Abstract
Two disparate polyketide families, the benzenediol lactones and the azaphilones, are produced by fungi using iterative polyketide synthase (iPKS) enzymes consisting of collaborating partner subunits. Exploitation of this common biosynthetic logic using iPKS subunit shuffling allowed the diversity-oriented combinatorial biosynthesis of unprecedented polyketide scaffolds new to nature, bearing structural motifs from both of these orthogonal natural product families. Starter unit acyltransferase domain replacements proved necessary but not sufficient to guarantee communication between iPKS subunits.
Graphical Abstract
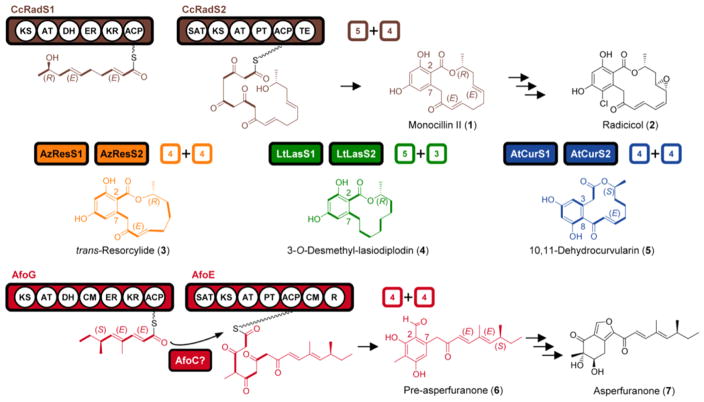
Benzenediol lactones (BDLs) and azaphilones are disparate structural classes of fungal polyketide natural products with an impressive array of biological activities.1,2 Thus, BDLs such as monocillin II (1, Figure 1), a resorcylic acid lactone (RAL) that is the precursor of radicicol (2), and the dihydroxyphenylacetic acid lactone (DAL) 10,11-dehydrocurvularin (5) all display anticancer and immune system modulatory activities.1,3 Phytotoxic RALs like trans-resorcylide (3) and 3-O-desmethyl-lasiodiplodin (4) show mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist and prostaglandin biosynthesis inhibitory activities in mammals.1 Pre-asperfuranone (6) is a biosynthetic intermediate of asperfuranone (7), an azaphilone that may find application as a synthetic precursor for lipoxygenase inhibitors to treat allergies, inflammation, and asthma.2,4
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis of BDLs and the azaphilone asperfuranone. Colored numerals: the number of ketide (C2) units (C–C bond in bold) incorporated by the hrPKS vs the nrPKS (“split” of the iPKS pair). Key: ACP, acyl carrier protein; AT, malonyl-CoA:ACP acyltransferase; CM, C-methyltransferase; DH, dehydratase; ER, enoylreductase; KR, ketoreductase; KS, ketosynthase; PT, product template; R, reductive release; SAT: starter unit:ACP transacylase; TE, thioesterase.
The biosynthesis of BDLs involves two sequentially acting iterative polyketide synthases (iPKSs).5 First, a highly reducing iPKS (hrPKS) produces a reduced linear polyketide that is transferred to a nonreducing iPKS (nrPKS) by the starter unit:ACP transacylase (SAT) domain, where it primes further chain elongation without reductions (Figure 1). Next, the nrPKS product template (PT) domain forms a resorcylic acid (connectivity: C2–C7) or a dihydroxyphenylacetic acid ring (C3–C8). Last, the nrPKS thioesterase (TE) domain releases the BDL scaffold as a macrolactone. Azaphilones feature a pyranoquinone or furanoquinone bicyclic core derived from an nrPKS-produced acyl benzaldehyde (ABH).2 For azaphilones such as 7, ABH biosynthesis on the nrPKS is primed by an hrPKS-derived reduced polyketide chain in a sequential biosynthetic scheme analogous to that of BDLs (Figure 1).6–8 Some other azaphilones use a convergent biosynthetic scheme, whereby the hrPKS product acylates a free pyranoquinone intermediate.9–11 Chimeric BDL scaffolds were previously generated by us using iPKS subunit shuffling among noncognate BDL synthase (BDLS) hrPKS and nrPKS partners.12 While domain replacements allowed the asperfuranone nrPKS to accept a single medium-chain fatty acid substrate offered either by the fatty acid synthase or another azaphilone hrPKS resident in Aspergillus nidulans, other attempts to force the enzyme to utilize alternative acyl substrates proved unproductive.13,14 As opposed to generating chimeric products based solely on the BDLs or alternatively on the azaphilones, in this work, we investigated whether we can bridge these two nonorthologous natural product groups by leveraging their common sequential biosynthetic logic and produce chimeric scaffolds that fuse orthogonal biosynthons from the two groups in a diversity-oriented combinatorial biosynthetic scheme.
