Abstract
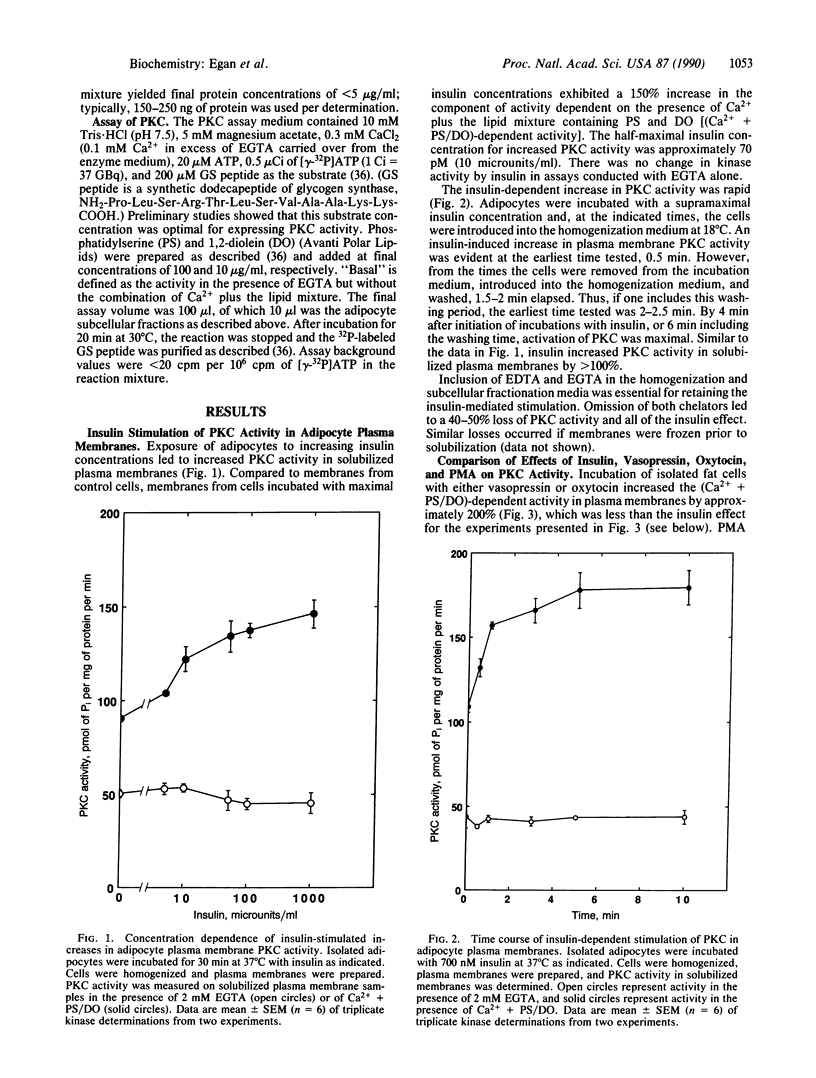
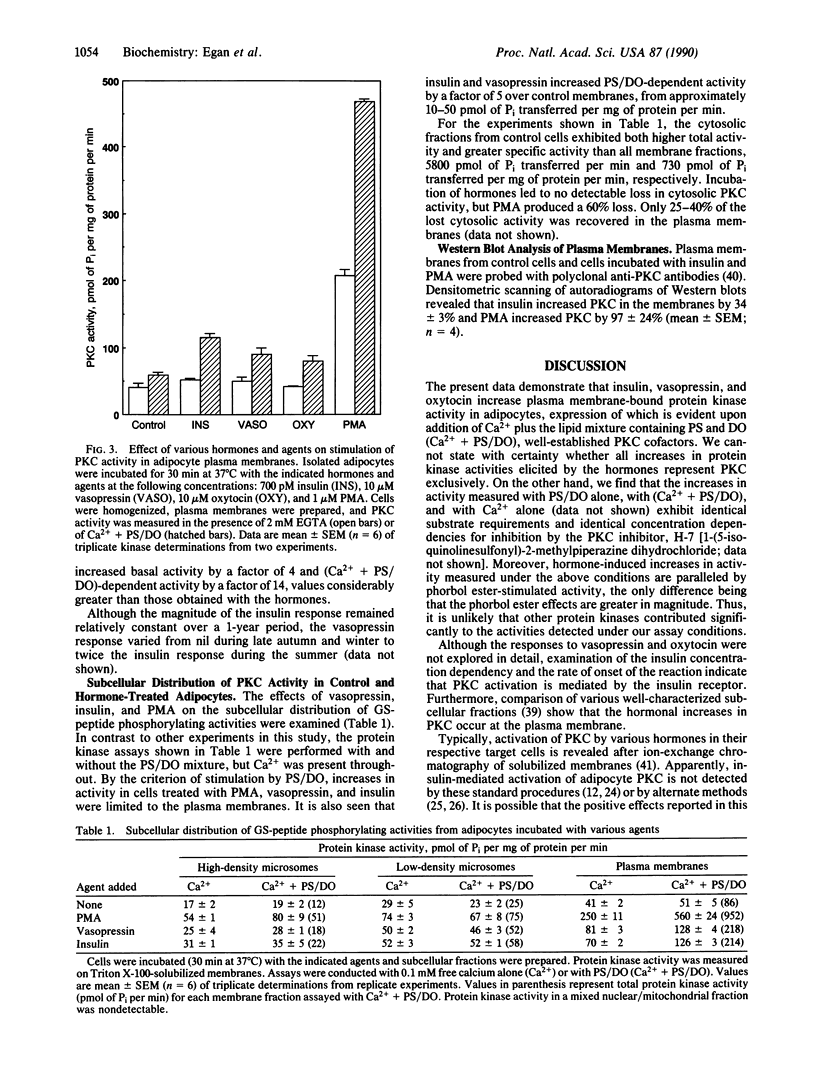
Incubation of isolated rat adipocytes with insulin, vasopressin, or oxytocin increased plasma membrane-bound protein kinase C (PKC) activity by 100-400%. PKC activity was assayed by a procedure that is virtually background-free, thus permitting assay of protein kinase activity in highly diluted samples of solubilized membranes. Hormone-dependent increases in PKC activity were limited to plasma membranes. Stimulation of the kinase was half-maximal with 70 pM insulin, and the hormone effect was rapid. Oxytocin and vasopressin produced effects on PKC similar to insulin, but the magnitude of the vasopressin stimulation exhibited seasonal variations. Treatment of cells with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) resulted in a loss of PKC activity from the cytosol and a gain in plasma membrane activity, indicative of translocation of the enzyme. With activity measurements it was not possible to determine if insulin stimulated a translocation of the kinase. However, Western blot analysis of plasma membranes with polyclonal antibodies directed against PKC suggest that at least some of the insulin-stimulated PKC activity resulted from enzyme translocation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P. H., Richelsen B., Juhl H. Evidence that phorbol ester-activated pathways are not directly involved in the action of insulin in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90666-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augert G., Exton J. H. Insulin and oxytocin effects on phosphoinositide metabolism in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3600–3609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Witters L. A., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Quamo S. N. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13304–13315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherqui G., Caron M., Wicek D., Lascols O., Capeau J., Picard J. Insulin stimulation of glucose metabolism in rat adipocytes: possible implication of protein kinase C. Endocrinology. 1986 May;118(5):1759–1769. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-5-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Peterson-Yantorno K., O'Brien T. G. Insulin and phorbol ester stimulate conductive Na+ transport through a common pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):963–967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Konda T. S., Standaert M. L., Davis J. S., Pollet R. J., Farese R. V. Insulin increases membrane and cytosolic protein kinase C activity in BC3H-1 myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3633–3639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W. Structure-function relationships in the adipose cell. I. Ultrastructure of the isolated adipose cell. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):326–341. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin B., Leitner J. W., Sussman K. E., Sherman N. A. Insulin and glucose modulate protein kinase C activity in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):570–575. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80880-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. J., Chang M. K., Londos C. A tandem chromatographic column method for assaying cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C with synthetic peptide substrates. Anal Biochem. 1988 Dec;175(2):552–561. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90583-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Davis J. S., Barnes D. E., Standaert M. L., Babischkin J. S., Hock R., Rosic N. K., Pollet R. J. The de novo phospholipid effect of insulin is associated with increases in diacylglycerol, but not inositol phosphates or cytosolic Ca2+. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):269–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2310269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Konda T. S., Davis J. S., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J., Cooper D. R. Insulin rapidly increases diacylglycerol by activating de novo phosphatidic acid synthesis. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):586–589. doi: 10.1126/science.3107122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Kuo J. Y., Babischkin J. S., Davis J. S. Insulin provokes a transient activation of phospholipase C in the rat epididymal fat pad. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8589–8592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Standaert M. L., Barnes D. E., Davis J. S., Pollet R. J. Phorbol ester provokes insulin-like effects on glucose transport, amino acid uptake, and pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in BC3H-1 cultured myocytes. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2650–2655. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A., Fain J. N. Effect of insulin, catecholamines and calcium ions on phospholipid metabolism in isolated white fat-cells. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):781–789. doi: 10.1042/bj1860781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn B. P., Colliton J. W., McDermott J. M., Witters L. A. Phorbol esters, but not insulin, promote depletion of cytosolic protein kinase C in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):1119–1125. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves C. B., McDonald J. M. Insulin and phorbol ester stimulate phosphorylation of a 40-kDa protein in adipocyte plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11286–11292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Becton D. L., Somers S. D., Gray P. W., Adams D. O. Interferon-gamma modulates protein kinase C activity in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1378–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanif K., Goren H. J., Hollenberg M. D., Lederis K. Oxytocin action. Mechanisms for insulin-like activity in isolated rat adipocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):381–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Hardie D. G. Insulin and phorbol ester stimulate phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase at similar sites in isolated adipocytes. Lack of correspondence with sites phosphorylated on the purified enzyme by protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heasley L. E., Johnson G. L. Regulation of protein kinase C by nerve growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and phorbol esters in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8646–8652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Earp H. S., Harden T. K. Long-term phorbol ester treatment down-regulates protein kinase C and sensitizes the phosphoinositide signaling pathway to hormone and growth factor stimulation. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C in agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7610–7619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., García-Sáinz J. A. Phorbol esters and calcium-mobilizing hormones increase membrane-associated protein kinase C activity in rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 18;968(1):138–141. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman T. W., Strohsnitter W., Scheid C. R., Schimmel R. J. Phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylinositol labelling in adipose tissue. Relationship to the metabolic effects of insulin and insulin-like agents. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):489–498. doi: 10.1042/bj2120489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honnor R. C., Dhillon G. S., Londos C. cAMP-dependent protein kinase and lipolysis in rat adipocytes. I. Cell preparation, manipulation, and predictability in behavior. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15122–15129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P., Huang F. L. Immunochemical characterization of rat brain protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14781–14787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Ramlal T., Koivisto U. M. Stimulation of Na+/H+ exchange by insulin and phorbol ester during differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. Relation to hexose uptake. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):296–304. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepfer-Hobelsberger B., Wieland O. H. Insulin activates phospholipase C in fat cells: similarity with the activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Jun;36(1-2):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Membrane effects of tumor promoters: stimulation of sugar uptake in mammalian cell cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Jun;99(3):451–460. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. J., Dubyak G. R., Moore R. M., Vander Kooy D. Oxytocin activates the inositol-phospholipid-protein kinase-C system and stimulates prostaglandin production in human amnion cells. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):1771–1777. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-1771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlbacher C., Karnieli E., Schaff P., Obermaier B., Mushack J., Rattenhuber E., Häring H. U. Phorbol esters imitate in rat fat-cells the full effect of insulin on glucose-carrier translocation, but not on 3-O-methylglucose-transport activity. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):865–870. doi: 10.1042/bj2490865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington S. R., Martin B. R. Insulin-stimulated phosphoinositide metabolism in isolated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11039–11045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pershadsingh H. A., Shade D. L., McDonald J. M. Insulin-dependent alterations of phorbol ester binding to adipocyte subcellular constituents. Evidence for the involvement of protein kinase C in insulin action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 30;145(3):1384–1389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91591-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. G., DiGirolamo M., Merrill A. H., Jr, Lambeth J. D. Insulin-stimulated hexose transport and glucose oxidation in rat adipocytes is inhibited by sphingosine at a step after insulin binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6773–6779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Jones A. B. Metabolism of isolated fat cells. 3. The similar inhibitory action of phospholipase C (Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin) and of insulin on lipolysis stimulated by lipolytic hormones and theophylline. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):140–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Vasopressin rapidly stimulates protein kinase C in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Oct;129(1):124–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Sherline P., Fox J. A. Insulin-stimulated diacylglycerol production results from the hydrolysis of a novel phosphatidylinositol glycan. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1116–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund G., Hansson A., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Rapid effects of phorbol esters on isolated rat adipocytes. Relationship to the action of protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):407–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smal J., De Meyts P. Role of kinase C in the insulin-like effects of human growth hormone in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):1232–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smal J., De Meyts P. Sphingosine, an inhibitor of protein kinase C, suppresses the insulin-like effects of growth hormone in rat adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4705–4709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommercorn J., Mulligan J. A., Lozeman F. J., Krebs E. G. Activation of casein kinase II in response to insulin and to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8834–8838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Activation of S6 kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. P., Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Hormone- and tumor promoter-induced activation or membrane association of protein kinase C in intact cells. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:399–411. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Horn R. S., Adler A., Albert K. A., Walaas O. Insulin increases membrane protein kinase C activity in rat diaphragm. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 17;220(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80837-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. R., Pluznik D. H., Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Antigen-induced increase in protein kinase C activity in plasma membrane of mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8193–8197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Khalaf N., Czech M. P. Insulin stimulates a membrane-bound serine kinase that may be phosphorylated on tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3972–3976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Werve G., Proietto J., Jeanrenaud B. Tumour-promoting phorbol esters increase basal and inhibit insulin-stimulated lipogenesis in rat adipocytes without decreasing insulin binding. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 15;225(2):523–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2250523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



