Abstract
Engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) are key drivers for the development of highly sophisticated new technologies. As all new attainments, the rapidly increasing used of ENMs raise concerns about their safety for the environment and humans. There is growing evidence showing that if engineered nanomaterials are released into the environment, there is a possibility that they could cause harm to aquatic microorganisms. Among the divers effects triggering their toxicity the ability of ENMs to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) capable of oxidizing biomolecules is currently considered a central mechanism of toxicity. Therefore, development of sensitive tools for quantification of the ROS generation and oxidative stress are highly sought. After briefly introducing ENMs-induced ROS generation and oxidative stress in the aquatic microorganisms (AMOs), this overview paper focuses on a new optical biosensor allowing sensitive and dynamic measurements of H2O2 in real-time using multiscattering enhanced absorption spectroscopy. Its principle is based on sensitive absorption measurements of the heme protein cytochrome c whose absorption spectrum alters with the oxidation state of constituent ferrous FeII and ferric FeIII. For biological applications cytochrome c was embedded in porous random media resulting in an extended optical path length through multiple scattering of light, which lowers the limit of detection to a few nM of H2O2. The sensor was also integrated in a microfluidic system containing micro-valves and sieves enabling more complex experimental conditions. To demonstrate its performance, abiotic absorption measurements of low concentrations of dye molecules and 10 nm gold particles were carried out achieving limits of detection in the low nM range. Other biologically relevant reactive oxygen species can be measured at sub-μM concentrations, which was shown for glucose and lactate through enzymatic reactions producing H2O2. In ecotoxicological investigations H2O2 excreted by aquatic microorganisms exposed to various stressors were measured. Pro-oxidant effects of nano-TiO2 and nano-CuO towards green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii were explored in various exposure media and under different light illuminations. Dynamics of Cd2+ induced effects on photosynthetic activity, sensitisation and recovery of cells of C. reinhardtii was also studied.
Keywords: Ecotoxicity, Nanomaterials, Reactive oxygen species, Oxidative stress, Hydrogen peroxide, Optical biosensor, Multiscattering, Absorption spectroscopy
Background
The material revolution engendered by nanotechnological advances in the last decades has not only enabled the development of highly sophisticated fine-tuned materials for new applications but also confronted established risk assessment and regulatory affairs with new challenges: the possible (eco-)toxicological implications of the expected increment of engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) discharged into environmental compartments [1].
Natural water bodies, one environmental sink of discharged ENMs, are estimated to receive 0.4–7% of the total global mass flow of ENMs [2]. Once in the aquatic systems ENMs interact with different biotic and abiotic components and potentially harm different organisms [3]. There is currently an agreement [4] that three major phenomena drive the detrimental effects of the ENMs to aquatic organisms: (i) their dissolution, (ii) their organism-dependent cellular uptake and (iii) the induction of oxidative stress and consequent cellular damages. The ability of ENMs to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) capable of oxidizing biomolecules is currently considered a central (but by no means sole) mechanism of toxicity, potentially leading to oxidative stress and damage (Fig. 1) [5–12].
Fig. 1.
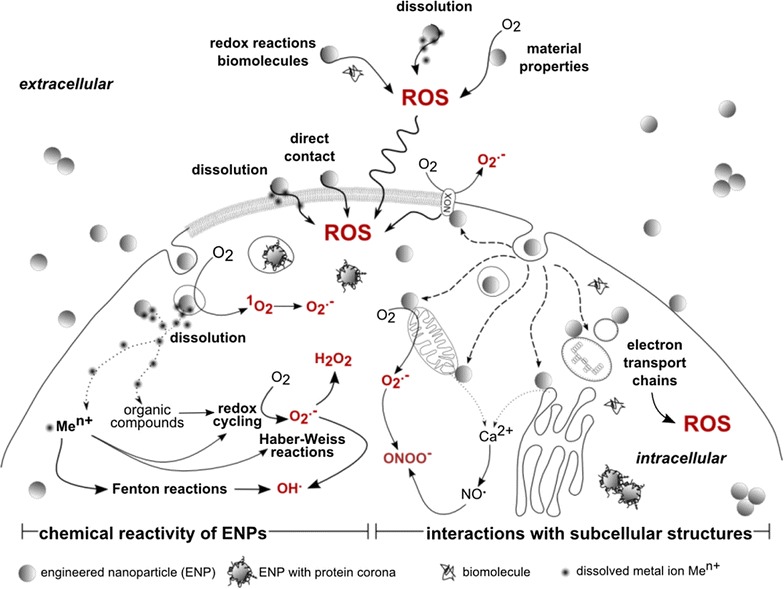
Mechanisms of ROS generation by engineered nanomaterials via intracellular chemical reactivity (left hand side) or via physical interactions with subcellular compartments (right hand side). ENPs generate ROS by direct and indirect chemical reactions. Direct reactions involve the photoexcitation of O2, which yields singlet oxygen (1O2) and superoxide (O·−2). Indirect chemical reactions involve reactions between leached ENP constituents (e.g. metal ions, organic compounds) that engage in redox cycling that yields superoxide (O·−2) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or in hydroxyl radical (OH·) producing Fenton and Haber–Weiss reactions. ROS yielding interactions encompass the interference with electron transfer chains in chloroplasts, peroxisomes, mitochondria and the endoplasmatic reticulum. Furthermore, interactions of ENPs and mitochondria or the endoplasmatic reticulum can also cause a loss of organelle membrane integrity that triggers the release of Ca2+ ions from interior stores, which may activate ROS generating Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent enzymes, i.e. certain nitrogen monoxide synthase isoforms that produce NO·. Interactions with NADPH oxidase (NOX) complexes in the cell membrane yield O·−2 [29]. Illustration adapted from Unfried, Albrecht [29], not to proportion.
Reprinted with permission from (Nanotoxicology 2014; 8: 605–630). Copyright (2014)
It is postulated that increased levels of ROS and oxidative damage will occur in exposed organisms (despite the presence of basal or enhanced antioxidant defence systems of repair and replacement), which may be linked to some aspect of impaired biological functions at cellular or higher levels of organization [13]. Thus, from the nanoecotoxicological perspective seeking the elucidation of environmental hazards of ENMs, it follows that an in-depth understanding of their toxic mode of action, that is, of normal and ENM-stimulated ROS production as well as antioxidant levels in aquatic organisms is required. This will allow to quantitatively link the presence of ENMs with pro-oxidant processes and to estimate the expected degree by which ENM-stimulated oxidative damage may potentially affect overall health of organism.
Hence, there has been a keen interest in the detection and quantification of ROS in aqueous and biological systems, which is a technically tricky task due to their very low concentration in the pico- to micromolar range and their extremely short-lived nature with half times ranging from nanoseconds to hours [14]. Most conventional ROS sensing methods rely on exogenous probes or resulting endogenous reaction products and molecular biomarkers reflecting oxidative damage and antioxidant status [13, 15–17]; they suffer one major technical drawback—the invasive nature of the detection method itself [18].
The present article provides an overview of the main findings of the project “Non-invasive continuous monitoring of the interaction between nanoparticles and aquatic microorganisms” within in the framework of the Swiss National Research Program 64 on the Opportunities and Risk of Nanomaterials. The review begins with a brief introduction in the ENMs-induced ROS generation and oxidative stress in the aquatic microorganisms (AMOs) as well as short presentation of the existing detection techniques. The newly developed method for non-invasive quantification of extracellular H2O2 in real-time and monitoring with an unprecedented limit of detection is described, while its capabilities are illustrated by exploring the pro-oxidants effects of the ENMs to AMOs [18].
ENMs and oxidative stress in aquatic microorganisms
Investigations performed in the mid-90’s led to the conclusion that nanoparticles have the ability to stimulate the generation of reactive oxygen (ROS) and nitrogen species (RNS) at or near the cell surface and to induce oxidative stress [10, 12, 19]. The oxidative stress hypothesis was successfully expanded into nanotoxicology and recognised as a major mechanism for nanoparticle induced effects [23]. Therefore, the impacts of ENMs on the pro-oxidant/antioxidant equilibrium can provide relevant information on their ecotoxicical importance [5].
