Abstract
Background
Few studies have investigated the relationship between living arrangements and dietary intake among evacuees after disasters.
Objectives
To examine the relationship between living arrangements and dietary intake using the data of a large-scale cohort survey of evacuees after the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011.
Methods
73,433 residents in evacuation zones responded to the Fukushima Health Management Survey questionnaire. Subjects were excluded if they did not report their living conditions or were missing more than three pieces of information about dietary intake. The data of 52,314 subjects (23,149 men and 29,165 women ≥15 years old) were used for the analyses. Evacuees' living arrangements were characterized into three categories: evacuation shelters or temporary housing, rental houses or apartments, or a relative's home or their own home. Dietary intake was characterized in terms of grains, fruits and vegetables, meat, soybean products, dairy products, and fish. Daily consumption of the third quartile (Q3) or higher for each food group was defined as ‘high consumption’. Prevalence ratios (PRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using modified Poisson regression analyses.
Results
Modified Poisson regression analyses showed that, compared with respondents living in a relative's home or their own home, the PRs and 95% CIs for the people living in rental apartments of high consumption of fruits and vegetables (non-juice), meat, soybean products, and dairy products were 0.69 (95% CI, 0.61–0.77), 0.82 (95% CI, 0.73–0.91), 0.89 (95% CI, 0.83–0.94), and 0.83 (95% CI, 0.74–0.93) respectively. The corresponding PRs and 95% CIs for people living in evacuation shelters or temporary housing were 0.83 (95% CI, 0.78–0.88), 0.90 (95% CI, 0.86–0.95), 0.94 (95% CI, 0.91–0.97), and 0.91 (95% CI, 0.86–0.96) for high consumption of fruits and vegetables (non-juice), meat, soybean products, and dairy products, respectively.
Conclusion
The present study suggests that, after the earthquake, living in non-home conditions was associated with poor dietary intake of fruits and vegetables (non-juice), meat, soybean products, and dairy products, suggesting the need for early improvements in the provision of balanced meals among evacuees living in non-home conditions.
Keywords: Great East Japan earthquake, Living arrangements, Dietary intake
1. Introduction
The Great East Japan Earthquake of March 11, 2011, which was followed by a gigantic tsunami and the radiation release of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, was a historic and tremendous disaster in Japan. The radiation dose was estimated to be quite low.1 However, evacuees began to suffer day-to-day, long-lasting anxiety and deterioration of quality of life due to worries about the radiation. In response to concerns about the physical and mental well-being of evacuees of the disaster, the Fukushima Health Management Survey was conducted soon afterwards to investigate effects of the long-term low-dose radiation exposure caused by the accident. Health examinations and questionnaires were also used to assess the health and living conditions of evacuees as a baseline survey for follow-up study.2
Significant deterioration of lifestyle among evacuees was a big concern. Soon after the disaster, most evacuees started living in evacuation shelters for a few months.3 After about half a year, some of them began to transfer to temporary accommodations, where only basic necessities were supplied by the local government.3 Other survivors moved to their relatives' homes or returned to their own homes.
Nutrition or dietary intake among evacuees after disasters is tremendously important for their health maintenance. However, studies of nutrition among evacuees are very limited. A few studies have shown that, after the earthquake, better living conditions and ready access to gas utilities were associated with a healthier diet among evacuees.3,4 However, the studies neither focused on living arrangements nor looked at the consumption of certain food groups. Other studies have shown an inverse or null association between socio-demographic factors and balanced diet.5–7 However, none of these covered the post-disaster situation.
Thus, the present study was conducted to examine the association between living arrangements and dietary intake among evacuees after the Great East Japan Earthquake.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
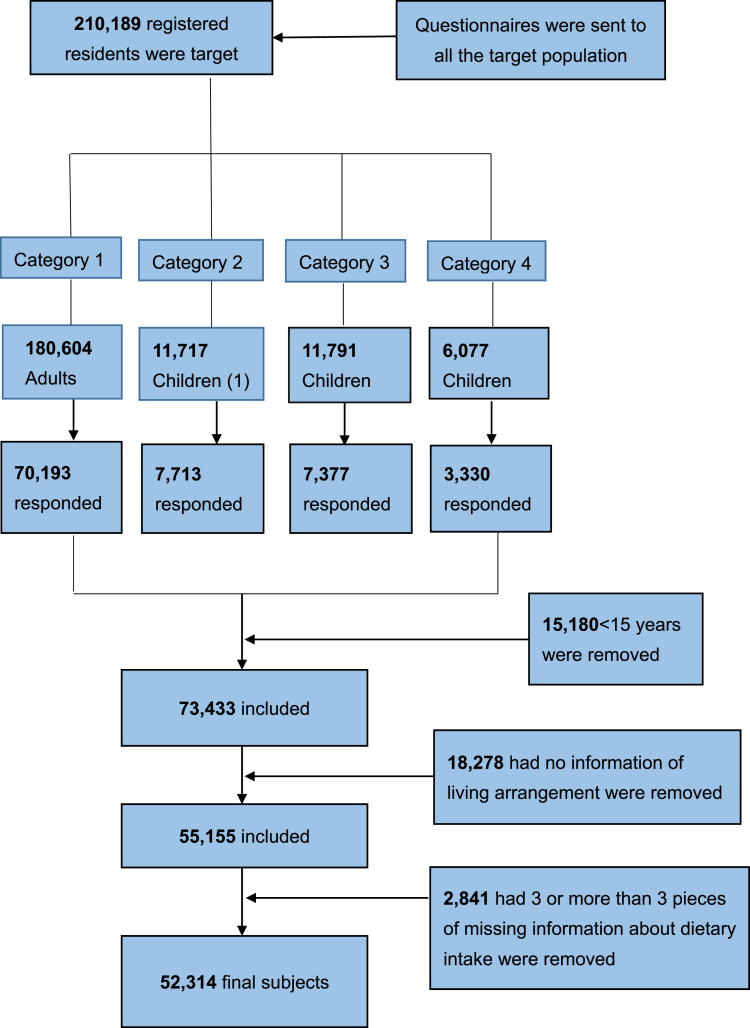
The details of the survey, which was approved by the ethics review committee of Fukushima Medical University (No. 1316), have been described elsewhere.1–3 Fig. 1 shows how the subjects were collected. In brief, the target population was 210,189 officially registered residents of the Great East Japan Earthquake evacuation zones, including Hirono Town, Naraha Town, Tomioka Town, Kawauchi Village, Futaba Town, Namie Town, Katsurao Village, Minamisoma City, Tamura City, Yamakiya District of Kawamata Town and Itate Village. In 2012, questionnaires were sent out to all registered residents. As shown in Fig. 1, 70,193 of 180,604 residents in category 1 (38.9%), 7713 of 11,717 residents in category 2 (65.8%), 7377 of 11,791 residents in category 3 (62.6%), and 3330 of 6077 residents in category 4 responded to the questionnaire.2 After exclusion of 15,180 aged <15 years, 73,433 people were included in the Mental Health and Lifestyle Survey (response rate: 40.7%).
Fig. 1. Flow chart of collection of the subjects.
Subjects were excluded for the analyses if they did not report their living conditions or had more than three missing pieces of information in the questions about dietary intake. After exclusion, the data of 52,314 subjects (23,149 men and 29,165 women aged 15 years old and over) were used for the analyses.
