Abstract
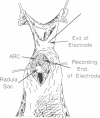
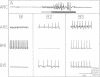
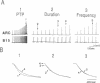
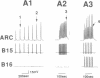
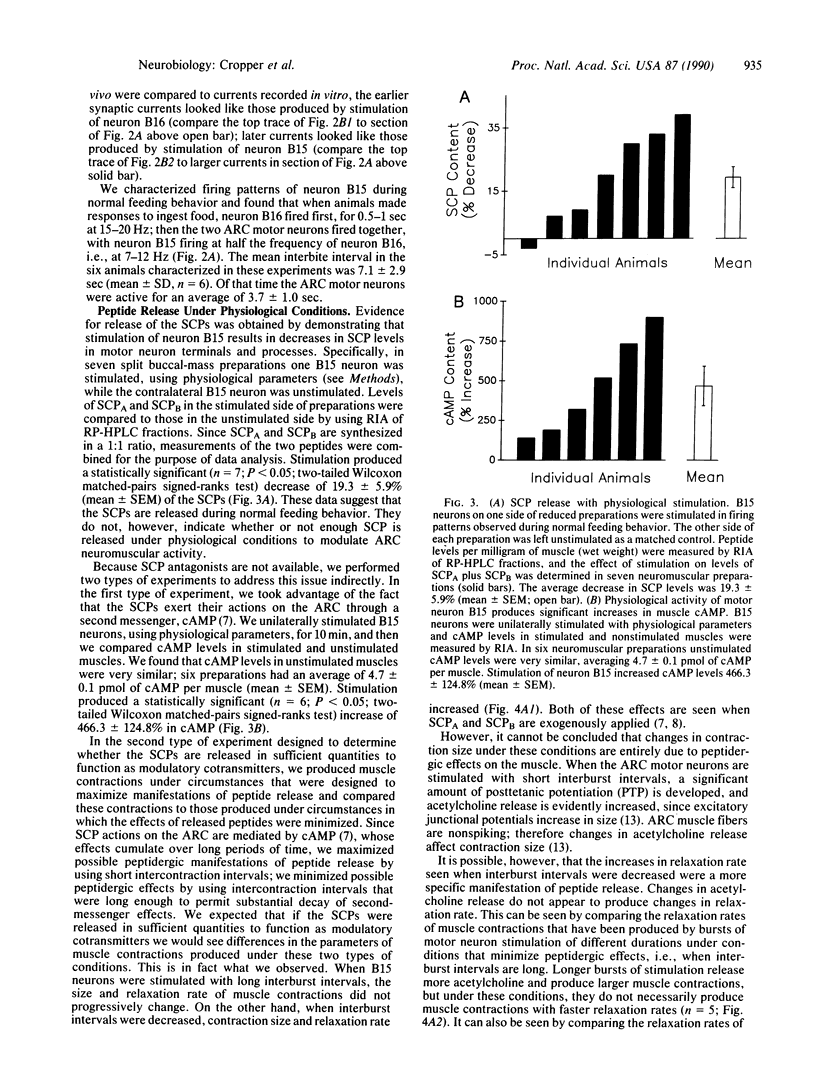
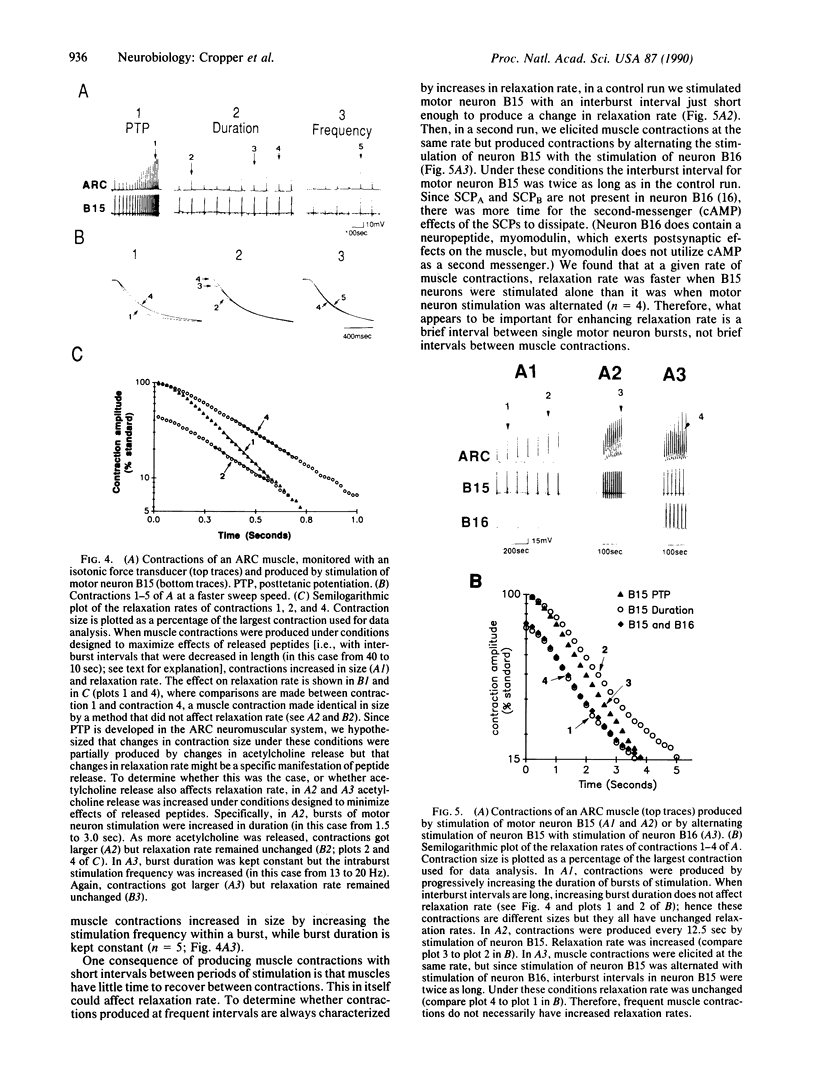
In previous studies, we demonstrated that B15, one of the two cholinergic motor neurons of the accessory radula closer muscle of Aplysia, synthesizes two peptides, small cardioactive peptides A and B (SCPA and SCPB), that, when exogenously applied, increase the size and relaxation rate of muscle contractions elicited by motor neuron stimulation. In the present experiments, we obtained evidence that the SCPs are released under physiological conditions. Specifically, we characterized firing patterns of motor neuron B15 during normal behavior, simulated them in vitro, and demonstrated that this type of neuronal activity produces decreases in SCP levels in neuronal processes and terminals. We also obtained evidence that suggests that enough SCP is released under physiological conditions to modulate neuromuscular activity in the accessory radula closer. We demonstrated that physiological activity of neuron B15 produces significant increases in muscle cAMP levels. Furthermore, increases in the size and relaxation rate of muscle contractions can be produced by changes in stimulation parameters that are also likely to maximize effects of released endogenous SCPA and SCPB.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. E., O'Shea M. Peptide cotransmitter at a neuromuscular junction. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):286–289. doi: 10.1126/science.6134339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop C. A., Wine J. J., Nagy F., O'Shea M. R. Physiological consequences of a peptide cotransmitter in a crayfish nerve-muscle preparation. J Neurosci. 1987 Jun;7(6):1769–1779. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01769.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. L., Weiss K. R., Kupfermann I. Motor control of buccal muscles in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Jan;41(1):157–180. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cropper E. C., Lloyd P. E., Reed W., Tenenbaum R., Kupfermann I., Weiss K. R. Multiple neuropeptides in cholinergic motor neurons of Aplysia: evidence for modulation intrinsic to the motor circuit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3486–3490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cropper E. C., Miller M. W., Tenenbaum R., Kolks M. A., Kupfermann I., Weiss K. R. Structure and action of buccalin: a modulatory neuropeptide localized to an identified small cardioactive peptide-containing cholinergic motor neuron of Aplysia californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cropper E. C., Tenenbaum R., Kolks M. A., Kupfermann I., Weiss K. R. Myomodulin: a bioactive neuropeptide present in an identified cholinergic buccal motor neuron of Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5483–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacklet J. W., Rine J. Facilitation at neuromuscular junctions: contribution to habituation and dishabituation of the Aplysia gill withdrawal reflex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1267–1271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlman J. R., Li C., Calabrese R. L. FMRF-amide-like substances in the leech. II. Bioactivity on the heartbeat system. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2310–2317. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02310.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfermann I. Feeding behavior in Aplysia: a simple system for the study of motivation. Behav Biol. 1974 Jan;10(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6773(74)91644-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfermann I., Weiss K. R. Activity of an identified serotonergic neuron in free moving Aplysia correlates with behavioral arousal. Brain Res. 1982 Jun 10;241(2):334–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuslansky B., Weiss K. R., Kupfermann I. Mechanisms underlying satiation of feeding behavior of the mollusc Aplysia. Behav Neural Biol. 1987 Sep;48(2):278–303. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(87)90836-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd P. E. Fast axonal transport of modulatory neuropeptides from central ganglia to components of the feeding system in Aplysia. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3507–3514. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03507.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd P. E., Kupfermann I., Weiss K. R. Evidence for parallel actions of a molluscan neuropeptide and serotonin in mediating arousal in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2934–2937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd P. E., Schacher S., Kupfermann I., Weiss K. R. Release of neuropeptides during intracellular stimulation of single identified Aplysia neurons in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9794–9798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons D. W., ter Maat A., Pinsker H. M. Selective recording and stimulation of individual identified neurons in freely behaving Aplysia. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.6612336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. C., Weiss K. R., Goldstein R. S., Kupfermann I. The role of a modulatory neuron in feeding and satiation in Aplysia: effects of lesioning of the serotonergic metacerebral cells. J Neurosci. 1989 May;9(5):1562–1578. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-05-01562.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Lundberg J. M., Astrand P. Neuropeptide Y--a cotransmitter with noradrenaline and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the sympathetic nerves of the mouse vas deferens? A biochemical, physiological and electropharmacological study. Neuroscience. 1986 May;18(1):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takami K., Kawai Y., Uchida S., Tohyama M., Shiotani Y., Yoshida H., Emson P. C., Girgis S., Hillyard C. J., MacIntyre I. Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide on contraction of striated muscle in the mouse. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Sep 30;60(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss K. R., Cohen J. L., Kupfermann I. Modulatory control of buccal musculature by a serotonergic neuron (metacerebral cell) in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Jan;41(1):181–203. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whim M. D., Lloyd P. E. Frequency-dependent release of peptide cotransmitters from identified cholinergic motor neurons in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9034–9038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]