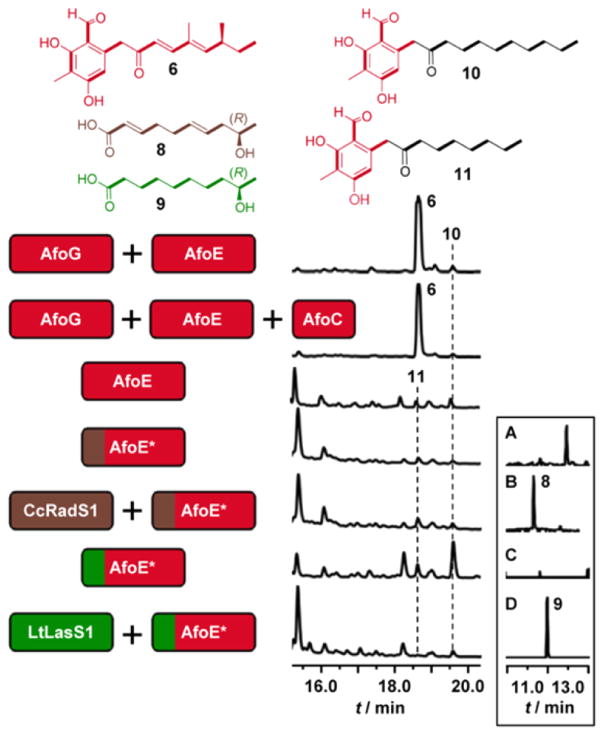
Co-expression of the A. nidulans asperfuranone hrPKS–nrPKS pair AfoG and AfoE8 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae BJ5464-NpgA15,16 led to the production of the expected ABH 6 (5.1 mg/L, Figure 2). ABH 6 was previously isolated from the azaphilone producer Penicillium multicolor17 and from engineered A. nidulans strains.4,7,8 S. cerevisiae strains expressing the AfoG–AfoE pair, or AfoE alone, also produced two ABHs primed by medium-chain fatty acids (10, 0.13 mg/L and 11, trace amounts, Figure 2). Indeed, 10 was previously isolated from A. nidulans upon exchange of SATAfoE (Supporting Information).13,14 Thus, similar to BDL nrPKSs,18,19 the azaphilone nrPKS AfoE also routinely engages in a metabolic cross-talk with the fatty acid biosynthesis of its host cell.
Figure 2.
Combinatorial biosynthesis with BDL hrPKSs and AfoE. HPLC profiles recorded at 300 nm and LCMS-selected ion chromatograms (inset: (A and B) m/z 207 [M + Na]+; (C and D) m/z 211 [M + Na]+) of S. cerevisiae BJ5464-NpgA expressing hrPKS-nrPKS pairs. Unlabeled peaks: yeast metabolites unrelated to the iPKS products. Split-color boxes (*): replacement of SATAfoE by SATBDLS to enforce coupling.
AfoC, a putative esterase/lipase, was speculated to transfer dimethyloctanoate from AfoG to AfoE (Figure 1).7 Similarly, the AfoC orthologue AzaC was suggested to off-load the AzaB hrPKS product during azanigerone biosynthesis in A. niger.9 In contrast, Cox et al. proposed that AfoC plays a role in the formation of the furan ring of 7.20,21 Considering the controversial role of AfoC, we coexpressed afoC with afoG and afoE in S. cerevisiae BJ5464-NpgA. However, the yield of 6 did not increase, nor were any additional metabolites produced (Figure 2). Thus, AfoC is neither necessary nor does it contribute to the formation of 6 in the heterologous system. This argues against the proposed role of AfoC in chain transfer,7 but it is in agreement with the direct transfer of acyl chains between collaborative iPKSs.6,22 Meanwhile, the absence of new metabolites was not surprising since furan ring formation requires a more advanced precursor than 6.