2.2. Dietary intake assessment and questionnaire
In developing a common questionnaire for a baseline survey of the survivors, we broadly investigated their health statuses and lifestyles. A short food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) was used to examine food intake. We selected 19 items, and the frequency of consumption of these foods during the previous 6 months was assessed in the questionnaire. The FFQ in the present study was a modified version of the one has been used in the Hiroshima/Nagasaki Life Span Study, and its validity has been reported previously.8
The 19 items were divided into 8 food groups: The fruits and vegetables (total) was composed of a non-juice subgroup (fruits, green vegetables, red and orange vegetables, and light-colored vegetables) and a fruit and vegetable juice subgroup (fruit juice and vegetable juice) in light of different outcomes related to the consumption of the two subgroups in some previous studies.9,10 The others were meat (chicken, beef, pork, ham, and sausages), soybean products (natto [fermented soybeans], miso soup, tofu dishes, and boiled bean dishes), dairy products (milk, soy milk, yogurt, and Lactobacillus drinks), fish (e.g., sashimi, cooked/boiled/fried fish), rice, and bread. Questions asked about the frequency of consumption (i.e., the approximate number of times a week on average during the previous several days) for the five food groups; answers were ‘none’, ‘less than once per week’, ‘once or twice per week ’, ‘3–4 times per week’, ‘5–6 times per week’, or ‘every day’.
Participants were required to select an answer from six options about their living conditions: evacuation shelter, temporary housing, rental housing or apartment, a relative's home, their own home, or other. For analysis, evacuation shelters and temporary housing were combined due to their similarity, and the last option was considered as non-informative due to its ambiguity.
Depression was measured by the Japanese version of the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale (K6), which has been validated.11,12 In the K6, participants were asked if they had the following symptoms during the preceding 30 days: feeling so sad that nothing could cheer them up; feeling nervous, hopeless, restless, or fidgety; feeling everything was an effort; and feeling worthless. Each question was rated on a 5-point Likert-type scale from 0 (none of the time) to 4 (all of the time), with higher scores signifying worse mental health status (range: 0–24).1
Data relating to smoking and drinking status were also obtained from the questionnaire. The options for smoking status were non-smoker, former smoker, or current smoker. The options for drinking status were ‘once or more per month’, ‘previous drinker’, or ‘less than once per month’. Self-reported health status was also investigated, with five options: ‘very good’, ‘good’, ‘normal’, ‘poor’, or ‘very poor’. Respondents selected education status from ‘elementary school and junior high school’, ‘high school ’, ‘vocational college or junior college ’, or ‘university (4 years) or graduate school’. In addition, changes of work situation since the disaster were also obtained using the questionnaire. Five options were provided: ’started a new job’, ‘became unemployed ’, ‘changed jobs’, ‘income has increased’, ‘income has decreased’, or ‘other’.
2.3. Statistical analysis
For the frequency of dietary intake of each food group, the daily midpoint for each frequency category was used. For example, ‘3–4 times per week’ was assessed as 0.5 times per day. Subjects who had three or more missing pieces of information in questions about dietary intake were excluded from the analyses. For subjects who had one or two missing answers, median frequencies of all food items were used to replace the missing data. For each food group, daily consumption of the third quartile (Q3) or higher for that food group was defined as ‘high consumption’.
Prevalence ratios (PRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using modified Poisson regression models. Adjustment variables consisted of age (≤44 years [reference], 45–54, 55–64, 65–74, or ≥75 years), drinking status (once or more per month[reference], previous drinker, or less than once per month), smoking status (non-smoker [reference], ex-smoker, or current smoker), perceived health status (very good [reference], good, normal, poor, or very poor), mental health status (K6 <13 or K6 ≥13), education status (elementary school and junior high school, high school, vocational college or junior college, or university [4 years] or graduate school), becoming unemployed (yes or no), and change of work (yes or no). All analyses were conducted using SAS software version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
3. Results
Frequencies of daily consumption of each food group are shown in Table 1. Among all participants, the mean consumption of each food group was 2.18 times/day for fruits and vegetables (total), 1.91 for fruits and vegetables (non-juice), 0.28 for fruits and vegetables (juice), 0.74 for meat, 1.63 for soybean products, 0.82 for dairy products, 0.42 for fish, and 1.26 for rice and bread among all participants. For fruits and vegetables (total), 20.7% of men were classified as having ‘high consumption’ because they scored at or above the Q3 daily frequency (3.00), while the respective prevalence for women was 29.3%. The corresponding prevalence for men versus women for fruits and vegetables (non-juice), fruits and vegetables (juice), meat, soybean products, dairy products, and fish were 19.2% vs. 28.5%, 31.7% vs. 32.9%, 30.4% vs. 34.5%, 69.9% vs. 71.5%, 21.0% vs. 33.3%, 51.9% vs. 52.6%, and 37.3% vs.62.7%, respectively. The results suggest that women were more likely to have higher frequency of consumption of all the examined food groups than men.
Table 1. Frequency of food group consumption (n = 52,314).
| Food group | Number of times per day | Number of times ≥ third quartile times per day | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Third quartile times | Men (%) | Women (%) | ||
| Fruits and vegetable (total) | 2.18 | 3.00 | 20.7 | 29.3 | <0.001 |
| Fruits and vegetables (non-juice) | 1.91 | 2.57 | 19.2 | 28.5 | <0.001 |
| Fruits and vegetables (juice) | 0.28 | 0.29 | 31.7 | 32.9 | 0.004 |
| Meat | 0.74 | 2.93 | 30.4 | 34.5 | <0.001 |
| Soybean products | 1.63 | 2.21 | 69.9 | 71.5 | <0.001 |
| Milk products | 0.82 | 1.21 | 21.0 | 33.3 | <0.001 |
| Fish | 0.42 | 0.50 | 51.9 | 52.6 | 0.094 |
| Rice and bread | 1.26 | 1.50 | 37.3 | 62.7 | <0.001 |
Table 2 shows demographic information according to consumption of each food group for all subjects. For all food groups, subjects with high consumption were more likely to live in non-evacuation conditions, be women, be current smokers, be current drinkers, have normal or good perceived health, have good mental health status (K6 <13), and have senior middle school or vocational college education status. In addition, subjects with high consumption were much less likely to have lost their job or changed their work. For fruits and vegetables (total and non-juice) and fish, subjects with high consumption were more likely to be elderly. However, there were young subjects who were likely to have high consumption of vegetable and fruits (juice), meat, beans, and rice. For milk, the middle age group had the highest consumption.
