Abstract
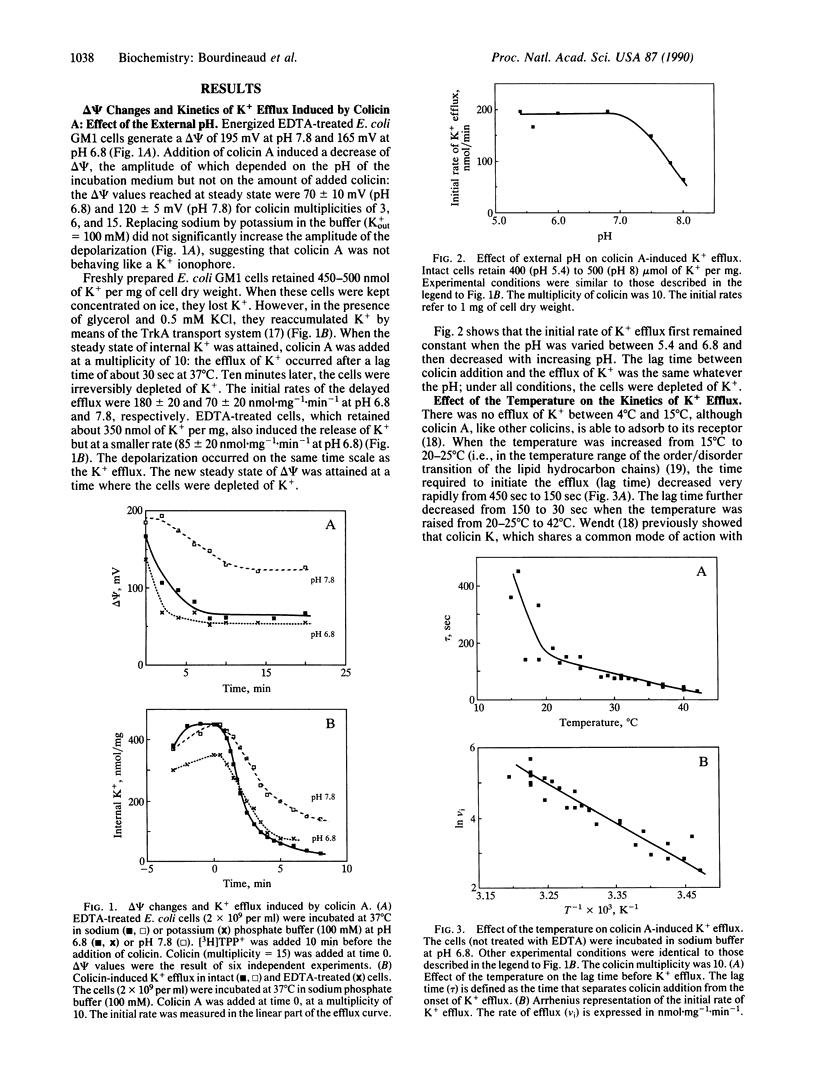
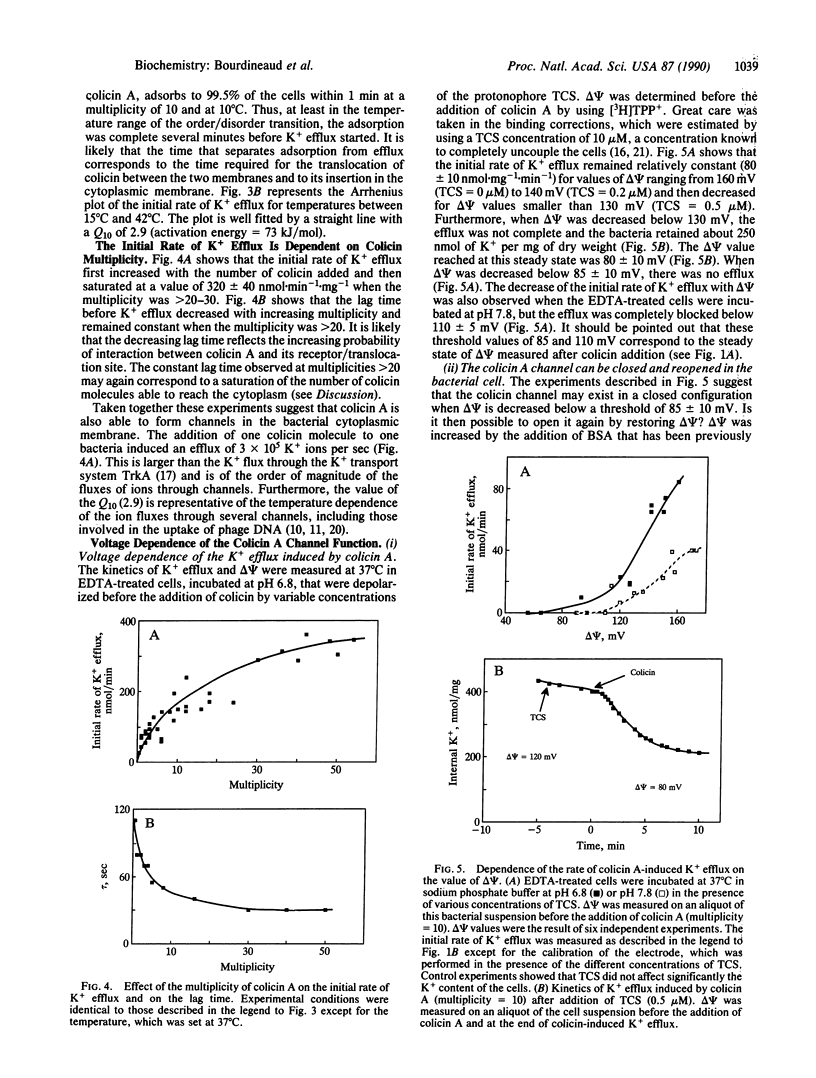
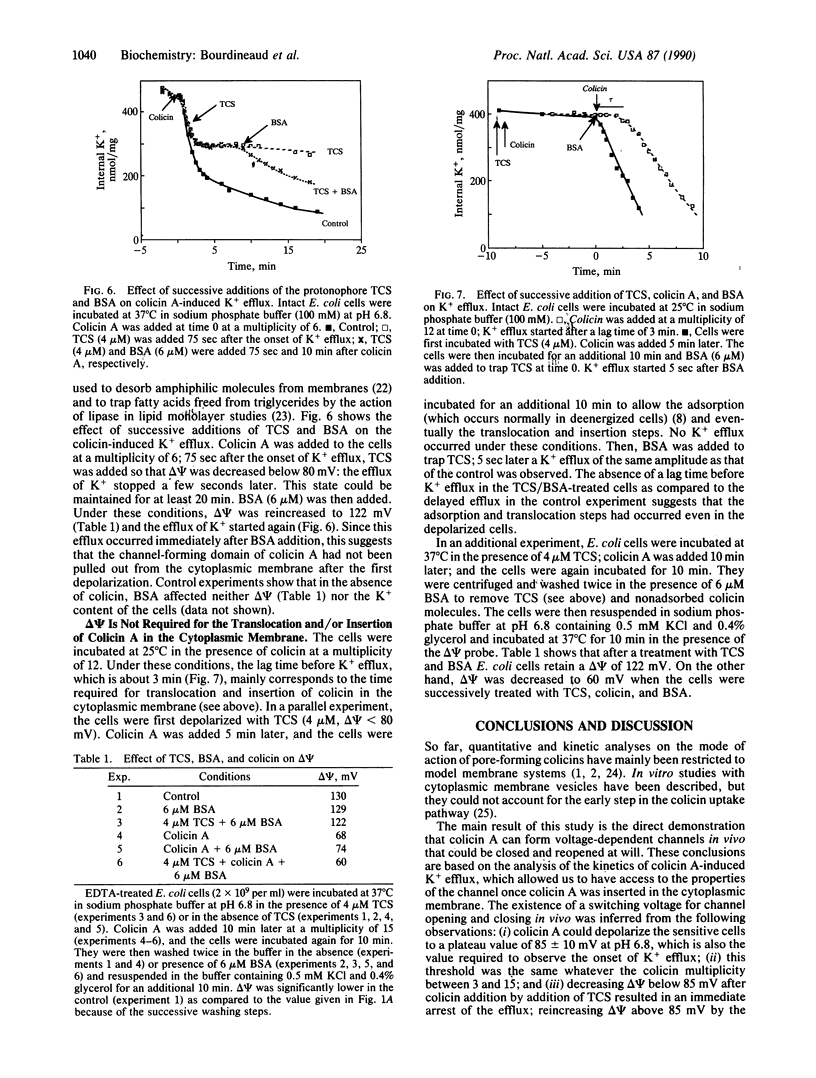
The kinetics of K+ efflux caused by colicin A in Escherichia coli-sensitive cells have been investigated by using a K(+)-selective electrode. The order of magnitude of the rate of K+ efflux per colicin molecule was comparable to that of ion channels. The dependence of K+ efflux upon multiplicity, pH, temperature, and membrane potential (delta psi) was determined. The translocation of colicin A from the outer membrane receptor to the inner membrane and insertion into the inner membrane required a fluid membrane, but once inserted, the channel properties showed little dependence upon the state of the lipids. At a given multiplicity, the lag time before the onset of K+ efflux was found to reflect the time required for translocation and/or insertion of colicin into the cytoplasmic membrane. Opening of the channel only occurred above a threshold value of delta psi of 85 +/- 10 and 110 +/- 5 mV at pH 6.8 and 7.8, respectively. Conditions were designed for closing and reopening of the channel in vivo. These conditions allowed us to test separately the delta psi requirements for translocation and channel opening: translocation and/or insertion did not appear to require delta psi. The channel formed in vivo featured properties similar to that of the channel in lipid planar bilayers.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baty D., Frenette M., Lloubès R., Geli V., Howard S. P., Pattus F., Lazdunski C. Functional domains of colicin A. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):807–811. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger P., Letellier L. Characterization of ion channels involved in the penetration of phage T4 DNA into Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9767–9775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruggemann E. P., Kayalar C. Determination of the molecularity of the colicin E1 channel by stopped-flow ion flux kinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4273–4276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Lazdunski C. J. Purification and molecular properties of a new colicin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collarini M., Amblard G., Lazdunski C., Pattus F. Gating processes of channels induced by colicin A, its C-terminal fragment and colicin E1 in planar lipid bilayers. Eur Biophys J. 1987;14(3):147–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00253839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Dankert J. R., Uratani Y. The membrane channel-forming bacteriocidal protein, colicin El. