Abstract
Background
Experiencing a false positive (FP) screening mammogram is economically, physically and emotionally burdensome which may affect future screening behavior, by delaying the next scheduled mammogram or by avoiding screening altogether. We sought to examine the impact of a FP screening mammogram on the subsequent screening mammography behavior.
Methods
Delay in obtaining subsequent screening was defined as any mammogram performed more than 12 months from index mammogram. The Kaplan-Meier (product limit) estimator and Cox proportional hazards model were used to estimate the unadjusted delay and the hazard ratio of delay of the subsequent screening mammogram within the next 36 months from the index mammogram date.
Results
650,232 true negative (TN) and 90,918 FP mammograms from 261,767 women were included. The likelihood of a subsequent mammogram was higher in women experiencing a TN result than women experiencing a FP result (85.0% vs 77.9%, P <0.001). The median delay in returning to screening was higher for FP vs TN (13 months vs 3 months, P <0.001). Women with TN result were 36% more likely to return to screening in the next 36 months compared to women with a FP result HR=1.36 (95% CI: 1.35–1.37). Experiencing a FP mammogram increases the risk of late stage at diagnosis compared to prior TN mammogram (P<0.001).
Conclusions
Women with a FP mammogram were more likely to delay their subsequent screening compared to women with a TN mammogram.
Impact
A prior FP experience may subsequently increase the 4-year cumulative risk of late stage at diagnosis.
Introduction
Screening mammography is an established routine public health procedure for the early detection of breast cancer and has been shown to reduce mortality from the disease (1). Along with the benefits of early detection, mammography screening is also associated with false positive (FP) results that lead to unnecessary additional imaging and biopsy procedures as well as associated financial costs, lost time and psychological and physical morbidity (2–4). FP rates have been estimated to be as high as 10% of screening mammograms (5) and roughly 50% of women who screen annually for 10 years can expect at least one FP mammogram finding of which 7–17% will require biopsy (6,7). The FP screening mammogram issue is part of an ongoing debate regarding the extent to which the risk of mammography screening might outweigh the benefits in certain women (8,9). Therefore, the most recent guidelines set forth by the United States Preventative Task Force (USPSTF) advised against routine screening in women aged 40–49 years of age and women 75 years or older (10).
Furthermore, a FP mammogram could lead women to alter their future screening behavior, either by delaying the next scheduled mammogram or foregoing the exam altogether. Studies that have examined the potential impact of a FP mammogram on subsequent adherence to screening mammography recommendations have yielded inconsistent findings. Several studies found that rescreening rates were actually higher among women who experienced a FP as opposed to a TN (11,12) while other studies found no difference in re-screening rates based on screening mammography outcome (13–16). Still other reports documented lower re-screening rates for women experiencing FP compared with those with TN mammograms (17–20). A 2007 meta-analysis which pooled data from the above studies found that in Europe and Canada, women who experienced a FP screening mammogram were less likely to return for their next screen compared to women with TN screen finding. Conversely, women in the United States were associated with greater subsequent screening mammography adherence after experiencing a FP (21). The primary study objective was to examine the impact of a FP screening mammogram on the receipt of subsequent screening mammography among a racially diverse population in a network of mammography centers within a large health care organization. The secondary objective was to determine whether the experience of a FP result at index mammogram increases the risk of subsequent late stage disease for those women subsequently diagnosed with breast cancer.
Materials and Methods
Mammography screening data on women were obtained from a large Health Care Organization with multiple facilities in the greater metropolitan Chicago area. Facilities within this healthcare organization used PenRad to collect radiology information and patient characteristics (22). PenRad was first introduced in 2001 and was implemented at all facilities by 2005. Breast cancer incidence data were obtained from the Illinois State Cancer Registry (ISCR) (23) which collects information on all incident cancer cases in the state of Illinois.
The radiology data set included patient-level data on demographic characteristics and risk factors, and exam-level data on procedure types and results that were performed between January 1st, 2001 and December 31st, 2014. Each mammogram was interpreted by the reading radiologist and was given a score using the American College of Radiology (ACR) classification system known as Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BIRADS). BIRADS assessment for screening and diagnostic mammography ranges from 0 to 5 such that 0 = need additional imaging evaluation, 1 = negative finding, 2 = benign finding, 3 = probably benign finding, 4 = suspicious abnormality, and 5 = finding highly suggestive of malignancy.