Table 2. Baseline characteristics of participants according to food intakes.
| Fruits and vegetable (total) | Fruits and vegetable (non-juice) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poor intake | Enough intake | Poor intake | Enough intake | ||
| Living arrangement | Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 5329 (13.7%) | 1708 (12.8%) | 5443 (13.8%) | 1594 (12.5%) |
| Rental house, apartment | 17,246 (44.2%) | 5015 (37.6%) | 17,602 (44.5%) | 4659 (36.5%) | |
| Relatives' home or own home | 16,407 (42.1%) | 6609 (49.6%) | 16,510 (41.7%) | 6506 (28.3%) | |
| Sex | Men | 18,362 (47.1%) | 4787 (35.9%) | 18,699 (47.3%) | 4450 (34.9%) |
| Women | 20,620 (52.9%) | 8545 (64.1%) | 20,856 (52.7%) | 8309 (65.1%) | |
| Age, years | 15–49 | 16,172 (41.5%) | 2959 (22.2%) | 16,686 (42.2%) | 2445 (19.2%) |
| 50–64 | 12,295 (31.5%) | 3709 (27.8%) | 12,370 (31.3%) | 3634 (28.5%) | |
| ≥65 | 10,515 (27.0%) | 6664 (50.0%) | 10,499 (26.5%) | 6680 (52.4%) | |
| Drinking status | ≥once/month | 19,313 (49.4%) | 7729 (58.0%) | 19,630 (49.6%) | 7412 (58.1%) |
| Previous drinker | 1248 (3.2%) | 539 (4.0%) | 1296 (3.3%) | 491 (3.9%) | |
| <once/month | 17,948 (46.0%) | 4767 (35.8%) | 18,146 (45.9%) | 4569 (35.8%) | |
| Smoking status | Current smoker | 20,425 (52.4%) | 8692 (65.2%) | 20,673 (52.3%) | 8444 (66.2%) |
| Never-smoker | 8434 (21.6%) | 2760 (20.7%) | 8586 (21.7%) | 2608 (20.4%) | |
| Previous smoker | 9387 (24.1%) | 1449 (10.9%) | 9363 (24.2%) | 1273 (10.0%) | |
| Health condition | Very bad | 1711 (4.5%) | 573 (4.4%) | 1764 (4.5%) | 520 (4.2%) |
| Bad | 5425 (14.2%) | 1767 (13.6%) | 5506 (14.2%) | 1686 (13.5%) | |
| Normal | 24,460 (63.9%) | 8048 (61.9%) | 24,723 (63.6%) | 7785 (62.5%) | |
| Good | 6008 (15.7%) | 2363 (18.2%) | 6154 (15.8%) | 2217 (17.8%) | |
| Very good | 695 (1.8%) | 261 (2.0%) | 702 (1.8%) | 254 (2.0%) | |
| Depression status | K6 <13 | 33,909 (87.0%) | 11,476 (86.1%) | 34,332 (86.8%) | 11,053 (86.6%) |
| K6 ≥13 | 5073 (13.0%) | 1856 (13.9%) | 5223 (13.2%) | 1706 (13.4%) | |
| Education status | Elementary school and middle school | 9372 (24.0%) | 3539 (26.6%) | 9376 (23.7%) | 3535 (27.7%) |
| Senior middle school | 19,351 (49.6%) | 5924 (44.4%) | 19,665 (49.7%) | 5610 (44.0%) | |
| Vocational college | 6071 (15.6%) | 2202 (16.5%) | 6211 (15.7%) | 2062 (16.2%) | |
| Undergraduate school and graduate school | 2981 (7.7%) | 1183 (8.9%) | 3065 (7.8%) | 1099 (8.6%) | |
| Unemployment | Yes | 7591 (19.5%) | 2209 (16.6%) | 7740 (19.6%) | 2060 (16.2%) |
| No | 31,391 (80.5%) | 11,123 (83.4%) | 31,815 (80.4%) | 10,699 (83.9%) | |
| Change of work | Yes | 1699 (4.4%) | 22,176 (2.2%) | 1731 (4.4%) | 258 (2.0%) |
| No | 37,283 (95.6%) | 13,042 (97.8%) | 37,824 (95.6%) | 12,501 (98.0%) | |
| Fruits and vegetable (juice) | Meat | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poor intake | Enough intake | Poor intake | Enough intake | ||
| Living arrangement | Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 4629 (13.1%) | 2408 (14.2%) | 5047 (14.3%) | 1990 (11.7%) |
| Rental house, apartment | 14,897 (42.1%) | 7364 (43.5%) | 14,526 (41.2%) | 7735 (45.3%) | |
| Relatives' home or own home | 15,854 (44.8%) | 7162 (42.3%) | 15,670 (44.5%) | 7346 (43.0%) | |
| Sex | Men | 15,810 (44.7%) | 7339 (43.3%) | 16,124 (45.8%) | 7025 (41.2%) |
| Women | 19,570 (55.3%) | 9595 (56.7%) | 19,119 (54.3%) | 10,046 (58.9%) | |
| Age, years | 15–49 | 12,667 (35.8%) | 6464 (38.2%) | 10,924 (31.0%) | 8207 (48.1%) |
| 50–64 | 11,549 (32.6%) | 4455 (26.3%) | 11,674 (33.1%) | 4330 (25.4%) | |
| ≥65 | 11,164 (31.6%) | 6015 (35.5%) | 12,645 (35.9%) | 4534 (26.6%) | |
| Drinking status | ≥once/month | 17,766 (50.2%) | 9276 (54.8%) | 17,906 (50.8%) | 9136 (53.5%) |
| Previous drinker | 1147 (3.2%) | 640 (3.8%) | 1270 (3.6%) | 517 (3.0%) | |
| <once/month | 16,013 (45.3%) | 6702 (39.6%) | 15,543 (44.1%) | 7172 (42.0%) | |
| Smoking status | Current smoker | 19,214 (54.3%) | 9903 (58.5%) | 19,214 (54.5%) | 9900 (34.0%) |
| Never-smoker | 7748 (21.9%) | 3446 (20.4%) | 7892 (22.4%) | 3302 (19.3%) | |
| Previous smoker | 7703 (21.8%) | 3133 (18.5%) | 7301 (20.7%) | 3526 (20.7%) | |
| Health condition | Very bad | 1465 (4.2%) | 819 (4.9%) | 1378 (4.0%) | 906 (5.4%) |
| Bad | 4830 (13.9%) | 2362 (14.2%) | 4610 (13.3%) | 2582 (15.4%) | |
| Normal | 22,281 (64.2%) | 10,227 (61.6%) | 21,885 (63.4%) | 10,623 (63.4%) | |
| Good | 5521 (15.9%) | 2850 (17.2%) | 5993 (17.4%) | 2378 (14.2%) | |
| Very good | 622 (1.8%) | 334 (2.0%) | 681 (2.0%) | 275 (1.6%) | |
| Depression status | K6<13 | 33,909 (87.0%) | 11,476 (86.1%) | 30,544 (86.7%) | 14,841 (86.9%) |
| K6≥13 | 5073 (13.0%) | 1856 (13.9%) | 4699 (13.3%) | 2230 (13.1%) | |
| Education status | Elementary school and middle school | 8904 (25.2%) | 4007 (23.7%) | 9482 (26.9%) | 3429 (20.1%) |
| Senior middle school | 17,183 (48.6%) | 8092 (47.8%) | 16,970 (48.2%) | 8350 (48.7%) | |
| Vocational college | 5483 (15.5%) | 2790 (16.5%) | 5044 (14.3%) | 3229 (18.9%) | |
| Undergraduate school and graduate school | 2697 (7.6%) | 1467 (8.7%) | 2585 (7.3%) | 1579 (9.3%) | |
| Unemployment | Yes | 4522 (12.8%) | 2407 (14.2%) | 6602 (18.7%) | 3198 (18.7%) |
| No | 30,858 (87.2%) | 14,527 (85.8%) | 28,641 (81.3%) | 13,873 (81.3%) | |
| Change of work | Yes | 1364 (4.4%) | 625 (3.7%) | 1227 (3.4%) | 762 (4.5%) |
