Abstract
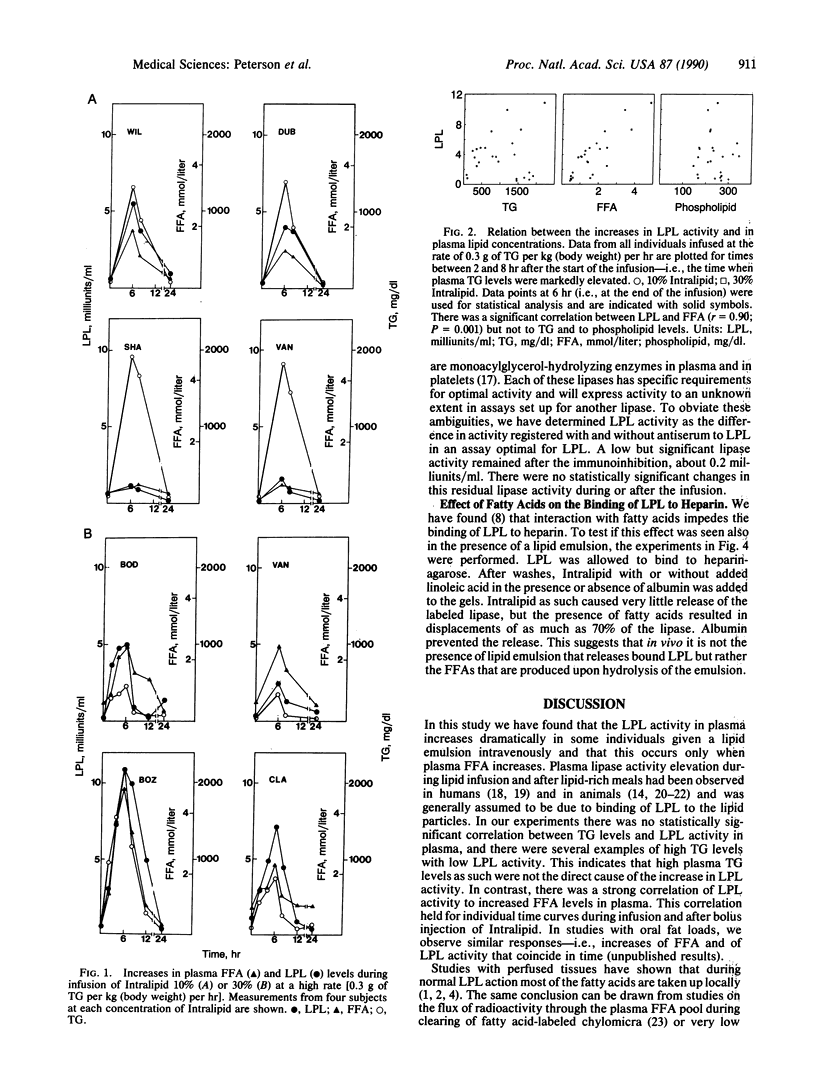
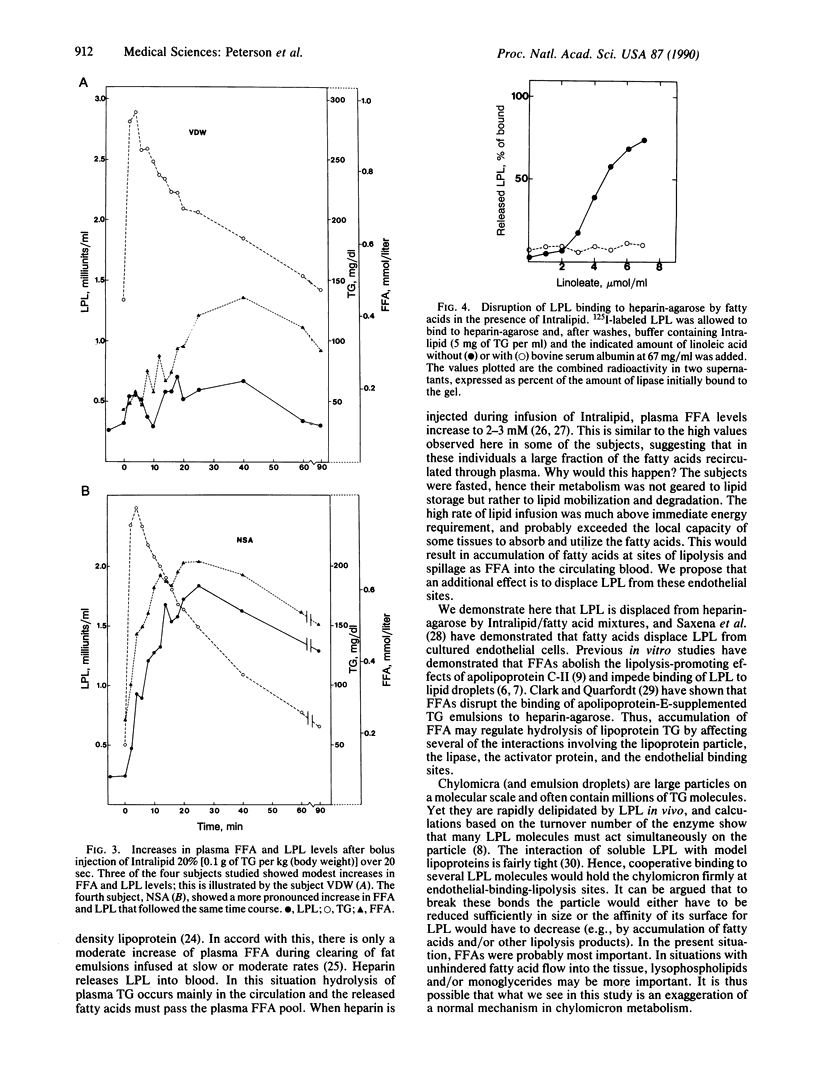
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) catalyzes the flux-generating step in transport of fatty acids from lipoprotein triacylglycerols into tissues for use in metabolic reactions. In vitro studies have shown that fatty acids can bind to the enzyme and impede its other interactions. In this study we have searched for evidence of fatty acid control of LPL in vivo by rapid infusion of a triacylglycerol emulsion to healthy volunteers. During infusion the activity of LPL but not of hepatic lipase increased in plasma, but to different degrees in different individuals. The time course for the increase in LPL activity differed from that for triacylglycerols but followed the plasma levels of free fatty acids. This was true during infusions and when the emulsion was given as a bolus injection. In particular there were several instances when plasma triacylglycerol levels were very high but free fatty acids and LPL activity remained low. Model studies with bovine LPL showed that fatty acids displace the enzyme from heparin-agarose. We suggest that in situations when fatty acids are generated more rapidly by LPL than they are used by the local tissue, they cause dissociation of the enzyme from its binding to endothelial heparin sulfate and are themselves released into circulation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Binding of active and inactive forms of lipoprotein lipase to heparin. Effects of pH. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):409–413. doi: 10.1042/bj2260409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Apolipoprotein CII enhances hydrolysis of monoglycerides by lipoprotein lipase, but the effect is abolished by fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase. Mechanism of product inhibition. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):557–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase: some effects of activator proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):549–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beylot M., Chayvialle J. A., Riou J. P., Souquet J. C., Sautot G., Cohen R., Mornex R. Regulation of somatostatin secretion in man: study of the role of free fatty acids and ketone bodies. Metabolism. 1984 Nov;33(11):988–993. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläckberg L., Blind P. J., Ljungberg B., Hernell O. On the source of bile salt-stimulated lipase in human milk: a study based on serum concentrations as determined by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1985 Jun;4(3):441–445. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198506000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolzano K., Sailer S., Sandhofer F., Braunsteiner H. Uber das Verhalten der endogenen Lipoproteidlipase-Aktivität im Plasma während einer intravenösen Fettinfusion bei Normalpersonen und Patienten mit Hypertriglyceridämie. Klin Wochenschr. 1967 Nov 1;45(21):1104–1106. doi: 10.1007/BF01754042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Walldius G. Fatty acids incorporation into human adipose tissue in hypertriglyceridaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun 21;6(3):195–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1976.tb00512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. D., Risser T. R., Cully M., Reaven G. M. Is the hypertriglyceridemia associated with insulin deficiency caused by decreased lipoprotein lipase activity? Diabetes. 1979 Oct;28(10):893–898. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.10.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. B., Quarfordt S. H. Apolipoprotein effects on the lipolysis of perfused triglyceride by heparin-immobilized milk lipase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4778–4783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J. Monoglyceride hydrolase activities of rat plasma and platelets. Their properties and roles in the activity of lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):876–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean L. R., Larsen W. J., Jackson R. L. Interaction of lipoprotein lipase with phospholipid vesicles: effect on protein and lipid structure. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):873–878. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenström J., Carpentier Y. A., Askanazi J., Robin A. P., Elwyn D. H., Hensle T. W., Kinney J. M. Free fatty acid mobilization and oxidation during total parenteral nutrition in trauma and infection. Ann Surg. 1983 Dec;198(6):725–735. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198312000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVECRONA T., GEORGE E. P., BORGSTROM B. Chylomicron metabolism. Fed Proc. 1961 Dec;20:928–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Bengtsson G. Immunochemical properties of lipoprotein lipase. Development of an immunoassay applicable to several mammalian species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 16;752(1):38–45. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson E., Nordenström J., Nilsson-Ehle P., Hagenfeldt L. Lipolytic and anticoagulant activities of a low molecular weight fragment of heparin. Eur J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;15(4):215–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1985.tb00171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Distribution of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase between plasma and tissues: effect of hypertriglyceridemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 4;837(3):262–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner I., DeSanctis J. Kinetics of product inhibition and mechanisms of lipoprotein lipase activation by apolipoprotein C-II. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3711–3717. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON D. S., JEFFRIES G. H., FRENCH J. E. Studies on the interaction of chyle and plasma in the rat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1954;39(3):165–176. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1954.sp001068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAILER S., SANDHOFER F., BRAUNSTEINER H. STEUERUNG DER ENDOGENEN LIPOPROTEID-LIPASE-AKTIVITAET IM PLASMA BEI NORMALPERSONEN UND PATIENTEN MIT ESSENTIELLER HYPERLIPAEMIA. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1965 May 7;90:865–868. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1111430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena U., Witte L. D., Goldberg I. J. Release of endothelial cell lipoprotein lipase by plasma lipoproteins and free fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4349–4355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Olivecrona T. Effect of albumin on products formed from chylomicron triacylclycerol by lipoprotein lipase in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 22;487(3):472–486. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafrir E., Biale Y. Effect of experimental hypertriglyceridaemia on tissue and serum lipoprotein lipase activity. Eur J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;1(1):19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1970.tb00592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternby B., Akerström B. Immunoreactive pancreatic colipase, lipase and phospholipase A2 in human plasma and urine from healthy individuals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 11;789(2):164–169. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Durkot M. J. Role of very low density lipoproteins in the energy metabolism of the rat. J Lipid Res. 1985 Feb;26(2):210–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaidan H., Dhanireddy R., Hamosh M., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Hamosh P. Lipid clearing in premature infants during continuous heparin infusion: role of circulating lipases. Pediatr Res. 1985 Jan;19(1):23–25. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198501000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