Family history was self-reported and was defined as none (no first or second degree relatives affected), weak (only second degree relatives affected), moderate (one first degree relatives over age 50 affected), and strong (multiple first degree relatives affected or one under age 50). Age was determined by taking the difference between date of index mammogram and date of birth. Race/ethnicity was self-reported as Non-Hispanic (nH) White, nH-Black, Hispanic, other and unknown. Personal history of prior biopsy was defined as present if a prior biopsy existed in the radiology dataset or if it was self-reported. Time since last mammogram was defined as 9–18 months, 19–30 months, >30 months and no prior mammogram based on the radiology dataset. Breast density was defined following the ACR classification as composed almost entirely of fat, scattered fibroglandular densities, heterogeneously dense and extremely dense.
Women with a prior history of breast cancer or who developed breast cancer anytime during the study period were excluded from these analyses as were women with a history of breast reduction, breast implants and breast reconstruction or mastectomy. Screening mammograms which were preceded by any radiologic exam in the prior 9 months were also excluded. In the case of multiple exams on the same day, only the first exam in the sequence was used in the analysis.
A linkage of 755,567 screening mammograms completed between 2001 and 2010 to ISCR patients diagnosed with breast cancer for diagnosis years 2001–2011 was performed. To allow 12 months of follow up for cancer diagnosis, we restricted our analytic dataset to include bilateral screening mammograms that were performed January 1, 2001 and December 31, 2010. Based on the mammograms interpretation and cancer status within 12 months of the screen, screening mammograms were defined as true positive (TP), true negative (TN), FP and false negative (FN) screens. For these analyses, we compared the experiences of women with FP and TN mammograms. The unit of analysis was the screening mammogram.
A TN mammogram was defined as any mammogram with BIRADS (1,2,3) and that cancer was not detected in the subsequent 12 months from date of screening mammogram. Whereas, a FP mammogram was defined as any mammogram with BIRADS (0,4,5) and that cancer was not detected in the subsequent 12 months from date of screening mammogram. The burden of FP was defined as the number of additional imaging after a FP mammogram and morbidity was defined as the receipt of biopsy after a FP mammogram. Women with a TN mammogram were assumed to have no additional work up during the follow up period.
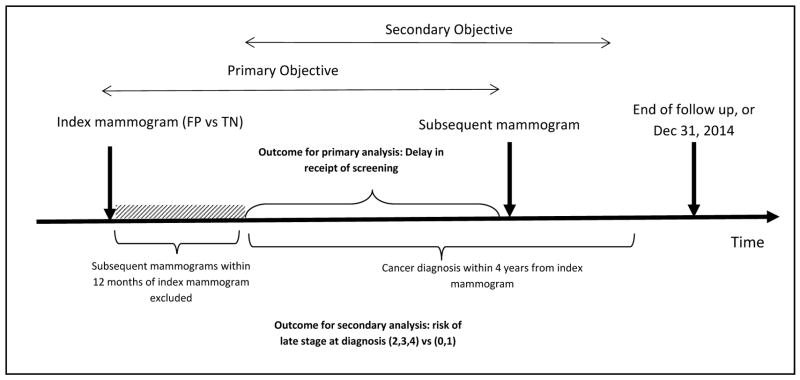
Because the recommended interval for routine screening is at least 12 months, we defined the index date (T=0) as 365 days after the index screening date. Therefore, any index screening mammograms that were followed with a subsequent screening mammogram prior to 12 months were excluded (N= 14,417 1.9%). Follow up period was defined as the number of months between the index date and the date of the subsequent screening mammogram or 36 months, whichever came first. Women who did not return to screening at our network were considered right censored and their follow up time was estimated as the difference between index date and December 31, 2014. This date was used because our data included all screening mammograms that were performed on or before December 31, 2014. The dependent variable for the primary analysis was the number of months (T) after index date for both TN and FP mammograms (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Primary and secondary analyses design overview FP vs TN.
The first arrow represents the index mammogram (true negative and false positive mammograms only). The shaded area represents the first 12 months after index mammogram and index date (T=0) was defined at the end of the shaded area. Mammograms that were followed by a screening mammogram within 12 months were excluded. The second arrow represents the subsequent mammogram after index mammogram. For the secondary analyses the cumulative risk of late stage at diagnosis was estimated over a 4 years period following the index mammogram.
In an additional analysis we adjusted the follow up time to account for the time required to resolve a positive mammogram by setting the index date to be the date of the last diagnostic procedure related to the index mammogram on file.
For the primary objective, we excluded exams from women who were diagnosed with breast cancer at any point during our study period. For the secondary analysis in which we examined the impact of FP on stage at diagnosis, we excluded screens that were followed with a breast cancer diagnosis in the subsequent 12 months as well as cancers that were diagnosed more than 48 months from screening mammogram. The dependent variable was late stage at diagnosis which was defined according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) and categorized as late stage (stage 2, 3, 4) vs. early stage at diagnosis (stage 0 or 1).
