors can give rise to all major cell types of the frog retina. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1142–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.2449732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]