The toxicity of metal and metal oxide ENMs to organisms can be classified in direct and indirect effects [20, 21]. Direct toxic effects are principally controlled by their chemical composition and surface reactivity. Indirect effects are mainly governed by physical restraints, the release of toxic ions or the production of ROS. The latter is thought to result in elevated cellular response classified as defence, pro-inflammatory effects and cytotoxicity [22]. Toxicological effects of ENMs may include (i) inflammation related to generation of ROS and oxidative stress, depletion of glutathione and accumulation of oxidised glutathione in response to ROS generation, (ii) DNA and membrane damage, protein denaturation and immune reactivity, (iii) reduction or loss in photosynthetic activity in algae and plants. Direct toxic effects require, as a prerequisite, contact and adsorption of the ENMs with the AMOs [3, 23]. Once the ENMs are adsorbed, they may penetrate through the biological membrane and, therefore, be internalised (Fig. 2). Uptake mechanisms and different pathways leading to internalisation are discussed elsewhere [3, 4, 24]. It is important to note that ENMs can be internalised without necessarily inducing cytotoxicity, meaning that ENMs are not toxic per se [25]. However, ENMs are prone to adsorption of ambient pollutants, which can be transferred into the cells by ENMs acting as carriers (Trojan Horse effect). ENMs can trigger ROS formation extra- and intracellularly by direct and indirect chemical reactions [12] (Fig. 1). The mechanisms underlying the generation of the ROS in AMOs could involve (i) the release of metal ions from ENMs, (ii) the catalytic activity of ENMs and (iii) the redox properties at the particle surface. The pro-oxidant potential of ENMs strongly dependent of their chemical and physical properties, notably chemical composition and purity, particle size, shape and the resulting relative large reactive surface area and surface chemistry [7, 14]. For metal- containing ENMs, dissolution processes leading to ion release play a major role in terms of ecotoxicity. Many transition metal ions, such as Fe3+, Cu2+, Cr3+ are redox active and some of them, e.g. Fe and Cu can catalyse Fenton reactions yielding biologically highly reactive hydroxyl radicals OH·. The Haber–Weiss reactions in the presence of super oxide ions O2 − can also reduce redox-active metal ions which further couple to the Fenton reactions. Hence, valence state and bioavailability of redox-active ions are strongly related to the generation of ROS. Numerous inorganic ENMs, such as Ag, Pt, TiO2, CeO2, ZnO, CuO, SiO2 and different quantum dots were shown to generate ROS and induce oxidative stress in different organisms [5, 10, 12, 26–30]. Selected examples concerning ENM-induced oxidative stress or damage in microalgae, representative for aquatic phytoplankton are given in Table 1.
Fig. 2.
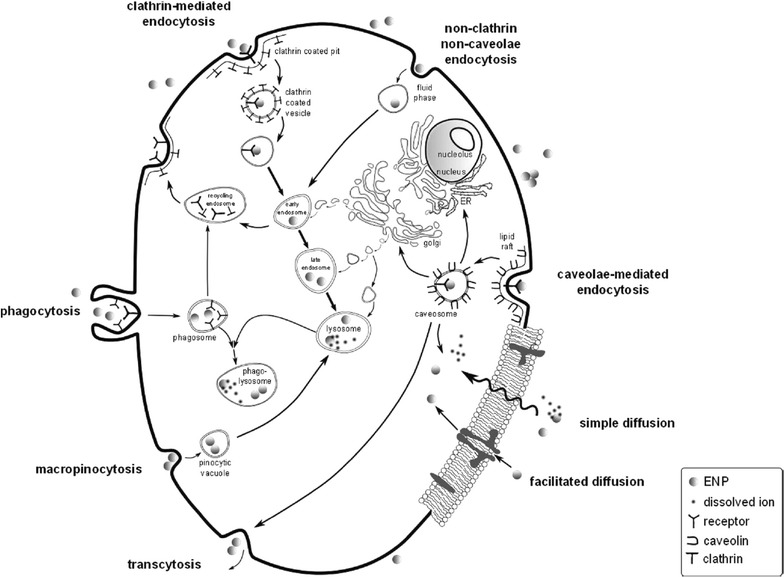
Active and passive cellular uptake pathways for ENMs in eukarotic cells. Passive uptake occurs via diffusion and facilitated diffusion via transport proteins, i.e. gated channel proteins and carrier proteins. Active uptake pathways involve transmembrane carrier proteins and endocytic pathways including receptor-mediated phagocytosis, clathrin-mediated endocytosis (120 nm, via clathrin-coated pits) and caveolae-mediated endocytosis (60 nm, via lipid rafts), non-specific endocytosis by macropinocytosis and non-clathrin, non-caveolae endocytosis (90 nm, fluid phase). All pathways except caveolae-mediated endocytosis and diffusion merge with the lysosomal degradation system comprising numerous vesicle maturation steps within the cell. A lysosome typically ranges from 200 to 500 nm in diameter. Phagocytosis is mediated by specific membrane-receptors that are activated upon contact with a ligand to produce phagosomes (>250 nm). During their maturation process, phagosomes transform into late phagosomes, which fuse with lysosomes to form phagolysosomes. During macropinocytosis, internalisation occurs via an unspecific invagination resulting in pinocytic vesicles (<150 nm), which eventually merge with lysosomes. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis and non-clathrin, non-caveolae-mediated endocytosis produces caveosomes that either transfer their contents into the Golgi apparatus, endoplasmatic reticulum (ER) or into the cytosol or may also undergo transcytosis.
Reprinted with permission from (Environmental Science-Nano 2014; 1: 214–232). Copyright (2014) Royal Society of Chemistry
Table 1.
Selected examples of ENM-induced oxidative stress or damage in microalgae
| ENM | Algae | Media | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | C. reinhardtii | SE | Generation of ROS by photocatalysis | [31] |
| TiO2 and UV light | C. reinhardtii | Lake water and MOPS buffer | [32] | |
| TiO2 | Chlorella sp. | OECD | Generation of intracellular ROS by HA | [33] |
| CdTe/CdS | C. reinhardtii | MES, MOPS, HEPES | Oxdative stress | [34] |
| Al2O3, SiO2, ZnO and TiO2 | Chlorella sp. | SE | ROS may not be the dominant mechanism for algal growth inhibition | [35] |
| Ag | C. vulgaris, Dunaliella tertiolecta | Growth medium BG-11 | ROS induced lipid peroxidation and a decrease of cell viability | [36] |
| Pt |
C. reinhardtii
P. subcapitata |
ISO 8692 medium and 4-fold diluted tris-acetate-phosphate medium | Substantial oxidative stress and negligible membrane damage; significant growth inhibition | [30] |
| Coated and uncoated CuO | C. reinhardtii | High salt medium | ROS formation may be the primary toxicity mechanism | [37] |
| CeO2 | P. subcapitata | Standard US EPA | The oxidative activity is mediated by OH and initiation of lipid peroxidation | [38] |
| Core–shell CuO | C. reinhardtii | High salt growth medium | ROS are responsible for chlorophyll deterioration, significant decrease of PSII primary photochemistry | [39] |
| CuO | C. reinhardtii | Various media, lake water | Oxidative stress and damage of membrane integrity | [40] |
| CuO and light | C. reinhardtii | Synthetic fresh water | Chlorophyll bleaching, oxidative stress and membrane damage; CuO and UV-light has synergistic effect | [41] |
| TiO2, CdTe and QDs | C. reinhardtii | CM growth medium | Lipid peroxidation induced by oxidative stress, QDs and TiO2 exhibit different mechanisms | [42] |
Photoactive ENMs including fullerenes and semiconducting metal oxides, such as TiO2, CuO, CeO2, ZnO and Al2O3, can generate ROS when illuminated [43, 44]. It has been demonstrated that these ENMs, the most prominent being TiO2, can activate molecular oxygen radicals, 1O2 and O2 −, which belong, together with OH·, to the biologically most potent ROS. It is well known that those photoactive particles are primarily active at wavelength in the UV regime (<390 nm) but it has also been demonstrated in several studies that TiO2 is capable to induce oxidative stress in the absence of light.
Overall, environmental contaminants, including ENMs, have the capability to induce generation of ROS in AMOs and, consequently, to alter the cellular redox homeostasis leading to oxidative stress. Oxidative stress occurs as a result of (i) increase in oxidant generation, (ii) reduction of antioxidant protection and (iii) failure to repair oxidative damage [45].
Towards development of the novel tool for non-invasive monitoring of the pro-oxidant effects of engineered nanomaterials
Various approaches are available to determine oxidative stress [46]: (i) Quantification of radicals, including O2 −, OH· and H2O2, (ii) quantification of oxidative damage markers and (iii) quantification of antioxidants. A schematic illustration of the main approaches is displayed in Fig. 3. Superoxide O2 −, represents one of the aboriginal forms of aerobic ROS. It is very reactive and short-living and can be converted to H2O2 through the reaction with SOD. H2O2 is one of the major and most stable ROS produced intracellularly by physiological and pathological processes and can cause oxidative damage. Its stability allows it to diffuse through the cell wall and can therefore be extracellularly detected [47]. Oxidative damage markers such as lipids, DNAs and proteins can be examined for alterations to quantify the extent of oxidative damage due to oxidative stress. Furthermore, several enzymes, such as SOD, CAT and GR, belonging to the antioxidative defence system, can be measured in order to quantify oxidative stress. Recent progress in fluorescent, luminescent and colorimetric ROS and RNS probes was comprehensively reviewed [48].
Fig. 3.
