Abstract
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β (GSK3β) is a serine/threonine kinase, known to regulate various cellular processes including proliferation, differentiation, survival, apoptosis as well as TRAIL-resistance. Thus pathways that can modulate GSK3β axis are important targets for cancer drug development. Our earlier studies have shown that combinatorial treatment with Troglitazone (TZD) and TRAIL can induce apoptosis in TRAIL-resistant cancer cells. The current studies were undertaken to investigate whether GSK3β pathway was modulated during this apoptosis. Our results indicated an increase in inhibitory GSK3βSer9 phosphorylation during apoptosis, mediated via AKT. At a later time, however, TZD alone and TRAIL-TZD combination produced a dramatic reduction of GSK3β expression, which was abolished by cycloheximide. Luciferase assays with GSK3β-luc promoter reporter showed that TZD can effectively antagonize GSK3β promoter activity. Since TZD is a ligand for transcription factor PPARγ and can activate AMPK, we determined their roles on antagonism of GSK3β. Knockdown of PPARγ was unable to restore GSK3β expression or antagonize GSK3βSer9 phosphorylation. Although pretreatment with Compound C (pharmacological inhibitor of AMPK) partially rescued GSK3β expression, knockdown of AMPKα1 or α2 alone or in combination were ineffective. These studies suggested a novel PPARγ-AMPK-independent mechanism of targeting GSK3β by TZD, elucidation of which might provide newer insights to improve our understanding of TRAIL-resistance.
Keywords: GSK3β, AKT, PPARγ, AMPK, apoptosis-resistance
INTRODUCTION
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a multifunctional serine/threonine kinase that has been implicated in regulating several fundamental processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, metabolism, survival and apoptosis [1], as well as various pathological conditions such as diabetes, oncogenesis and neurological diseases [2]. GSK3 derived its name from its phosphorylation activity toward glycogen synthase, thus linking it to glycogen metabolism. Since then, increasing research on GSK3 has significantly improved our understanding of this molecule. Two GSK-3 genes (α and β) have been cloned in mammals with strong sequence conservation within the catalytic domain between the homologues [3]. Due to its profound role in neurodegeneration, the efficacy of GSK3 inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease have also been tested [4]. GSK3 is known to phosphorylate and regulate the activities of more than 40 proteins, many of which are transcription factors [5]. This indicates the potential contribution of this enzyme in regulating a variety of cellular functions. The regulation of GSK3β activity is not completely understood and is believed to be mediated via a combination of phosphorylation, localization and interaction with other proteins [6, 7]. The major inhibitory phosphorylation is on Ser9 of GSK3β and Ser21 of GSK3α [8, 9] and can be phosphorylated by multiple upstream kinases including AKT [10].
In the cancer field, GSK-3β is commonly recognized as a putative tumor suppressor due to its well-established function as a repressor of β-catenin signaling [11] and phosphorylation-dependent down-regulation of cell-cycle regulators cyclin D1 [12], cdc25 [13], and c-Myc [14]. Paradoxically, it can also promote cell survival and oppose apoptosis [15, 16]. An involvement of GSK3β in mediating tumorigenic pathways is also indicated by its induced expression in various cancers including colon cancer [17], pancreatic cancer [18, 19], prostate cancer [20–22], and glioblastoma [23]. This notion is supported by recent studies suggesting an involvement of GSK3β in pancreatic cancer cell survival [24], dedifferentiation [19] as well as therapeutic resistance [25–27]. Similarly, GSK3β inhibition was shown to ameliorate apoptosis resistance in other types of cancer as well [28, 29]. A close connection of GSK3β in prostate cancer has been demonstrated earlier by the fact that increased cytoplasmic GSK3β correlated with the clinical stage and Gleason score in prostate tumor samples [30]. In addition, GSK3β was shown to positively regulate androgen receptor (AR) function [31, 20] and nuclear translocation [32]. An understanding of how GSK3β pathway is modulated during apoptotic signaling is thus important for the development of new and effective therapeutic approaches that can target GSK3β.
In recent studies with TRAIL-resistant cancer cells, we have observed that treatment with a combination of TRAIL and PPARγ ligand Troglitazone (TZD) induces profound apoptosis compared to either agent alone [33]. The aim of the present study was to determine whether GSK3β pathway was modulated by this combination treatment and to elucidate the potential mechanism. Our results indicate that in TRAIL-resistant prostate cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells, TRAIL and TZD treatment resulted in an induction of GSK3βSer9 phosphorylation (indicating inhibition) at an earlier stage during apoptosis. In addition, total GSK3β levels were significantly down-regulated by TZD alone and by TRAIL-TZD combination at a later stage that involved inhibition of transcription. This downregulation of GSK3β involved mechanisms independent of PPARγ and AMPK. In addition, although pharmacological inhibition was ineffective, knockdown of GSK3α and to a lesser extent GSK3β seemed to promote apoptosis when treated with TRAIL-TZD combination.
RESULTS
Combination treatment with TRAIL-TZD attenuates GSK3β pathway in cancer cells
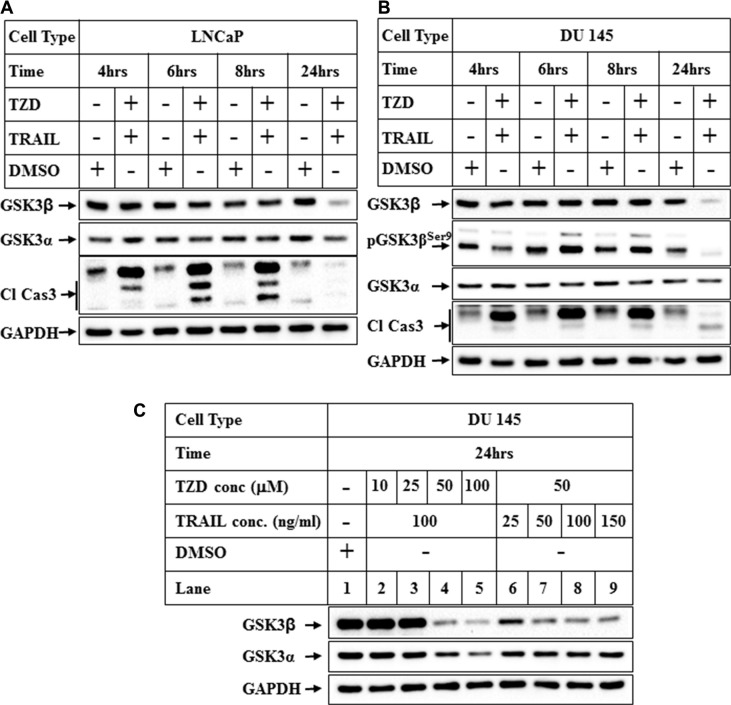
To understand the status of GSK3β pathway during apoptosis following treatment with TRAIL-TZD combination, prostate cancer cells (LNCaP and DU145) were treated with TRAIL-TZD combination for different lengths of time and changes in GSK3β levels were compared. Although total GSK3β expression was unaffected initially, prolonged treatment with TRAIL-TZD resulted in a significant reduction of total GSK3β expression in both cell types (Figure 1A, 1B 24 hrs). Reduction of total GSK3α, however was more modest. Similar regulation of GSK3β in both LNCaP (AR dependent) and DU145 (AR independent) cells suggested that this might be occurring independent of AR signaling. In addition, we also observed an increase of pGSK3βSer9 levels, which preceded reduction of total GSK3β and coincided with the period of active apoptosis (Figure 1B). The concentrations of both TRAIL and TZD needed to inhibit total GSK3β expression optimally were determined next. These studies designed with increasing concentrations of each agent indicated that combination of 100 ng/ml TRAIL and 50–100 μM TZD produced maximal effects on total GSK3β expression (Figure 1C). Thus the remaining studies were carried out with this combination.