| No | 34,016 (95.6%) | 16,309 (96.3%) | 34,016 (96.5%) | 16,309 (95.5%) | |
| Bean | Milk | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poor intake | Enough intake | Poor intake | Enough intake | ||
| Living arrangement | Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 2020 (13.2%) | 5017 (13.6%) | 5169 (13.7%) | 1868 (12.8%) |
| Rental house, apartment | 7868 (51.5%) | 14,393 (38.9%) | 16,451 (43.6%) | 5810 (39.9%) | |
| Relatives' home or own home | 5387 (35.3%) | 17,629 (47.6%) | 16,125 (42.7%) | 6891 (47.3%) | |
| Sex | Men | 6964 (45.6%) | 16,185 (43.7%) | 18,292 (48.5%) | 4857 (33.3%) |
| Women | 8311 (54.4%) | 20,854 (56.3%) | 19,453 (51.4%) | 9712 (66.7%) | |
| Age, years | 15–49 | 8534 (55.9%) | 10,597 (55.4%) | 15,008 (39.8%) | 4123 (28.3%) |
| 50–64 | 4162 (27.3%) | 11,842 (32.0%) | 11,782 (31.2%) | 4222 (29.0%) | |
| ≥65 | 2579 (16.9%) | 14,600 (39.4%) | 10,955 (29.0%) | 6224 (42.7%) | |
| Drinking status | ≥once/month | 7872 (51.5%) | 19,170 (51.8%) | 18,547 (49.1%) | 8495 (58.3%) |
| Previous drinker | 454 (3.0%) | 1333 (3.6%) | 1244 (3.3%) | 543 (3.7%) | |
| <once/month | 6808 (44.6%) | 15,907 (43.0%) | 17,472 (46.3%) | 5243 (36.0%) | |
| Smoking status | Current smoker | 7846 (51.4%) | 21,271 (73.1%) | 19,436 (54.5%) | 9681 (66.5%) |
| Never-smoker | 2881 (18.9%) | 8313 (22.4%) | 8258 (22.4%) | 2936 (20.2%) | |
| Previous smoker | 4308 (28.2%) | 6528 (17.6%) | 9308 (20.7%) | 1528 (10.5%) | |
| Health condition | Very bad | 829 (5.5%) | 1455 (4.0%) | 1673 (4.5%) | 611 (4.3%) |
| Bad | 2155 (14.4%) | 5037 (14.2%) | 5288 (14.3%) | 1904 (13.4%) | |
| Normal | 9233 (61.5%) | 23,275 (64.1%) | 23,521 (63.4%) | 8987 (63.1%) | |
| Good | 2460 (16.4%) | 5911 (16.3%) | 5901 (15.9%) | 2470 (17.4%) | |
| Very good | 340 (2.3%) | 616 (1.7%) | 694 (1.9%) | 262 (1.8%) | |
| Depression status | K6 <13 | 13,033 (85.3%) | 32,352 (87.4%) | 32,738 (86.7%) | 12,747 (86.8%) |
| K6 ≥13 | 2242 (14.7%) | 4687 (12.7%) | 5007 (13.3%) | 1922 (13.2%) | |
| Education status | Elementary school and middle school | 2786 (18.2%) | 10,125 (27.3%) | 9523 (25.2%) | 3388 (23.3%) |
| Senior middle school | 7920 (51.9%) | 17,355 (46.9%) | 18,382 (48.7%) | 6893 (47.3%) | |
| Vocational college | 2647 (17.3%) | 5626 (10.8%) | 5754 (15.2%) | 2519 (17.3%) | |
| Undergraduate school and graduate school | 1447 (9.5%) | 2717 (7.3%) | 2887 (7.7%) | 1277 (8.8%) | |
| Unemployment | Yes | 3082 (20.2%) | 6718 (18.1%) | 7215 (19.1%) | 2585 (17.4%) |
| No | 12,193 (79.8%) | 30,321 (81.9%) | 30,530 (80.9%) | 11,984 (82.3%) | |
| Change of work | Yes | 840 (5.5%) | 1149 (3.1%) | 1582 (4.2%) | 762 (2.8%) |
| No | 14,435 (94.5%) | 35,890 (96.9%) | 36,163 (95.8%) | 14,162 (97.2%) | |
| Fish | Rice | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poor intake | Enough intake | Poor intake | Enough intake | ||
| Living arrangement | Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 3222 (12.9%) | 3815 (13.9%) | 5320 (33.9%) | 1717 (12.0%) |
| Rental house, apartment | 11,769 (47.2%) | 10,492 (47.1%) | 15,728 (41.4%) | 6533 (45.7%) | |
| Relatives' home or own home | 9960 (39.9%) | 13,056 (47.7%) | 16,984 (44.7%) | 6032 (42.2%) | |
| Sex | Men | 11,136 (44.6%) | 12,013 (43.9%) | 17,824 (46.9%) | 5325 (37.3%) |
| Women | 13,815 (55.4%) | 15,350 (56.1%) | 20,208 (53.1%) | 8957 (62.7%) | |
| Age, years | 15–49 | 12,363 (49.6%) | 6768 (24.7%) | 12,904 (33.9%) | 6227 (43.6%) |
| 50–64 | 6938 (27.8%) | 9066 (33.1%) | 12,006 (31.6%) | 3998 (28.0%) | |
| ≥65 | 5650 (32.9%) | 11,529 (67.1%) | 13,122 (34.5%) | 4057 (28.4%) | |
| Drinking status | ≥once/month | 13,179 (52.8%) | 13,863 (50.7%) | 18,556 (48.8%) | 8486 (59.4%) |
| Previous drinker | 783 (3.1%) | 1004 (3.7%) | 1245 (3.3%) | 542 (3.8%) | |
| <once/month | 10,684 (42.8%) | 12,031 (44.0%) | 17,644 (46.4%) | 5071 (35.5%) | |
| Smoking status | Current smoker | 13,439 (53.9%) | 15,678 (57.3%) | 20,584 (54.5%) | 8533 (59.8%) |
| Never-smoker | 4948 (19.8%) | 6246 (22.8%) | 8356 (22.4%) | 2838 (19.9%) | |
| Previous smoker | 6102 (24.5%) | 4734 (17.3%) | 8194 (20.7%) | 2642 (18.5%) | |
| Health condition | Very bad | 1238 (5.1%) | 1046 (3.9%) | 1630 (4.4%) | 654 (4.7%) |
| Bad | 3620 (14.8%) | 3572 (13.3%) | 5154 (13.8%) | 2038 (14.5%) | |
| Normal | 15,403 (62.8%) | 17,105 (63.9%) | 23,528 (63.1%) | 8970 (63.9%) | |
| Good | 3838 (15.7%) | 4533 (16.9%) | 6229 (16.7%) | 2142 (15.3%) | |
| Very good | 430 (1.8%) | 526 (2.0%) | 726 (2.0%) | 230 (1.6%) | |
| Depression status | K6 <13 | 21,570 (85.5%) | 23,815 (87.0%) | 33,007 (86.8%) | 12,378 (86.7%) |
| K6 ≥13 | 3381 (13.6%) | 3548 (13.0%) | 5025 (13.2%) | 1904 (13.3%) | |
| Education status | Elementary school and middle school | 5313 (18.2%) | 7598 (27.8%) | 10,302 (27.1%) | 2609 (18.3%) |
| Senior middle school | 12,417 (51.9%) | 12,858 (47.0%) | 18,167 (47.8%) | 7108 (49.8%) | |
| Vocational college | 4192 (17.3%) | 4081 (14.9%) | 5510 (14.5%) | 2763 (19.4%) | |
| Undergraduate school and graduate school | 2209 (8.9%) | 1955 (7.1%) | 2800 (7.4%) | 1364 (9.6%) | |
| Unemployment | Yes | 4923 (19.7%) | 4877 (17.8%) | 7086 (18.6%) | 2714 (19.0%) |
| No | 20,028 (80.3%) | 22,486 (82.2%) | 30,946 (81.4%) | 11,568 (81.0%) | |
| Change of work | Yes | 1215 (4.9%) | 774 (2.8%) | 1438 (3.8%) | 551 (3.9%) |
| No | 23,736 (95.1%) | 26,589 (97.2%) | 36,594 (96.2%) | 13,731 (96.1%) | |
K6, Kessler Psychological Distress Scale.
