Abstract
Patients with lung adenocarcinoma may benefit from recently developed molecular targeted therapies. However, analogous advanced treatments are not available for patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma (lung SCC). The survival rate of patients with the advanced stage of lung SCC remains poor. Exploration of novel lung SCC oncogenic pathways might lead to new treatment protocols for the disease. Based on this concept, we have identified microRNA- (miRNA) mediated oncogenic pathways in lung SCC. It is well known that miR-145-5p (the guide strand) functions as a tumor suppressor in several types of cancer. However, the impact of miR-145-3p (the passenger strand) on cancer cells is still ambiguous. Expression levels of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p were markedly reduced in cancer tissues, and ectopic expression of these miRNAs inhibited cancer cell aggressiveness, suggesting that both miR-145-3p as well as miR-145-5p acted as antitumor miRNAs. We identified seven putative target genes (MTDH, EPN3, TPD52, CYP27B1, LMAN1, STAT1 and TXNDC12) that were coordinately regulated by miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in lung SCC. Among the seven genes, we found that metadherin (MTDH) was a direct target of these miRNAs. Kaplan–Meier survival curves showed that high expression of MTDH predicted reduced survival of lung SCC patients. We investigated pathways downstream from MTDH by using genome-wide gene expression analysis. Our data showed that several anti-apoptosis and pro-proliferation genes were involved in pathways downstream from MTDH in lung SCC. Taken together, both strands of miR-145, miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p are functional and play pivotal roles as antitumor miRNAs in lung SCC.
Keywords: microRNA-145-5p, microR-145-3p, tumor-suppressor, MTDH, lung squamous cell carcinoma
INTRODUCTION
Lung cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer-related death worldwide [1]. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer and is divided into three subtypes according to pathogenesis: adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma [2]. Recent developments in molecular targeted therapies have improved the overall survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma [3]. In contrast, there is a lack of effective therapeutic options to treat patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma (lung SCC) [3]. In that regard, cancer cell metastasis is known to be an important prognostic indicator of lung cancer. Thus, we hypothesized that current genomic approaches might be used to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying lung SCC metastasis and suggest improved treatments for this disease.
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a class of small non-coding RNAs. They are involved in the repression or degradation of target RNA transcripts in a sequence-dependent manner [4–6]. Aberrantly expressed miRNAs can dysregulate cellular RNA networks critical for normal cell function. The resultant failure of RNA networks promotes malignant transformation of cancer cells [7–9]. Identification of aberrantly expressed miRNAs is the first step to defining the oncogenic RNA networks in cancer cells. With that in mind, we used clinical specimens to construct miRNA expression signatures of various types of human cancer [10–14]. Using these signatures, we identified antitumor miRNAs and miRNA-regulated oncogenic genes [10–14]. Our recent studies of lung SCC revealed that miR-1/miR-133a clustered miRNAs, miR-206 and the miR-29-family inhibited cancer cell migration and invasion through targeting of several oncogenic genes, such as coronin-1C (CORO1C), c-MET and lysyl oxidase like 2 (LOXL2) [15–17].
Using miRNA expression signatures obtained by deep sequencing, we found that expression levels of miR-145-5p (the guide strand of pre-miR-145) and miR-145-3p (the passenger strand of pre-miR-145) were significantly reduced in cancer tissues, suggesting that these miRNAs functioned as tumor-suppressors [18]. It is believed that the guide strand RNA from duplex miRNA is retained to direct recruitment of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to target messenger RNAs. In contrast, the passenger strand RNA is degraded in the course of miRNA biogenesis [19]. Our recent study overturned this convention. We found that both the miR-144-5p strand and the miR-144-3p strand derived from pre-miR-144 acted as tumor suppressors in bladder cancer (BC) cells [20]. Moreover, we showed that miR-145-3p acted as a tumor-suppressor in BC cells, indicating that the passenger strand of miRNA has pivotal roles in human cancer pathogenesis [18].
Downregulation of miR-145-5p was reported in several cancers, establishing its function as a tumor-suppressor [21–26]. However, the role of miR-145-3p on lung cells is still ambiguous. The aims of the present study were to investigate the anti-tumor effects of miR-145-3p as well as miR-145-5p in lung cells. We also sought to identify oncogenic RNA networks in lung SCC and the genes regulated by these miRNAs. Our present data showed that miR-145-3p functions as a tumor-suppressor as well as miR-145-5p in lung SCC cells. Moreover, gene expression data and in silico database analysis showed that the metadherin gene (MTDH), also known as astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) was a direct target of both miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p regulation. Kaplan–Meier survival curves showed that high expression of MTDH predicted poorer survival of lung SCC patients. The discovery of new tumor-suppressor functions of both miRNAs strands of miR-145 (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p) provides new insight into the molecular mechanisms of lung SCC pathogenesis.
