Abstract
The Positive and Negative Affect Schedule – Direction (PANAS-D) questionnaire was translated from the French version developed by Nicolas and coworkers into Arabic-Tunisian language and administered to a sample of 519 athletes (mean age 19.43±3.78 years; 230 male, 229 female; 75 competing at international level, 287 at national level, 130 at regional level, and 27 at local level). A semi-confirmatory factor analysis was carried out in order to shed light on the factor structure of the questionnaire. Different models were tested, including the 1-factor, the 2-factor and the 3-factor structure models, and compared in terms of fitting indexes. Data support a 2-factor solution of the modified short version of the PANAS-D questionnaire.
Keywords: Semi-confirmatory factor analysis, Sport and exercise psychology
Specifications Table
| Subject area | Psychology |
| More specific subject area | Sport and exercise psychology |
| Type of data | Tables |
| How data were acquired | Administration of the questionnaire and analysis of data |
| Data format | Raw, analyzed |
| Experimental factors | Factor structure models, fitting indexes and factor loadings and multivariate analysis |
| Experimental features | Validation of the questionnaire through a semi-confirmatory factor analysis |
| Data source location | Tunisia |
| Data accessibility | Data are within this article |
Value of the data
-
•
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first translation of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule – Direction (PANAS-D) questionnaire in Arabic-Tunisian language.
-
•
These data could be useful for Arabic researchers in that could be used for further investigation in the field of sport and exercise psychology, both for replicating our findings and for discovering new ones.