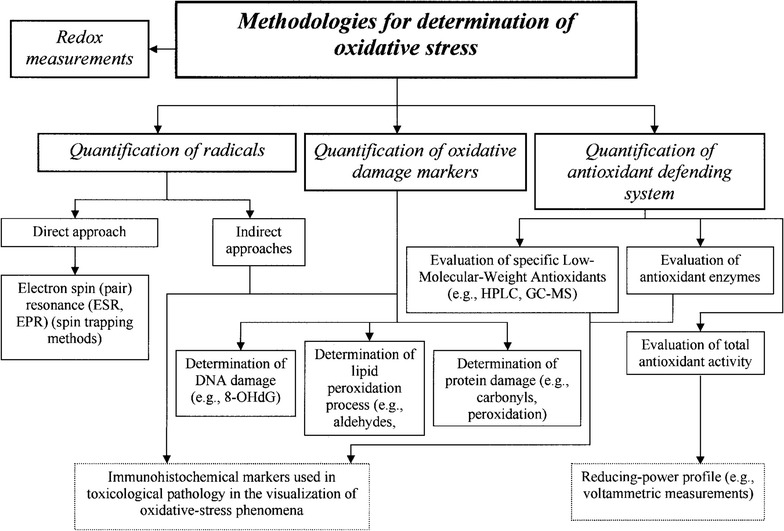
Classification of methods used to determine and quantify oxidative stress.
Reprinted with permission from (Toxicologic Pathology 2002; 30: 620–650). Copyright (2002) SAGE Publications
The above-mentioned oxidative stress “indicators” can provide a useful picture on the cell-ENM interactions. However, they are endpoint-based and qualitative, thus unable to provide quantitative information about the rate and amount of generated ROS. In addition they are often very laborious and fail to provide dynamic and continuous information on specific physiological phenomena happening at the exposed living cells.
Hereinafter a new, very sensitive detection scheme for continuous measurement of extracellular H2O2 based on multiscattering enhanced absorption spectroscopy is present. Its high sensitivity allows non-invasive and real time measurements of H2O2 related to aerobic cell activity, including oxidative stress. Stress-induced H2O2 can rapidly diffuse across plasma membranes [49, 50], is relatively long-lived (half-life 4–20 h, <1 s in living tissues) and, therefore, extracellular H2O2 could serve as an indicator of pro-oxidant processes [51–54]. A non-exhaustive list of H2O2 detection methods can be found in Table 2.
Table 2.
Selection of H2O2 detection methods [14]
| Technique/probe | Observable | LOD | Application notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct detection | Absorbance of H2O2 | mM | [55, 56] | |
| Cyt c | Absorbance | nM | Optimal reaction in low ionic strength solutions | [57, 58] |
| Xylenolorange + Fe3+ | Absorbance of complex | μM | Carried out in acidic acids | [59] |
| Xylenolorange + Ti4+ | Absorbance of complex | μM | Carried out in acidic acids | [59] |
| Luminol | Chemi-luminescence | nM | Interference with Mn2+ and Fe3+ | [60–62] |
| 2,7-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein (DCFH) | Fluorescence of product | pM-nM | Can be oxidised by other ROS | [16, 63] |
| p-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid | Fluorescence of product | nM | Optimal reaction at pH > 8.5 | [64, 65] |
Fluorescent and chemi-luminescent methods exhibit low LODs in the nM range. However, a major drawback of those methods is their incompatibility with bioorganisms and they are therefore endpoint detection schemes.
Multiscattering enhanced absorption spectroscopy (MEAS)
Thanks to its versatility, absorption spectroscopy has become a popular method with a broad range of applications. Adsorption spectroscopy provides a fast, simple and inexpensive method for the detection of a wide variety of targets [66]. Absorption spectroscopy can be applied in wide spectral span ranging from X-ray [67] to infrared light [68] and provides a beneficial tool for investigating biomolecules [69, 70]. In conventional absorption spectroscopy configurations the spectral light intensity, passed through the sample under test, is measured and normalised with respect to the intensity of the incident light. Knowing the optical path length (OPL) l through the sample and the absorption coefficient α of the analyte of interest, its concentration can be determined using Beer-Lambert’s law (1) [71].
| 1 |
I0 and I represent the light intensity before and after travelling through the sample, respectively. Long OPLs requires large amounts of analytes which are often costly, especially for biosamples.
Significant efforts have been put in the development of various techniques aiming to improve the sensitivity of absorption spectroscopy [72–74]. A simple and versatile technique, was presented by Koman et al. [75]. In order to extend the OPL and, thus, the sensitivity, advantages were taken from disordered media where the OPL is increased via multiple scattering since spatial variations of the refractive index prevent the light to follow the shortest trajectory. In a configuration containing suspended polystyrene (PS) beads, as schematically shown in Fig. 4, the limit of detection (LOD) was improved substantially [75].
Fig. 4.
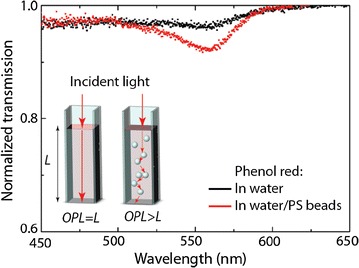
The presence of scatterers (500 nm polystyrene beads) in the MEAS configuration enhances the OPL and, consequently, lowers the LOD. Principle and transmission measurements of the absorption of phenol red in conventional and MEAS configurations.
Reprinted with permission from (Analytical Chemistry 2015; 87: 1536–1543). Copyright (2015) American Chemical Society
In order to demonstrate its performance MEAS was carried out on low concentrations of phenol red, envy green and 10 nm gold nanoparticles (AuNp). The absorbance A of standard and multiscattering experiments are displayed in Fig. 5 [75]. Using this approach, sensitivity and LOD of commercially available bioassays can be improved. This has been shown for OxiSelect, an assay for H2O2 detection [75].
| 2 |
Fig. 5.
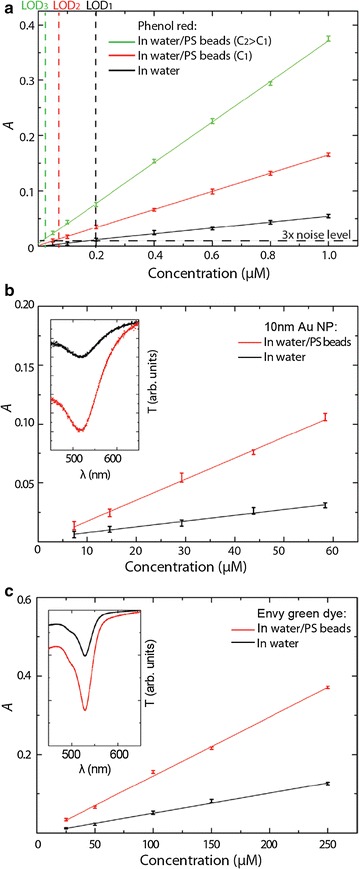
Absorption enhancement for a phenol red, b 10 nm Au NPs and c envy green for different concentrations C of 500 nm PS scatterers: C1 = 0.6 nM and C2 = 3 nM. The insets in b and c show the normalised transmission spectrum T and the LOD is defined as 3 times the noise level. The error bars correspond to the standard deviation over five independent measurements.
Reprinted with permission from (Analytical Chemistry 2015; 87: 1536–1543). Copyright (2015) American Chemical Society
According to Eq. (3) the sensitivity S for a certain analyte concentration becomes maximal. Hence, the OPL can be adjusted by selecting an adequate scatterer concentration and thereby optimised with respect to a specific application.
| 3 |
For a better understanding of the multiscattering phenomenon a probabilistic Monte Carlo approach was implemented (Fig. 6). Wavepackets are launched into the system containing randomly distributed PS beads. The random scattering angles were determined using Henyey-Greensteins approximation [76] which describes the scattering cross-section σ for an individual scatterer using Mie theory [77, 78]. The attenuation of each wavepacket was computed following Beer-Lambert’s law (1) and, finally, the residues of the individual wavepackets leaving the system were summed together. In order to achieve an appropriate accuracy the random trajectories of 108 wavepackets were calculated. The simulations showed excellent agreement with experimental results and allow prediction of OPLs for different concentrations, refractive indexes and sizes of the scatterers. Due to bead–bead interactions the proposed numerical approach is not accurate for high filling factors F [79] nevertheless, for F < 10% good numerical/experimental agreements were found [75].
Fig. 6.
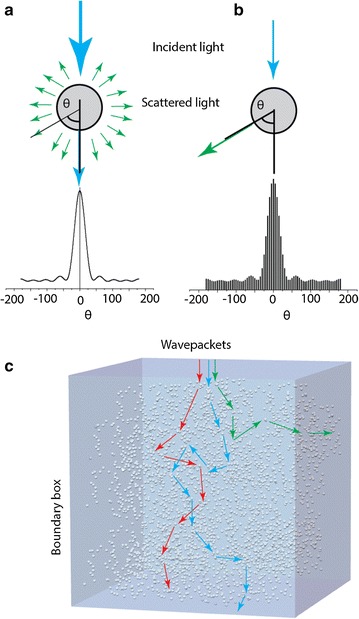
Schematic illustration of the numerical approach. a Intensity distribution of light scattered at a spherical object. b Intensity distribution of large amounts of wavepackets scattered at a spherical object. c Wavepackets travelling through a random media.