Figure 1. Attenuation of GSK3β pathway by combination treatment with TRAIL and TZD in prostate cancer cells.
(A) LNCaP and (B) DU 145 cells were treated with a combination of TRAIL (100 ng/ml) and Troglitazone (50 μM) for different periods of time followed by Western Blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (C) DU 145 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of TZD (10, 25, 50, 100 μM), or with increasing concentrations of TRAIL (25, 50, 100, 150 ng/ml) for 24 hrs followed by Western Blot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
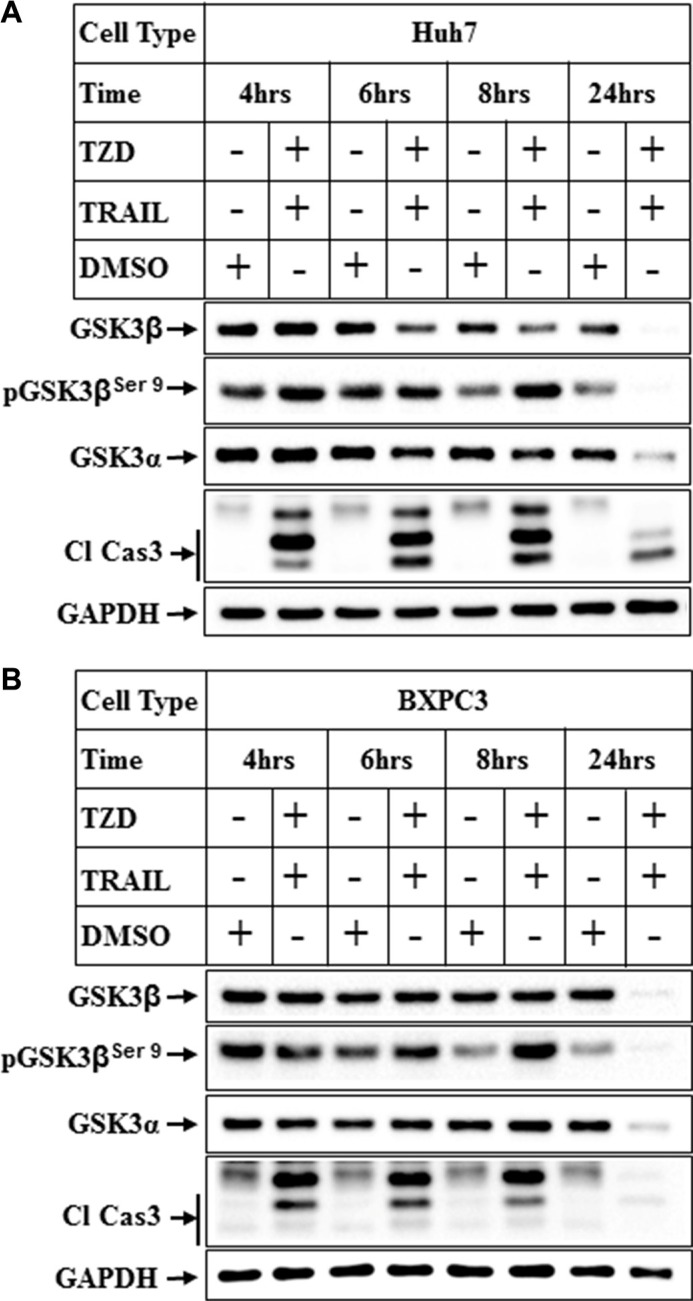
In order to determine whether this regulation of GSK3β is also present in other cancer cells, we determined the changes in GSK3β levels in hepatocellular carcinoma cells (Huh7) and pancreatic cancer cells (BXPC3). These also showed a dramatic reduction of total GSK3β and α expressions in Huh7 cells following treatment with TRAIL-TZD combination (Figure 2A). A similar time dependent reduction of total GSK3β and α was also observed in the BXPC3 cells (Figure 2B). These were also associated with an initial increase in the levels of pGSK3βSer9 in both cell types. These suggested that TRAIL-TZD-induced modulation of GSK3β pathway is present in various cancer cells and is a generalized event.
Figure 2. Attenuation of GSK3β pathway in various cancer cells by TRAIL and TZD treatment.
(A) Huh7 and (B) BxPC3 cells were treated with a combination of TRAIL (100 ng/ml) and Troglitazone (50 μM) for different periods of time followed by Western Blot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
Comparison of the effects of TRAIL and TZD alone or in combination in antagonizing GSK3β
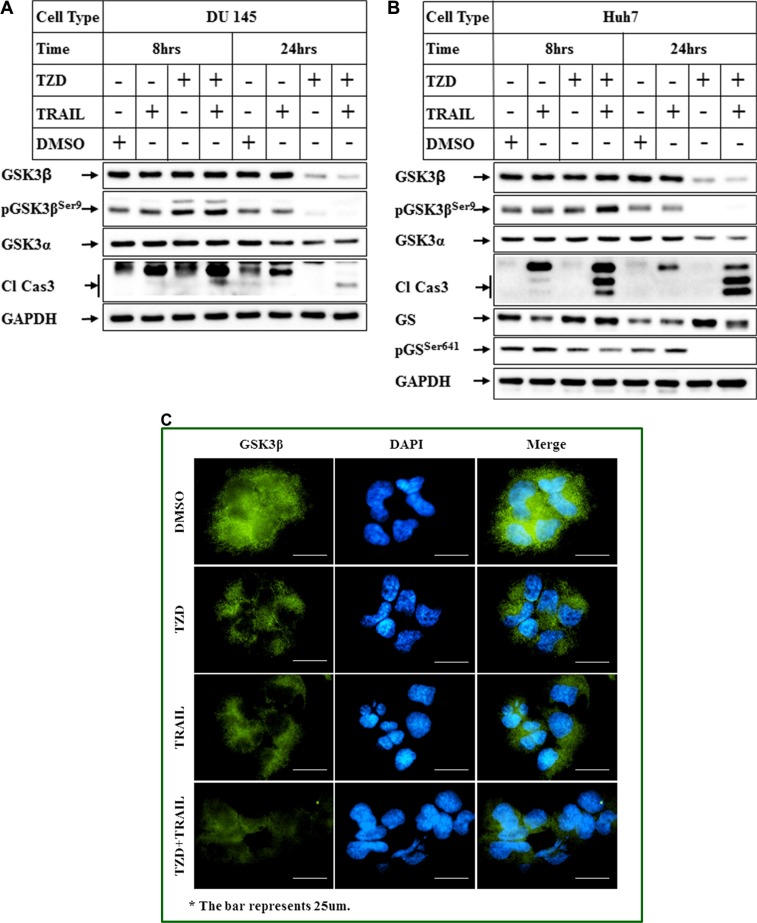
To understand the relative contribution of TRAIL or TZD alone and their combination in modulating total GSK3β expression, cells were treated with either agent alone or in combination and the effect on GSK3β levels was estimated. These studies indicated that treatment with TZD alone resulted in a significant attenuation of total GSK3β expression, which was further potentiated by TRAIL-TZD combination (Figure 3A, 3B). Antagonism of GSK3β axis by TZD and TRAIL-TZD was also evident from the reduction of GSK3β downstream target Glycogen Synthase Ser641 phosphorylation (Figure 3B, pGSSer641 panel). To determine whether TRAIL-TZD induced any change in GSK3β localization, Immunofluorescence studies were designed. These showed that treatment with TZD alone or in combination with TRAIL significantly reduced cytoplasmic and nuclear GSK3β levels (Figure 3C). These suggested TZD to be a major modulator of GSK3β expression.
