Abstract
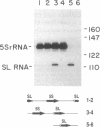
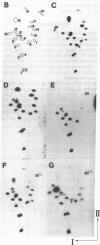
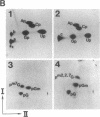
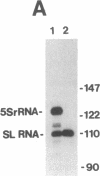
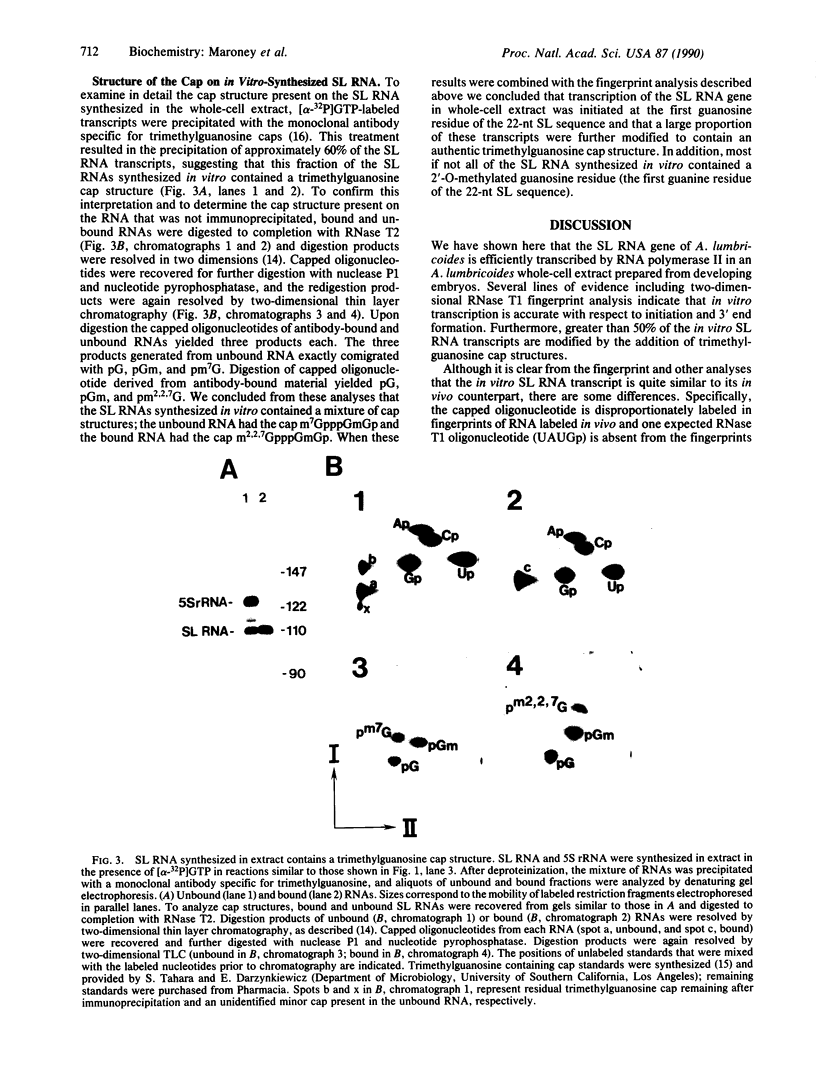
Maturation of a fraction of mRNAs in nematodes involves the acquisition of a common 5' terminal spliced leader sequence derived from a nonpolyadenylylated spliced leader RNA by trans splicing. We have developed a cell-free system prepared from Ascaris lumbricoides embryos that accurately and efficiently synthesized the spliced leader RNA of A. lumbricoides. Transcription of the spliced leader RNA was catalyzed by RNA polymerase II, and the majority of the spliced leader RNAs synthesized in vitro possessed a trimethylguanosine cap structure identical to that found on in vivo-synthesized spliced leader RNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenthal T., Thomas J. Cis and trans mRNA splicing in C. elegans. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzik J. P., Van Doren K., Hirsh D., Steitz J. A. Trans splicing involves a novel form of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):559–562. doi: 10.1038/335559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz E., Stepinski J., Ekiel I., Jin Y., Haber D., Sijuwade T., Tahara S. M. Beta-globin mRNAs capped with m7G, m2.7(2)G or m2.2.7(3)G differ in intrinsic translation efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8953–8962. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Maroney P. A., Branch A., Benenfield B. J., Robertson H. D., Nilsen T. W. Accurate processing of human pre-rRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4422–4431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R. Pre-mRNA splicing by complementation with purified human U1, U2, U4/U6 and U5 snRNPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9415–9429. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Hirsh D. A trans-spliced leader sequence on actin mRNA in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90613-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. In vitro synthesis of vertebrate U1 snRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):287–292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroney P. A., Hannon G. J., Nilsen T. W. Accurate and efficient RNA polymerase III transcription in a cell-free extract prepared from Ascaris suum embryos. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jul;35(3):277–283. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. Cap trimethylation of U snRNA is cytoplasmic and dependent on U snRNP protein binding. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Price D. H., Marzluff W. F. Synthesis of U1 RNA in a DNA-dependent system from sea urchin embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3674–3678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Shambaugh J., Denker J., Chubb G., Faser C., Putnam L., Bennett K. Characterization and expression of a spliced leader RNA in the parasitic nematode Ascaris lumbricoides var. suum. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3543–3547. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W. Trans-splicing in nematodes. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Nov;69(4):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura S. Minor components in transfer RNA: their characterization, location, and function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1972;12:49–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C., Busslinger M. In vivo and in vitro expression of U7 snRNA genes: cis- and trans-acting elements required for RNA polymerase II-directed transcription. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):539–549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takacs A. M., Denker J. A., Perrine K. G., Maroney P. A., Nilsen T. W. A 22-nucleotide spliced leader sequence in the human parasitic nematode Brugia malayi is identical to the trans-spliced leader exon in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7932–7936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. D., Conrad R. C., Blumenthal T. The C. elegans trans-spliced leader RNA is bound to Sm and has a trimethylguanosine cap. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):533–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren K., Hirsh D. Trans-spliced leader RNA exists as small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):556–559. doi: 10.1038/335556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volckaert G., Fiers W. A micromethod for base analysis of 32P-labeled oligoribonulcleotides. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90530-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]