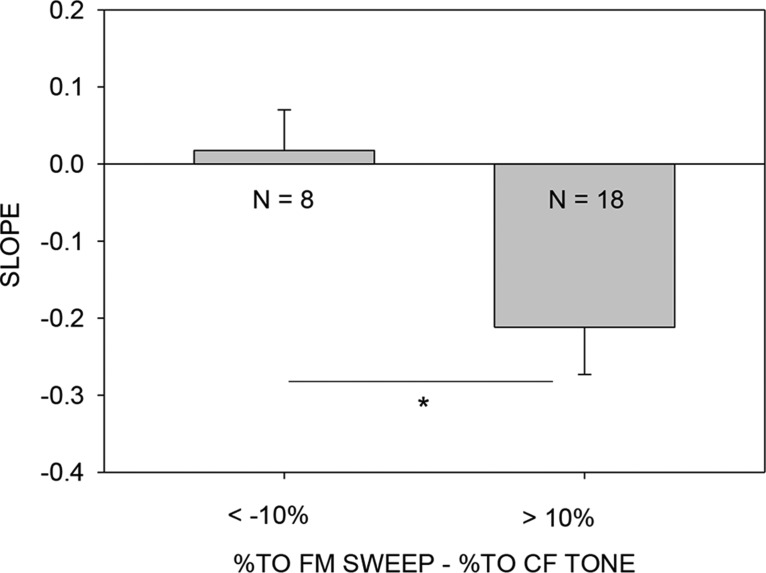
Figure 11.
Level-dependent changes in the timing of high-frequency inhibition enhance level selectivity for FM sweeps. Neurons that were more level selective for downward FM sweeps (%TO difference > +10%) than for CF tones had a significantly more negative slope (e.g., Fig. 10) of the regression line between 50% arrival time of inhibition and two-tone level compared with neurons that were more level selective for CF tones than sweeps (%TO difference < -10%) (t test, p = 0.029).