Pairing CcRadS1, AzResS1, LtLasS1, or AtCurS1 with AfoE yielded none of the expected hybrid ABHs even after SATAfoE was exchanged for the cognate SATBDLS (Figure 2). Failure to obtain the expected products with the AfoE–SATBDLS hybrids was not due to generally disabled nrPKSs, since these enzymes still produced the fatty acyl ABHs 10 (0.08–0.5 mg/L) and 11 (0.03–0.1 mg/L) when expressed in the host without hrPKS partners. Importantly, the fatty acyl chains that were readily utilized to generate 10 and 11 are of the same lengths as those generated by our BDL hrPKSs (CcRadS1 and LtLasS1: pentaketides as in 10; AzResS1 and AtCurS1: tetraketides as in 11). Remarkably, the only difference between the accepted decanoate for 10 and the rejected (9R)-hydroxydecanoate (9) from LtLasS1 is the presence of the Ω-1 hydroxyl group in the latter. Thus, AfoE refuses BDL acyl chains not simply because of their lengths but because they contain more oxidized carbon centers. We had previously shown that noncognate BDLS subunits readily generate hybrid polyketides in vivo if their collaboration is enforced by SAT exchanges.12 In contrast, these and other experiments13 show that the replacement of the SAT domain alone is not always sufficient to guarantee communication between noncognate iPKSs. For AfoE, and by extension other nrPKSs, the rest of the chassis retains a decisive role in substrate utilization.
Unexpectedly, pairing of CcRadS1 with AfoE–SATCcRadS2 and that of LtLasS1 with AfoE-SATLtLasS2 led to the production of the hrPKSs-derived pentaketides (8, 0.3 mg/L and 9, 3 mg/L, Figure 2). In contrast, the tetraketides of AzResS1 and AtCurS1 could not be detected upon pairing those enzymes with their cognate AfoE–SATBDLS. Compounds 8 and 9 were not detectable when CcRadS1 or LtLasS1 was expressed alone in the host. Pairing of these enzymes with the native AfoE or with their cognate BDL nrPKS partners similarly failed to afford these compounds.23 To the best of our knowledge, release and prominent accumulation of the reduced carboxylic acids from hrPKS subunits of collaborating iPKS systems has not been reported previously.
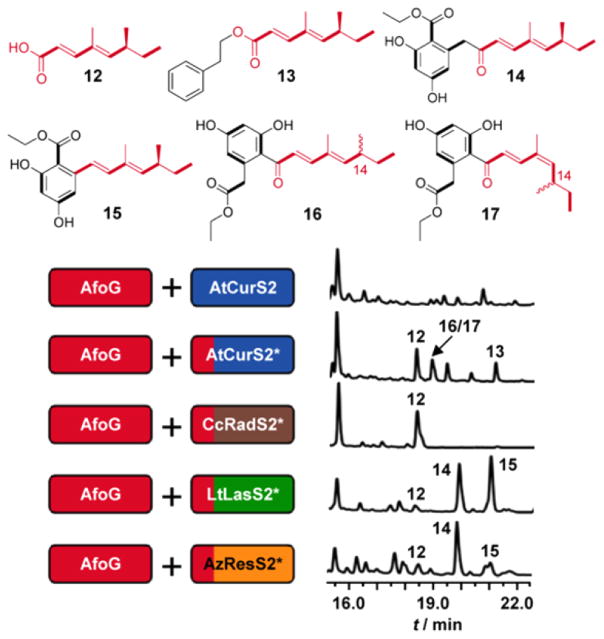
Pairing the asperfuranone hrPKS AfoG with CcRadS2, AzResS2, LtLasS2, or AtCurS2 led to no product formation. However, AfoG heterocombinations with chimeric BDL nrPKSs featuring SATAfoE proved to be more successful (Figure 3). First, all of these heterocombinations afforded the expected tetraketide product of AfoG as a free carboxylic acid in substantial amounts (12, 0.2–0.7 mg/L). The highest yielding strain, AfoG–AtCurS2–SATAfoE, also produced the phenethyl ester of 12 in good amounts (13, 0.3 mg/L). Compounds 12 and 13 were not detected in strains expressing either the native Afo pair or the AfoG–BDLS pairs without SATAfoE. Efficient production of 8, 9, and 12 suggests that these polyketides are off-loaded from the hrPKS by the cognate SAT domain, resulting in a SAT oxoester (SATCcRadS2) or thioester (SATLtLasS2, SATAfoE).22 In the absence of a productive interaction with the nrPKS KS domain, these esters afford the free carboxylic acids 8, 9, and 12 by hydrolysis. Release of 12 from SATAfoE (or from ACPAfoG) may also be facilitated by 2-phenylethanol, a phenylalanine catabolic product of the yeast host, leading to the formation of 13. In either case, the reductive release domain of AfoE is not expected to be involved, since RAfoE would produce aldehydes and not carboxylic acids.
