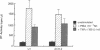Abstract
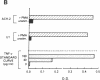
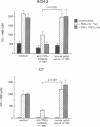
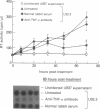
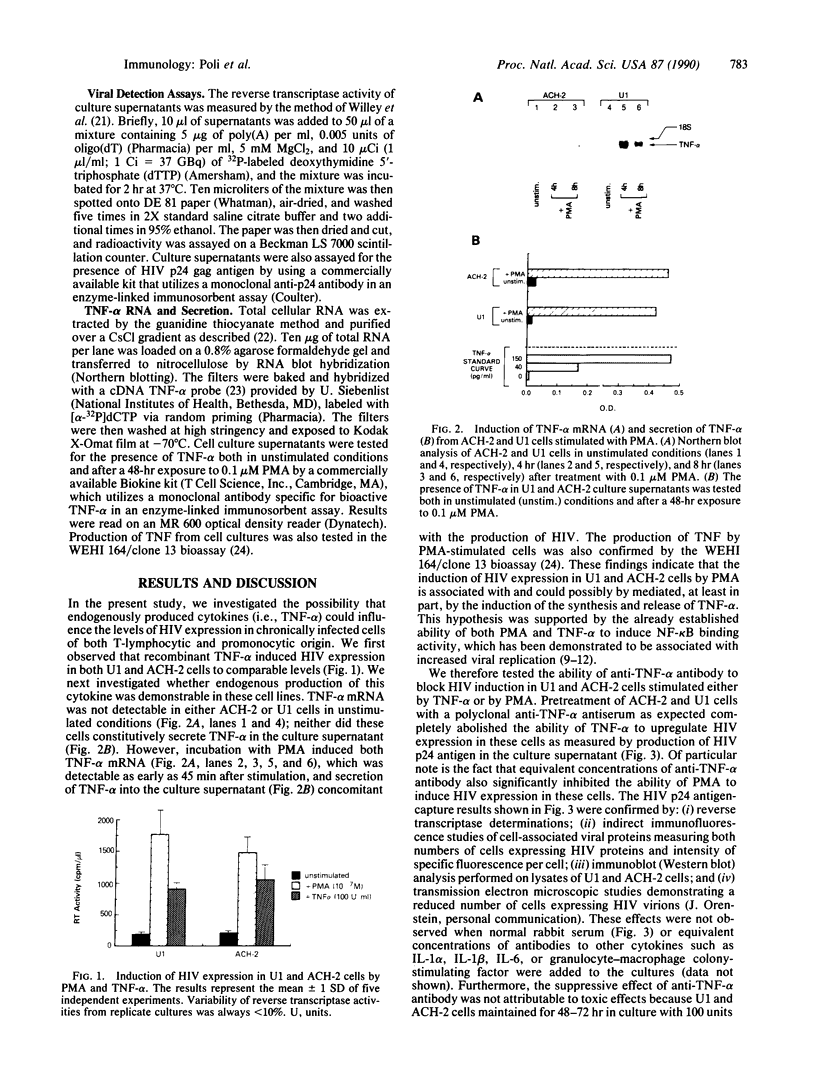
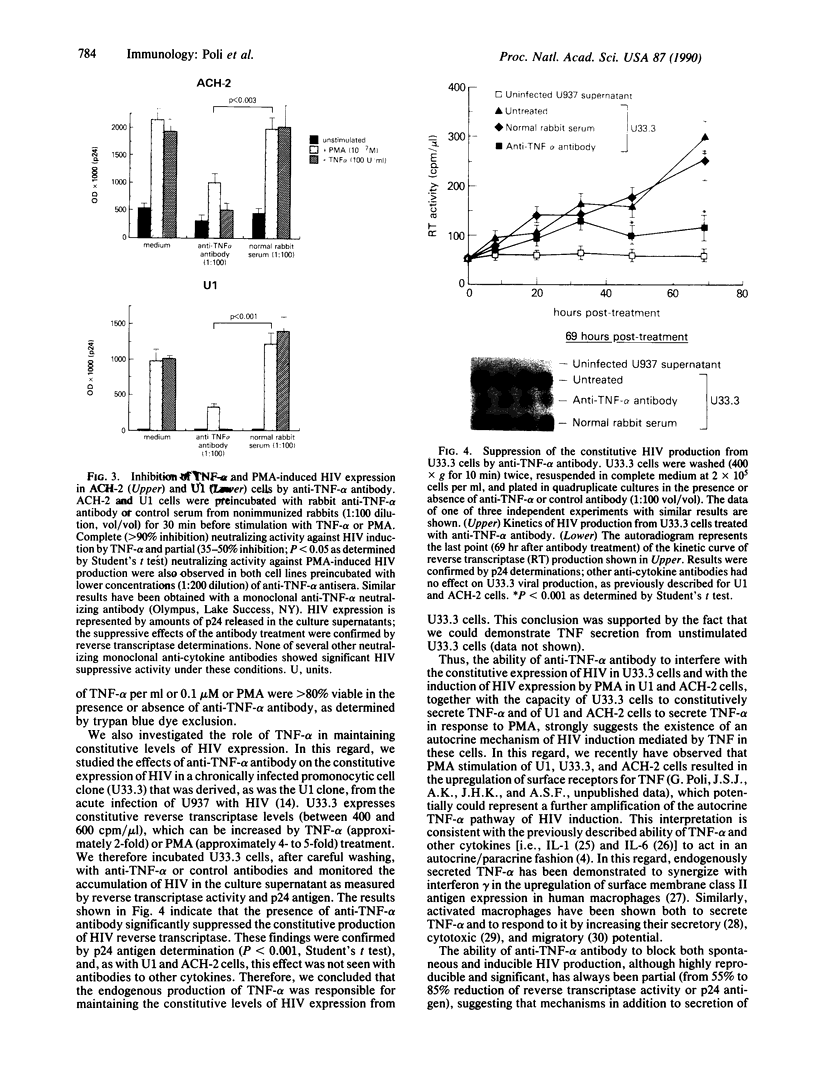
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) is an immunoregulatory cytokine capable of inducing viral expression in cells chronically infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), such as the promonocytic line U1 and the T-lymphocytic line ACH-2. In the present study, we demonstrate an autocrine mechanism of TNF-alpha-mediated HIV induction. Stimulation of U1 and ACH-2 cells with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) resulted in the induction of TNF-alpha mRNA and the secretion of TNF-alpha. Of note is the fact that anti-TNF-alpha antibodies significantly suppressed the expression of HIV in PMA-stimulated U1 and ACH-2 cells. Furthermore, anti-TNF-alpha antibodies also suppressed both the constitutive and inducible levels of viral expression in the chronically infected promonocytic clone U33.3. This study illustrates the interrelationship between the regulation of HIV expression and normal immunoregulatory mechanisms in that virus expression, both constitutive and induced, can be modulated by an autocrine pathway involving TNF-alpha, a cytokine involved in the complex network of regulation of the normal human immune response.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Mogensen S. C., Vuillier F., Fiers W., Virelizier J. L. Autocrine secretion of tumor necrosis factor under the influence of interferon-gamma amplifies HLA-DR gene induction in human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6087–6091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachwich P. R., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates interleukin-1 and prostaglandin E2 production in resting macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouse K. A., Powell D., Washington I., Poli G., Strebel K., Farrar W., Barstad P., Kovacs J., Fauci A. S., Folks T. M. Monokine regulation of human immunodeficiency virus-1 expression in a chronically infected human T cell clone. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino F., Rubartelli A., Aldinucci D., Sitia R., Torcia M., Shaw A., Di Guglielmo R. Interleukin 1 as an autocrine growth factor for acute myeloid leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2369–2373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. W., Jaffe H. W., Hardy A. M., Morgan W. M., Selik R. M., Dondero T. J. Epidemiology of HIV infection and AIDS in the United States. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):610–616. doi: 10.1126/science.3340847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):617–622. doi: 10.1126/science.3277274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Clouse K. A., Justement J., Rabson A., Duh E., Kehrl J. H., Fauci A. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces expression of human immunodeficiency virus in a chronically infected T-cell clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2365–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Justement J., Kinter A., Dinarello C. A., Fauci A. S. Cytokine-induced expression of HIV-1 in a chronically infected promonocyte cell line. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):800–802. doi: 10.1126/science.3313729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Justement J., Kinter A., Schnittman S., Orenstein J., Poli G., Fauci A. S. Characterization of a promonocyte clone chronically infected with HIV and inducible by 13-phorbol-12-myristate acetate. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1117–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Böhnlein E., Ballard D. W. HIV-1, HTLV-1 and normal T-cell growth: transcriptional strategies and surprises. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Leung K., Folks T. M., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Activation of HIV gene expression during monocyte differentiation by induction of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):70–73. doi: 10.1038/339070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Alvarez-Mon M., Delsing G. A., Fauci A. S. Lymphotoxin is an important T cell-derived growth factor for human B cells. