Abstract
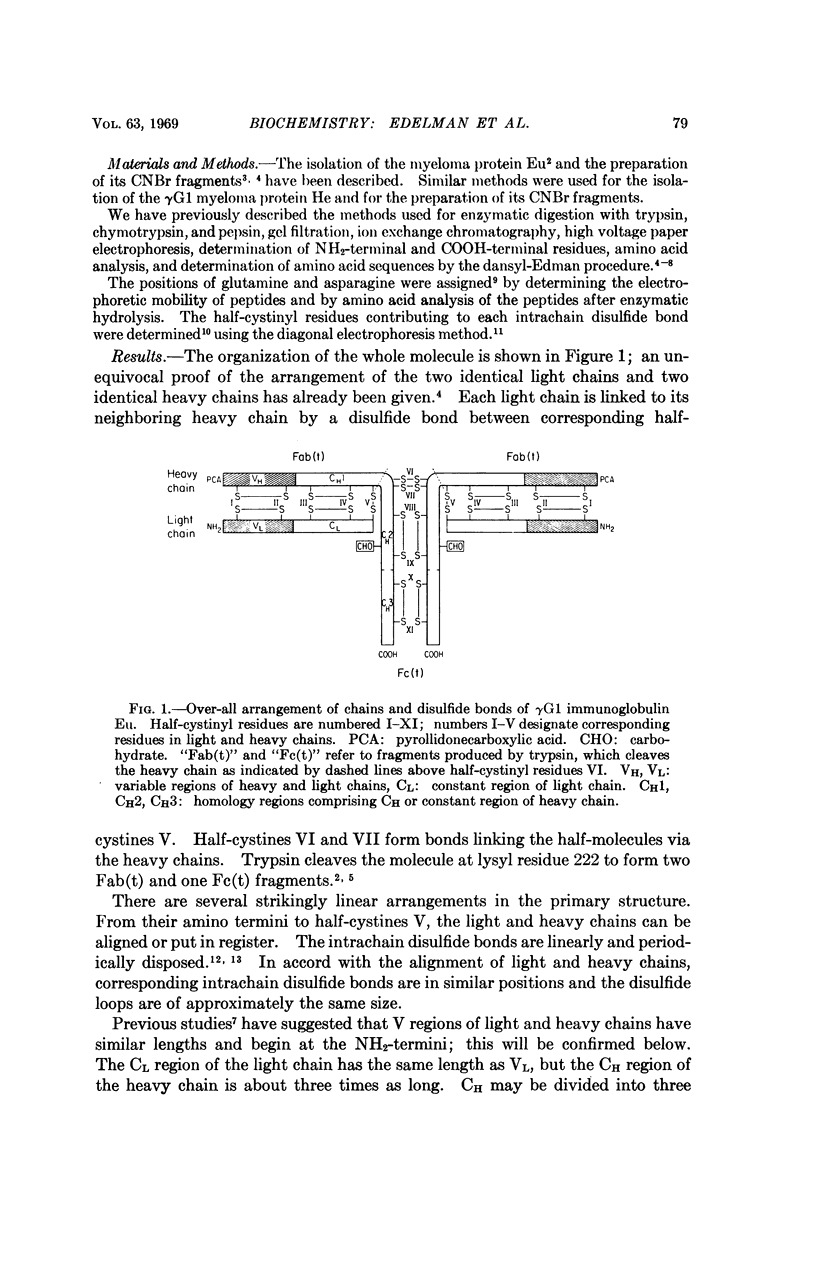
The complete amino acid sequence of a human γG1 immunoglobulin (Eu) has been determined and the arrangement of all of the disulfide bonds has been established. Comparison of the sequence with that of another myeloma protein (He) suggests that the variable regions of heavy and light chains are homologous and similar in length. The constant portion of the heavy chain contains three homology regions each of which is similar in size and homologous to the constant region of the light chain. Each variable region and each constant homology region contains one intrachain disulfide bond. The half-cystines participating in the interchain bonds are all clustered within a stretch of ten residues at the middle of the heavy chains.