Figure 3. Comparison of the effects of TRAIL and TZD alone or in combination in antagonizing GSK3β pathway.
(A) DU 145 and (B) Huh7 cells were treated with DMSO, TRAIL or TZD or a combination of TRAIL and TZD for 8 hrs and 24 hrs. Western Blot analyses were performed next with the indicated antibodies. (C) Huh7 cells plated in 4-well chamber slides were treated with DMSO, TZD, or TRAIL alone or in combination for 8 hrs. Immunofluorescence analysis with anti-GSK3β antibody was performed to detect endogenous GSK3β (green fluorescence). The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The images were captured on a Nikon ECLIPSE Ti microscope, equipped with a digital camera (Nikon DS-Qi2) at 40× magnification.
TZD inhibits total GSK3β at a transcriptional level
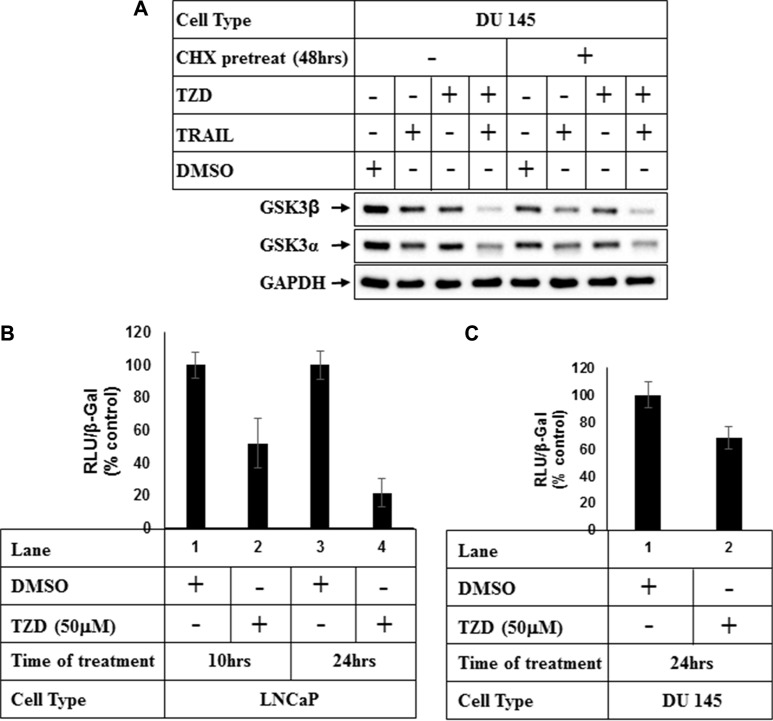
In an attempt to understand the mechanism how TZD regulates total GSK3β, studies were undertaken to determine whether the effects were at a post-translational level. Pretreatment with protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX) showed that although TZD reduced total GSK3β expression significantly in the absence of CHX (Figure 4A, compare lanes 1&3), it was unable to do so in the presence of CHX (compare lanes 5&7). These suggested that TZD attenuated total GSK3β levels not at a post-translational step and most likely regulated it at a transcriptional level or via modulating mRNA stability. To confirm any transcriptional regulation of GSK3β, we performed luciferase assays with GSK3β-promoter luciferase construct pGL3-GSK-3β-luc (−427/+66) [34] following treatment with TZD. These showed a significant attenuation of GSK3β promoter activity with TZD treatment in both LNCaP and DU145 cells in a time dependent manner (Figure 4B and 4C), suggesting that TZD can inhibit GSK3β transcription.
Figure 4. TZD treatment attenuates GSK3β expression at a transcriptional level.
(A) DU 145 cells were pretreated with 50 μg/ml Cycloheximide (CHX) for 48 hrs and then with DMSO or TRAIL, TZD alone or in combination for an additional 24 hrs. At the end of incubation, cells were harvested and equal amounts of total protein were analyzed by Western Blots with the antibodies indicated. (B) LNCaP or (C) DU 145 cells were transiently transfected with GSK-3β promoter luciferase vector [pGL3-GSK-3β-luc-(−427/+66)] and β-Galactosidase (β-Gal) vector for 48 hrs followed by treatment with DMSO, or TZD for the indicated periods of time. Luciferase and β-galactosidase assays were carried out next and RLU/β-Gal values were expressed as % control. The data in each set represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
TZD-induced attenuation of GSK-3β is PPARγ-independent
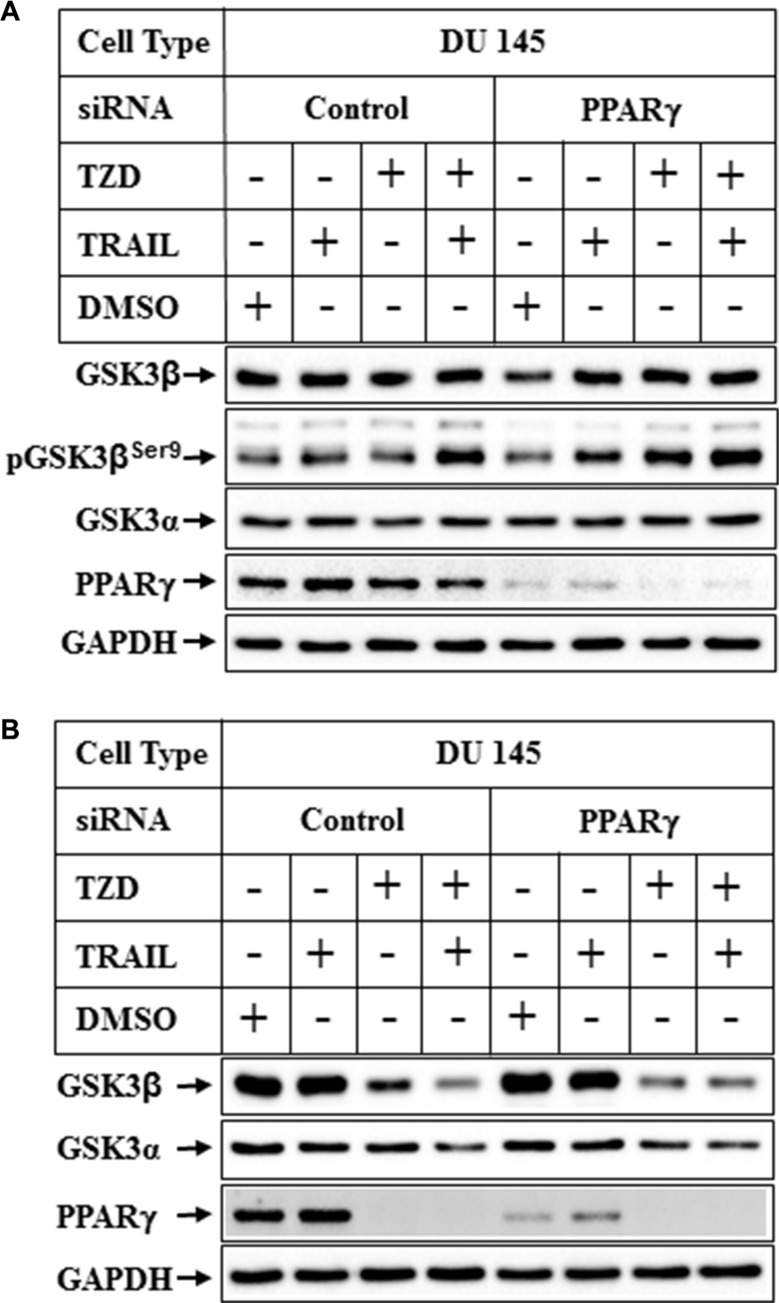
Since TZD is a ligand for transcription factor PPARγ, and GSK3β was regulated at a transcriptional level by TZD, we determined next whether PPARγ played any role in modulating GSK3β expression. To understand the role of PPARγ on GSK3β expression, endogenous PPARγ expression was knocked down using the smart pool hPPARγ-siRNA from Dharmacon. PPARγ-siRNA reduced PPARγ expression significantly (Figure 5A, 5B, PPARγ-siRNA lanes), but was unable to antagonize TZD or TRAIL-TZD-induced reduction of total GSK3β expression (Figure 5B, compare lanes 3&4 with 7&8). These studies also revealed that, TRAIL-TZD-mediated induction of pGSK3βSer9 was independent of PPARγ (Figure 5A).