Patient characteristics by mammogram result (TN vs FP) and by stage at diagnosis were tabulated. The Kaplan-Meier (product limit) estimator was used to estimate the overall unadjusted delay in return to screening by mammogram result (TN vs FP), and log-rank tests were used to compare the differences between the two curves. Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the hazard ratio for delay in the receipt of subsequent screening mammogram within the next 36 months from the index mammogram date. Women who did not return to screening at this network were right censored as well as women who returned to screening after 36 months from index mammogram date. In addition to mammogram result (TN vs FP), the model included variables for age, race/ethnicity, family history of breast cancer, mammographic breast density, parity, prior history of biopsy, time since last screening mammogram, calendar year, availability of comparison film and facility. Stratum-specific hazard ratios were generated using the same model as above with the addition of each individual product term between the index mammogram result and the variable of interest. Similar results were observed when using the proportional hazards model with an independent working assumption and robust sandwich covariance matrix estimate to account for the intracluster dependence. Therefore, the proportional hazards model without clustering was used.
In addition to multivariable models described above, a propensity score matching technique was used to match on the probability of a FP result. Logistic regression modeling was used to predict the probability of being FP vs TN adjusting for decade of age, race/ethnicity, family history of breast cancer, mammographic breast density, parity, prior history of biopsy, time since last screening mammogram, calendar year, availability of comparison film at interpretation, facility and any possible interaction terms that were significant at an alpha 0.05 level. Off support probabilities were excluded and greedy matching algorithm without replacement was used to match 1–1 TN and FP mammograms (24). The matched dataset was then analyzed using Kaplan-Meier estimator to estimate the probability of returning to screening by index mammogram result. Proportional hazards modeling was used to estimate the risk of not returning to recommended screening by index mammogram result.
To estimate the probability of late stage at diagnosis following a FP or TN screening mammogram, logistic regression with Generalized Estimating Equations (GEE) was utilized to account for clustering of screening mammograms within patients. All analyses were conducted using SAS (version 9.4; SAS Institute Inc, Cary, North Carolina) All p-values are two-sided.
Results
A total of 741,150 screening mammograms (FP=90,918, TN=650,232) from 261,767 women were included in this study. The overall FP rate was 12.3%. Women experiencing a FP result were less likely to have a subsequent screen in the database than women experiencing a TN result (22.1% vs 15.0% P-value <0.001). Women who did not return for screening at these facilities may have forgone screening altogether (a substantively important result of this study) or may have sought subsequent screening elsewhere (may have been lost to follow-up). Women with FP mammograms were younger, premenopausal and were more likely to be experiencing their first mammogram screening. Also, they were more likely to be nH-Black, have denser breasts and were less likely to have a comparison film available at interpretation (Table 1).
Table 1.
Patient characteristics of 741,150 screening mammograms by mammogram result for the period 2001–2010
| TN
|
FP
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | |
| Loss to Follow up1 | ||||
| Yes | 97,380 | 15 | 20,073 | 22.1 |
| No | 552,852 | 85 | 70,845 | 77.9 |
| Age | ||||
| <40 | 21,724 | 3.34 | 5,365 | 5.9 |
| 40–49 | 187,897 | 28.9 | 33,261 | 36.58 |
| 50–59 | 193,036 | 29.69 | 26,058 | 28.66 |
| 60–69 | 131,839 | 20.28 | 15,069 | 16.57 |
| 70–79 | 87,294 | 13.43 | 8,633 | 9.5 |
| 80+ | 28,442 | 4.37 | 2,532 | 2.78 |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| nH White | 362,647 | 55.77 | 49,319 | 54.25 |
| nH Black | 151,171 | 23.25 | 25,121 | 27.63 |
| Other | 136,414 | 20.98 | 16,478 | 18.13 |
| Breast Density2 | ||||
| Fatty | 52,823 | 8.12 | 5,479 | 6.03 |
| Scattered | 266,089 | 40.92 | 31,747 | 34.92 |
| Heterogeneous | 276,742 | 42.56 | 45,560 | 50.11 |
| Dense | 54,512 | 8.38 | 7,961 | 8.76 |
| Family history | ||||
| None | 440,106 | 67.68 | 60,593 | 66.65 |
| Weak | 101,063 | 15.54 | 14,587 | 16.04 |
| Moderate | 77,450 | 11.91 | 10,715 | 11.79 |
| Strong | 31,613 | 4.86 | 5,023 | 5.52 |
| Parity | ||||
| Nulliparous | 79,395 | 12.21 | 11,151 | 12.26 |
| Parous | 516,967 | 79.51 | 69,331 | 76.26 |
| Missing | 53,870 | 8.3 | 10,436 | 11.5 |
| Menopause | ||||
| Pre-menopausal | 143,505 | 22.06 | 28,217 | 31.04 |
| post-menopausal | 506,727 | 77.93 | 62,701 | 68.96 |
| Prior Biopsy | ||||
| Yes | 114,582 | 17.62 | 75,164 | 82.67 |
| No | 535,650 | 82.38 | 15,754 | 17.33 |
| Time since last screen | ||||
| 9–18 | 370,815 | 57.03 | 37,811 | 41.59 |
| 19–30 | 114,806 | 17.66 | 13,943 | 15.34 |
| >30 | 80,005 | 12.3 | 12,814 | 14.09 |
| First Screen | 84,606 | 13.01 | 26,350 | 28.98 |
| Comparison Film | ||||
| Yes | 540,995 | 83.2 | 60,746 | 66.81 |
| No | 109,237 | 16.8 | 30,172 | 33.19 |
TN – True negative; FP – False positive; nH-non Hispanic
Loss to Follow up was defined as those who never returned to screening in the database;
237 exams were missing breast density
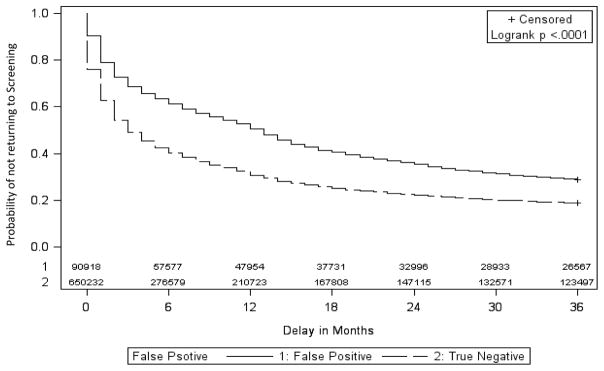
Regardless of index screen result, younger and premenopausal women as well as women who were obtaining their first screening mammogram or whose prior mammogram occurred more than 30 months before the index screen were more likely to delay their subsequent screening (Table 2). The median delay in return to screening was higher for FP than for TN mammograms (13 months vs 3 months, P-value <0.001) (Figure 2). Delays in returning for subsequent screening were consistently longer after a FP mammogram than after a TN mammogram across strata of patient characteristics (Table 2).
Table 2.
Mean and median delay in months for follow-up screening mammography by patient characteristics and mammogram findings
| TN
|
P-value2 | FP
|
P-value2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % Returned1 | Median | N | % Returned1 | Median | |||
| Age | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| <40 | 21,724 | 56 | 28 | 5,365 | 53 | 32 | ||
| 40–49 | 187,897 | 80 | 5 | 33,261 | 70 | 14 | ||
| 50–59 | 193,036 | 84 | 3 | 26,058 | 74 | 12 | ||
| 60–69 | 131,839 | 86 | 2 | 15,069 | 77 | 9 | ||
| 70–79 | 87,294 | 83 | 2 | 8,633 | 74 | 9 | ||
| 80+ | 28,442 | 67 | 4 | 2,532 | 58 | 14 | ||
| Ethnicity | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| nH White | 362,647 | 84 | 2 | 49,319 | 73 | 12 | ||
| nH Black | 151,171 | 84 | 4 | 25,121 | 73 | 11 | ||
| Other | 136,414 | 72 | 6 | 16,478 | 60 | 20 | ||
| Breast Density3 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Fatty | 52,823 | 79 | 4 | 5,479 | 64 | 16 | ||
| Scattered | 266,089 | 81 | 3 | 31,747 | 72 | 12 | ||
| Heterogeneous | 276,742 | 81 | 3 | 45,560 | 72 | 12 | ||
| Dense | 54,512 | 81 | 4 | 7,961 | 68 | 15 | ||
| Family history | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| None | 440,106 | 79 | 4 | 60,593 | 69 | 13 | ||