Figure 3.
Combinatorial biosynthesis with AfoG and BDL nrPKSs. HPLC traces were recorded at 300 nm for S. cerevisiae BJ5464-NpgA cotransformed with hrPKS–nrPKS pairs. Unlabeled peaks: yeast metabolites unrelated to iPKS products. Split-color boxes (*): replacement of SATBDLS by SATAfoE.
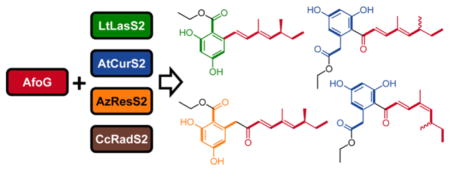
While 12 was the sole product of the AfoG–CcRadS2–SATAfoE pair, the strains with the three other AfoG–BDLS–SATAfoE heterocombinations produced the ethyl ester derivatives of the expected hybrid acyl benzenediol acids (ABAs, Figure 3). These ABA ethyl esters all feature the dimethyl tetraketide biosynthon of asperfuranone. This substrate was accepted by the BDLS nrPKSs, successfully extended with the appropriate number of ketide (C2) units, and cyclized in the PT-programmed register to produce the expected resorcylic or dihydroxyphenyl-acetic acid rings. Considering the substantial steric bulk introduced by the two methyl substituents in the branched acyl chain, this represents a remarkable flexibility on the part of the BDL nrPKSs. Nucleophilic attack by ethanol from yeast metabolism was the favored mechanism for the release of these ABAs, since hydrolysis of the TE oxoesters to produce free ABAs or pyrone formation with the C9 self-enol was not evident.19 Thus, the strain expressing the AfoG–LtLasS2–SATAfoE heterocombination produced 0.2 mg/L of the heptaketide 15. This ABA ethyl ester displays the expected 4 + 3 “split” (i.e., the AfoG-derived dimethyl tetraketide was extended by three additional ketide units by the nrPKS) and features the predicted resorcylic acyl ring (C2–C7 first ring connectivity established by PTLtLasS223,24). In addition to 15, the strain also produced the octaketide 14 (0.12 mg/L) with an apparent 4 + 4 split. Stuttering (incorporation of an extra ketide unit) by LtLasS2 was seen previously.12,23 Surprisingly, the strain expressing the AfoG–AzResS2–SATAfoE pair yielded the same two products: 14 (0.2 mg/L) with the expected 4 + 4 split and 15 (0.05 mg/L), with an apparent 4 + 3 split. While AzResS2 is programmed to incorporate four ketide units and may also stutter,23 production of the heptaketide 15 requires AzResS2 to “sputter” (incorporate one fewer ketide units). Sputtering has been observed with the zearalenone nrPKS18 as well as with a chimera of the asperfuranone nrPKS AfoE.13
Pairing AfoG with AtCurS2-SATAfoE provided the C12(13) cis/trans (1:0.7) isomeric and C14 racemic mixture of the ADA ethyl esters 16 and 17 (combined yield: 0.4 mg/L). We propose that the E-C12(13) double bond in (14S)-16 (originating as the E-C4(5) double bond of the AfoG-derived biosynthon4,8) may undergo spontaneous E/Z isomerization during fermentations and/or workup of the extracts to yield 16 and 17. Similar isomerizations were also detected with the chaetochiversins and paraphaeosporins in fermentations with Chaetomium chiversii and Paraphaeosphaeria quadriseptata.25 The absence of Z isomers of 6, 13, and 14 suggests a possible role that the phenolic OH at ortho and para positions to the acyl chain in 16 may play to facilitate the enolization of the conjugated C9 ketone, as a prelude toward E/Z isomerization at C12(13) with concomitant racemization at C14.