Reprinted with permission from (Analytical Chemistry 2015; 87: 1536–1543). Copyright (2015) American Chemical Society
Sensitive real-time detection of H2O2
MEAS was employed to improve the sensitivity for the detection of H2O2 in aqueous solutions. The detection principle is based on sensitive adsorption measurements of the heme protein cytochrome c (cyt c) [18], since the absorption spectrum of cyt c depends on the oxidation state of its heme group [80]. The catalytic redox behaviour of cyt c reduces H2O2 into water whereas the ferrous FeII heme group is oxidised into the ferric FeIII heme group providing information on the H2O2 concentration in its environment. Cyt c exhibits three oxidation state-dependent absorption peaks in the visible range, namely, at λ = 530 nm in the oxidised and λ = 520 and λ = 550 nm in the reduced state. The absorption at λ = 542 nm and λ = 556 nm provide adequate reference signals since at those wavelengths the absorption is independent of the oxidation state (Fig. 7). The sensing molecules, cyt c, were embedded in a porous matrix consisting of either aggregated PS beads or a filter membrane. The aggregates were prepared as follows: PS beads were suspended in an aqueous solution of cyt c prior to addition of glutaraldehyde to crosslink cyt c resulting in cyt c/PS beads aggregates [18]. Transmission measurements were performed using an inverted microscope and the temporal evolution of a normalised average oxidation state coefficient φ ranging from 0 to 1 for completely oxidised and reduced cyt c, respectively, was determined. Calibration experiments carried out for this configuration with known concentrations of H2O2 revealed a LOD below 100 pM which enables continuous measurements of the dynamics of ROS produced by bioorganisms when undergoing stress situations [18].
Fig. 7.
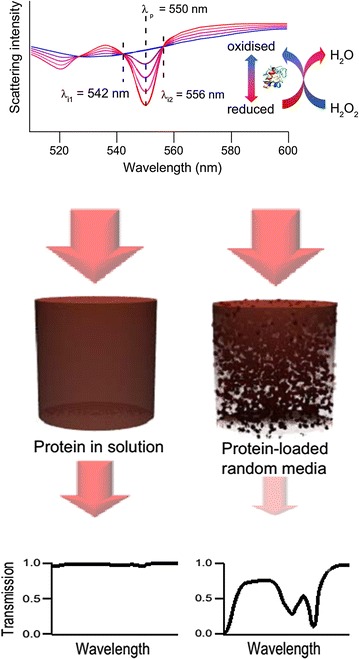
Spectrum of cyt c in its oxidised and reduced state. The intermediate states reflect an average value of oxidised and reduced cyt c. Absorption measurements in transmission configuration without and with multiscattering enhancement.
Reprinted with permission from (Scientific Reports 2013; 3: 3447). Copyright (2013) Nature Publishing Group
Since H2O2 is the reaction product of many enzymatic reactions [Eq. (4)] [81], its real-time detection combined with those reactions enables the detection of further metabolites such as glucose and lactate.
| 4 |
Koman et al. presented a detection scheme for sensitive and real-time detection of those metabolites [40]. Taking advantage of the above presented multiscattering approach they were detected with sub-micromolar LODs. Moreover, this enzymatic approach allows real-time measurements of multiple analytes in parallel which offers the possibility to follow the evolution of several metabolites. This feasibility has been demonstrated using the example of parallel detection of glucose and H2O2.
Portable setup and microfluidic chip
To step towards reliable and sensitive routine H2O2 measurements, a portable setup containing a multiscattering sensing element was built (Fig. 8) [82]. An aqueous solution of cyt c was spotted onto a porous filter membrane using a microarray robot with a delivery volume of 5 nl of 4 mM cyt c solution. Subsequently, the cyt c was crosslinked with vaporous glutaraldehyde in order to retain the cyt c in the membrane. Using the membrane approach the reproducibility of the amplification was remarkably improved compared to the aggregates described in the previous section. A closed chamber delimited by an o-ring and two glass cover slips was employed to carry out static experiments (Fig. 8a). The sensing element was placed at the bottom of the chamber prior to the measurements. Figure 9a shows the time evolution of φ in the static regime for different H2O2 concentrations in PBS buffer solution [82]. Measurements performed in this configuration exhibit a signal enhancement due to multiscattering, on the order of 5. In a further step the configuration was extended with a multi-layered microfluidic arrangement containing micro-valves and sieves [83], enabling more complex experimental sequences; for instance exposure/rinsing steps to study recovery or sensitisation of bioorganisms. Schematic overview and photographs of the principle of the portable oxidative stress sensor (POSS) are displayed in Fig. 10. The implementation of microsieves offers the possibility to perform experiments with non-adhering bioorganisms such as algae, which are retained in the reaction chamber as illustrated in Fig. 10h, i. The sensing element is placed in the microfluidic channel in order to minimise possible interferences between organisms and analytes. Figure 9b shows the differential oxidation state coefficient Δφ vs. H2O2 concentration for the static and microfluidic regime. Δφ defined as the difference between the initial value of φt = 0 and the value at time t: . The calibration curve resembles a sigmoidal shape when increasing H2O2 concentration, which is typical for ligand binding assays and can be fitted using a 4-parameter logistic model [84]. For the given configuration with a porous membrane a LOD of 40 nM of H2O2 was achieved [82]. Exposing the sensing element to reducing agents the cyt c alters from its ferric FeIII state to its ferrous FeII state. Hence, after reducing an oxidised sensing element can be reused. This has been shown by exposing the sensing spot to AA. Four consecutive oxidation/reduction cycles were carried out without lowering the performance of the sensor [82]. Furthermore, glucose and H2O2 and lactate and H2O2 were simultaneously measured adding glucose (GOx) and lactate oxidase (LOx), respectively, for the enzymatic conversion into H2O2 [Eq. (4)] [40]. Thus, to avoid that the fast conversion already takes place in the solution the oxidase was incorporated inside the sensing element. In practise, a mixture of oxidase and cyt c was deposited onto the filter membrane prior to crosslinking with glutaraldehyde, as described above for cyt c. An unambiguous measurement of glucose and lactate concentrations requires simultaneous measurements of the substrate (glucose and lactate in the present cases) and H2O2 with subsequent subtraction of the background H2O2 contribution. For the sake of completeness, it should be mentioned that, due to diffusion issues, interferences were observed when placing the sensing elements for the substrate and H2O2 in the same chamber. This problem was solved by adapting the microfluidic configuration to separate the sensing elements [40]. Finally, LODs as low as 240 and 110 nM for lactate and glucose, respectively, were achieved for the configuration at hand.
Fig. 8.
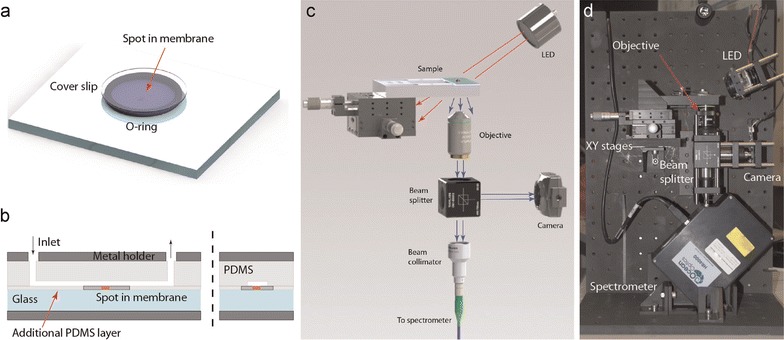
Portable setup (a) closed chamber for static measurements, b microfluidic channel for flow experiments, c schematic drawing of the portable setup and d front view photograph.
Reprinted with permission from (Biosensing and Bioelectronics 2015; 68: 245–252). Copyright (2015) Elsevier
Fig. 9.
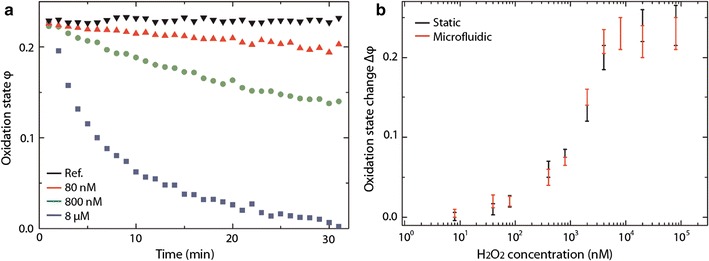
a Time evolution of the oxidation coefficient φ for different H2O2 concentrations in the static regime. b Differential oxidation coefficient Δφ vs. H2O2 concentration in the static and microfluidic regime.
Reprinted with permission from (Biosensing and Bioelectronics 2015; 68: 245–252). Copyright (2015) Elsevier
Fig. 10.