| Weak | 101,063 | 81 | 3 | 14,587 | 74 | 12 | ||
| Moderate | 77,450 | 81 | 2 | 10,715 | 77 | 9 | ||
| Strong | 31,613 | 81 | 2 | 5,023 | 73 | 12 | ||
| Parity | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Nulliparous | 79,395 | 85 | 2 | 11,151 | 75 | 12 | ||
| Parous | 516,967 | 83 | 3 | 69,331 | 26 | 12 | ||
| Missing | 53,870 | 61 | 11 | 10,436 | 47 | 15 | ||
| Menopause | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Pre-menopausal | 143,505 | 68 | 10 | 28,217 | 59 | 22 | ||
| post-menopausal | 506,727 | 85 | 3 | 62,701 | 76 | 10 | ||
| Prior Biopsy | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 535,650 | 80 | 4 | 15,754 | 70 | 13 | ||
| Yes | 114,582 | 86 | 2 | 75164 | 77 | 10 | ||
| Time since last screen | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 9–18 | 370,815 | 89 | 1 | 37,811 | 83 | 4 | ||
| 19–30 | 114,806 | 81 | 6 | 13,943 | 76 | 12 | ||
| >30 | 80,005 | 69 | 13 | 12,814 | 65 | 19 | ||
| First Screen | 84,606 | 57 | 24 | 26,350 | 53 | 31 | ||
| Comparison Film | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Yes | 540,995 | 85 | 3 | 60,746 | 78 | 8 | ||
| No | 109,237 | 63 | 16 | 30,172 | 44 | 26 | ||
TN – True negative; FP – False positive; nH-non Hispanic;
% returned to screening within 36 months;
Log Rank Test;
237 exams were missing breast density;
Figure 2.
Kaplan-Meier estimates for time to next screen in months by index mammogram result
In the adjusted proportional hazards model, women with TN result were 36% more likely to return to screening in the next 36 months compared to women with a FP result HR=1.36 (95% CI: 1.35–1.37). In addition, a FP result was consistently associated with delays in subsequent screening within strata of patient characteristics and screening history (Table 3).
Table 3.
Overall and stratified hazards ratios of returning to screening among true negative compared to false positive mammograms
| HR (TN vs. FP)1 | P-value | |
|---|---|---|
| Overall | 1.36 (1.35, 1.37) | <0.001 |
| Stratum-Specific | ||
| Calendar Year | ||
| ≤2005 | 1.31 (1.30, 1.33) | <0.001 |
| > 2005 | 1.4 (1.39, 1.42) | <0.001 |
| Race/Ethnicity | ||
| nH-Whites | 1.42 (1.40, 1.43) | <0.001 |
| nH-Blacks | 1.28 (1.26, 1.30) | <0.001 |
| Other | 1.31 (1.28, 1.33) | <0.001 |
| Age group | ||
| <40 | 1.32 (1.30, 1.34) | <0.001 |
| 40–50 | 1.41 (1.39, 1.43) | <0.001 |
| 50–60 | 1.41 (1.38, 1.43) | <0.001 |
| 60–70 | 1.40 (1.37, 1.44) | <0.001 |
| 70–80 | 1.28 (1.22, 1.35) | <0.001 |
| 80+ | 1.03 (0.99, 1.07) | 0.10 |
| Time Since Screen | ||
| First Screen | 1.20 (1.18, 1.23) | <0.001 |
| 09–18 | 1.47 (1.46, 1.49) | <0.001 |
| 19–30 | 1.25 (1.22, 1.27) | <0.001 |
| >30 | 1.23 (1.20, 1.26) | <0.001 |
| Family History | ||
| None | 1.34 (1.33, 1.36) | <0.001 |
| weak | 1.42 (1.38, 1.45) | <0.001 |
| Moderate | 1.46 (1.42, 1.52) | <0.001 |
| Strong | 1.3 (1.32, 1.37) | <0.001 |
| Prior Biopsy | ||
| Yes | 1.49 (1.46, 1.52) | <0.001 |
| No | 1.33 (1.32, 1.34) | <0.001 |
| Comparison film | ||
| Yes | 1.22 (1.20, 1.24) | <0.001 |
| No | 1.41 (1.40, 1.42) | <0.001 |
TN – True negative; FP – False positive.
Cox Proportional Hazards model adjusted for mammogram result (FP vs TN), decade of age, race/ethnicity, calendar year, breast density, family history, time since last screen, history of prior biopsy, parity, availability of comparison film and screening facility.
To examine whether the classification of 10,746 (1.45%) screening mammograms with BIRADS 3 as TN impacted our results we performed sensitivity analyses in which we 1) excluded screens with BIRADS 3 or 2) included BIRADS as FP mammograms. The results in both scenarios were nearly identical to those reported when we classified mammograms with BIRADS 3 as TN.