Figure 5. Effect of PPARγ knockdown on TRAIL-TZD-induced modulation of GSK3β pathway.
Subconfluent DU 145 cells were transfected with either control-siRNA or PPARγ-siRNA for 72 hrs followed by treatment with TRAIL or TZD alone or in combination for 6 hrs (A) or 24 hrs (B). The samples were analyzed by Western blots with the antibodies indicated.
TZD-induced attenuation of GSK-3β is modulated by compound C independent of AMPK
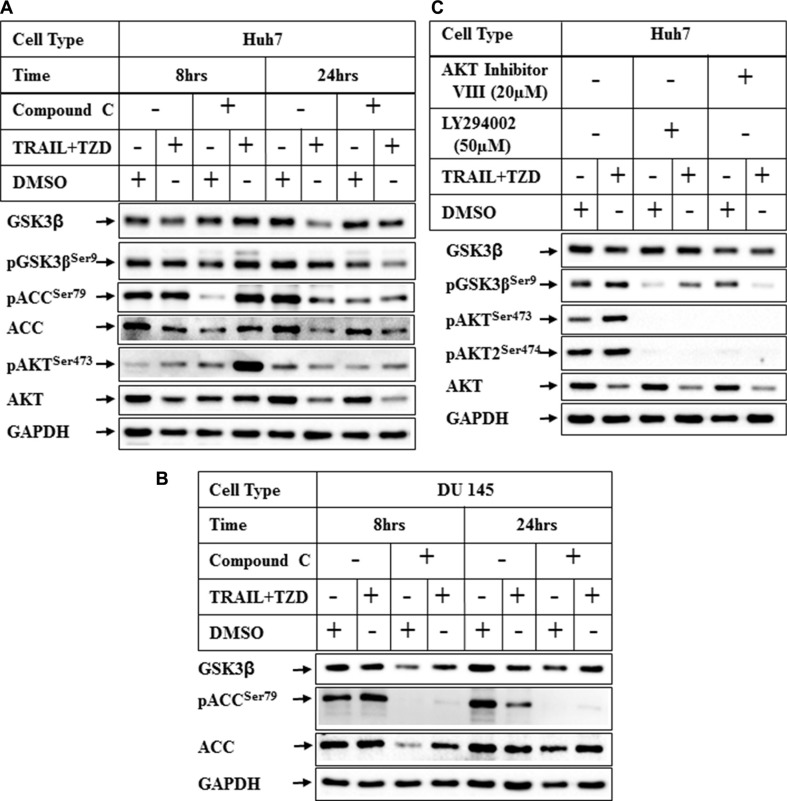
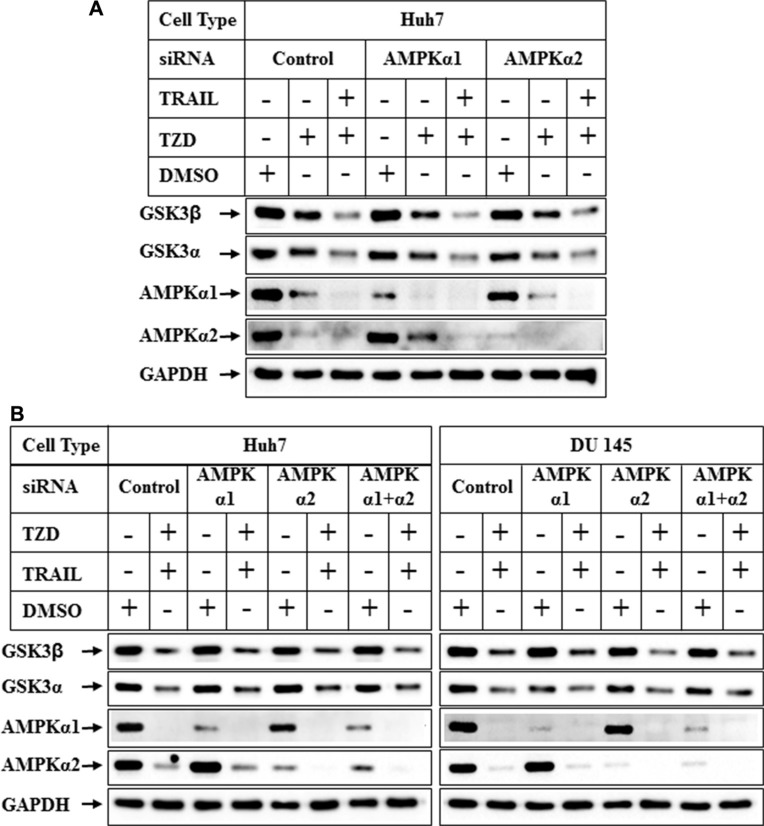
In recent studies we have demonstrated that TRAIL and TZD-combination can induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells involving AMPK pathway [35]. Since TZD can also activate AMPK [36, 37], we determined any role of AMPK in attenuating GSK3β pathway by pretreating the cells with Compound C (a known inhibitor of AMPK), prior to TRAIL-TZD treatment. These results showed that TRAIL-TZD-induced attenuation of total GSK3β expression at 24 hrs can be partially antagonized by Compound C pretreatment in both Huh7 and DU145 cells (Figure 6A, 6B, compare lanes 5, 6 and 7, 8, GSK3β panel). Compound C also inhibited pACCSer79 (AMPK downstream target) in both cell types (Figure 6A, 6B), indicating the efficacy of the inhibitor. This suggested a potential involvement of AMPK in mediating total GSK3β reduction. To confirm the participation of AMPK in mediating these effects, we determined the effect of TRAIL-TZD on GSK3β expression following knockdown of AMPKα. Surprisingly, siRNA-mediated knockdown of AMPKα1 or α2 alone was unable to antagonize TZD or TRAIL-TZD-induced attenuation of GSK3β expression (Figure 7A, compare lanes 2, 5 & 8 and lanes 3, 6 & 9). Knocking down AMPKα1 or α2 in combination also showed no effect in any of the cell types (Figure 7B, compare lanes 2, 4, 6 & 8). These suggested that GSK3β expression was regulated via a Compound C sensitive but AMPK-independent mechanism.
Figure 6. Effect of inhibition of AMPK and PI3K/AKT pathways on TRAIL-TZD-induced modulation of GSK3β pathway.
(A) Huh7 or (B) DU 145 cells were pretreated with 20 μM Compound C for 24 hrs followed by treatment with DMSO or TRAIL-TZD combination for 8 hrs and 24 hrs. The results were analyzed by Western blots. (C) Huh7 cells were pretreated with PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) or AKT Inhibitor VIII for 1 hr followed by TRAIL-TZD treatment for 8 hrs and Western blot analyses.
Figure 7. Effect of knockdown of AMPK α1 or α2 on TRAIL-TZD modulation of GSK3β pathway.