RESULTS
Expression levels of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in lung SCC clinical specimens and cell lines
We evaluated the expression levels of dual strand miRNAs of pre-miR-145 (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p) in lung SCC tissues. The expression levels of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p were significantly reduced in lung SCC tissues compared to noncancerous tissues (P = 0.0012 and P < 0.0001, respectively, Figure 1A). Spearman's rank test showed positive correlations between the expression of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p (R = 0.616 and P < 0.0001; Figure 1B).
Figure 1. The expression levels of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in lung SCC cells and their ectopic effects in cancer cells.
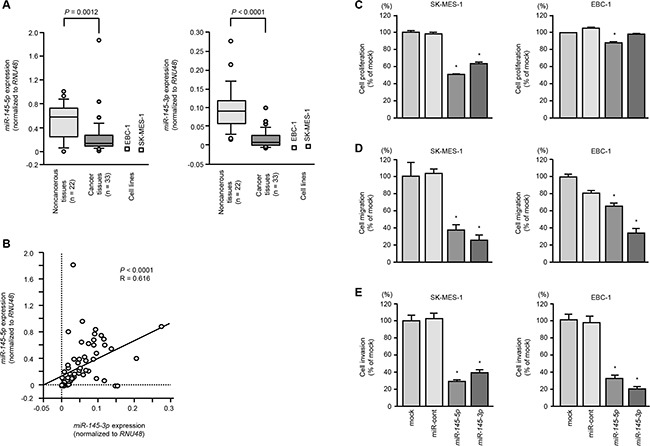
A. Expression levels of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in lung SCC clinical specimens and cell lines (SK-MES-1 and EBC-1) were determined by qRT-PCR. Data were normalized to RNU48 expression. B. Correlation of the expression levels of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p. C. Cell growth was determined by XTT assays 72 h after transfection with 10 nM miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p. *P < 0.05. D. Cell migration activity was determined by wound healing assays. *P < 0.001. E. Cell invasion activity was determined using Matrigel invasion assays. *P < 0.001.
The patients’ backgrounds and clinicopathological characteristics are summarized in Table 1A. Normal lung tissues are summarized in Table 1B. There were no significant relationships between any of the clinicopathological parameters (i.e., tumor grade, stage, metastasis, or survival rate) and the expression levels of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p (data not shown).
Table 1A. Characteristic of patients.
| Lung cancer | SCC | (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total number | 33 | ||
| Median age (range) | 70 (50 - 88) | ||
| Gender | |||
| Male | 31 | (93.9) | |
| Female | 2 | (6.1) | |
| Pathological tumor stage | |||
| IA | 5 | (15.2) | |
| IB | 8 | (24.2) | |
| IIA | 4 | (12.1) | |
| IIB | 6 | (18.2) | |
| IIIA | 8 | (24.2) | |
| IIIB | 1 | (3.0) | |
| unknown | 1 | (3.0) | |
| Differentiation | |||
| well | 8 | (24.2) | |
| moderately | 20 | (60.6) | |
| poorly | 3 | (9.1) | |
| unknown | 2 | (6.1) | |
| Pleural invasion | |||
| (+) | 15 | (45.5) | |
| (−) | 18 | (54.5) | |
| Venous invasion | |||
| (+) | 16 | (48.5) | |
| (−) | 17 | (51.5) | |
| Lymphatic invasion | |||
| (+) | 16 | (48.5) | |
| (−) | 17 | (51.5) |
Table 1B. Characteristic of Patients.
| Normal lung | n | |
|---|---|---|
| Total number | 22 | |
| Median age (range) | 71 (50 - 88) | |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 22 | |
| Female | 0 |
Effects of ectopic expression of miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p on cell proliferation, migration and invasion in SK-MES-1 and EBC-1 cells
To investigate the functional roles of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p, we performed gain-of-function studies using mature miRNA transfections of SK-MES-1 and EBC-1 cells. The expression levels of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p were significantly lower in two cell lines (Figure 1A).
XTT assays revealed significant inhibition of cell proliferation in SK-MES-1 cells transfected with miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p in comparison with mock or control transfectants (P < 0.05, Figure 1C). EBC-1 cells transfected with miR-145-3p, there was no significant inhibition of cell proliferation in comparison with control transfectants (Figure 1C).
Wound healing assays showed significant inhibition of cell migration activity after transfection with miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p (P < 0.001, Figure 1D).
Similarly, Matrigel invasion assays revealed that transfection with miR-145-5p of miR-145-3p reduced cell invasion activities (P < 0.001, Figure 1E).