The results after resetting the index date to account for the time required to resolve a FP mammogram were similar to the results that were observed when using the actual mammogram date as the index date. Briefly, the median delay in return to screening was higher for FP than for TN mammograms (12 months vs 3 months, P-value <0.001). Delays in returning for subsequent screening were consistently longer after a FP mammogram than after a TN mammogram across strata of patient characteristics. In the adjusted proportional hazards model, women with TN result were 36% more likely to return to screening compared to women with a FP result HR=1.36 (95% CI: 1.36–1.39) (Data not shown).
Compared to women who did not receive additional work up, women who received additional imaging were 24% less likely to return to screening HR=0.76 (95% CI: 0.758–0.772) and women who received imaging and biopsy were 34% less likely to return to screening HR=0.66 (95% CI:0.64–0.67) (P-value for trend <0.001). Among FPs only, women who experienced additional imaging and biopsy were 19% less likely to return to screening compared to women who received imaging only HR=1.19 (95% CI: 1.15–1.22).
We re-analyzed our primary results using propensity score matching. We matched 90,095 (99.1 % of all FPs in the dataset) FP index mammograms to a similar number of true negative mammograms. The proportion of women who did not return to screening was slightly higher among women who experienced a FP mammogram compared to women with a TN exam (22.1% vs 19.2%, P-value <0.001). The two cohorts were balanced in terms of women’s characteristics. Similar to the analysis which included all exams, delay in return to subsequent mammograms was longer among women with FP compared to women with TN mammograms. The median delay was 13 months among FP compared to 6 months among TN (P-value <0.001). After adjusting for patient characteristics, the chance of returning to screening was 34% higher in women with TN exams compared to women with FP mammograms HR=1.33 (95% CI: 1.32–1.35).
For the 751,347 screening mammograms defined as either false positive or true negative, 4-year cumulative risk of a late stage at diagnosis was found to be higher following a FP mammogram compared to a TN mammogram (0.4% vs 0.3%, for FP vs TN respectively, p=0.001, results not tabulated). Similar results were observed when adjusting for patient and clinical factors as well as clustering within patients such that the risk of late stage at diagnosis was 20% higher in FP compared to TN (p-value <0.001). Similarly, delays in returning to subsequent screening also increased the risk of late stage at diagnosis such that the risk increases by 0.3% for every one additional month delay (p<0.001, data not shown).
Discussion
We sought to examine how the experience of a FP mammogram might impact adherence to subsequent mammography screening in a large cohort of women from a single healthcare organization. Our results suggest that women who had a FP mammogram were less likely to return for screening within the following 36 months compared to those with TN mammogram results. This finding is consistent with another US-based study that used secondary data from telephone interviews and medical claims records for calendar years 2005–2008 on 2406 women which were followed for 36 months. This study found that 22.1% of women with FP mammogram compared to 15% of women with TN mammogram delayed their receipt of the subsequent screening (25). Conversely, studies conducted more than a decade ago using data from the 1990s found that women who experienced FP mammogram had better adherence to subsequent screening compared to women with a true negative mammogram exam outcome (11,12,26).
Several other studies from Europe and Canada found no difference in re-screening (13–16,27), and yet others have reported lower re-screening rates among FPs than among TNs (18–20,28–30). These inconsistent results suggest both secular and geographic variation in the impact of FP mammography on adherence to screening recommendations among the USA, Europe and Canada (21). The conflicting results for international comparisons may be attributed to variations in screening practices such as screening intervals are shorter in the US than in Europe, greater emphasis on accuracy in Europe by double readings which have been reported to result in 3 to 5% lower recall rates compared to the US, and differences in national mammography programs for Europe and US public and private screening providers. The inconsistency between the majority of the USA studies and our study might be explained by secular changes in how women perceive and adapt to a FP mammogram, which may be related to changes in guidelines (USPSTF guidelines 2002 and 2009) and increased awareness of the balance of benefits and harms of mammography screening over the last decade.
Our study findings suggest that the delay in returning to recommended mammography screening practices increased the risk of subsequent diagnoses with late stage breast cancer. A similar observation was reported from a study in the United Kingdom which found an increased likelihood of late stage at diagnosis among women with FP compared to those with TN mammogram results OR=1.37 (95% CI: 0.67–2.28) (20).
Some women who experience a FP result might decide to get their next screening mammogram 12 months after the completion of their diagnostic work-up, rather than 12 months after their last screen. When we adjusted the follow-up time for women with a FP screen to begin at the date of the last diagnostic procedure, our results were similar to the results generated when using the screening mammogram date as the index date. Thus, the potential for a perceived shift in the appropriate date for the next screen among women with a FP index mammogram could not account for the association of a FP result with delayed subsequent screening.