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1144–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.3500512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Miller A., Fauci A. S. Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha on mitogen-activated human B cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):786–791. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., Henriksen-DeStefano D., May L. T., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. Induction of beta 2-interferon by tumor necrosis factor: a homeostatic mechanism in the control of cell proliferation. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Yoshiyama H., Hamamoto Y., Yamamoto N., Soma G., Mizuno D., Kobayashi N. Enhancement of HIV replication and giant cell formation by tumor necrosis factor. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Apr;5(2):139–146. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming W. J., Bersani L., Mantovani A. Tumor necrosis factor is chemotactic for monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1469–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Smith D., Jarrett-Nedwin J., Pennica D., Goeddel D. V., Gray P. W. Human lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor genes: structure, homology and chromosomal localization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6361–6373. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Matsuyama T., Mori S., Hamamoto Y., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N., Josephs S. F., Wong-Staal F., Shimotohno K. Augmentation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression by tumor necrosis factor alpha. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Apr;5(2):131–138. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R., Epstein L. B. Tumour necrosis factor as immunomodulator and mediator of monocyte cytotoxicity induced by itself, gamma-interferon and interleukin-1. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):86–89. doi: 10.1038/323086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Orenstein J. M., Kinter A., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S. Interferon-alpha but not AZT suppresses HIV expression in chronically infected cell lines. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):575–577. doi: 10.1126/science.2470148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranki A., Valle S. L., Krohn M., Antonen J., Allain J. P., Leuther M., Franchini G., Krohn K. Long latency precedes overt seroconversion in sexually transmitted human-immunodeficiency-virus infection. Lancet. 1987 Sep 12;2(8559):589–593. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92985-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. M., Sorrell S. J., Lange M., Grieco M. H. Tumor necrosis factor and HIV P24 antigen levels in serum of HIV-infected populations. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(5):436–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux-Lombard P., Modoux C., Cruchaud A., Dayer J. M. Purified blood monocytes from HIV 1-infected patients produce high levels of TNF alpha and IL-1. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Mar;50(3):374–384. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Smith D. H., Lasky L. A., Theodore T. S., Earl P. L., Moss B., Capon D. J., Martin M. A. In vitro mutagenesis identifies a region within the envelope gene of the human immunodeficiency virus that is critical for infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):139–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.139-147.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipfel P. F., Irving S. G., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Complexity of the primary genetic response to mitogenic activation of human T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1041–1048. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]