Abstract
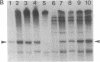
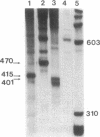
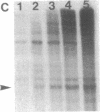
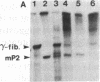
Transcriptionally active nuclear extracts were prepared from mouse testes to study the transcription of the testis-specific mouse protamine 2 (Prm-2) gene in vitro. The testicular system is unique among mammalian in vitro transcription systems in regard to its temperature optimum. In extracts made from prepuberal testes, the temperature optimum for in vitro transcription of Prm-2 is 30 degrees C, similar to somatic in vitro systems. However, in adult testis extracts, the optimum temperature for Prm-2 transcription is 20 degrees C. The different temperature optima seen in vitro for prepuberal and adult testes extracts parallels in vivo physiological temperature sensitivities of the differentiating male germ cells. The testis system also differs from other in vitro transcription systems in its divalent metal cation and ionic strength requirements for optimal transcription. The mouse Prm-2 gene is maximally transcribed at a MgCl2 concentration of 3-5 mM and over a KCl concentration range of 40-100 mM. By using the testis in vitro transcription system to study the Prm-2 gene by deletion analysis, we have determined that positive promotion for the gene lies within the region -170 to -82 from the start of transcription. This region contains a putative Sp-1 binding site. Additional upstream sequences appear to repress Prm-2 transcription in a heterologous transcription system.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. L., O'Brien D. A., Jones C. C., Rockett D. L., Eddy E. M. Expression of heat shock proteins by isolated mouse spermatogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3260–3266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Millette C. F., Bhatnagar Y. M., O'Brien D. A. Dissociation of the mouse testis and characterization of isolated spermatogenic cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):480–494. doi: 10.1177/25.7.893996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors that activate the Ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):699–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Karin M. A pituitary-specific trans-acting factor can stimulate transcription from the growth hormone promoter in extracts of nonexpressing cells. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrás T., Peterson C. A., Piatigorsky J. Evidence for positive and negative regulation in the promoter of the chicken delta 1-crystallin gene. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. E., Peschon J. J., Behringer R. R., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Protamine 3'-untranslated sequences regulate temporal translational control and subcellular localization of growth hormone in spermatids of transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):793–802. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy H. A., McLaughlin M., Feigelson P. Nuclear factors from expressing tissues interact in vitro with a rat alpha-2u globulin gene intron. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1754–1759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold B., Fujimoto H., Kramer J. M., Erickson R. P., Hecht N. B. Haploid accumulation and translational control of phosphoglycerate kinase-2 messenger RNA during mouse spermatogenesis. Dev Biol. 1983 Aug;98(2):392–399. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson D. R., Costa R. H., Xanthopoulos K. G., Darnell J. E. One factor recognizes the liver-specific enhancers in alpha 1-antitrypsin and transthyretin genes. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):786–788. doi: 10.1126/science.3257586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Friedman N., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. Positive and negative regulatory elements in the mouse albumin enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J. M., Dixon G. H. The GC box as a silencer. Biosci Rep. 1987 Dec;7(12):955–963. doi: 10.1007/BF01122129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J. M., Dixon G. H. Transcription of a trout protamine gene in vitro: the effects of alteration of promoters. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 May;62(5):291–300. doi: 10.1139/o84-041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Peschon J. J., Yelick P. C., Palmiter R. D., Hecht N. B. Sequence homologies in the mouse protamine 1 and 2 genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 6;950(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawetz S. A., Dixon G. H. Sequence similarities of the protamine genes: implications for regulation and evolution. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(4):291–297. doi: 10.1007/BF02101190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L., Holmgren-König M., Khoury G. Transcriptional "silencer" element in rat repetitive sequences associated with the rat insulin 1 gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3151–3155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. S., O'Brien D. A., Hou E. W., Versola J., Rockett D. L., Eddy E. M. Differential activity and synthesis of lactate dehydrogenase isozymes A (muscle), B (heart), and C (testis) in mouse spermatogenic cells. Biol Reprod. 1989 Jan;40(1):173–180. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod40.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Bucci L. R., Trostle-Weige P. K., Brock W. A. Histone variants in rat spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):230–240. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L. Separation of spermatogenic cells and nuclei from rodent testes. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;15:15–54. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muglia L., Rothman-Denes L. B. Cell type-specific negative regulatory element in the control region of the rat alpha-fetoprotein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7653–7657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J. Regulation of rat insulin 1 gene expression: evidence for negative regulation in nonpancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschon J. J., Behringer R. R., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Spermatid-specific expression of protamine 1 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5316–5319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Hecht N. B., Hollingshead P. G., Johnson P. A., Leong J. A., Pitts S. L. Haploid-specific transcription of protamine-myc and protamine-T-antigen fusion genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1748–1755. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Aoyama A., Inoue T., Miura M., Okano H., Mikoshiba K. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse myelin basic protein promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3122–3126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanhauser S. M., Hecht N. B. Nucleotide sequence of the rat protamine 2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4395–4395. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Suzuki Y. Faithful transcription initiation of fibroin gene in a homologous cell-free system reveals an enhancing effect of 5' flanking sequence far upstream. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90371-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]