Diversity-oriented combinatorial biosynthesis with fungal iPKSs promises to expand the polyketide structural space toward unprecedented carbon skeletons that may be exploited for drug discovery. Previously, we showed that subunit shuffling among the orthologous BDLS family of collaborating iPKSs is a facile approach to generate such biosynthetic diversity.12 The work presented here attempted to extend this methodology toward nonorthologous collaborating iPKSs and thus merge two disparate polyketide families, the BDLs and the asperfuranones. The asperfuranone nrPKS AfoE turned out to be a fastidious catalyst accepting only straight-chain fatty acids by cross-talk with the host primary metabolism but rejecting polar acyl chains from four different BDL hrPKSs in spite of SAT exchanges. Accumulation of the hrPKS products as free acids in these hybrid systems indicated that SAT domain-catalyzed transfer of the hrPKS products is a necessary but not sufficient precondition of further chain extension by the nrPKS. This further confirms a proposed gating function practiced by the KS26 and/or other domains of the nrPKS chassis.19 Meanwhile, release of the hrPKS products also provides a scalable method to synthesize substituted medium chain fatty acids (such as 8, 9, and 12) in biological systems for use as synthetic building blocks. Gratifyingly, productive interactions emerged between the hrPKS AfoE and three of the four BDL nrPKSs, enforced with SAT exchanges. This led to the incorporation of unprecedented, orthogonal, branched acyl chains into BDL-related ARA and ADA ethyl esters new to nature. Both AfoE and the BDL nrPKSs retained their intrinsic biosynthetic programs and built their idiosyncratic biosynthons so that the chimeric system combined into novel unnatural products such as 14–17. The foreign substrate nevertheless led to compensatory adjustments in the overall size of the polyketide products14 by provoking stuttering or sputtering of the nrPKS. In conclusion, this work suggests that continued expansion of the polyketide space by iPKS engineering will require, beyond transplanted SAT domains, a better understanding of the multistep, sequential decision gating functions of nrPKSs, and an improved aptitude to manipulate the factors that determine the acceptability of orthogonal acyl chains transferred to hybrid nrPKSs for further chain extension.27
Supplementary Material
Figure S1. The chemical structures of compounds 6 and 8-17
Figure S2. The UV absorption spectra of compounds 6, 8, and 10-17
Figure S3. Key HMBC (→), 1H-1H-COSY (—) and 1D NOE (←→) correlations for compounds 8 and 13-17
Figure S4. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Pre-asperfuranone (6) in CD3COCD3
Figure S5. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Pre-asperfuranone (6) in CD3COCD3
Figure S6. DEPT135 spectrum (100 MHz) of Pre-asperfuranone (6) in CD3COCD3
Figure S7. HR ESI-MS of Compound 8
Figure S8. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S9. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S10. 1H-1H COSY Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S11. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S12. HMBC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S13. HR ESI-MS of Compound 9
Figure S14. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 9 in CDCl3
Figure S15. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 9 in CDCl3.
Figure S16. HR ESI-MS of Compound 10.
Figure S17. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 10 in CDCl3.
Figure S18. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 10 in CDCl3.
Figure S19. HR ESI-MS of Compound 11.
Figure S20. HR ESI-MS of Compound 12.
Figure S21. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 12 in CDCl3.
Figure S22. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 12 in CDCl3
Figure S23. HR ESI-MS of Compound 13.
Figure S24. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S25. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S26. 1H-1H COSY Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S27. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S28. HMBC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S29. HR ESI-MS of Compound 14.
Figure S30. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S31. 13C NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S32. 1H-1H COSY Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S33. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S34. Key HMBC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S35. HR ESI-MS of Compound 15.
Figure S36. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S37. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S38. 1H-1H COSY Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S39. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S40. Key HMBC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S41. HR ESI-MS of Compounds 16/17.
Figure S42. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compounds 16/17 in CDCl3.
Figure S43. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compounds 16/17 in CDCl3.
Figure S44. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compounds 16/17 in CDCl3.