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):173–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenette M., Knibiehler M., Baty D., Géli V., Pattus F., Verger R., Lazdunski C. Interactions of colicin A domains with phospholipid monolayers and liposomes: relevance to the mechanism of action. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2509–2514. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazi A., Delamourd L., Shechter E. Absence of a unique relationship between active transport of lactose and protonmotive force in E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazi A., Schechter E., Letellier L., Labedan B. Probes of membrane potential in Escherichia coli cells. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80717-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould J. M., Cramer W. A. Studies on the depolarization of the Escherichia coli cell membrane by colicin E1. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5491–5497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Jetten M. E. Energy requirement for the initiation of colicin action in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 14;387(1):12–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J. Colicins and other bacteriocins with established modes of action. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:125–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B., Letellier L. Membrane potential changes during the first steps of coliphage infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):215–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski C. J., Baty D., Geli V., Cavard D., Morlon J., Lloubes R., Howard S. P., Knibiehler M., Chartier M., Varenne S. The membrane channel-forming colicin A: synthesis, secretion, structure, action and immunity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 11;947(3):445–464. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letellier L., Boulanger P. Involvement of ion channels in the transport of phage DNA through the cytoplasmic membrane of E. coli. Biochimie. 1989 Jan;71(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(89)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkhosyan S. R., Rekesh A. N. The effect of nonreceptor adsorption on the lethal action of colicin E1. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez M. C., Lazdunski C., Pattus F. Isolation, molecular and functional properties of the C-terminal domain of colicin A. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1501–1507. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K. Requirement of heat and metabolic energy for the expression of inhibitory action of colicin K. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 6;389(2):370–379. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. W., Pattus F., Tucker A. D., Tsernoglou D. Structure of the membrane-pore-forming fragment of colicin A. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):93–96. doi: 10.1038/337093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattus F., Cavard D., Crozel V., Baty D., Adrian M., Lazdunski C. pH-dependent membrane fusion is promoted by various colicins. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2469–2474. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Waters F. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VIII. Potassium transport mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):325–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J. C., Eccleston J. F., Barchi R. L. Cation selectivity characteristics of the reconstituted voltage-dependent sodium channel purified from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7519–7526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Konisky J. Effect of colicins Ia and E1 on ion permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6167–6171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsapis A., Kepes A. Transient breakdown of the permeability barrier of the membrane of Escherichia coli upon hypoosmotic shock. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 15;469(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt L. Mechanism of colicin action: early events. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1236–1241. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1236-1241.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