(A) Subconfluent Huh7 cells were transiently transfected with either control-siRNA, or AMPKα1-siRNA or AMPKα2-siRNA separately for 72 hrs followed by treatment with DMSO, TZD or TRAIL-TZD combination for 24 hrs. The samples were analyzed by western blots. (B) Huh7 and DU 145 cells were transiently transfected with either control-siRNA, AMPKα1-siRNA, AMPKα2-siRNA or a combination of AMPKα1 and AMPKα2-siRNA for 72 hrs. The cells were harvested following a treatment with DMSO or TRAIL-TZD combination for 24 hrs and analyzed by Western blots.
In these experiments we also observed that Compound C pretreatment was unable to antagonize TRAIL-TZD-induction of pGSK3βSer9 levels and rather showed minor induction, and a corresponding hyper-activation of AKT (Figure 6A, pGSK3βSer9 and pAKTSer473 panels, compare lanes 2 & 4). To determine whether PI3Kinase and AKT was mediating GSK3βSer9 phosphorylation in TRAIL-TZD pathway, cells were pretreated with either the PI3Kinase inhibitor (LY294002) or the AKT inhibitor (AKT inhibitor VIII) followed by TRAIL-TZD treatment. LY294002 significantly antagonized basal and TRAIL-TZD-induced GSK3βSer9 phosphorylation levels which was fully antagonized by AKT inhibitor VIII (Figure 6C, compare lanes 2, 4 & 6, pGSK3βSer9 panel). pAKTSer473 or pAKT2Ser474 levels were completely abolished by LY294002, suggesting its efficacy in antagonizing PI3Kinase activation. These interesting results suggested that TRAIL-TZD likely increases GSK3βSer9 phosphorylation via a mechanism that involves AKT and upstream PI3Kinase pathways.
Effect of GSK-3β inhibition on TRAIL-TZD-induced apoptosis
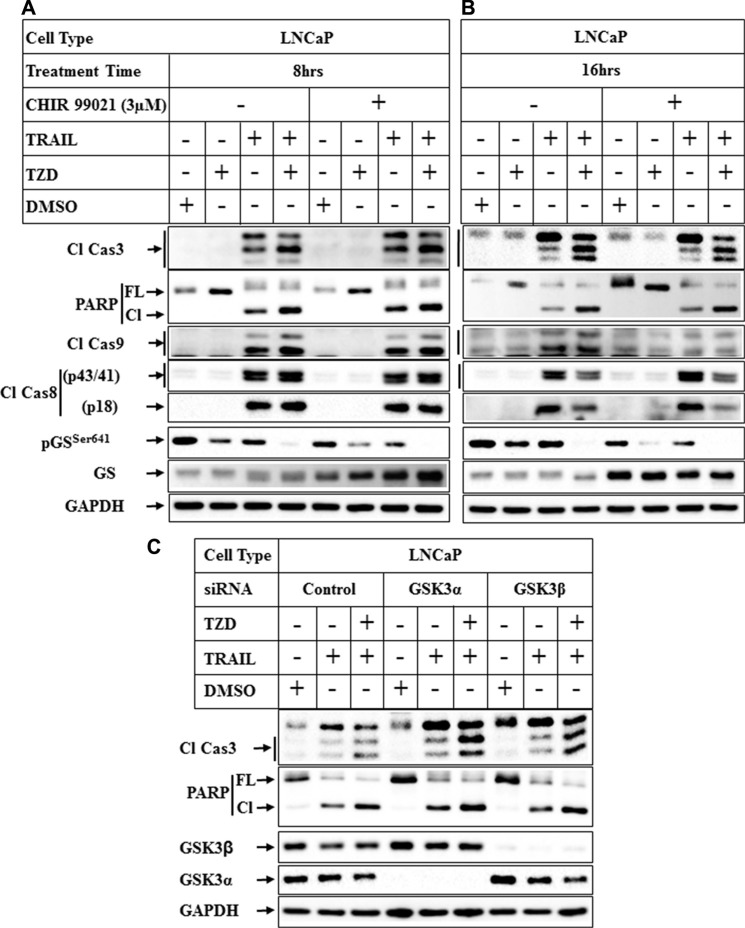
To understand whether antagonism of GSK3β was necessary to promote apoptosis, cells were pretreated with pharmacological inhibitors of GSK3β followed by treatment with TRAIL or TRAIL-TZD. Pretreatment with CHIR 99021, a specific inhibitor of GSK3β [38] produced no significant increase on TRAIL or TRAIL-TZD-induced apoptosis after 8 hrs or 16 hrs of treatment (Figure 8A and 8B). CHIR 99021, however, inhibited pGSSer641 levels, suggesting its efficacy in inhibiting GSK3β activity. Similar results were obtained with two other inhibitors, GSK3β inhibitor VIII and Kenpaullone (Supplementary Figure S1 and S2). To confirm the role of GSK3β in mediating apoptosis or resistance, GSK3β or GSK3α was knocked down first followed by treatment with TRAIL or TRAIL-TZD. Knockdown of GSK3α and to a lesser extent GSK3β seemed to increase TRAIL-TZD-induced Caspase 3 and PARP cleavage, (Figure 8C, compare lanes 3, 6 & 9). On the other hand, TRAIL-induced Caspase 3 and PARP cleavage was only marginally increased by GSK3α knockdown, while knockdown of GSK3β produced no major effect (compare lanes 2, 5, 8). These suggested that antagonism of both isoforms are necessary to increase TRAIL-TZD-induced apoptosis, and GSK3α seems to be important in TRAIL-induced apoptosis.
Figure 8. Effect of inhibition of GSK3β pathway on TRAIL-TZD-induced apoptosis.
LNCaP cells were pretreated with 3 μM CHIR 99021 for 1 hr followed by treatment with DMSO, TZD, TRAIL or TRAIL-TZD combination for 8 hrs (A) or 16 hrs (B). Western blot analyses were performed next with the indicated antibodies. (C) Subconfluent LNCaP cells transiently transfected separately with control-siRNA, GSK3α-siRNA or GSK3β-siRNA for 72 hrs followed by treatment with DMSO, TRAIL or TRAIL-TZD combination for 16 hrs. The samples were analyzed by Western blots.
DISCUSSION
The serine/threonine kinase GSK3β plays important roles in the pathogenesis of a wide variety of diseases that include neurodegenerative diseases (e.g. Parkinson's Disease), inflammatory diseases and cancer [39–41]. GSK3β expression is known to be induced in several cancer types, which include colon cancer [17], pancreatic cancer [18, 19], prostate cancer [20–22] and glioblastoma [23]. Increasing evidence points towards a pro-oncogenic role of GSK3β in various cancer types due to its effects in promoting cell proliferation and survival [17, 42]. Particularly, in pancreatic cancer cells GSK3β pathway was associated with increased NFκB activity, increased cancer cell survival [24], tumor dedifferentiation [19] and tumor resistance [25, 26]. There is also a strong evidence supporting a role of GSK3β in prostate cancer where it is involved in promoting androgen receptor function and nuclear translocation [20, 31, 32]. In addition, increased cytoplasmic GSK3β in prostate tumor samples correlated with the clinical stage and Gleason score [30]. While all these suggest that targeting GSK3β might be an important and effective means of controlling cancer progression, therapeutic options currently available are limited. This is because majority of the available pharmacological inhibitors of GSK3β have limited specificity and also target several other protein kinases [38].