Figure S45. 1D NOESY Spectra (400 MHz) of Compounds 16/17 in CDCl3.
Figure S46. Comparison of the chemical structures of compounds 10, 1815 and 1915
Figure S47. Proposed mechanism for E/Z isomerization with concomitant racemization to form 16 and 17
The E/Z isomerization at C12(13) with concomitant racemization at C14 of natural (14S)-16 is proposed to involve a plausible keto-enol-type tautomerization and cis-trans isomerization during fermentations and/or workup of the resulting extracts to yield an inseparable mixture of (14R/S)-16 and (14R/S)-17.
Table S1. PCR primers used in this study
Table S2. 1H NMR (400 MHz) and 13C NMR (100 MHz) data of compounds 8, 13, and 14 (δ in ppm, J in Hz).
Table S3. 1H NMR (400 MHz) and 13C NMR (100 MHz) data of compounds 15, 16, and 17 (δ in ppm, J in Hz).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (MCB-0948751 to I.M.), the National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB755700 to M.L. and Y.X), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570093 to Y.X), the Jiangsu Overseas Research and Training Program (to Y.L), and the National Cancer Institute (R01CA090265 to A.A.L.G.). We are grateful to Lida Han (Biotechnology Research Institute, Beijing) for the MS/MS spectra and accurate mass measurements.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
The Supporting Information is available free of charge on the ACS Publications website at DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b00110.
Complete description of methods and additional results; tables and figures, including structure elucidation for compounds 6 and 8–17; proposed mechanism for isomerization and racemization of 16 and 17 (PDF)
References
- 1.Shen W, Mao H, Huang Q, Dong J. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;97:747. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.11.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gao JM, Yang SX, Qin JC. Chem Rev. 2013;113:4755. doi: 10.1021/cr300402y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Winssinger N, Fontaine JG, Barluenga S. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9:1419. doi: 10.2174/156802609789895665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Somoza AD, Lee KH, Chiang YM, Oakley BR, Wang CC. Org Lett. 2012;14:972. doi: 10.1021/ol203094k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chooi YH, Tang Y. J Org Chem. 2012;77:9933. doi: 10.1021/jo301592k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Winter JM, Cascio D, Dietrich D, Sato M, Watanabe K, Sawaya MR, Vederas JC, Tang Y. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:9885. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b04520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chiang YM, Oakley CE, Ahuja M, Entwistle R, Schultz A, Chang SL, Sung CT, Wang CC, Oakley BR. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:7720. doi: 10.1021/ja401945a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chiang YM, Szewczyk E, Davidson AD, Keller N, Oakley BR, Wang CC. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:2965. doi: 10.1021/ja8088185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zabala AO, Xu W, Chooi YH, Tang Y. Chem Biol. 2012;19:1049. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Winter JM, Sato M, Sugimoto S, Chiou G, Garg NK, Tang Y, Watanabe K. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:17900. doi: 10.1021/ja3090498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Balakrishnan B, Karki S, Chiu SH, Kim HJ, Suh JW, Nam B, Yoon YM, Chen CC, Kwon HJ. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;97:6337. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4745-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Xu Y, Zhou T, Zhang S, Espinosa-Artiles P, Wang L, Zhang W, Lin M, Gunatilaka AAL, Zhan J, Molnár I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:12354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406999111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liu T, Sanchez JF, Chiang YM, Oakley BR, Wang CC. Org Lett. 2014;16:1676. doi: 10.1021/ol5003384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu T, Chiang YM, Somoza AD, Oakley BR, Wang CC. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:13314. doi: 10.1021/ja205780g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhou H, Qiao K, Gao Z, Vederas JC, Tang Y. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:41412. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.183574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ma SM, Li JW, Choi JW, Zhou H, Lee KK, Moorthie VA, Xie X, Kealey JT, Da Silva NA, Vederas JC, Tang Y. Science. 2009;326:589. doi: 10.1126/science.1175602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Matsuzaki K, Tahara H, Inokoshi J, Tanaka H, Masuma R, Omura S. J Antibiot. 1998;51:1004. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.51.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhou H, Zhan J, Watanabe K, Xie X, Tang Y. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:6249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800657105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Xu Y, Zhou T, Zhang S, Xuan LJ, Zhan J, Molnár I. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:10783. doi: 10.1021/ja4041362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.al Fahad A, Abood A, Simpson TJ, Cox RJ. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2014;53:7519. doi: 10.1002/anie.201403450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Davison J, al Fahad A, Cai M, Song Z, Yehia SY, Lazarus CM, Bailey AM, Simpson TJ, Cox RJ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:7642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201469109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Foulke-Abel J, Townsend CA. ChemBioChem. 2012;13:1880. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201200267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xu Y, Zhou T, Espinosa-Artiles P, Tang Y, Zhan J, Molnár I. ACS Chem Biol. 2014;9:1119. doi: 10.1021/cb500043g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Xu Y, Zhou T, Zhou Z, Su S, Roberts SA, Montfort WR, Zeng J, Chen M, Zhang W, Zhan J, Molnár I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:5398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301201110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wijeratne EMK, Paranagama PA, Gunatilaka AAL. Tetrahedron. 2006;62:8439. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vagstad AL, Bumpus SB, Belecki K, Kelleher NL, Townsend CA. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:6865. doi: 10.1021/ja3016389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Huitt-Roehl CR, Hill EA, Adams MM, Vagstad AL, Li JW, Townsend CA. ACS Chem Biol. 2015;10:1443. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. The chemical structures of compounds 6 and 8-17
Figure S2. The UV absorption spectra of compounds 6, 8, and 10-17
Figure S3. Key HMBC (→), 1H-1H-COSY (—) and 1D NOE (←→) correlations for compounds 8 and 13-17
Figure S4. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Pre-asperfuranone (6) in CD3COCD3
Figure S5. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Pre-asperfuranone (6) in CD3COCD3
Figure S6. DEPT135 spectrum (100 MHz) of Pre-asperfuranone (6) in CD3COCD3
Figure S7. HR ESI-MS of Compound 8
Figure S8. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S9. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S10. 1H-1H COSY Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S11. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S12. HMBC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 8 in CD3OD
Figure S13. HR ESI-MS of Compound 9
Figure S14. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 9 in CDCl3
Figure S15. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 9 in CDCl3.
Figure S16. HR ESI-MS of Compound 10.
Figure S17. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 10 in CDCl3.
Figure S18. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 10 in CDCl3.
Figure S19. HR ESI-MS of Compound 11.
Figure S20. HR ESI-MS of Compound 12.
Figure S21. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 12 in CDCl3.
Figure S22. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 12 in CDCl3
Figure S23. HR ESI-MS of Compound 13.
Figure S24. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S25. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S26. 1H-1H COSY Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S27. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S28. HMBC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 13 in CDCl3.
Figure S29. HR ESI-MS of Compound 14.
Figure S30. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S31. 13C NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S32. 1H-1H COSY Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S33. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S34. Key HMBC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 14 in CDCl3.
Figure S35. HR ESI-MS of Compound 15.
Figure S36. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S37. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S38. 1H-1H COSY Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S39. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S40. Key HMBC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compound 15 in CD3OD.
Figure S41. HR ESI-MS of Compounds 16/17.
Figure S42. 1H NMR Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compounds 16/17 in CDCl3.
Figure S43. 13C NMR Spectrum (100 MHz) of Compounds 16/17 in CDCl3.
Figure S44. HSQC Spectrum (400 MHz) of Compounds 16/17 in CDCl3.
Figure S45. 1D NOESY Spectra (400 MHz) of Compounds 16/17 in CDCl3.
Figure S46. Comparison of the chemical structures of compounds 10, 1815 and 1915
Figure S47. Proposed mechanism for E/Z isomerization with concomitant racemization to form 16 and 17
The E/Z isomerization at C12(13) with concomitant racemization at C14 of natural (14S)-16 is proposed to involve a plausible keto-enol-type tautomerization and cis-trans isomerization during fermentations and/or workup of the resulting extracts to yield an inseparable mixture of (14R/S)-16 and (14R/S)-17.
Table S1. PCR primers used in this study
Table S2. 1H NMR (400 MHz) and 13C NMR (100 MHz) data of compounds 8, 13, and 14 (δ in ppm, J in Hz).
Table S3. 1H NMR (400 MHz) and 13C NMR (100 MHz) data of compounds 15, 16, and 17 (δ in ppm, J in Hz).