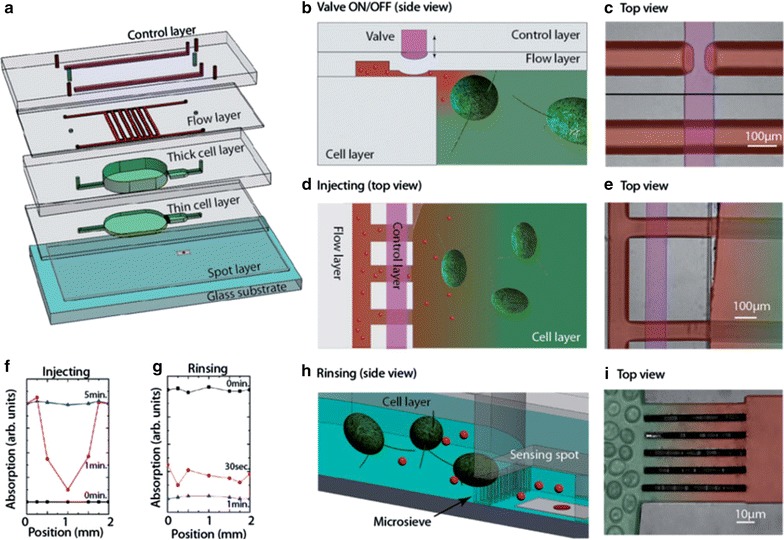
a Conceptual design of the multilayered microfluidic configuration, b–e principle of operation of the microfluidic valves, schematic drawings and photographs, f, g time evolution of the analyte concentration for filling and rinsing action, h, i schematic drawing and photograph of the micro sieve.
Reprinted with permission from (Nanotoxicology 2016; 10: 1041–1050). Copyright (2016) Taylor & Francis
Here ENM-induced H2O2 excretion by cells exposed to ENMs was monitored with a recently developed optical biosensor in a portable setup (POSS; portable oxidative stress sensor) specifically designed for field experimentation [82]. In this way, POSS may contribute to the elucidation of ENM-specific pro-oxidant interactions with cells and thus help to narrow the gap between material innovation and sound risk assessment.
Selected applications to probe the pro-oxidant effect of nanoparticles to microalga C. reinhardtii
To demonstrate the performances of the developed sensing tool, the pro-oxidant effects of CuO and TiO2 nanoparticles to green alga C. reinhardtii, a representative model AMO are presented [32, 85] together with measurements of the potential to generate abiotic ROS as well as oxidative stress and membrane damage. These two ENMs were chosen since they have different properties—CuO nanoparticles have a tendency to dissolve, while nano-TiO2 is rather inert; (ii) both have photocatalytic properties; (iii) nano-CuO is with relatively high toxic potential [86], while nano-TiO2 is moderately toxic; (iv) they are of high environmental relevance given their increasing use in different products.
The nanoparticle-induced cellular pro-oxidant process in C. reinhardtii were studied using the newly developed cytochrome c biosensor for the continuous quantification of extracellular H2O2 and fluorescent probes (CellRoxGreen for oxidative stress and propidium iodide for membrane integrity [32, 41, 87]) in combination with flow cytometry. Both the dynamics of abiotic (ENM only) and biotic (ENM + cells) pro-oxidant processes related to the exposure of C. reinhardtii to nano-CuO and nano-TiO2 are present below.
Nano-CuO
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii were exposed to CuO nanoparticles in five different media, namely TAP, MOPS, OECD, MES and Geneva lake water [85] and the biological responses including growth, size increase, chlorophyll autofluorescence, intracellular ROS and membrane damage were quantified.
The concentration of Cu ions dissolved from the nano-CuO in the different media increased in the order: MOPS < MES < Geneva lake water < OECD < TAP. Nano-CuO exposure induced oxidative stress and membrane damage, but the intensity of the effects was susceptible to medium and exposure duration [40]. Comparison of the exposure of C. reinhardtii to nano-CuO and released Cu2+ revealed that in all but one of the five different exposure media free ionic copper was likely the main toxicity-mediating factor. However, a threshold concentration of Cu2+ must be reached for biological effects to occur. However, a nano-CuO particle effect was observed in cells exposed in the Good’s buffer MOPS, in which nano-CuO dissolution was very low. These findings highlight how the dominant toxicity mediating factors change with exposure medium, time and the biological endpoint considered and thus demonstrate that nanotoxicity is a highly dynamic process. Furthermore, the observed ROS generation and oxidative stress observed in C. reinhardtii exposed to nano-CuO in lake water, were in line with the increasing extracellular H2O2 determined using the POSS (Fig. 11). Abiotic H2O2 formation by nano-CuO was also observed, but the values were much lower than those found in the presence of algae. Simultaneous exposure of C. reinhardtii to nano-CuO and simulated solar light induced synergistic effect in ROS generation, whereas exposure to ionic copper and the same solar simulated light conditions resulted in antagonistic effects [41, 87]. No measurable alterations in nano-CuO aggregation, copper dissolution or abiotic ROS production were found under the tested light irradiations suggesting that the synergistic effects are not associated with light-induced changes in nano-CuO properties in the exposure medium [40, 41]. Nano-CuO toxicity to microalgae is generally recognized to be associated with the amount of copper released by the nanoparticles [41]. However, the combined effects observed for light irradiation and CuO-NPs could not be explained with the measured copper dissolution suggesting that under stressful light conditions other mechanisms of actions might be involved.
Fig. 11.
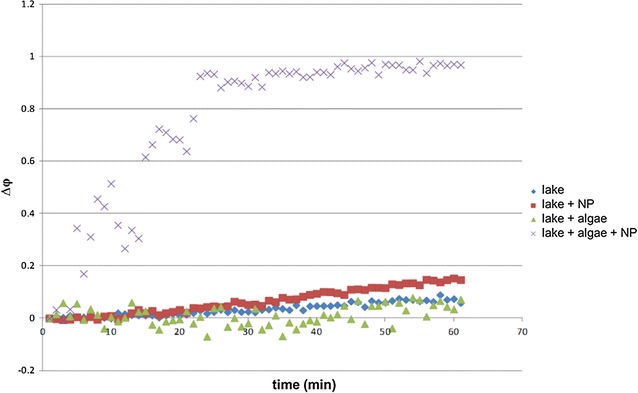
Time evolution of the differential oxidation coefficient Δφ during an exposure for 60 min to nano-CuO, C. reinhardtii and nano-CuO and C. reinhardtii in lake water. A control experiment was carried out in lake water
Nano-TiO2
The nano-TiO2 exposure experiments were performed in MOPS and water sampled from lake of Geneva [32]. The observed pro-oxidant effects were strongly dependent on the exposure concentration and medium. In lake water exposures the proportion of cells affected by oxidative stress increased with the concentration of nano-TiO2, with highest responses obtained for algae exposed to 100 and 200 mg L−1 nano-TiO2. Similarly, membrane damage predominantly occurred in lake water rather than in MOPS. UV light pre-treatment of TiO2 enhanced median intracellular ROS levels in lake water exposure while no significant effect was found in MOPS.
In MOPS H2O2 concentrations (c H2O2) determined using POSS were highest at the start and decayed to values close to the LOD after 60 min exposure (Fig. 12) in all treatments. c H2O2 values were higher in UV pre-treated samples at nearly all concentrations (except 10 mg L−1 nano-TiO2). The initial c H2O2 peaks are possibly due to the formation of hole/electron pairs and their subsequent photocatalytic reaction with H2O and O2 at the surface of the nano-TiO2 particles [88]. Results suggest that nano-TiO2 behaves as both peroxide source and sink through photocatalytic reactions at the surface of the nanoparticles. Experiments carried out with lake water did not exhibit initial peroxide peak concentrations after sonication. This may be explained by ROS quenching species in the form of dissolved organic matter (DOM), which, in contrast to MOPS, are present in lake water.
Fig. 12.
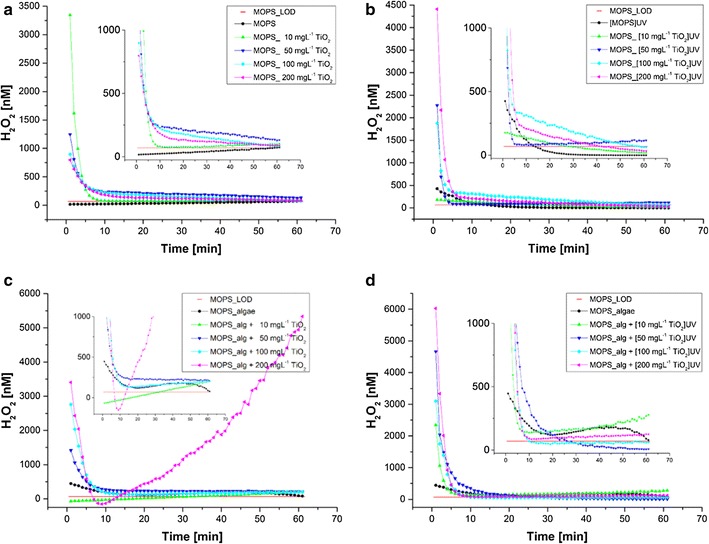
Extracellular H2O2 [nM] (c H2O2) produced during 60 min by four nano-TiO2 concentrations with (b, d) and without UV pre-treatment (a, c) in abiotic (a, b) and biotic (c, d) conditions in the MOPS buffer: nano-TiO2 only (a), nano-TiO2 after 20 min UV pre-treatment (b), algae exposed to nano-TiO2 (c) and algae exposed to UV pre-treated nano-TiO2 (d). The horizontal red line represents the LOD and insets depict enlargements of the respective 0–1000 nM concentration range
Reprinted with permission from (RSC Advances 2016; 6: 115271–115283). Copyright (2016) Royal Society of Chemistry
The biotic exposure experiments revealed higher decay rates of the initial peaks at the beginning of the experiments, suggesting a peroxide annihilation by algae.