Table 3 shows the characteristics of the participants according to living arrangements. The subjects living in non-evacuation conditions were more likely to be women, elderly or middle-aged, current smokers, current drinkers, have normal or worse perceived health, and be non-college graduates, which may due to age. In addition, subjects living in non-evacuation conditions, especially those living in relatives' or their own homes, were less likely to report losing their jobs or changing their work.
Table 3. Baseline characteristics of participants according to living arrangements.
| Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | Rental house, apartment | Relatives' home or own home | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Men | 3210 (45.6%) | 9667 (43.4%) | 10,272 (44.6%) |
| Women | 3827 (54.4%) | 12,594 (56.6%) | 12,744 (55.4%) | |
| Age, years | 15–49 | 1908 (10.0%) | 2216 (13.9%) | 2913 (22.3%) |
| 50–64 | 10,880 (56.9%) | 6481 (40.5%) | 4900 (28.5%) | |
| ≥65 | 6343 (33.2%) | 7307 (45.7%) | 9366 (54.5%) | |
| Drinking status | ≥once/month | 3787 (53.8%) | 11,019 (49.5%) | 12,236 (53.2%) |
| Previous drinker | 315 (4.5%) | 692 (3.1%) | 780 (3.4%) | |
| <once/month | 2755 (39.2%) | 10,314 (46.3%) | 9646 (41.9%) | |
| Smoking status | Current smoker | 3849 (33.9%) | 11,819 (10.3%) | 13,449 (58.4%) |
| Never-smoker | 1523 (27.3%) | 4649 (78.2%) | 5022 (21.8%) | |
| Previous smoker | 1437 (37.9%) | 5411 (8.3%) | 3988 (17.3%) | |
| Health condition | Very bad | 202 (2.9%) | 950 (4.3%) | 1132 (5.0%) |
| Bad | 708 (10.3%) | 2856 (13.1%) | 3628 (16.1%) | |
| Normal | 4233 (61.5%) | 13,658 (62.5%) | 14,617 (64.8%) | |
| Good | 1544 (22.4%) | 3943 (18.0%) | 2884 (12.8%) | |
| Very good | 201 (2.9%) | 460 (2.1%) | 295 (1.3%) | |
| Depression status | K6 <13 | 5897 (83.8%) | 18,769 (84.3%) | 20,719 (90.0%) |
| K6 ≥13 | 1140 (16.2%) | 3492 (15.7%) | 2297 (10.0%) | |
| Education status | Elementary school and middle school | 2376 (33.8%) | 3768 (16.9%) | 6767 (29.4%) |
| Senior middle school | 3342 (49.6%) | 11,437 (51.4%) | 10,496 (45.6%) | |
| Vocational college | 763 (10.2%) | 4104 (18.4%) | 3406 (14.8%) | |
| Undergraduate school and graduate school | 228 (11.7%) | 2273 (10.2%) | 1663 (7.2%) | |
| Unemployment | Yes | 2096 (29.8%) | 5916 (26.6%) | 1788 (7.8%) |
| No | 4941 (70.2%) | 16,345 (73.4%) | 21,228 (92.2%) | |
| Change of work | Yes | 235 (3.3%) | 1292 (5.8%) | 462 (2.0%) |
| No | 6802 (96.7%) | 20,969 (94.2%) | 22,554 (98.0%) | |
K6, Kessler Psychological Distress Scale.
Table 4 shows the PRs and 95% CIs for consumption of each food group at a daily frequency of greater than or equal to the respective Q3 value for the whole population and men and women separately using a modified Poisson regression model. Respondents living in rental houses or apartments and evacuation shelters or temporary housing were more likely to have lower consumption of most food groups, including fruits and vegetables (non-juice), meat, soybean products, dairy products, fish, rice, and bread. In the multivariable-adjusted model, the results remained the same, except for fish, rice, and bread, for which PR was no longer significant. Compared with people living in a relative's homes or their own home (references), the PRs and 95% CIs for people living in rental houses or apartments having high consumption of fruits and vegetables (non-juice), meat, soybean products, and dairy products were 0.69 (95% CI, 0.61–0.77),0.82 (95% CI, 0.73–0.91), 0.89 (95% CI, 0.83–0.94), and 0.83 (95% CI, 0.74–0.93), respectively. The corresponding PRs and 95% CIs for people living in evacuation shelters or temporary housing were 0.87 (95% CI, 0.82–0.92), 0.83 (95% CI, 0.78–0.88), 0.90 (95% CI, 0.86–0.95), 0.94 (95% CI, 0.91–0.97), and 0.91 (95% CI, 0.86–0.96). However, this tendency was inverted for consumption of fruit and vegetable juices. Compared with people living in a relative's home or their own home, the PR and 95% CI for people living in rental houses or apartments to have high consumption of fruit and vegetable juices was 1.23 (95% CI, 1.11–1.36), and the corresponding value for people living in evacuation shelters or temporary housing was 1.11 (95% CI, 1.06–1.17).
Table 4. Prevalence ratios for dietary intake of each group on modified Poisson regression analyses.