To investigate the synergistic effects of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p, we performed functional assays (cell proliferation, migration and invasion assays) with co-transfection of mature miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in EBC-1 cells. In this assays, we did not detected the synergistic effects by using these miRNAs transfection (Supplementary Figure S1)
Identification of target genes coordinately regulated by miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in lung SCC cells
To identify target genes coordinately regulated by miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p, we performed a combination of in silico analyses, oligomicroarray expression analyses and Gene Omnibus database (GEO) analyses.
The TargetScan database showed that 4,405 and 3,164 genes have putative target sites for miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in their 3′UTRs, respectively. Next, we performed genome-wide gene expression analysis using EBC-1 cells (GEO accession number GSE77790). Genes downregulated (log2 ratio < -1.0) by transfection with miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p were selected as putative target genes. A total of 314 and 155 genes were downregulated in miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p transfectants, respectively. We found that there were 13 common genes targeted by both miRNAs. Finally, to evaluate upregulated genes in clinical NSCLC specimens, we examined gene expression profiles in the GEO database (accession numbers GSE19188).
A total of 7 putative candidate genes for both miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p regulation were identified (Table 2). A flow chart describing the strategy for analysis of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p target genes is shown in Figure 2A. We examined real-time RT-qPCR analyses of EBC-1 cells to investigate whether restoration of miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p expression altered the expression of 7 genes mRNA. The mRNA expression levels of 7 candidate genes were shown in Figure 2B. Among these genes, MTDH, EPN3, LMAN1, STAT1, and TXNDC12 were significantly repressed in miR-145-5p transfectants as compared with mock- or miR-control-transfected cells. All candidate target genes were significantly repressed in miR-145-3p transfectants as compared with mock- or miR-control-transfected cells.
Table 2. Downregulated genes in miR-145-5p/3p transfectant.
| Entrez Gene ID | common target | Gene name | miR-145-5p | miR-145-3p | miR-145-5p transfection (log2) | miR-145-3p transfection (log2) | GSE19188 (fold-change) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| conserved | poorly conserved | poorly conserved | ||||||
| 92140 | MTDH | metadherin | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1.03 | −1.34 | 1.29 |
| 55040 | EPN3 | epsin 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | −1.00 | −1.28 | 6.01 |
| 7163 | TPD52 | tumor protein D52 | 0 | 2 | 1 | −1.18 | −1.26 | 2.66 |
| 1594 | CYP27B1 | cytochrome P450, family 27, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | −1.74 | −1.40 | 2.12 |
| 79748 | LMAN1 | lectin, mannose-binding, 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | −1.08 | −1.14 | 1.78 |
| 6772 | STAT1 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, 91kDa | 0 | 1 | 1 | −1.30 | −1.01 | 1.61 |
| 51060 | TXNDC12 | thioredoxin domain containing 12 (endoplasmic reticulum) | 0 | 1 | 1 | −2.13 | −2.72 | 1.20 |
Figure 2. Identification of genes coordinately regulated by miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p.
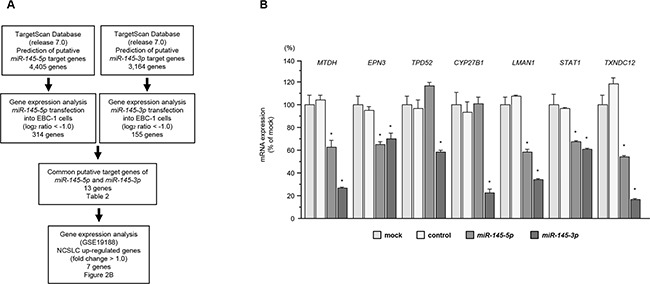
A. Flow chart illustrates the strategy for analysis of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p target genes in lung SCC cells. B. Identification of target genes of miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p. Expression levels of 7 mRNAs (MTDH, EPN3, TPD52, CYP27B1, LMAN1, STAT1 and TXNDC12) were evaluated by qRT-PCR in EBC-1 cells 72 h after transfection with miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p. GUSB was used as an internal control. *P < 0.0001.
We did not detected the synergistic effects (co-transfection of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p) for expression status of MTDH in SK-MES-1 and EBC-1 cells (Supplementary Figure S2).
MTDH was direct target by miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in lung SCC cells
We performed real-time RT-qPCR and Western blotting analyses of SK-MES-1 and EBC-1 cells to investigate whether restoration of miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p expression altered the expression of MTDH mRNA and MTDH protein. The mRNA and protein expression levels of MTDH/MTDH were significantly repressed in miR-miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p transfectants as compared with mock- or miR-control-transfected cells (Figure 3A and 3B).
Figure 3. Direct regulation of MTDH by miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p in lung SCC cells.