-
•
These data could be useful for the scientific community in that could be used to shed light on the factor structure of the PANAS-D questionnaire.
1. Data
This paper contains psychometric data on the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule – Direction (PANAS-D) questionnaire – which can be used in order to assess the relationships between intensity and direction of affects and variables such as coping, attainment of achievement, goals and sport satisfaction – translated from French into Arabic-Tunisian language (Table 1) and administered to a cluster of athletes whose characteristics are reported in Table 2. Different factor models were tested and fitting indexes were computed to find the best solution (Table 3), whose descriptive statistics and standardized factor loadings are shown in Table 4, Table 5, respectively. The impact of gender, age and experience level are shown in Table 6.
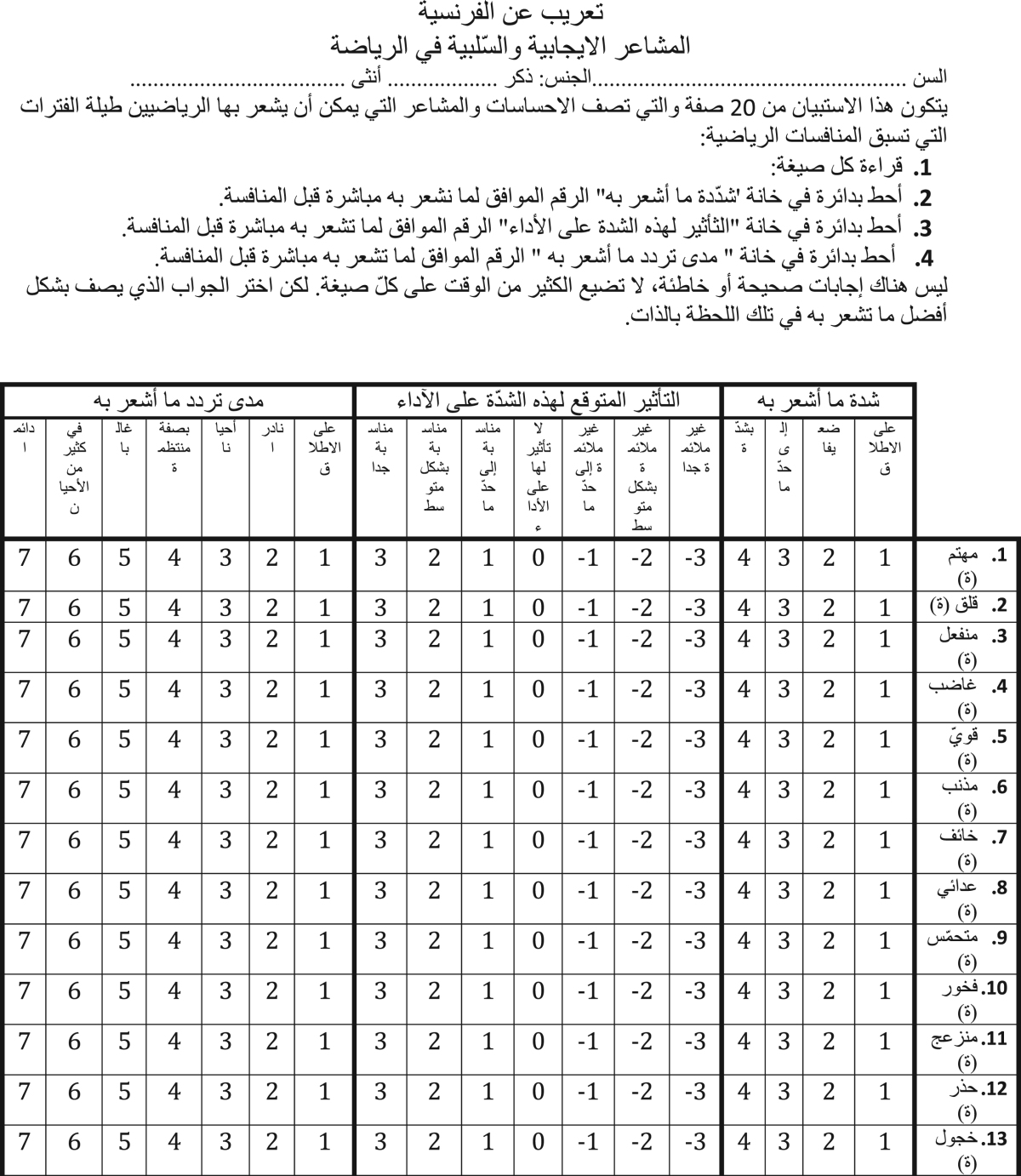
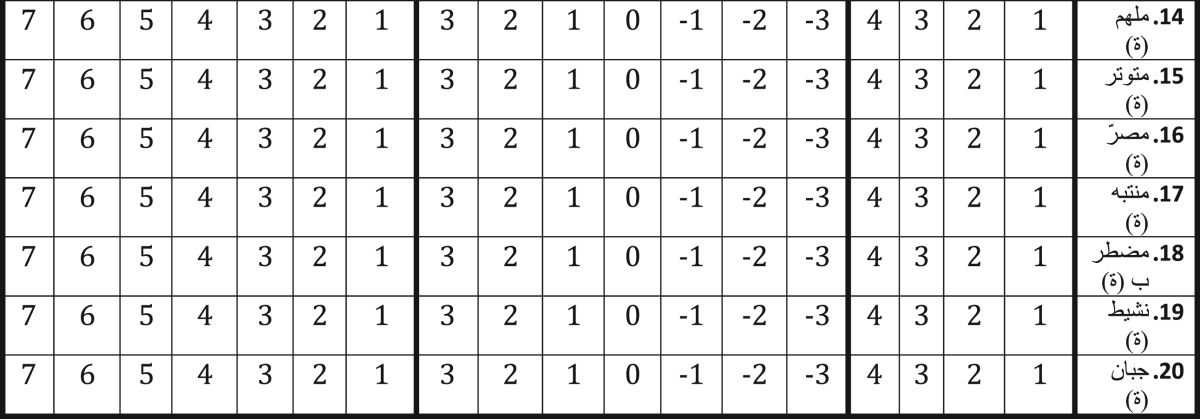
Table 1.
Translated version of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule – Direction (PANAS-D) questionnaire from French into Arabic-Tunisian language.
Table 2.
General descriptive statistics of the recruited sample of athletes to which the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule – Direction (PANAS-D) questionnaire in Arabic-Tunisian language has been administered.
| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 19.43±3.78 | |
| Gender | Male | 289 (55.7%) |
| Female | 230 (44.3%) | |
| Experience level | International | 75 (14.5%) |
| National | 287 (55.3%) | |
| Regional | 130 (25.0%) | |
| Local | 27 (5.2%) | |
Table 3.