In an attempt to overcome this limitation of GSK3β inhibitors, in the current study we aimed at elucidating the mechanism by which GSK3β expression can be antagonized in cancer cells. Although TZD-mediated antagonism of GSK3β was reported earlier [43], those studies provided limited insight towards the mechanism involved. Our results show that treatment with a combination of TRAIL and TZD which induces potent apoptosis [35], also antagonized the expression of total GSK3β in various cancer cells. More in depth analysis showed that TZD alone can significantly attenuate GSK3β expression, which inhibited total GSK3β via antagonizing its transcription. Since TZD is a ligand of PPARγ, we determined whether PPARγ played any role in this antagonism via designing siRNA-mediated knockdown experiments. Surprisingly, TZD-induced antagonism seemed to be PPARγ-independent. This is supported by several earlier studies that have showed that TZD can antagonize expression of β-catenin [44], cyclin D1 [45], c-myc [46] independent of PPARγ. Since TZD is known to activate AMPK and our earlier studies showed the involvement of AMPK pathway in TRAIL-TZD-induced apoptosis, we hypothesized that AMPK might be involved in regulating GSK3β expression. In fact, pretreatment with a pharmacological inhibitor of AMPK (Compound C) was capable of partially reversing the inhibitory effects of TRAIL-TZD on total GSK3β expression. However, these effects of Compound C seemed to be AMPK-independent, since knocking down AMPKα1 or α2 alone or in combination was unable to reverse the expression of GSK3β in the presence of TRAIL-TZD. Several studies have reported AMPK-independent effects of Compound C [47], which seems to involve antagonism of mTOR pathway in T cells [48] and multiple mechanisms in human gliomas [49]. It is unclear who the mediators are downstream of TZD or TRAIL-TZD that regulate GSK3β expression in the cancer cells. Earlier studies by Zhang et al. have shown that mutant K-Ras induces GSK3β transcription in pancreatic cancer cells via MAPK involving E-twenty six 2 (ETS2) transcription factor and p300 histone acetyltransferase [34]. Since TZD is known to inhibit the ETS pathway [50, 51], it seems possible that the inhibitory effects of TZD on GSK3β might involve ETS transcription factors. More molecular approaches are needed to firmly establish this in TZD-GSK3β axis.
To understand whether GSK3β inhibition plays a major role in mediating TRAIL-TZD-induced apoptosis or increased TRAIL sensitivity in cancer cells, we pretreated cells with different pharmacological inhibitors of GSK3β- CHIR 99021, GSK3β inhibitor VIII and Kenpaullone followed by treatment with TRAIL alone or a combination of TRAIL and TZD. These results showed that these inhibitors can successfully antagonize GSK3β pathway as indicated by the corresponding reduction of pGSSer641 levels, but produced no effect on apoptosis. To validate these, we also studied the effect of knocking down either GSK3α or GSK3β on TRAIL or TRAIL-TZD-induced apoptosis. In these studies, although knocking down GSK3α and to a lesser extent GSK3β increased TRAIL-TZD-induced caspase 3 and PARP cleavage (indicating apoptosis), TRAIL-induced effects were potentiated only by GSK3α knockdown. Similar observations were also reported by other investigators, where inhibition of GSK3β in pancreatic cancer cells significantly inhibited NFκB activity but failed to sensitize to gemcitabine [18]. In a separate study, Lithium-induced inhibition of GSK3β antagonized chemotherapy-induced apoptosis [52]. On the contrary, studies in colon cancer cells showed that either pharmacological inhibition or siRNA-mediated knockdown of GSK3β augmented TZD-induced reduction of NFκB activity, cell growth inhibition and apoptosis induction [43]. The reason behind these discrepancies is not quite clear, but indicates the complexity of GSK3β pathway which might be cancer-type specific and needs further analysis. In fact, GSK3β is known to have a paradoxical role in mediating intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of cellular apoptosis [53]. Various other studies have shown the involvement of GSK3β in specific pathways of apoptosis [54, 55, 52]. As described earlier and in view of multiple cellular effects regulated by GSK3β, it is unclear at this point which major biological effects are mediated via inhibition of GSK3β. It remains a possibility that TZD-mediated antagonism of GSK3β/α axis might mediate a non-apoptotic form of cell death (or necroptosis) as was reported by others [56]. Necroptosis is a form of programmed necrosis that involves death receptors and specific signal transduction pathways mediated by receptor-interacting protein (RIP) kinases [57, 58]. TZD has also been shown to be involved in necroptosis [59]. Despite this complexity, our studies provide a novel insight towards a pathway in which TZD can antagonize GSK3β expression and might be effective in targeting those cancers which rely on GSK3β activity for proliferation and survival.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reagents and antibodies
RPMI and DMEM, DMEM F12 tissue culture media, Lipofectamine 2000 and β-galactosidase assay kit were purchased from Invitrogen; the luciferase Assay Reagent from Promega (Madison, WI); Troglitazone, TRAIL and Cycloheximide (CHX) were purchased from EMD Biosciences (Gibbstown, NJ), Compound C, AKT Inhibitor VIII, LY294002, Kenpaullone and AR-A014418 were from EMD Millipore (Billerica, MA), CHIR 99021 was from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). The antibodies utilized were obtained from the following sources: poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), caspase-3, GSK-3β, phospho-GSK-3βSer9, GSK3α, AKT, pAKTSer473, pAKT2Ser474, PPARγ, AMPKα1 and α2, GS, pGSSer641 from Cell Signaling Technologies (Danvers, MA); GAPDH from Ambion Inc. (Austin, TX). The GSK3β promoter luciferase plasmid (pGL3-GSK-3β-luc (−427/+66) was obtained from the laboratory of Dr. Daniel D. Billadeau, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN [34].
Cell culture
Human Prostate cancer cells (LNCaP, DU 145), pancreatic cancer cells (BxPC3) were obtained from ATCC and maintained in RPMI (LNCaP, DU 145) and DMEM (BxPC3) media supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 IU/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin. Human HCC cells (Huh7) were obtained as described [60] and grown in DMEM/F12 media. In TRAIL and TZD experiments, cells were treated with 100 ng/ml TRAIL or 50 μm TZD (unless indicated otherwise) alone or in combination for various lengths of time followed by Western blot analysis. In the studies with CHX, the cells were pretreated with 50 μg/ml of CHX for 48 hrs followed by TRAIL-TZD for 24 hrs. For the inhibitor experiments, cells were pretreated for 1 hour or 24 hours with the respective inhibitors, followed by TRAIL-TZD treatment for various lengths of time.
Luciferase assays
Sub-confluent populations of cells were transiently transfected with GSK-3β luciferase promoter pGL3-GSK-3β-luc (−427/+66), along with β-galactosidase vector (to correct for transfection efficiency) utilizing Lipofectamine-2000 as per the manufacturer's instructions. After 24 hours of recovery in the growth medium, the cells were treated with TRAIL-TZD for various lengths of time; the cells were harvested after treatment and luciferase and β-galactosidase assays were performed as described earlier [61]. Each transfection was performed in triplicate, and each experiment was repeated at least twice. Luciferase and β-galactosidase (β-gal) assays were performed using a luminometer (Berthold Technologies, Centro XS3 LB 960) and a plate reader (Power Wave XS, Biotek), respectively. The results obtained were calculated as the ratio of relative light units (RLU) to β-gal values (RLU/β-gal) and expressed as the % increase compared with controls.
Small interference RNA (siRNA)
siRNA smart pool against hPPARγ (L-003436-00), hAMPKα1 (L-005027-00), hAMPKα2 (L-005361-00), hGSK3β (L-003010-00) and hGSK3α (L-003009-00) were purchased from Dharmacon (Lafayette, CO). A negative control siRNA from Ambion Inc. (Austin, TX) was used as control siRNA. siRNA transfection was performed using Lipofectamine 2000 as per the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, subconfluent cells plated in 35 mm plates were transfected with 50 nM of either control siRNA or target protein-siRNA for 24 h followed by recovery in serum containing medium. The transfected cells were treated after 72 hours of transfection with either DMSO or TRAIL or TZD alone or in combination for various lengths of time followed by western blot analysis.