Overall, our findings showed that (i) irrespective of the medium, agglomerated nano-TiO2 in the micrometer size range produced measurable abiotic H2O2 concentrations in biologically relevant media, which is enhanced by UV irradiation, (ii) c H2O2 undergo decay and are highest in the first 10–20 min of exposure and (iii) the generation of H2O2 and/or the measured H2O2 concentration is a dynamic process modified by the ambient medium as well as nano-TiO2 concentrations and the presence of cells.
Comparison of the extracellular H2O2 measurements and intracellular oxidative stress [32, 82] further showed significant differences between extracellular and intracellular pro-oxidant processes. Indeed, an increase of the intracellular oxidative stress was found under the conditions where no significant increase in extracellular biotic H2O2 was measured. The above observation indicates that extracellular H2O2 measurements cannot directly serve as a predictor of cellular pro-oxidant processes or oxidative stress in C. reinhardtii, however, they provide valuable information about the extracellular dynamics of the most stable ROS in the extracellular medium.
Extracellular H2O2 measurements during altering illumination regimes
It is well known that light conditions influence the metabolic activity of algae and therefore cellular ROS generation [89, 90]. ROS released by photosynthetic organisms generally originate from the photosystems II and I [89, 90] (PSII and PSI) located in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast. Disturbances of the electron transport chain from PSII to PSI favour reduction of molecular oxygen O2 to O2 − which triggers a reaction cascade leading to the formation of OH and H2O2 [91]. According to previous studies, chloroplast derived H2O2 is able to diffuse out of the chloroplast [92] and through the cell walls and is, therefore, present in the extracellular media. Here, we examined the dynamics of extracellular H2O2 during altering illumination regimes. C. reinhardtii in model medium were exposed to 100 nM of Cd2+ in different light conditions [18].
| 5 |
Figure 13 indicates an enhanced H2O2 production rate and no production delay under light conditions suggesting a correlation between ROS regulation and the activity of the photosystems.
Fig. 13.
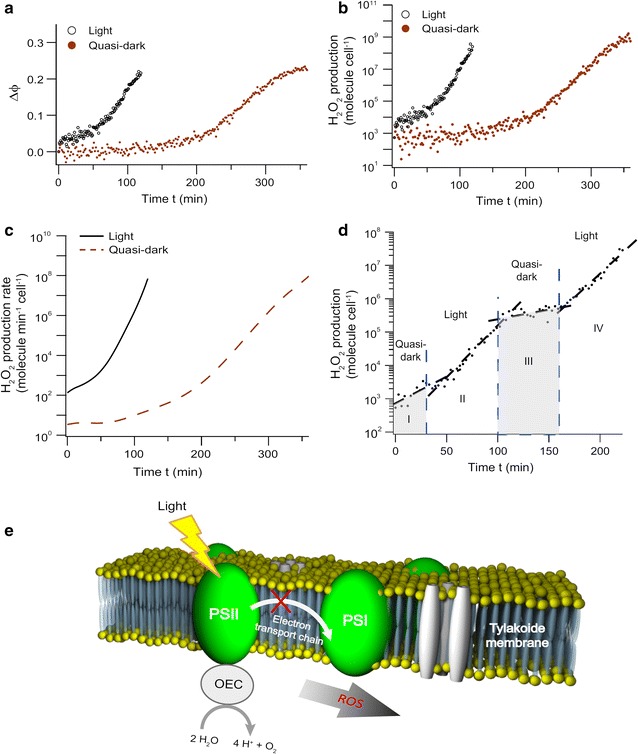
Dark- and light-adapted C. reinhardtii are exposed to 100 nM of Cd(II). Time evolution of (a) the differential oxidation state coefficient Δϕ, b the H2O2 production and c the H2O2 production rate. After injection of Cd(II) the light-adapted algae under illumination start excreting H2O2 without delay, whereas there is a production delay under dark conditions. d ROS production for dark-adapted algae exposed to 100 nM of Cd(II) when the illumination is successively turned on and off during the measurement. e These data support the following action mechanism of Cd(II) on the photosynthetic apparatus of C. reinhardtii: Cd(II) binding to the plastoquinone pool disturbs the electron transport chain between PSII and PSI. Upstream, the light driven electron extraction from oxygen evolving complex (OEC) remains functional and generates light-dependant ROS at the PSII acceptor side.
Reprinted with permission from (Scientific Reports 2013; 3: 3447). Copyright (2013) Nature Publishing Group
Recovery and sensitisation
In contrast to end-point measurements, sensitive and non-invasive continuous H2O2 measurements enable the investigation of recovery and sensitisation. To demonstrate the practicability of such experiments the C. reinhardtii were repeatedly exposed to Cd2+, using a microfluidic configuration as described above [83]. Cd2+ concentrations are typically <10 nM in fresh water. However, higher concentrations of Cd2+ were found in the exposure media containing CdSe quantum dots [5] or CdTe/CdS [34].
Extracellular H2O2 concentrations were measured while C. reinhardtii were exposed to 100 and 500 nM of Cd2+ [step (1)]. A subsequent rinsing [step (2)] and further exposure to Cd2+ [step (3)], even at 100 nM, exhibits an increased H2O2 production rate compared to the previous exposure (Fig. 14).
1st exposure of C. reinhardtii to Cd2+ → H2O2 production
Rinsing
2nd exposure of C. reinhardtii to Cd2+ → increased production rate of H2O2
Fig. 14.
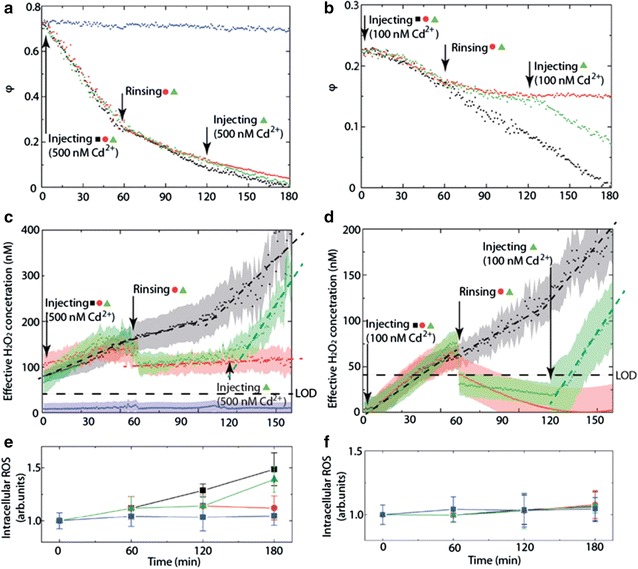
Algae exposure to Cd2+. Oxidative state coefficient φ versus time for: a 500 nM and b 100 nM exposure cycles. c, d Extracellular H2O2 concentration C H2O2. Intracellular ROS measured a fluorescence method for e 500 and f 100 nM Cd2+ exposures for identical cycles as in a and b.
Reprinted with permission from (Nanotoxicology 2016; 10: 1041–1050). Copyright (2016) Taylor & Francis
This shows that exposure to even low concentration of Cd2+ leads to a sensitisation of exposed cells, thus suggesting an adverse impact on the health of microorganisms. In parallel, intracellular ROS was assessed based on the fluorescence intensity of de-esterified H2DFC-DA [93]. At high Cd2+ concentrations (500 nM) intra- and extracellular measurements correlated very well, confirming the suitability of extracellular H2O2 measurements as indicator of cellular stress. However, unlike extracellular H2O2 concentrations, intracellular levels remain stable in the 100 nM exposure, suggesting an efficient ROS/AOX regulation through the cell walls.
Conclusions and outlook
This review paper provides a short overview on nanoparticle toxicity for aquatic microorganisms based on the paradigm of oxidative stress and highlights the recent developments of an optical biosensor based on absorption measurements of cyt c for the sensitive, non-invasive and continuous measurement of H2O2. The use of this new tool for studying the pro-oxidant effects of ENMs to aquatic microorganisms was demonstrated by exposing the representative aquatic microorganism C. reinhardtii to nano-CuO and nano-TiO2 in various exposure media and under different light treatments. Sensitive continuous measurements of extracellular H2O2 provided valuable information on both the potency of the studied nano-CuO and nano-TiO2 to generate ROS as well as on the mechanisms of toxicity. The results were in good agreement with the oxidative stress and membrane damage results obtained under the same conditions using a combination of fluorescent staining with flow cytometry. The developed biosensor allows rapid measurement of the rate and amount of H2O2 measured in the extracellular medium in response to cell exposure to ENMs. Hence, detailed knowledge of the dynamics of H2O2 excretion can provide valuable insights into complex biological responses. The development of the portable setup and the multi-layered microfluidic chip with an integrated optical sensor for the continuous sensitive detection of extracellular H2O2 opens novel avenues for new types of exposure experiments, leading to a better understanding of ROS biology as well as to numerous opportunities for nanoecotoxicological studies. Developing and employing new sensing tools and methods enables conducting experiments under more realistic conditions such as environmental relevant concentrations, aged nanomaterials and simultaneous exposure to various stressors. Furthermore, studying the dynamics of cellular metabolites leads to new insights in the extremely complex adverse outcome pathways.