These data support the hypothesis that immunoglobulins evolved by gene duplication after early divergence of V genes, which specified antigen-binding functions, and C genes, which specified other functions of antibody molecules. Each polypeptide chain may therefore be specified by two genes, V and C, which are fused to form a single gene (translocation hypothesis). The internal homologies and symmetry of the molecule suggest that homology regions may have similar three-dimensional structures each consisting of a compact domain which contributes to at least one active site (domain hypothesis). Both hypotheses are in accord with the linear regional differential of function in antibody molecules.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. R., Hartley B. S. Location of disulphide bridges by diagonal paper electrophoresis. The disulphide bridges of bovine chymotrypsinogen A. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):214–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1010214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catley B. J., Moore S., Stein W. H. The carbohydrate moiety of bovine pancreatic deoxyribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):933–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummingham B. A., Gottlieb P. D., Konigsberg W. H., Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. V. Partial amino acid sequence of the light chain. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1983–1994. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer W. J., Bennett J. C. The molecular basis of antibody formation: a paradox. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):864–869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Gall W. E., Waxdal M. J., Konigsberg W. H. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. I. Isolation and characterization of the whole molecule, the polypeptide chains, and the tryptic fragments. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1950–1958. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Gally J. A. Antibody structure, diversity, and specificity. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1968 Jun;21(2):328–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H. On the biological role of glycoproteins. J Theor Biol. 1966 Jan;10(1):89–113. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C., Pink J. R. Structural studies of immunoglobulin G. Nature. 1969 Jan 11;221(5176):145–148. doi: 10.1038/221145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall W. E., Cunningham B. A., Waxdal M. J., Konigsberg W. H., Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. IV. The interchain disulfide bonds. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1973–1982. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb P. D., Cunningham B. A., Waxdal M. J., Konigsberg W. H., Edelman G. M. Variable regions of heavy and light polypeptide chains of the same gammaG-immunoglobulin molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):168–175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. L., Delaney R., Fellows R. E., Lebovitz H. E. The evolutionary origins of the immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1762–1769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Ein D. Immunologlobulin lambda chain structure: two genes, one polypeptide chain. Nature. 1968 Nov 23;220(5169):764–767. doi: 10.1038/220764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Milstein C. P., Feinstein A. Non-allelic nature of the basic sequences of normal immunoglobulin K chains. Nature. 1969 Jan 11;221(5176):151–154. doi: 10.1038/221151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinck J. R., Milstein C. Disulphide bridges of a human immunoglobulin G protein. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):941–942. doi: 10.1038/216941a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Cunningham B. A., Bennett C., Konigsberg W. H., Edelman G. M. Amino acid sequence of the Fc region of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1414–1421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Doolittle R. F. Antibody active sites and immunoglobulin molecules. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):13–25. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Thorpe N. O. On the location and structure of the active sites of antibody molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner L. A., Porter R. R. The interchain disulfide bonds of a human pathological immunoglobulin. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3957–3970. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe N. O., Deutsch H. F. Studies on papain produced subunits of human gamma-G-globulins. II. Structures of peptides related to the genetic Gm activity of gamma-G-globulin Fc-fragments. Immunochemistry. 1966 Jul;3(4):329–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. W., Bennich H. Subfragments from the Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin G. Isolation and physicochemical charaterization. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(2):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj1070171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxdal M. J., Konigsberg W. H., Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. 3. Arrangement of the cyanogen bromide fragments. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1967–1972. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxdal M. J., Konigsberg W. H., Henley W. L., Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. II. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide fragments. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikler M., Köhler H., Shinoda T., Putnam F. W. Macroglobulin structure: homology of mu and gamma heavy chains of human immunoglobulins. Science. 1969 Jan 3;163(3862):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3862.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