| Living arrangement | High consumption, n (%) | Total | Men (n = 23,149) | Women (n = 29,165) | Total | Men (n = 23,149) | Women (n = 29,165) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR (95% CI)a | PR (95% CI)a | PR (95% CI)a | PR (95% CI)b | PR (95% CI)b | PR (95% CI)b | |||
| Fruits and vegetables (total) | Relatives' home or own home | 6609 (28.7) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Rental house, apartment | 5015 (22.5) | 0.71 (0.63–0.79) | 0.75 (0.62–0.89) | 0.69 (0.61–0.80) | 0.76 (0.68–0.86) | 0.82 (0.70–0.99) | 0.74 (0.64–0.86) | |
| Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 1708 (24.3) | 0.84 (0.79–0.89) | 0.86 (0.79–0.94) | 0.83 (0.79–0.89) | 0.87 (0.82–0.92) | 0.91 (0.82–1.00) | 0.86 (0.80–0.93) | |
| Fruits and vegetables (non-juice) | Relatives' home or own home | 6506 (28.3) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Rental house, apartment | 4659 (20.9) | 0.63 (0.56–0.70) | 0.66 (0.55–0.80) | 0.62 (0.54–0.71) | 0.69 (0.61–0.77) | 0.75 (0.61–0.91) | 0.67 (0.58–0.78) | |
| Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 1594 (22.7) | 0.79 (0.75–0.84) | 0.81 (0.74–0.89) | 0.79 (0.73–0.84) | 0.83 (0.78–0.88) | 0.86 (0.78–0.95) | 0.82 (0.76–0.88) | |
| Fruits and vegetables (juice) | Relatives' home or own home | 7162 (16.6) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Rental house, apartment | 7364 (18.5) | 1.22 (1.11–1.34) | 1.26 (1.10–1.45) | 1.19 (1.05–1.35) | 1.23 (1.11–1.36) | 1.30 (1.12–1.51) | 1.17 (1.02–1.34) | |
| Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 2408 (17.5) | 1.10 (1.05–1.16) | 1.12 (1.05–1.20) | 1.09 (1.02–1.16) | 1.11 (1.06–1.17) | 1.14 (1.06–1.23) | 1.08 (1.01–1.16) | |
| Meat | Relatives' home or own home | 7346 (31.9) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Rental house, apartment | 7735 (34.8) | 0.79 (0.71–0.87) | 0.86 (0.74–1.01) | 0.74 (0.65–0.84) | 0.82 (0.73–0.91) | 0.90 (0.77–1.06) | 0.76 (0.66–0.87) | |
| Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 1990 (28.3) | 0.89 (0.84–0.93) | 0.93 (0.86–1.00) | 0.86 (0.80–0.92) | 0.90 (0.86–0.95) | 0.95 (0.88–1.03) | 0.87 (0.81–0.94) | |
| Soybean products | Relatives' home or own home | 17,629 (76.6) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Rental house, apartment | 14,393 (64.7) | 0.86 (0.81–0.92) | 0.86 (0.79–0.95) | 0.87 (0.79–0.94) | 0.89 (0.83–0.94) | 0.89 (0.80–0.98) | 0.89 (0.81–0.97) | |
| Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 5017 (71.3) | 0.93 (0.90–0.96) | 0.93 (0.89–0.97) | 0.93 (0.89–0.97) | 0.94 (0.91–0.97) | 0.94 (0.89–0.99) | 0.94 (0.90–0.99) | |
| Milk products | Relatives' home or own home | 2.442 (10.6) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Rental house, apartment | 1903 (8.6) | 0.78 (0.70–0.86) | 0.79 (0.67–0.94) | 0.79 (0.69–0.90) | 0.83 (0.74–0.93) | 0.85 (0.71–1.03) | 0.83 (0.72–0.95) | |
| Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 628 (8.9) | 0.88 (0.84–0.93) | 0.89 (0.82–0.97) | 0.89 (0.83–0.95) | 0.91 (0.86–0.96) | 0.92 (0.84–1.01) | 0.91 (0.85–0.98) | |
| Fish | Relatives' home or own home | 13,056 (56.7) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Rental house, apartment | 10,492 (47.1) | 0.91 (0.85–0.98) | 0.91 (0.82–1.02) | 0.91 (0.83–1.01) | 0.94 (0.87–1.02) | 0.95 (0.84–1.07) | 0.94 (0.85–1.05) | |
| Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 3815 (54.2) | 0.95 (0.92–0.99) | 0.95 (0.90–1.01) | 0.96 (0.91–1.00) | 0.97 (0.93–1.01) | 0.97 (0.92–1.03) | 0.97 (0.92–1.02) | |
| Rice and bread | Relatives' home or own home | 1717 (24.4) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Rental house, apartment | 6533 (29.4) | 0.88 (0.79–0.98) | 0.91 (0.82–1.01) | 0.91 (0.83–1.01) | 0.94 (0.84–1.05) | 1.00 (0.83–1.19) | 0.91 (0.79–1.05) | |
| Evacuation shelter or temporary housing | 6023 (26/2) | 0.94 (0.89–0.99) | 0.95 (0.90–1.01) | 0.96 (0.91–1.00) | 0.97 (0.92–1.02) | 1.00 (0.91–1.09) | 0.96 (0.89–1.03) |
CI, confidence interval; K6, Kessler Psychological Distress Scale; PR, prevalence ratio.
Age-adjusted.
Further adjusted for age (18–44, 45–54, 55–64, 65–74, or ≥75 years), drinking status (≥once/month, previous drinker, or < once/month), smoking status (current smoker, never smoker, or previous smoker), perceived health condition (very good, good, normal. bad, or very bad), mental health status (K6 <13 or ≥13), education status (elementary school and middle school, senior middle school, vocational college, or undergraduate school and graduate school), unemployment (yes or no), change of work (yes or no).
Table 5 shows that, irrespective of gender, unemployment was inversely associated with higher intakes of fruits and vegetables (non-juice) and soybean products, with PRs of 0.86 (95% CI, 0.75–0.99) and 0.84 (95% CI, 0.72–0.98), respectively, which means that the people who lost their job after the disaster were more likely to have low consumption of these food groups. For women, on the other hand, change of work was inversely associated with high intakes of soybean products and fish, with corresponding PRs of 0.89 (95% CI, 0.82–0.96) and 0.89 (95% CI, 0.80–0.99) (see Table 6).
Table 5. Prevalence ratios for work status on modified Poisson regression analyses.
| Unemployment | Total | Men (n = 23,149) | Women (n = 29,165) | Unemployment | Total | Men (n = 23,149) | Women (n = 29,165) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR (95% CI)a | PR (95% CI)a | PR (95% CI)a | PR (95% CI)b | PR (95% CI)b | PR (95% CI)b | |||
| Fruits and vegetables | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.95 (0.91–1.00) | 0.90 (0.83–0.98) | 0.96 (0.91–1.02) | Yes | 1.02 (0.97–1.07) | 0.97 (0.89–1.06) | 1.02 (0.96–1.09) | |
| Fruits and vegetables (non-juice) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.94 (0.89–0.98) | 0.87 (0.80–0.95) | 0.95 (0.89–1.00) | Yes | 1.02 (0.97–1.09) | 0.95 (0.87–1.04) | 1.02 (0.96–1.09) | |
| Fruits and vegetables (juice) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.99 (0.95–1.03) | 0.98 (0.92–1.04) | 1.00 (0.95–1.06) | Yes | 0.98 (0.94–1.02) | 0.96 (0.90–1.02) | 0.99 (0.94–1.05) | |
| Meat | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.96 (0.93–1.00) | 0.90 (0.84–0.96) | 1.00 (0.96–1.05) | Yes | 0.99 (0.95–1.03) | 0.90 (0.84–0.97) | 1.03 (0.98–1.09) | |
| Soybean products | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.99 (0.97–1.02) | 0.97 (0.93–1.01) | 1.00 (0.97–1.04) | Yes | 1.03 (1.00–1.06) | 1.01 (0.96–1.05) | 1.05 (1.01–1.09) | |
| Milk products | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.98 (0.94–1.02) | 0.91 (0.84–0.98) | 0.99 (0.94–1.04) | Yes | 1.03 (0.98–1.08) | 0.98 (0.90–1.07) | 1.02 (0.97–1.08) | |
| Fish | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.98 (0.95–1.02) | 0.98 (0.93–1.03) | 0.99 (0.95–1.03) | Yes | 1.00 (0.97–1.04) | 0.99 (0.94–1.05) | 1.01 (0.97–1.06) | |
| Rice and bread | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.97 (0.94–1.02) | 0.93 (0.86–1.00) | 0.99 (0.94–1.04) | Yes | 0.98 (0.94–1.02) | 0.92 (0.85–1.00) | 0.99 (0.94–1.05) |
CI, confidence interval; K6, Kessler Psychological Distress Scale; PR, prevalence ratio.
Age-adjusted.