Strengths of this study include the availability of screening and diagnostic records of prior exams that were conducted within our network and the large number of exams from a diverse community-based cohort. Other studies (12, 26) have used women as the unit of analysis to estimate the probability of returning to the subsequent screening mammography which may be subject to recall bias because of the possible differences in the accuracy of the recollection of prior exams such that women who have experienced a prior false positive result may have a better memory of their experience than women with a prior TN exam.
This study has several limitations as well. First, we could not account for insurance status in our analysis as these data were not available in our data collection system. Women who are uninsured or underinsured may be more likely to be truly lost to follow-up if they lack a medical insurance. Alternatively, underinsured women may be more likely to delay or forgo altogether subsequent screening as a result of a FP screen, perhaps due to the concern regarding high out of pocket costs.
In these analyses, we included the 14% of exams that were not followed by a subsequent screening mammogram within our network as right censored. It is possible that these women may have never returned to screening or could have received their mammography screening somewhere else outside our network. It is also possible that some women who appeared to delay their subsequent screen may have obtained another screen elsewhere in the interim, outside this healthcare organization and thus not captured by our radiology database. This limitation may have impacted our results by differentially inflating the median follow up for FP and TN mammograms. When excluding those who did not have a subsequent mammogram in the system, we still observed longer median time to return to subsequent screening in women with FP compared to their TN counterparts (7 months vs 2 months, p-value <0.001). Similar finding was also observed after resetting the index date to account for the time required to resolve a FP mammogram. Given the high percentage (86%) of index screens were associated with a subsequent screen, loss to follow-up would appear to be modest, but this is could not be determined empirically.
In conclusion, our study found that women who experienced a FP mammogram were more likely to delay their subsequent screening compared to women with a TN mammogram. The finding is important in that women who experience a FP mammogram result should be provided with more information about the continued benefits of mammography screening and encouraged to maintain adherence to screening mammography recommendations.
Acknowledgments
GRANT SUPPORT
This work was supported by a grant from the Agency for Health Research and Quality to Dr. Garth H. Rauscher from the University of Illinois at Chicago (Grant # 1 R01 HS018366-01A1)
Dr. Friedewald have received grand funding for research from Hologic and she is an occasional consultant for Hologic. She is on the speakers’ bureau for Bard.
We thank the Illinois women diagnosed with breast cancer whose information was reported to the Illinois State Cancer Registry thereby making this research possible. The conclusions, opinions, and recommendations expressed are not necessarily the conclusions, opinions, or recommendations of the Illinois State Cancer Registry.
Footnotes
IRB Statement: The study was reviewed and approved by the institutional review boards at all participating institutions including the University of Illinois Chicago and Advocate Health Care facilities and departments.
No other potential conflict of interest to disclose.
References
- 1.Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, Fryback DG, Clarke L, Zelen M, et al. Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005 Oct 27;353:1784–92. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chubak J, Boudreau DM, Fishman PA, Elmore JG. Cost of breast-related care in the year following false positive screening mammograms. Med Care. 2010 Sep;48:815–20. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181e57918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brodersen J, Siersma VD. Long-term psychosocial consequences of false-positive screening mammography. Ann Fam Med. 2013 Mar-Apr;11:106–15. doi: 10.1370/afm.1466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brett J, Bankhead C, Henderson B, Watson E, Austoker J. The psychological impact of mammographic screening. A systematic review. Psychooncology. 2005 Nov;14:917–38. doi: 10.1002/pon.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kerlikowske K, Hubbard RA, Miglioretti DL, Geller BM, Yankaskas BC, Lehman CD, et al. Comparative effectiveness of digital versus film-screen mammography in community practice in the United States: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2011 Oct 18;155:493–502. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mushlin AI, Kouides RW, Shapiro DE. Estimating the accuracy of screening mammography: a meta-analysis. Am J Prev Med. 1998 Feb;14:143–53. doi: 10.1016/s0749-3797(97)00019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rosenberg RD, Yankaskas BC, Abraham LA, Sickles EA, Lehman CD, Geller BM, et al. Performance benchmarks for screening mammography. Radiology. 2006 Oct;241:55–66. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2411051504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gotzsche PC, Jorgensen KJ. Screening for breast cancer with mammography. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 4;6:CD001877. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001877.pub5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Woloshin S, Schwartz LM. The benefits and harms of mammography screening: understanding the trade-offs. JAMA. 2010 Jan 13;303:164–5. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for breast cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009 Nov 17;151:716, 26, W-236. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-10-200911170-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lipkus IM, Halabi S, Strigo TS, Rimer BK. The impact of abnormal mammograms on psychosocial outcomes and subsequent screening. Psychooncology. 2000 Sep-Oct;9:402–10. doi: 10.1002/1099-1611(200009/10)9:5<402::aid-pon475>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pinckney RG, Geller BM, Burman M, Littenberg B. Effect of false-positive mammograms on return for subsequent screening mammography. Am J Med. 2003 Feb 1;114:120–5. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lerman C, Trock B, Rimer BK, Boyce A, Jepson C, Engstrom PF. Psychological and behavioral implications of abnormal mammograms. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Apr 15;114:657–61. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-8-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pisano ED, Earp J, Schell M, Vokaty K, Denham A. Screening behavior of women after a false-positive mammogram. Radiology. 1998 Jul;208:245–9. doi: 10.1148/radiology.208.1.9646820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.O’Sullivan I, Sutton S, Dixon S, Perry N. False positive results do not have a negative effect on reattendance for subsequent breast screening. J Med Screen. 2001;8:145–8. doi: 10.1136/jms.8.3.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Andersen SB, Vejborg I, von Euler-Chelpin M. Participation behaviour following a false positive test in the Copenhagen mammography screening programme. Acta Oncol. 2008;47:550–5. doi: 10.1080/02841860801935483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hofvind SS, Wang H, Thoresen S. The Norwegian Breast Cancer Screening Program: re-attendance related to the women’s experiences, intentions and previous screening result. Cancer Causes Control. 2003 May;14:391–8. doi: 10.1023/a:1023918610664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chiarelli AM, Moravan V, Halapy E, Majpruz V, Mai V, Tatla RK. False-positive result and reattendance in the Ontario Breast Screening Program. J Med Screen. 2003;10:129–33. doi: 10.1177/096914130301000306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brett J, Austoker J. Women who are recalled for further investigation for breast screening: psychological consequences 3 years after recall and factors affecting re-attendance. J Public Health Med. 2001 Dec;23:292–300. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/23.4.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McCann J, Stockton D, Godward S. Impact of false-positive mammography on subsequent screening attendance and risk of cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2002;4:R11. doi: 10.1186/bcr455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brewer NT, Salz T, Lillie SE. Systematic review: the long-term effects of false-positive mammograms. Ann Intern Med. 2007 Apr 3;146:502–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-146-7-200704030-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.PENRAD Imaging: Colorado Springs Radiologists: Diagnostic Imaging Colorado PenRad Imaging [Internet] Colorado Springs: Technologies of Plymouth, MN; 2015. Available from: http://www.penrad.com/ [Google Scholar]
- 23.Illinois State Cancer Registry, public dataset, 1986–2012 [Internet] Illinois Department of Public Health; 2014. [updated November, 2014]. Available from: http://www.idph.state.il.us/cancer/statistics.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Parsons LS. Reducing bias in a propensity score matched-pair sample using Greedy matching techniques. Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth Annual SAS Users Group International Conference; Long Beach, Calif. April 22–25, 2001; Cary, N.C: SAS Institute; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 25.DeFrank JT, Rimer BK, Bowling JM, Earp JA, Breslau ES, Brewer NT. Influence of false-positive mammography results on subsequent screening: do physician recommendations buffer negative effects? J Med Screen. 2012 Mar;19:35–41. doi: 10.1258/jms.2012.011123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Burman ML, Taplin SH, Herta DF, Elmore JG. Effect of false-positive mammograms on interval breast cancer screening in a health maintenance organization. Ann Intern Med. 1999 Jul 6;131:1–6. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-131-1-199907060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lampic C, Thurfjell E, Sjoden PO. The influence of a false-positive mammogram on a woman’s subsequent behaviour for detecting breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2003 Aug;39:1730–7. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(02)00451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hofvind S, Ursin G, Tretli S, Sebuodegard S, Moller B. Breast cancer mortality in participants of the Norwegian Breast Cancer Screening Program. Cancer. 2013 Sep 1;119:3106–12. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Alamo-Junquera D, Murta-Nascimento C, Macia F, Bare M, Galceran J, Ascunce N, et al. Effect of false-positive results on reattendance at breast cancer screening programmes in Spain. Eur J Public Health. 2012 Jun;22:404–8. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckr057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Roman R, Sala M, De La Vega M, Natal C, Galceran J, Gonzalez-Roman I, et al. Effect of false-positives and women’s characteristics on long-term adherence to breast cancer screening. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Nov;130:543–52. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1581-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]