Abstract
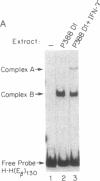
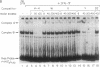
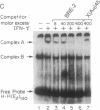
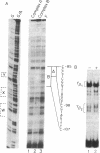
Interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) is a potent inducer of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens during normal immune responses and in abnormal responses in autoimmune disease. In this report we identify two nuclear factors whose binding to the murine E beta class II MHC beta-chain gene is regulated by this cytokine. IFN-gamma stimulation of murine macrophages results in the appearance of increased binding of one protein complex, complex A, and decreased binding of a second, faster migrating protein complex, complex B. Although the contact residues for both of these proteins lie within the highly conserved Y-box transcriptional element, their binding specificity differs. The protein in complex B is a CCAAT-box-binding protein that may be similar or identical to NF-Y or YB1, previously identified class II Y-box-binding proteins. The DNA sequence requirements for the binding of the slower migrating complex, complex A, are not limited to CCAAT-box sequences but include sequences upstream of the Y box. These upstream sequences are required both for IFN-gamma-induced gene transcription and for IFN-gamma-induced modulation of binding activity. These data suggest a model in which upstream sequences contribute to formation of a lymphokine-regulated complex downstream. The IFN-gamma-induced binding protein described as complex A in this report differs from the IFN-gamma, -alpha, or -beta-induced nuclear factors previously identified.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaldi I., Reith W., Berte C., Mach B. Induction of HLA class II genes by IFN-gamma is transcriptional and requires a trans-acting protein. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):999–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benech P., Vigneron M., Peretz D., Revel M., Chebath J. Interferon-responsive regulatory elements in the promoter of the human 2',5'-oligo(A) synthetase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4498–4504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Flavell R. A., Sharp P. A. A gamma-interferon-induced factor that binds the interferon response sequence of the MHC class I gene, H-2Kb. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1139–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Boettger E. C., Flavell R. A. Transcriptional activation of HLA-DR alpha by interferon gamma requires a trans-acting protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boitard C., Michie S., Serrurier P., Butcher G. W., Larkins A. P., McDevitt H. O. In vivo prevention of thyroid and pancreatic autoimmunity in the BB rat by antibody to class II major histocompatibility complex gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6627–6631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothby M., Gravallese E., Liou H. C., Glimcher L. H. A DNA binding protein regulated by IL-4 and by differentiation in B cells. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1559–1562. doi: 10.1126/science.3144043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothby M., Liou H. C., Glimcher L. H. Differences in DNA sequence specificity among MHC class II X box binding proteins. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):1005–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Strominger J. L. Regulation of a transfected human class II major histocompatibility complex gene in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger E. C., Blanar M. A., Flavell R. A. Cycloheximide, an inhibitor of protein synthesis, prevents gamma-interferon-induced expression of class II mRNA in a macrophage cell line. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(4):215–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00345497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier D. K., Schiffenbauer J., Woulfe S. L., Zacheis M., Schwartz B. D. Characterization of the cDNA encoding a protein binding to the major histocompatibility complex class II Y box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7322–7326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Durand B., Marfing C., Le Meur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Conserved major histocompatibility complex class II boxes--X and Y--are transcriptional control elements and specifically bind nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6249–6253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsett D. L., Keshet I., Winocour E. Quantitation of a simian virus 40 nonhomologous recombination pathway. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):218–228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.218-228.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertsch-Ruggio D., Schoenberg D. R., Vogel S. N. Induction of macrophage Ia antigen expression by rIFN-gamma and down-regulation by IFN-alpha/beta and dexamethasone are regulated transcriptionally. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1582–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Folsom V., Tonegawa S. Cell type-specific enhancer element associated with a mouse MHC gene, E beta. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):594–597. doi: 10.1038/310594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A., Trowsdale J. Complete nucleotide sequence of a functional HLA-DP beta gene and the region between the DP beta 1 and DP alpha 1 genes: comparison of the 5' ends of HLA class II genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1607–1621. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreidberg J. A., Kelly T. J. Genetic analysis of the human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2903–2909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Boothby M. R., Glimcher L. H. Distinct cloned class II MHC DNA binding proteins recognize the X box transcription element. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.3140376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster A. D., Ravetch J. V. Genomic characterization of a gamma-interferon-inducible gene (IP-10) and identification of an interferon-inducible hypersensitive site. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3723–3731. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Glimcher L. H., Paul W. E., Schwartz R. H. Magnitude of response of histocompatibility-restricted T-cell clones is a function of the product of the concentrations of antigen and Ia molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6019–6023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Hara N., Tanaka R., Fujiwara M. Immunohistochemical analysis of the rat central nervous system during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, with special reference to Ia-positive cells with dendritic morphology. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3668–3676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The nucleotide sequence of a 5.5-kilobase DNA segment containing the mouse kappa immunoglobulin J and C region genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa K., Doyle C., Strominger J. L. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with conserved sequences of human class II major histocompatibility complex genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Collins T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Gitlin J. D., Fiers W., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Reiss C. S. Lymphocytes recognize human vascular endothelial and dermal fibroblast Ia antigens induced by recombinant immune interferon. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):726–729. doi: 10.1038/305726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Ting J. P. Upstream DNA sequences required for tissue-specific expression of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4254–4258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Burke P. A., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferon-induced transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene accompanies binding of inducible nuclear factors to the interferon consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5884–5888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoskiewicz M. J., Colvin R. B., Schneeberger E. E., Russell P. S. Widespread and selective induction of major histocompatibility complex-determined antigens in vivo by gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1645–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teyton L., Lotteau V., Turmel P., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L., Pujol J. P., Loyau G., Piatier-Tonneau D., Auffray C., Charron D. J. HLA DR, DQ, and DP antigen expression in rheumatoid synovial cells: a biochemical and quantitative study. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1730–1738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Mavrothalassitis G., Papamatheakis J. Multiple regulatory regions on the 5' side of the mouse E alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3075–3079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. Y., Nakanishi M., Peterlin B. M. B-cell-specific and interferon-gamma-inducible regulation of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8598–8602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widera G., Burkly L. C., Pinkert C. A., Böttger E. C., Cowing C., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Flavell R. A. Transgenic mice selectively lacking MHC class II (I-E) antigen expression on B cells: an in vivo approach to investigate Ia gene function. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward J. G., Omer K. W., Stuart P. M. MHC class II transcription in different mouse cell types. Differential requirement for protein synthesis between B cells and macrophages. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):4062–4069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Kingston R. E., Morimoto R. I. Human HSP70 promoter contains at least two distinct regulatory domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]