Different factor models of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule – Direction (PANAS-D) questionnaire in Arabic-Tunisian version have been tested. Abbreviations: AGFI (adjusted goodness of fit index); CFI (comparative fit index); df (degrees of freedom); GFI (goodness of fit index); NCP (non-centrality parameter); NNFI (non-normed fit index); RMSEA (root mean square error of approximation); SRMR (standardized root mean square residual).
| Fitting index |
Intensity |
Direction |
Intensity |
Direction |
Intensity |
Direction |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-factor | 1-factor (modified scale) | 1-factor | 1-factor (modified scale) | 2-factor | 2-factor (modified scale) | 2-factor | 2-factor (modified scale) | 3-factor | 3-factor (modified scale) | 3-factor | 3-factor (modified scale) | |
| χ2 | 1031.958 | 94.544 | 1469.127 | 223.607 | 670.976 | 30.859 | 754.357 | 47.553 | 369.907 | 192.042 | 546.291 | 303.947 |
| Df | 170 | 35 | 170 | 44 | 151 | 19 | 151 | 19 | 133 | 75 | 133 | 75 |
| p-value | P=0.000010 | P=0.000010 | P=0.000010 | P=0.000010 | P=0.000010 | P=0.044335 | P=0.000010 | P=0.000335 | P=0.000010 | P=0.000010 | P=0.000010 | P=0.000010 |
| χ2 for independence model | 1997.355 | 975.620 | 2960.519 | 1630.449 | 1997.355 | 511.509 | 2960.519 | 859.787 | 1997.355 | 1321.845 | 2960.519 | 2105.890 |
| Df | 190 | 45 | 190 | 55 | 190 | 36 | 190 | 36 | 190 | 120 | 190 | 120 |
| RMSEA | 0.099 | 0.057 | 0.121 | 0.089 | 0.082 | 0.035 | 0.087 | 0.054 | 0.059 | 0.055 | 0.077 | 0.077 |
| NCP | 220.150 | 45.325 | 220.150 | 56.980 | 195.545 | 24.605 | 195.545 | 24.605 | 172.235 | 97.125 | 172.235 | 97.125 |
| NNFI | 0.47 | 0.92 | 0.48 | 0.86 | 0.64 | 0.95 | 0.73 | 0.93 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.79 | 0.82 |
| CFI | 0.52 | 0.94 | 0.53 | 0.89 | 0.71 | 0.98 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.85 | 0.88 |
| GFI | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| AGFI | 0.86 | 0.99 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| GFI without diagonal values | 0.67 | 0.97 | 0.68 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| AGFI without diagonal values | 0.63 | 0.97 | 0.65 | 0.97 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| SRMR | 0.1032 | 0.97 | 0.1311 | 0.0573 | 0.0715 | 0.0309 | 0.0622 | 0.0315 | 0.0451 | 0.0419 | 0.0495 | 0.0453 |
Table 4.
Descriptive statistics of the best fitting 2-factor structure of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule – Direction (PANAS-D) questionnaire in Arabic-Tunisian language. Abbreviations: df (degrees of freedom); KMO (Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin).
| Descriptive statistics |
Intensity |
Direction |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-factor (original, non modified scale) | 2-factor (modified scale) | 2-factor (original, non modified scale) | 2-factor (modified scale) | |
| Determinant of the matrix | 0.019989530135988 | 0.369785741011195 | 0.003029814842235 | 0.187834259983683 |
| Bartlett׳s statistic | 1997.4 (df=190; P=0.000010) | 511.5 (df=36; P=0.000010) | 2960.5 (df=190; P=0.000010) | 859.8 (df=36; P=0.000010) |
| KMO test | 0.76600 | 0.68598 | 0.82458 | 0.75729 |
Table 5.
Standardized factor loading for intensity and direction scales of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule – Direction (PANAS-D) questionnaire in Arabic-Tunisian language.
| Variable |
INTENSITY |
DIRECTION |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | |
| V5 | 0.564 | 0.705 | ||
| V7 | 0.790 | 0.592 | ||
| V12 | 0.546 | 0.692 | ||
| V13 | 0.353 | 0.553 | ||
| V15 | 0.559 | 0.652 | ||
| V16 | 0.545 | 0.595 | ||
| V17 | 0.508 | 0.587 | ||
| V18 | 0.317 | 0.531 | ||
| V19 | 0.459 | 0.514 | ||
| Variance | 1.398 | 1.149 | 1.940 | 1.346 |
| Reliability estimate | 0.659 | 0.691 | 0.769 | 0.679 |
Table 6.