Authors’ contributions
CHS contributed to the development of the sensor and to the coordination of the experiments, NVM carried out the experiments on AMOs, VK contributed to the development of the sensor and the AMO experiments, VS coordinated the AMO experiments, PB coordinated the characterisation of the nano-particles, OJFM participated in the coordination of the study and manuscript writing, CHS, NvM and VS wrote the manuscript, all authors edited and approved the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Swiss National Research Program NRP 64 Project No. 406440-131280/1 of the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable since it is a review article. Data are available from the original publications.
Consent for publication
We accept the submission conditions.
Funding
Swiss National Research Program NRP 64 Project No. 406440-131280/1 of the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Abbreviations
- ENMs
engineered nanomaterials
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- AOX
antioxidant
- AMO
aquatic microorganism
- MEAS
multiscattering enhanced absorption spectroscopy
- OPL
optical path length
- LOD
limit of detection
- POSS
portable oxidative stress sensor
- AuNp
gold nanoparticle
- cyt c
cytochrome c
- PSI
photosystem I
- PSII
photosystem II
- MES
2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid
- MOPS
3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid
- TAP
N-Tris[hydroxymethyl]methyl-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid
- OECD
OECD standard media
- DOM
dissolved organic matter
- SOD
superoxide dismutase
- CAT
catalase
- GR
glutathion reductase
- AA
ascorbic acid
- HA
humic acid
- SRFA
Suwannee River fulvic acid
- EDTA
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
Contributor Information
Christian Santschi, Email: christian.santschi@epfl.ch.
Nadia Von Moos, Email: nadia.vonmoos@epfl.ch.
Volodymyr B. Koman, Email: koman@mit.edu
Vera I. Slaveykova, Email: vera.slaveykova@unige.ch
Paul Bowen, Email: paul.bowen@epfl.ch.
Olivier J. F. Martin, Email: olivier.martin@epfl.ch
References
- 1.Miller G, Wickson F. Risk analysis of nanomaterials: exposing nanotechnology’s naked emperor. Rev Policy Res. 2015;32(4):485–512. doi: 10.1111/ropr.12129. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Keller AA, et al. Global life cycle releases of engineered nanomaterials. J Nanopart Res. 2013;15(6):1–17. doi: 10.1007/s11051-013-1692-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.von Moos N, Bowen P, Slaveykova VI. Bioavailability of inorganic nanoparticles to planktonic bacteria and aquatic microalgae in freshwater. Environ Sci Nano. 2014;1(3):214–232. doi: 10.1039/c3en00054k. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ivask A, et al. Mechanisms of toxic action of Ag, ZnO and CuO nanoparticles to selected ecotoxicological test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: a comparative review. Nanotoxicology. 2014;8:57–71. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2013.855831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Burello E, Worth AP. A theoretical framework for predicting the oxidative stress potential of oxide nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology. 2011;5(2):228–235. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2010.502980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhang H, et al. Use of metal oxide nanoparticle band gap to develop a predictive paradigm for oxidative stress and acute pulmonary inflammation. ACS Nano. 2012;6(5):4349–4368. doi: 10.1021/nn3010087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nel A, et al. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science. 2006;311(5761):622–627. doi: 10.1126/science.1114397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Djurisic AB, et al. Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles: mechanisms, characterization, and avoiding experimental artefacts. Small. 2015;11(1):26–44. doi: 10.1002/smll.201303947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xia T, et al. Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett. 2006;6(8):1794–1807. doi: 10.1021/nl061025k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Donaldson K, Beswick PH, Gilmour PS. Free radical activity associated with the surface of particles: a unifying factor in determining biological activity? Toxicol Lett. 1996;88(1–3):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(96)03752-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Manke A, Wang L, Rojanasakul Y. Mechanisms of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. BioMed Res Int. 2013;2013:118. doi: 10.1155/2013/942916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.von Moos N, Slaveykova V. Oxidative stress induced by inorganic nanoparticles in bacteria and aquatic microalgae—state of the art and knowledge gaps. Nanotoxicology. 2014;8(6):605–630. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2013.809810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Livingstone DR. Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar Pollut Bull. 2001;42(8):656–666. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Burns JM, et al. Methods for reactive oxygen species (ROS) detection in aqueous environments. Aquat Sci. 2012;74(4):683–734. doi: 10.1007/s00027-012-0251-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bartosz G. Oxidative stress in plants. Acta Physiol Plant. 1997;19(1):47–64. doi: 10.1007/s11738-997-0022-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gomes A, Fernandes E, Lima J. Fluorescence probes used for detection of reactive oxygen species. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 2005;65(2–3):45–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jbbm.2005.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Valavanidis A, et al. Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2006;64(2):178–189. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Suarez G, et al. Sensing the dynamics of oxidative stress using enhanced absorption in protein-loaded random media. Sci Rep. 2013;3:3447. doi: 10.1038/srep03447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lushchak VI. Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol. 2011;101(1):13–30. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Quigg A, et al. Direct and indirect toxic effects of engineered nanoparticles on algae: role of natural organic matter. Acs Sustain Chem Eng. 2013;1(7):686–702. doi: 10.1021/sc400103x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miao AJ, et al. The algal toxicity of silver engineered nanoparticles and detoxification by exopolymeric substances. Environ Pollut. 2009;157(11):3034–3041. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.05.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nel AE, et al. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat Mater. 2009;8(7):543–557. doi: 10.1038/nmat2442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Neal AL. What can be inferred from bacterium-nanoparticle interactions about the potential consequences of environmental exposure to nanoparticles? Ecotoxicology. 2008;17(5):362–371. doi: 10.1007/s10646-008-0217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhao F, et al. Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and cytotoxicity of nanomaterials. Small. 2011;7(10):1322–1337. doi: 10.1002/smll.201100001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Auffan M, et al. Relation between the redox state of iron-based nanoparticles and their cytotoxicity toward Escherichia coli. Environ Sci Technol. 2008;42(17):6730–6735. doi: 10.1021/es800086f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li KG, et al. Surface interactions affect the toxicity of engineered metal oxide nanoparticles toward Paramecium. Chem Res Toxicol. 2012;25(8):1675–1681. doi: 10.1021/tx300151y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Brown DM, et al. Size-dependent proinflammatory effects of ultrafine polystyrene particles: a role for surface area and oxidative stress in the enhanced activity of ultrafines. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2001;175(3):191–199. doi: 10.1006/taap.2001.9240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wilson MR, et al. Interactions between ultrafine particles and transition metals in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002;184(3):172–179. doi: 10.1006/taap.2002.9501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Unfried K, et al. Cellular responses to nanoparticles: target structures and mechanisms. Nanotoxicology. 2007;1(1):52–71. doi: 10.1080/00222930701314932. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sorensen SN, et al. A multimethod approach for investigating algal toxicity of platinum nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol. 2016;50(19):10635–10643. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b01072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chen LZ, et al. Toxicological effects of nanometer titanium dioxide (nano-TiO2) on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2012;84:155–162. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.07.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.von Moos N, et al. Pro-oxidant effects of nano-TiO2 on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii during short-term exposure. RSC Adv. 2016;6(116):115271–115283. doi: 10.1039/C6RA16639C. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lin DH, et al. The influence of dissolved and surface-bound humic acid on the toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to Chlorella sp. Water Res. 2012;46(14):4477–4487. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.05.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Domingos RF, et al. Bioaccumulation and efects of CdTe/CdS quantum dots on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii—nanoparticles or the free ions? Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45(18):7664–7669. doi: 10.1021/es201193s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ji J, Long ZF, Lin DH. Toxicity of oxide nanoparticles to the green algae Chlorella sp. Chem Eng J. 2011;170(2–3):525–530. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.11.026. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Oukarroum A, et al. Inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles in two green algae, Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella tertiolecta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2012;78:80–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Perreault F, et al. Polymer coating of copper oxide nanoparticles increases nanoparticles uptake and toxicity in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Chemosphere. 2012;87(11):1388–1394. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rogers NJ, et al. Physico-chemical behaviour and algal toxicity of nanoparticulate CeO2 in freshwater. Environ Chem. 2010;7(1):50–60. doi: 10.1071/EN09123. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Saison C, et al. Effect of core-shell copper oxide nanoparticles on cell culture morphology and photosynthesis (photosystem II energy distribution) in the green alga, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat Toxicol. 2010;96(2):109–114. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Koman VB, Santschi C, Martin OJF. Multiscattering-enhanced optical biosensor: multiplexed, non-invasive and continuous measurements of cellular processes. Biomed Opt Express. 2015;6(7):2353–2365. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.002353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cheloni G, Marti E, Slaveykova VI. Interactive effects of copper oxide nanoparticles and light to green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat Toxicol. 2016;170:120–128. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.11.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang JX, et al. Toxicity assessment of manufactured nanomaterials using the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Chemosphere. 