Abstract
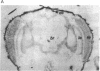
A Drosophila gene encoding a homologue of vertebrate arrestin was isolated by subtractive hybridization and identified as a member of a set of genes that are preferentially expressed in the visual system. This gene encodes a 364-amino acid protein that displays greater than 40% amino acid sequence identity with human and bovine arrestin. Interestingly, the Drosophila homologue lacks the C-terminal sequences that were postulated to interact with rhodopsin during the quenching of the phototransduction cascade in the vertebrate visual response. These findings are discussed in terms of invertebrate phototransduction. The Drosophila gene was mapped cytogenetically to chromosomal position 36D1-2, near the ninaD locus. However, the arrestin gene does not appear to be the ninaD locus, as sequence analysis of three ethylmethane sulfate-induced ninaD mutant alleles reveals no alteration in amino acid sequence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benovic J. L., Kühn H., Weyand I., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Functional desensitization of the isolated beta-adrenergic receptor by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: potential role of an analog of the retinal protein arrestin (48-kDa protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8879–8882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg D. D., Lodish H. F. Complexity of nuclear and polysomal RNAs in growing Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):268–284. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld A., Erusalimsky J., Heichal O., Selinger Z., Minke B. Light-activated guanosinetriphosphatase in Musca eye membranes resembles the prolonged depolarizing afterpotential in photoreceptor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7116–7120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary O., Heichal O., Blumenfeld A., Cassel D., Suss E., Barash S., Rubinstein C. T., Minke B., Selinger Z. Coupling of photoexcited rhodopsin to inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in fly photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6939–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Levine M., Garber R. L., Gehring W. J. An improved in situ hybridization method for the detection of cellular RNAs in Drosophila tissue sections and its application for localizing transcripts of the homeotic Antennapedia gene complex. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):617–623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist R., Jukes T. H., Moise H., Goodman M., Moore G. W. The evolution of the globin family genes: concordance of stochastic and augmented maximum parsimony genetic distances for alpha hemoglobin, beta hemoglobin and myoglobin phylogenies. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):39–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde D. R., Mecklenburg K. L., Pollock J. A., Vihtelic T. S., Benzer S. Twenty Drosophila visual system cDNA clones: one is a homolog of human arrestin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1008–1012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsow C. M., Wacker W. B. Pineal reactivity of anti-retina sera. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 Feb;16(2):181–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Hall S. W., Wilden U. Light-induced binding of 48-kDa protein to photoreceptor membranes is highly enhanced by phosphorylation of rhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):473–478. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Wilden U. Deactivation of photoactivated rhodopsin by rhodopsin-kinase and arrestin. J Recept Res. 1987;7(1-4):283–298. doi: 10.3109/10799898709054990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer-Safer P. R., Levine M., Ward D. C. Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Pugh E. N., Jr ATP mediates rapid reversal of cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase activation in visual receptor membranes. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):734–736. doi: 10.1038/287734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Isono K., Pye Q., Pak W. L. Gene encoding cytoskeletal proteins in Drosophila rhabdomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):985–989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Jones K., Hafen E., Rubin G. Rescue of the Drosophila phototransduction mutation trp by germline transformation. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1040–1043. doi: 10.1126/science.3933112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila ninaC locus encodes two photoreceptor cell specific proteins with domains homologous to protein kinases and the myosin heavy chain head. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):757–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90413-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Gery I., Ballintine E. J., Wacker W. B. Cellular immune responsiveness of uveitis patients to retinal S-antigen. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980 Feb;89(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(80)90108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Kuwabara T., de Monasterio F. M., Wacker W. B. S-antigen uveitis in primates. A new model for human disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Jun;99(6):1090–1092. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930011090021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Tousa J. E., Baehr W., Martin R. L., Hirsh J., Pak W. L., Applebury M. L. The Drosophila ninaE gene encodes an opsin. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):839–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneuwly S., Shortridge R. D., Larrivee D. C., Ono T., Ozaki M., Pak W. L. Drosophila ninaA gene encodes an eye-specific cyclophilin (cyclosporine A binding protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5390–5394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh B. H., Stamnes M. A., Seavello S., Harris G. L., Zuker C. S. The ninaA gene required for visual transduction in Drosophila encodes a homologue of cyclosporin A-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):67–70. doi: 10.1038/338067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara T., Dietzschold B., Craft C. M., Wistow G., Early J. J., Donoso L. A., Horwitz J., Tao R. Primary and secondary structure of bovine retinal S antigen (48-kDa protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6975–6979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker W. B., Donoso L. A., Kalsow C. M., Yankeelov J. A., Jr, Organisciak D. T. Experimental allergic uveitis. Isolation, characterization, and localization of a soluble uveitopathogenic antigen from bovine retina. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):1949–1958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Hall S. W., Kühn H. Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G. J., Katial A., Craft C., Shinohara T. Sequence analysis of bovine retinal S-antigen. Relationships with alpha-transducin and G-proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaki K., Takahashi Y., Sakuragi S., Matsubara K. Molecular cloning of the S-antigen cDNA from bovine retina. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):904–910. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaki K., Tsuda M., Shinohara T. The sequence of human retinal S-antigen reveals similarities with alpha-transducin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Inoue H., Hotta Y. Absence of phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase in the head of a Drosophila visual mutant, norpA (no receptor potential A). J Biochem. 1985 Apr;97(4):1251–1254. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman R., Cheasty J. E. A 48 kDa protein arrests cGMP phosphodiesterase activation in retinal rod disk membranes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman R., Cheasty J. E. Sites of arrestin action during the quench phenomenon in retinal rods. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 10;238(2):379–384. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S., Cowman A. F., Rubin G. M. Isolation and structure of a rhodopsin gene from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S., Montell C., Jones K., Laverty T., Rubin G. M. A rhodopsin gene expressed in photoreceptor cell R7 of the Drosophila eye: homologies with other signal-transducing molecules. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1550–1557. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01550.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]