Multivariate analysis of the best fitting 2-factor solution of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule – Direction (PANAS-D) questionnaire in Arabic-Tunisian language.
| Variable | Value | F | Sig. | η2 | Observed power | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | Pillai׳s Trace | 0.714 | 29.385 | 0.000 | 0.714 | 1.000 |
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.286 | 29.385 | 0.000 | 0.714 | 1.000 | |
| Lawley-Hotelling Trace | 2.501 | 29.385 | 0.000 | 0.714 | 1.000 | |
| Roy׳s Largest Root | 2.501 | 29.385 | 0.000 | 0.714 | 1.000 | |
| Age | Pillai׳s Trace | 0.158 | 2.208 | 0.000 | 0.158 | 1.000 |
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.842 | 2.208 | 0.000 | 0.158 | 1.000 | |
| Lawley-Hotelling Trace | 0.188 | 2.208 | 0.000 | 0.158 | 1.000 | |
| Roy׳s Largest Root | 0.188 | 2.208 | 0.000 | 0.158 | 1.000 | |
| Gender | Pillai׳s Trace | 0.191 | 2.778 | 0.000 | 0.191 | 1.000 |
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.809 | 2.778 | 0.000 | 0.191 | 1.000 | |
| Lawley-Hotelling Trace | 0.236 | 2.778 | 0.000 | 0.191 | 1.000 | |
| Roy׳s Largest Root | 0.236 | 2.778 | 0.000 | 0.191 | 1.000 | |
| Experience level | Pillai׳s Trace | 0.639 | 3.195 | 0.000 | 0.213 | 1.000 |
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.478 | 3.280 | 0.000 | 0.218 | 1.000 | |
| Lawley-Hotelling Trace | 0.862 | 3.367 | 0.000 | 0.223 | 1.000 | |
| Roy׳s Largest Root | 0.491 | 5.795 | 0.000 | 0.329 | 1.000 | |
| Gender * experience level | Pillai׳s Trace | 0.513 | 2.434 | 0.000 | 0.171 | 1.000 |
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.562 | 2.489 | 0.000 | 0.175 | 1.000 | |
| Lawley-Hotelling Trace | 0.651 | 2.544 | 0.000 | 0.178 | 1.000 | |
| Roy׳s Largest Root | 0.377 | 4.449 | 0.000 | 0.274 | 1.000 | |
2. Experimental design, materials and methods
The PANAS-D questionnaire in its original version comprises two scales (intensity and direction), each one of 20-item adjective checklist subscales (10 items corresponding to positive emotions and 10 items corresponding to negative emotions). It was translated from the French version [1] into Arabic-Tunisian, following the linguistic validation method proposed by Vallerand, termed as double translation/back translation [2].
The project received ethical approval from the Tunis University, Tunisia, and all participants provided written informed consent. Prior to data collection, permission was obtained from the team manager and the coach to conduct the study survey in athletes. Athletes were informed about the purpose and procedures of the study, and were told that the results would be made available to them upon completion of the study. Athletes who agreed to participate in the study were instructed about the survey procedures for the study. All participating athletes completed the demographic information.
A semi-confirmatory factor analysis was carried out using Factor software (version 9.2).
The multivariate analysis was performed in order to investigate the impact of parameters, such as age, gender and experience level, using SPSS (version 23.0, IBM Inc., USA).
Footnotes
Transparency data associated with this article can be found in the online version at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2017.02.019.
Transparency document. Supplementary material
Supplementary material
.
References
- 1.Nicolas M., Martinent G., Campo M. Evaluation of the psychometric properties of a modified Positive and Negative Affect Schedule including a Direction scale (PANAS-D) among French athletes. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2014;15(3):227–237. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vallerand R. Vers une méthodologie de la validation trans-culturelle de questionnaires psychologiques: implications pour la recherche en langue française. Psychol. Can. 1989;30:662–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material