Figure 7. AKT-dependent lymphocyte-induced PD-L1 upregulation on SCCs.
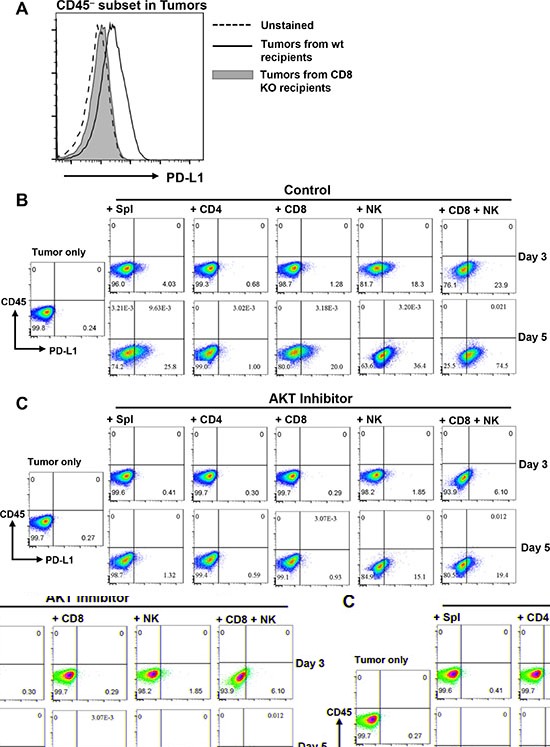
(A) PD-L1 expression on CD45− subset in tumors isolated from wt or CD8−/− recipients as indicated. Data are representative results from 3 independent experiments. (B) KRS-SCC tumor cells were cultured either alone (Tumor only) or with wt B6 splenocytes (Spl), CD4+, CD8+, NK or CD8+ plus NK cells for 3 or 5 days. Cultured cells were harvested and examined for CD45 vs PD-L1 expression via flow cytometry. (C) KRS-SCC tumor cells were cultured either alone (Tumor only) or with different subsets of lymphocytes as described above in the presence of AKT inhibitor (GSK690693, 10 μM). (D) The presence of SMAD4 protein was confirmed in Smad4 expressing SCC line (K5/S2) by western blot with mouse splenocytes (Spl control) as positive control, KRS-SCC as negative control and β-actin as loading control. (E) Smad4 expressing SCC tumor cell line was cultured either alone (Tumor cell line only) or with wt B6 splenocytes (Tumor + Spl) for 5 days. Cultured cells were harvested and examined for CD45 vs PD-L1 expression via flow cytometry. Data are representative results from more than three independent experiments for panel B–E.