Further adjusted for age (18–44, 45–54, 55–64, 65–74, or ≥75 years), drinking status (≥once/month, previous drinker, or < once/month), smoking status (current smoker, never smoker, or previous smoker), perceived health condition (very good, good, normal. bad, or very bad), mental health status (K6 <13 or ≥13), education status (elementary school and middle school, senior middle school, vocational college, or undergraduate school and graduate school), unemployment (yes or no), change of work (yes or no).
Table 6. Prevalence ratios for work status on modified Poisson regression analyses.
| Change of work | Total | Men (n = 23,149) | Women (n = 29,165) | Change of work | Total | Men (n = 23,149) | Women (n = 29,165) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR (95% CI)a | PR (95% CI)a | PR (95% CI)a | PR (95% CI)b | PR (95% CI)b | PR (95% CI)b | |||
| Fruits and vegetables (total) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.81 (0.72–0.92) | 0.78 (0.65–0.95) | 0.84 (0.72–0.98) | Yes | 0.84 (0.75–0.95) | 0.84 (0.69–1.02) | 0.84 (0.72–0.98) | |
| Fruits and vegetables (non-juice) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.82 (0.72–0.93) | 0.72 (0.58–0.90) | 0.89 (0.76–1.04) | Yes | 0.85 (0.75–0.97) | 0.79 (0.63–0.98) | 0.89 (0.76–1.04) | |
| Fruits and vegetables (juice) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.97 (0.89–1.05) | 0.99 (0.92–1.11) | 0.95 (0.85–1.07) | Yes | 0.98 (0.91–1.07) | 1.01 (0.89–1.13) | 0.97 (0.86–1.09) | |
| Meat | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.97 (0.93–1.02) | 0.92 (0.85–1.00) | 1.00 (0.95–1.06) | Yes | 0.99 (0.95–1.10) | 1.10 (0.99–1.22) | 0.97 (0.87–1.07) | |
| Soybean products | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.94 (0.90–1.00) | 1.00 (0.92–1.09) | 0.89 (0.82–0.97) | Yes | 1.03 (1.00–1.06) | 0.84 (0.72–0.98) | 0.88 (0.80–0.97) | |
| Milk products | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.90 (0.81–0.99) | 0.85 (0.71–1.01) | 0.93 (0.83–1.05) | Yes | 0.95 (0.90–1.10) | 1.01 (0.93–1.10) | 0.90 (0.82–0.98) | |
| Fish | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.93 (0.86–1.00) | 0.97 (0.88–1.08) | 0.89 (0.80–0.99) | Yes | 0.93 (0.86–1.00) | 0.97 (0.88–1.08) | 0.88 (0.79–0.98) | |
| Rice and bread | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Yes | 0.92 (0.84–1.00) | 0.90 (0.78–1.03) | 0.94 (0.84–1.05) | Yes | 0.94 (0.86–1.02) | 0.94 (0.81–1.08) | 0.94 (0.84–1.05) |
CI, confidence interval; K6, Kessler Psychological Distress Scale; PR, prevalence ratio.
Age-adjusted.
Further adjusted for age (18–44, 45–54, 55–64, 65–74, or ≥75 years), drinking status (≥once/month, previous drinker, or < once/month), smoking status (current smoker, never smoker, or previous smoker), perceived health condition (very good, good, normal. bad, or very bad), mental health status (K6 <13 or ≥13), education status (elementary school and middle school, senior middle school, vocational college, or undergraduate school and graduate school), unemployment (yes or no), change of work (yes or no).
4. Discussion
In our cohort study of evacuees of the Great East Japan Earthquake, our baseline survey inquired about consumption frequencies for eight food groups: fruits and vegetables (non-juice), fruits and vegetables (juice), meat, soybean products, dairy products, and fish. The results showed that living arrangements were associated with dietary intake of various foods. Compared with participants living in a relative's homes or their own home, people of both genders living in evacuation shelters or temporary housing and rental houses or apartments were more likely to have lower consumption of fruits and vegetables (non-juice) and dairy products, as well as higher consumption of fruit and vegetable juices. Moreover, women in the same living arrangements were more likely to have lower consumption of meat and soybean products.
The present large-scale study is the first to show that non-home conditions were associated with poor dietary intake of most food groups. Similar studies were very limited. Another baseline survey in a cohort of survivors from Iwate prefecture after the Great East Japan Earthquake showed that, during the year after the disaster, better living conditions were associated with prudent dietary patterns, which were characterized by high intakes of fish and shellfish, soybean products, fruits and vegetables, and dairy products.3 However, in that study, living conditions were characterized by self-reporting, so living arrangements could not be accurately identified.
Several points of cautions should be made when interpreting our results. First, some previous studies have suggested that it would be difficult for evacuees living in shelters to have balanced meals due to shortages of cooking equipment and utilities, such as gas, or due to some form of food shortage after the Great East Japan Earthquake.4,13 In the present study, some of the evacuees (about 20%) had lived in a shelter before moving out several months later. Less than 2% of the subjects still lived in shelters when this survey was conducted, so we do not expect that there was any shortage of cooking equipment among the subjects. However, for those who did not live in a home, the much more limited space and simpler equipment for cooking than residents previously had might have been an obstacle to eating balanced daily meals.
Second, there was no association between living arrangements and consumption of fish in the multivariable model. This result is reasonable because fish, which is common in the traditional Japanese diet, is very prevalent in rice balls and bento (Japanese boxed lunches). Even people living in evacuation shelters or temporary housing who may have had less access to cooking equipment could have easily consumed fish from rice balls and bento provided by the government. Likewise, the respondents living in rental houses or apartments, most of whom were youths or single adults, could readily buy rice balls and bento from convenience stores, so it would not have been difficult for them to consume fish, either.
Third, living conditions, including living environment, economic level, and work status, are often considered as a socio-demographic indicator. With regard to the present study, obviously those who live in a relative's home or their own home would have been more familiar with their surroundings and perceive better access to supermarkets, which may in turn promote more balanced daily dietary intakes. Several studies have also examined the relationship between living environment, economic level, and dietary patterns, but these studies have yielded inconsistent results.5–7 A cross-sectional study of young Brazilian adults showed that dietary patterns for fruits and vegetables were not significantly associated with living environment and work status.5 On the other hand, another cross-sectional study conducted in four French urban zones showed that migrant status was associated with risk of low-frequency consumption of fruits and vegetables (<3.5 times per day) and dairy products (<2 times per day).7 In addition, respondents with severe food insufficiency were more likely to be low consumers of fruits and vegetables, meat, seafood, and eggs (less than once per day), as well as dairy products. A low monthly food budget, temporary housing in a shelter, and lack of household income were all associated with low seafood consumption.6 An American study showed that, among 828 low-income housing residents in greater Boston, perceived supermarket access was strongly associated with increased fruit and vegetable intake. Respondents who did not report a supermarket within walking distance from home, despite the presence of a supermarket within 1 km, consumed significantly fewer fruits and vegetables than those who were aware of having a supermarket within walking distance.7
We conducted further analyses to identify the association between living arrangement and consumptions of each food group stratified by age (data not shown). Living in home conditions was associated with high consumption of fruits and vegetables (whether total or non-juice), most significantly among 15–49 year olds. These subjects were most likely to live with their families, so that their balanced dietary intake may be easily influenced by living condition or cooking equipment.
Further, an association was observed between juice consumption and living arrangements. The evacuees living in non-home conditions were more likely to have high consumption of fruit and vegetable juices, which may be one of the reasons for weight gain among these subjects. Though supermarkets may have been less accessible, juices were easy enough to get from vending machines, which are omnipresent in Japan. What is more, it is possible that the evacuees living in non-home conditions had a special need or craving for juice because of their lack of fresh fruits and vegetables.