Western blot analysis
Western blot analysis was performed utilizing procedures described previously [60, 62]. Briefly, equal amounts of total cell extracts were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes, and subjected to Western blot analysis utilizing various antibodies.
Immunofluorescence microscopy
Immunofluorescence microscopy was performed as reported earlier [63]. Briefly, Huh7 cells plated in 4-well chamber slides were treated with DMSO, TZD, or TRAIL alone or in combination for 8 hrs and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M PBS, pH 7.4 and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in 0.1 M PBS. Rabbit-anti GSK3β antibody and fluorochrome-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody was used as primary and secondary antibodies respectively. They were also stained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) to show the nucleus. Images were captured on a Nikon ECLIPSE Ti microscope, equipped with a digital camera (Nikon DS-Qi2) at 40 × magnification.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FIGURES
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Daniel D. Billadeau, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN for providing the GSK3β promoter luciferase plasmid (pGL3-GSK-3β-luc (−427/+66) [34].
Abbreviations
- AMPK
AMP-activated protein kinase
- AR
Androgen Receptor
- β-Gal
β-galactosidase
- CHX
Cycloheximide
- GS
Glycogen Synthase
- GSK3α
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 alpha
- GSK3β
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 beta
- HCC
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- mTOR
Mammalian Target of Rapamycin
- NFκB
Nuclear Factor κB
- PARP
Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase
- PPARγ
Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor gamma
- RLU
Relative light units
- siRNA
Small Interference RNA
- TRAIL
Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand
- TZD
Troglitazone
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to the study.
GRANT SUPPORT
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health grants CA178063 (to B.R.) and CA176846 (to A.R.), Department of Defense Award W81XWH-10-1-0195 (to B. R.), and the Veterans Affairs Merit Award grants BX003296 (to B. R.) and BX002703, BX002355 (to A. R.).
REFERENCES
- 1.Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Woodgett JR. GSK-3: Functional Insights from Cell Biology and Animal Models. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011;4:40. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jope RS, Johnson GV. The glamour and gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29:95–102. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2003.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Woodgett JR. Judging a protein by more than its name: GSK-3. Sci STKE. 2001;2001:re12. doi: 10.1126/stke.2001.100.re12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bhat RV, Budd Haeberlein SL, Avila J. Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a drug target for CNS therapies. J Neurochem. 2004;89:1313–1317. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sutherland C. What Are the bona fide GSK3 Substrates? Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;2011:505607. doi: 10.4061/2011/505607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McManus EJ, Sakamoto K, Armit LJ, Ronaldson L, Shpiro N, Marquez R, Alessi DR. Role that phosphorylation of GSK3 plays in insulin and Wnt signalling defined by knockin analysis. EMBO J. 2005;24:1571–1583. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Taelman VF, Dobrowolski R, Plouhinec JL, Fuentealba LC, Vorwald PP, Gumper I, Sabatini DD, De Robertis EM. Wnt signaling requires sequestration of glycogen synthase kinase 3 inside multivesicular endosomes. Cell. 2010;143:1136–1148. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.11.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sutherland C, Leighton IA, Cohen P. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta by phosphorylation: new kinase connections in insulin and growth-factor signalling. Biochem J. 1993;296:15–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2960015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sutherland C, Cohen P. The alpha-isoform of glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle is inactivated by p70 S6 kinase or MAP kinase-activated protein kinase-1 in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1994;338:37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature. 1995;378:785–789. doi: 10.1038/378785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rubinfeld B, Albert I, Porfiri E, Fiol C, Munemitsu S, Polakis P. Binding of GSK3beta to the APC-beta-catenin complex and regulation of complex assembly. Science. 1996;272:1023–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5264.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis and subcellular localization. Genes Dev. 1998;12:3499–3511. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.22.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kang T, Wei Y, Honaker Y, Yamaguchi H, Appella E, Hung MC, Piwnica-Worms H. GSK-3 beta targets Cdc25A for ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis, and GSK-3 beta inactivation correlates with Cdc25A overproduction in human cancers. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:36–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lutterbach B, Hann SR. Hierarchical phosphorylation at N-terminal transformation-sensitive sites in c-Myc protein is regulated by mitogens and in mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:5510–5522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin O, Woodgett JR. Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation. Nature. 2000;406:86–90. doi: 10.1038/35017574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rottmann S, Wang Y, Nasoff M, Deveraux QL, Quon KC. A TRAIL receptor-dependent synthetic lethal relationship between MYC activation and GSK3beta/FBW7 loss of function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:15195–15200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505114102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shakoori A, Ougolkov A, Yu ZW, Zhang B, Modarressi MH, Billadeau DD, Mai M, Takahashi Y, Minamoto T. Deregulated GSK3beta activity in colorectal cancer: its association with tumor cell survival and proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;334:1365–1373. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mamaghani S, Patel S, Hedley DW. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition disrupts nuclear factor-kappaB activity in pancreatic cancer, but fails to sensitize to gemcitabine chemotherapy. BMC cancer. 2009;9:132. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ougolkov AV, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Bilim VN, Smyrk TC, Chari ST, Billadeau DD. Aberrant nuclear accumulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in human pancreatic cancer: association with kinase activity and tumor dedifferentiation. Clinical cancer research. 2006;12:5074–5081. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liao X, Thrasher JB, Holzbeierlein J, Stanley S, Li B. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta activity is required for androgen-stimulated gene expression in prostate cancer. Endocrinology. 2004;145:2941–2949. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rinnab L, Schutz SV, Diesch J, Schmid E, Kufer R, Hautmann RE, Spindler KD, Cronauer MV. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in androgen-responsive prostate cancer cell lines: are GSK inhibitors therapeutically useful? Neoplasia. 2008;10:624–634. doi: 10.1593/neo.08248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhu Q, Yang J, Han S, Liu J, Holzbeierlein J, Thrasher JB, Li B. Suppression of glycogen synthase kinase 3 activity reduces tumor growth of prostate cancer in vivo. Prostate. 2011;71:835–845. doi: 10.1002/pros.21300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Miyashita K, Kawakami K, Nakada M, Mai W, Shakoori A, Fujisawa H, Hayashi Y, Hamada J, Minamoto T. Potential therapeutic effect of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta inhibition against human glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:887–897. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ougolkov AV, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Savoy DN, Urrutia RA, Billadeau DD. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta participates in nuclear factor kappaB-mediated gene transcription and cell survival in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2076–2081. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kitano A, Shimasaki T, Chikano Y, Nakada M, Hirose M, Higashi T, Ishigaki Y, Endo Y, Takino T, Sato H, Sai Y, Miyamoto K, Motoo Y, et al. Aberrant glycogen synthase kinase 3beta is involved in pancreatic cancer cell invasion and resistance to therapy. PLoS One. 2013;8:e55289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mamaghani S, Simpson CD, Cao PM, Cheung M, Chow S, Bandarchi B, Schimmer AD, Hedley DW. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibition Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis. PLoS One. 2012;7:e41102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang JS, Herreros-Villanueva M, Koenig A, Deng Z, de Narvajas AA, Gomez TS, Meng X, Bujanda L, Ellenrieder V, Li XK, Kaufmann SH, Billadeau DD. Differential activity of GSK-3 isoforms regulates NF-kappaB, TRAIL- or TNFalpha induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1142. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mayes PA, Dolloff NG, Daniel CJ, Liu JJ, Hart LS, Kuribayashi K, Allen JE, Jee DI, Dorsey JF, Liu YY, Dicker DT, Brown JM, Furth EE, et al. Overcoming hypoxia-induced apoptotic resistance through combinatorial inhibition of GSK-3beta and CDK1. Cancer Res. 2011;71:5265–5275. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liao X, Zhang L, Thrasher JB, Du J, Li B. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta suppression eliminates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:1215–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Li R, Erdamar S, Dai H, Sayeeduddin M, Frolov A, Wheeler TM, Ayala GE. Cytoplasmic accumulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is associated with aggressive clinicopathological features in human prostate cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:2077–2081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mazor M, Kawano Y, Zhu H, Waxman J, Kypta RM. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 represses androgen receptor activity and prostate cancer cell growth. Oncogene. 2004;23:7882–7892. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schutz SV, Cronauer MV, Rinnab L. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta promotes nuclear export of the androgen receptor through a CRM1-dependent mechanism in prostate cancer cell lines. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109:1192–1200. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Senthivinayagam S, Mishra P, Paramasivam SK, Yallapragada S, Chatterjee M, Wong L, Rana A, Rana B. Caspase-mediated Cleavage of {beta}-Catenin Precedes Drug-induced Apoptosis in Resistant Cancer Cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:13577–13588. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900248200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang JS, Koenig A, Harrison A, Ugolkov AV, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Couch FJ, Billadeau DD. Mutant K-Ras increases GSK-3beta gene expression via an ETS-p300 transcriptional complex in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 2011;30:3705–3715. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Santha S, Viswakarma N, Das S, Rana A, Rana B. Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand (TRAIL)-Troglitazone-induced Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells Involve AMP-activated Protein Kinase. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:21865–21875. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.663526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.LeBrasseur NK, Kelly M, Tsao TS, Farmer SR, Saha AK, Ruderman NB, Tomas E. Thiazolidinediones can rapidly activate AMP-activated protein kinase in mammalian tissues. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006;291:E175–181. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00453.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Xiang X, Saha AK, Wen R, Ruderman NB, Luo Z. AMP-activated protein kinase activators can inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells by multiple mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;321:161–167. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.06.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bain J, Plater L, Elliott M, Shpiro N, Hastie CJ, McLauchlan H, Klevernic I, Arthur JS, Alessi DR, Cohen P. The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J. 2007;408:297–315. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Beurel E, Grieco SF, Jope RS. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;148:114–131. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.11.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Golpich M, Amini E, Hemmati F, Ibrahim NM, Rahmani B, Mohamed Z, Raymond AA, Dargahi L, Ghasemi R, Ahmadiani A. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3beta) signaling: Implications for Parkinson's disease. Pharmacol Res. 2015;97:16–26. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Domoto T, Pyko IV, Furuta T, Miyashita K, Uehara M, Shimasaki T, Nakada M, Minamoto T. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is a pivotal mediator of cancer invasion and resistance to therapy. Cancer Sci. 2016 doi: 10.1111/cas.13028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cao Q, Lu X, Feng YJ. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta positively regulates the proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells. Cell Res. 2006;16:671–677. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ban JO, Kwak DH, Oh JH, Park EJ, Cho MC, Song HS, Song MJ, Han SB, Moon DC, Kang KW, Hong JT. Suppression of NF-kappaB, GSK-3beta is involved in colon cancer cell growth inhibition by the PPAR agonist troglitazone. Chem Biol Interact. 2010;188:75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wei S, Lin LF, Yang CC, Wang YC, Chang GD, Chen H, Chen CS. Thiazolidinediones modulate the expression of beta-catenin and other cell-cycle regulatory proteins by targeting the F-box proteins of Skp1-Cul1-F-box protein E3 ubiquitin ligase independently of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;72:725–733. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.035287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wei S, Yang HC, Chuang HC, Yang J, Kulp SK, Lu PJ, Lai MD, Chen CS. A novel mechanism by which thiazolidinediones facilitate the proteasomal degradation of cyclin D1 in cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:26759–26770. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802160200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Akinyeke TO, Stewart LV. Troglitazone suppresses c-Myc levels in human prostate cancer cells via a PPARgamma-independent mechanism. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;11:1046–1058. doi: 10.4161/cbt.11.12.15709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Emerling BM, Viollet B, Tormos KV, Chandel NS. Compound C inhibits hypoxic activation of HIF-1 independent of AMPK. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:5727–5731. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.11.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rao E, Zhang Y, Li Q, Hao J, Egilmez NK, Suttles J, Li B. AMPK-dependent and independent effects of AICAR and compound C on T-cell responses. Oncotarget. 2016;7:33783–95. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Liu X, Chhipa RR, Nakano I, Dasgupta B. The AMPK inhibitor compound C is a potent AMPK-independent antiglioma agent. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:596–605. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kitamura S, Miyazaki Y, Hiraoka S, Toyota M, Nagasawa Y, Kondo S, Kiyohara T, Shinomura Y, Matsuzawa Y. PPARgamma inhibits the expression of c-MET in human gastric cancer cells through the suppression of Ets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;265:453–456. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kotake D, Hirasawa N. Activation of a retinoic acid receptor pathway by thiazolidinediones induces production of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor in OP9 adipocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;707:95–103. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.03.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Beurel E, Kornprobst M, Blivet-Van Eggelpoel MJ, Ruiz-Ruiz C, Cadoret A, Capeau J, Desbois-Mouthon C. GSK-3beta inhibition by lithium confers resistance to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis through the repression of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) expression. Exp Cell Res. 2004;300:354–364. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Beurel E, Jope RS. The paradoxical pro- and anti-apoptotic actions of GSK3 in the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathways. Prog Neurobiol. 2006;79:173–189. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2006.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Crowder RJ, Freeman RS. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta activity is critical for neuronal death caused by inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase or Akt but not for death caused by nerve growth factor withdrawal. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:34266–34271. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006160200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Song L, De Sarno P, Jope RS. Central role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase-3 activation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44701–44708. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206047200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Grassilli E, Narloch R, Federzoni E, Ianzano L, Pisano F, Giovannoni R, Romano G, Masiero L, Leone BE, Bonin S, Donada M, Stanta G, Helin K, Lavitrano M. Inhibition of GSK3B bypass drug resistance of p53-null colon carcinomas by enabling necroptosis in response to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:3820–3831. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe T, Kroemer G. Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:700–714. doi: 10.1038/nrm2970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Vanden Berghe T, Vanlangenakker N, Parthoens E, Deckers W, Devos M, Festjens N, Guerin CJ, Brunk UT, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P. Necroptosis, necrosis and secondary necrosis converge on similar cellular disintegration features. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:922–930. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yan S, Yang X, Chen T, Xi Z, Jiang X. The PPARgamma agonist Troglitazone induces autophagy, apoptosis and necroptosis in bladder cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014;21:188–193. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2014.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mishra P, Paramasivam SK, Thylur RP, Rana A, Rana B. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligand-mediated apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells depends upon modulation of PI3Kinase pathway independent of Akt. J Mol Signal. 2010;5:20. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-5-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Mishra P, Senthivinayagam S, Rangasamy V, Sondarva G, Rana B. Mixed lineage kinase-3/JNK1 axis promotes migration of human gastric cancer cells following gastrin stimulation. Mol Endocrinol. 2010;24:598–607. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pradeep A, Sharma C, Sathyanarayana P, Albanese C, Fleming JV, Wang TC, Wolfe MM, Baker KM, Pestell RG, Rana B. Gastrin-mediated activation of cyclin D1 transcription involves beta-catenin and CREB pathways in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:3689–3699. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Thylur RP, Senthivinayagam S, Campbell EM, Rangasamy V, Thorenoor N, Sondarva G, Mehrotra S, Mishra P, Zook E, Le PT, Rana A, Rana B. Mixed lineage kinase 3 modulates beta-catenin signaling in cancer cells. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2011;286:37470–37482. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.298943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.