2008;73(7):1121–1128. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Adams LK, Lyon DY, Alvarez PJJ. Comparative eco-toxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Res. 2006;40(19):3527–3532. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Brunet L, et al. Comparative photoactivity and antibacterial properties of C-60 fullerenes and TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol. 2009;43(12):4355–4360. doi: 10.1021/es803093t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kumari K, Khare A, Dange S. The applicability of oxidative stress biomarkers in assessing chromium induced toxicity in the fish Labeo rohita. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:1. doi: 10.1155/2014/782493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nyska A, Kohen R. Oxidation of biological systems: oxidative stress phenomena, antioxidants, redox reactions, and methods for their quantification. Toxicol Pathol. 2002;30(6):620–650. doi: 10.1080/01926230290166724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Armoza-Zvuloni R, Shaked Y. Release of hydrogen peroxide and antioxidants by the coral Stylophora pistillata to its external milieu. Biogeosciences. 2014;11(17):4587–4598. doi: 10.5194/bg-11-4587-2014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chen X, et al. Recent progress in the development of fluorescent, luminescent and colorimetric probes for detection of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Chem Soc Rev. 2016;45(10):2976–3016. doi: 10.1039/C6CS00192K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dynowski M, et al. Plant plasma membrane water channels conduct the signalling molecule H2O2. Biochem J. 2008;414:53–61. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bienert GP, et al. Specific aquaporins facilitate the diffusion of H2O2 across membranes. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(2):1183–1192. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603761200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Li C, et al. Electrochemical detection of extracellular hydrogen peroxide released from RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells based on horseradish peroxidase-hydroxyapatite nanohybrids. Analyst. 2011;136(6):1116–1123. doi: 10.1039/C0AN00825G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gonzalez-Sanchez MI, et al. Electrochemical detection of extracellular hydrogen peroxide in Arabidopsis thaliana: a real-time marker of oxidative stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2013;36(4):869–878. doi: 10.1111/pce.12023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Demidchik V. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in plants: from classical chemistry to cell biology. Environ Exp Bot. 2015;109:212–228. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2014.06.021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM. Free radicals in biology and medicine. 4. Oxford: Oxford University Press Inc.; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Morgan MS, et al. Ultraviolet molar absorptivities of aqueous hydrogen peroxide and hydroperoxyl ion. Anal Chim Acta. 1988;215(1–2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(00)85294-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lin CL, Rohatgi NK, Demore WB. Ultraviolet-absorption cross-section of hydrogen-peroxide. Geophys Res Lett. 1978;5(2):113–115. doi: 10.1029/GL005i002p00113. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Abrams R, Altschul AM, Hogness TR. Cytochrome c peroxidase II. The peroxidase-hydrogen peroxide complex. J Biol Chem. 1942;142(1):303–316. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Altschul AM, Abrams R, Hogness TR. Cytochrome c peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1940;136(3):777–794. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gupta BL. Microdetermination techniques for H2O2 in irradiated solutions. Microchem J. 1973;18(4):363–374. doi: 10.1016/0026-265X(73)90059-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Armstrong WA, Humphreys WG. A let independent dosimeter based on chemiluminescent determination of H2O2. Can J Chem Back Year. 1965;43(9):2576. doi: 10.1139/v65-354. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Malavolti NL, Pilosof D, Nieman TA. Optimization of experimental variables for the chemi-luminescent determination of glucose in microporous membrane flow cells. Anal Chem. 1984;56(12):2191–2195. doi: 10.1021/ac00276a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kok GL. Measurements of H2O2 in rainwater. Atmos Environ. 1980;14(6):653–656. doi: 10.1016/0004-6981(80)90048-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Keston AS, Brandt R. Fluorometric analysis of ultramicro quantities of H2O2. Anal Biochem. 1965;11(1):1. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hwang H, Dasgupta PK. Fluorometric flow-injection determination of aqueous peroxides at nanomolar level using membrane reactors. Anal Chem. 1986;58(7):1521–1524. doi: 10.1021/ac00298a055. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lazrus AL, et al. Automated fluorometric method for hydrogen-peroxide in air. Anal Chem. 1986;58(3):594–597. doi: 10.1021/ac00294a024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Barth A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta Bioenerg. 2007;1767(9):1073–1101. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2007.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zubavichus Y, et al. X-ray absorption spectroscopy of the nucleotide bases at the carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen K-edges. J Phys Chem B. 2008;112(44):13711–13716. doi: 10.1021/jp802453u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zaera F. New advances in the use of infrared absorption spectroscopy for the characterization of heterogeneous catalytic reactions. Chem Soc Rev. 2014;43(22):7624–7663. doi: 10.1039/C3CS60374A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Pradier C-M, et al. Specific binding of avidin to biotin immobilised on modified gold surfaces: fourier transform infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy analysis. Surf Sci. 2002;502–503:193–202. doi: 10.1016/S0039-6028(01)01932-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Namjou K, et al. Determination of exhaled nitric oxide distributions in a diverse sample population using tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy. Appl Phys B Lasers Opt. 2006;85(2–3):427–435. doi: 10.1007/s00340-006-2301-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Bohren CF, Huffman DR. Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. New York: Wiley; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wong YH, Thomas RL, Hawkins GF. Surface and subsurface structure of solids by laser photoacoustic spectroscopy. Appl Phys Lett. 1978;32(9):538–539. doi: 10.1063/1.90120. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Greener J, Abbasi B, Kumacheva E. Attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for on-chip monitoring of solute concentrations. Lab Chip. 2010;10(12):1561–1566. doi: 10.1039/c001889a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Okeefe A, Deacon DAG. Cavity ring-down optical spectrometer for absorption-measurements using pulsed laser sources. Rev Sci Instrum. 1988;59(12):2544–2551. doi: 10.1063/1.1139895. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Koman VB, Santschi C, Martin OJF. Multiscattering-enhanced absorption spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2015;87(3):1536–1543. doi: 10.1021/ac502267q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Henyey LG, Greenstein JL. Diffuse radiation in the galaxy. Astrophys J. 1941;93(1):70–83. doi: 10.1086/144246. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Uppu R, Tiwari AK, Mujumdar S. Coherent random lasing in diffusive resonant media. In: Chigrin DN, editor. Fourth international workshop on theoretical and computational nanophotonics. Amer Inst Physics: Melville; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Mujumdar S, et al. Monte Carlo calculations of spectral features in random lasing. J Nanophoton. 2010;4:39. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Liew SF, et al. Short-range order and near-field effects on optical scattering and structural coloration. Opt Express. 2011;19(9):8208–8217. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.008208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Butt WD, Keilin D. Absorption Spectra and some other properties of cytochrome c and of its compounds with ligands. Proc R Soc Ser B Biol Sci. 1962;156(965):429. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1962.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Wilson R, Turner APF. Glucose oxidase: an ideal enzyme. Biosens Bioelectron. 1992;7(3):165–185. doi: 10.1016/0956-5663(92)87013-F. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Koman VB, et al. Portable oxidative stress sensor: dynamic and non-invasive measurements of extracellular H2O2 released by algae. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;68:245–252. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.12.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Koman VB, et al. New insights into ROS dynamics: a multi-layered microfluidic chip for ecotoxicological studies on aquatic microorganisms. Nanotoxicology. 2016;10:1–10. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2016.1144826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Findlay JWA, Dillard RF. Appropriate calibration curve fitting in ligand binding assays. Aaps J. 2007;9(2):E260–E267. doi: 10.1208/aapsj0902029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.von Moos N, Maillard L, Slaveykova VI. Dynamics of sub-lethal effects of nano-CuO on the microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii during short-term exposure. Aquat Toxicol. 2015;161:267–275. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Auffan M, et al. Chemical stability of metallic nanoparticles: a parameter controlling their potential cellular toxicity in vitro. Environ Pollut. 2009;157(4):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Cheloni G, Cosio C, Slaveykova VI. Antagonistic and synergistic effects of light irradiation on the effects of copper on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat Toxicol. 2014;155:275–282. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Cho M, et al. Linear correlation between inactivation of E. coli and OH radical concentration in TiO2 photocatalytic disinfection. Water Res. 2004;38(4):1069–1077. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2003.10.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Asada K. Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions. Plant Physiol. 2006;141(2):391–396. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.082040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Pospisil P. Production of reactive oxygen species by photosystem II. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta Bioenerg. 2009;1787(10):1151–1160. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Barber J. Photosynthetic energy conversion: natural and artificial. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38(1):185–196. doi: 10.1039/B802262N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Mubarakshina MM, Ivanov BN. The production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in the plastoquinone pool of chloroplast thylakoid membranes. Physiol Plant. 2010;140(2):103–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2010.01391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Kim G, Lee YE, Kopelman R. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) detection with nanoprobes for biological applications: a mini-review. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1028:101–114. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-475-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable since it is a review article. Data are available from the original publications.