For the assessed changes of employment due to the earthquake, the present study showed that becoming unemployed was inversely associated with lower intake of fruits and vegetables (non-juice) and soybean products. In addition, a change of work was associated with lower intakes of soybean products and fish among women. Previous studies on the topic have yielded inconsistent results.13–16 A few studies have observed that households can conserve their dietary patterns during periods of economic crisis.14–16 However, one cross-sectional study reported that, during the 1996–1998 economic crisis in Indonesia, rich pregnant women experienced negative changes in fat intake, while poor pregnant women showed the reverse.17 However, due to the special status of the subjects in that study, the result can hardly be generalized for comparison with our results. One of the reasons for the observed dietary changes after unemployment or changing jobs may be age. Those who experienced unemployment and a change of work were much younger than those who did not (data not shown), and soybean products, as traditional Japanese food, are not as popular among youth as among the elderly.18 Therefore, the result of the current study was considered as a reasonable one.
The present study has some strengths. First, this is the first study to examine the association between living arrangements and dietary intake on such a large scale and under post-disaster conditions. Our results will certainly be valuable to all future post-disaster intervention research. Second, though the study had a cross-sectional design, the only possible causal relationship is that living arrangements led to certain dietary intakes; reverse causality is not reasonable. Therefore, the causal relationship can be inferred to some extent.
Some limitations of the present study should be considered. First, the overall response rate was low (40.7%), so sampling biases may exist in the present study. Second, some foods prevalent in Japan, such as pickles, were not included in the questionnaire. Intakes of these foods should be monitored because of the possibility of higher salt intake when they are excessively consumed. However, the main aim of this survey was to detect insufficient intake of the major food groups. Thus, a short list of food groups was used instead of adopting a comprehensive food questionnaire.3 Third, information on portion sizes was not estimated. Therefore, calculation of the amount of each item consumed was impossible. Fourth, under the extraordinary and unusual social circumstances that follow a major disaster, daily dietary intakes may be strongly influenced by changes in family relationships (e.g., death or physical separation) among the evacuees. However, the present study did not capture this information. The potential associations observed in this study will be investigated over a long period. Moreover, though most questionnaires were collected in the same period (from January 2012 to March 2012), it was difficult to estimate whether timing of the survey would affect the dietary intake of participants. However, the correlation coefficients between the results of 24-h diary and the FFQ were 0.32 for milk, 0.27 for fruits, 0.34 for rice, 0.28 for bread, 0.25 for miso soup, 0.14 for fish, and −0.03 for dry fish.8 The results showed that the FFQ is moderately correlated with the 24-h diary, with the exception of dry fish.8 Thus, we considered that the FFQ is suitable to assess dietary intake in the present study. We also plan to evaluate the performance of the 19-item FFQ used in the present study in the near future.
In conclusion, the living arrangements and dietary intakes of evacuees of the Great East Japan Earthquake of March 11, 2011 during the following year were widely surveyed. The results of the present study suggest that, after the earthquake, living in a relative's homes or their own home, rather than evacuation shelters or temporary housing, was associated with higher dietary intake of fruits and vegetables (all), fruits and vegetables (non-juice), meat, soybean products, and dairy products among residents of the evacuation zones. Our study suggests early improvements in the provision of balanced meals among evacuees living in non-home conditions could be done in several ways: providing adequate and balanced stockpiles of food; providing nutrition information by professional nutritionists; and quickly restoring access to food supplies for evacuees, such as setting up temporary grocery markets near them. Hopefully, governments and authorities will act as soon as possible in order to prepare for future disasters.
Conflicts of interest
None declared.
Acknowledgements
This Survey was conducted as part of Fukushima Prefecture's post-disaster recovery plans and supported by the national ‘Health Fund for Children and Adults Affected by the Nuclear Incident.’
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary data related to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.je.2016.08.002.
References
- 1.Yabe H, Suzuki Y, Mashiko H, et al. Psychological distress after the great East Japan earthquake and fukushima daiichi nuclear power plant accident: results of a mental health and lifestyle survey through the fukushima health management survey in fy2011 and fy2012. Fukushima J Med Sci. 2014;60:57–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yasumura S, Hosoya M, Yamashita S, et al. Fukushima health management survey group. Study protocol for the fukushima health management survey. J Epidemiol. 2012;22:375–383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nishi N, Yoshimura E, Ishikawa-Takata K, et al. Relationship of living conditions with dietary patterns among survivors of the great East Japan earthquake. J Epidemiol. 2013;5:376–381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Hoshi Y, Onodera K, Mizuno S, Sako K. What factors were important for dietary improvement in emergency shelters after the Great East Japan Earthquake? Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2014;23:159–166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Olinto MT, Willett WC, Gigante DP, Victora CG. Sociodemographic and lifestyle characteristics in relation to dietary patterns among young Brazilian adults. Public Health Nutr. 2011;14:150–159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Caspi CE, Kawachi I, Subramanian SV, Adamkiewicz G, Sorensen G. The relationship between diet and perceived and objective access to supermarkets among low-income housing residents. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75:1254–1262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Méjean C, Deschamps V, Bellin-Lestienne C, et al. Associations of socioeconomic factors with inadequate dietary intake in food aid users in France (The ABENA study 2004-2005). Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010;64:374–382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sauvaget C, Allen N, Hayashi M, Spencer E, Nagano J. Validation of a food frequency questionnaire in the Hiroshima/Nagasaki life span study. J Epidemiol. 2002;12:394–401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Muraki I, Imamura F, Manson JE, et al. Fruit consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from three prospective longitudinal cohort studies. BMJ. 2013;347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xi B, Li S1, Liu Z, et al. Intake of fruit juice and incidence of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Furukawa TA, Kawakami N, Saitoh M, et al. The performance of the Japanese version of the K6 and K10 in the World mental health survey Japan. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2008;17:152–158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sakurai K, Nishi A, Kondo K, Yanagida K, Kawakami N. Screening performance of K6/K10 and other screening instruments for mood and anxiety disorders in Japan. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;65:434–441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yanagihara H, Hatakeyama Y, Iwasaki T. Coordination by registered dieticians for nutritional and dietary support in disaster in Japan. West Pac Surveill Response J. 2012;3:46–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dore AR, Adair LS, Popkin BM. Low income Russian families adopt effective behavioral strategies to maintain dietary stability in times of economic crisis. J Nutr. 2003;11:3469–3475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Arroyo P, Loria A, Méndez O. Changes in the household calorie supply during the 1994 economic crisis in Mexico and its implications on the obesity epidemic. Nutr Rev. 2004;62:S163–S168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Thorne-Lyman AL, Valpiani N, Sun K, et al. Household dietary diversity and food expenditures are closely linked in rural Bangladesh, increasing the risk of malnutrition due to the financial crisis. J Nutr. 2010;140:182S–188S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hartini TN,Winkvist A, Lindholm L, Stenlund H, Persson V, Nurdiati DS, Surjono A. Nutrient intake and iron status of urban poor and rural poor without access to rice fields are affected by the emerging economic crisis: the case of pregnant Indonesian women. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2003;57:654–666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.The National Health and Nutrition Survey of 2012. http://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/kenkou_eiyou_chousa.html.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary data related to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.je.2016.08.002.