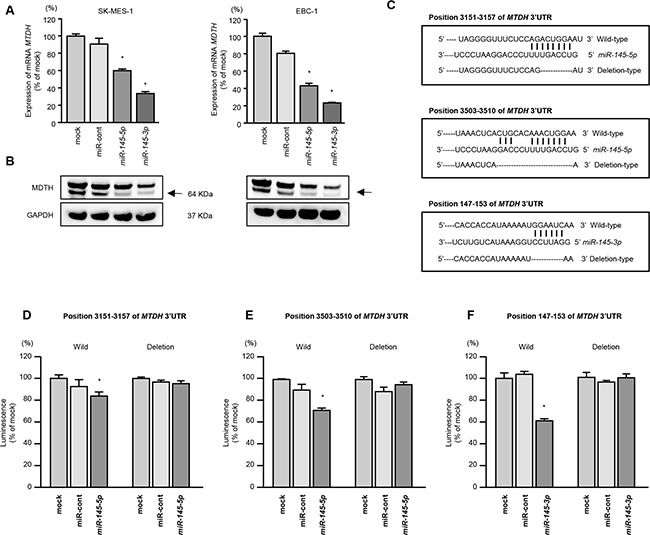
A. MTDH mRNA expression was evaluated by qRT-PCR in SK-MES-1 and EBC-1 cells 72 h after transfection with miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p. GUSB was used as an internal control. *P < 0.0001. B. MTDH protein expression was evaluated by Western blot analyses in SK-MES-1 and EBC-1 72 h after transfection with miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p. GAPDH was used as a loading control. C. miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p binding sites in the 3′-UTR of MTDH mRNA. (D-F) Dual luciferase reporter assays using vectors encoding putative miR-145-5p (positions 3,151-3,157 or 3,503-3,510) or miR-145-3p (147-153) target sites of the MTDH 3′-UTR for both wild-type and deleted regions. Normalized data were calculated as ratios of Renilla/firefly luciferase activities. *P = 0.0054, P < 0.001, and P < 0.001 for D-F., respectively.
We next performed luciferase reporter assays using EBC-1 cells to determine whether MTDH mRNA had target sites for miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p. The TargetScan database identified two putative target sites in the 3′-UTR of MTDH for miR-145-5p (position 3151-3157 and position 3503-3510) and one site for miR-145-3p (position 147-153) (Figure 3C). We used vectors encoding a partial wild-type sequence of the 3′-UTR of MTDH mRNA, including the predicted miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p target site, or a vector lacking the miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p target sites. We found that the luminescence intensity was significantly reduced by co-transfection with miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p and the vector carrying the wild-type 3′-UTR of MTDH. On the other hand, the luminescence intensity was not decreased when the seed sequences of the target sites were deleted from the vectors (P = 0.0054, P < 0.001, and P < 0.001, respectively; Figures 3D-3F).
Effects of silencing MTDH on cell aggressiveness in lung SCC cells
We investigated the oncogenic function of MTDH in lung SCC cells by using si-MTDH transfectants. We evaluated the knockdown efficiency of si-MTDH transfection in lung SCC cells. Present data indicated that si-MTDH effectively downregulated MTDH/MTDH expression in lung SCC cells (Figure 4A and 4B).
Figure 4. Effects of MTDH silencing in lung SCC cell lines.
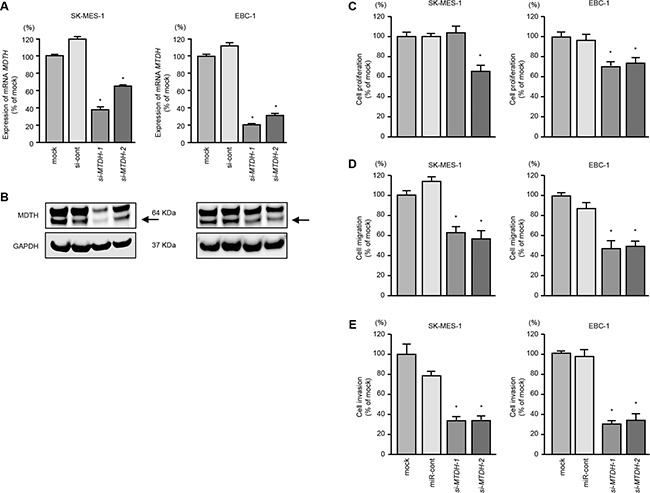
A. MTDH mRNA expression was evaluated by qRT-PCR in SK-MES-1 and EBC-1 72 h after transfection with si-MTDH-1 or si-MTDH-2. GUSB was used as an internal control. B. MTDH protein expression was evaluated by Western blot analysis in SK-MES-1 and EBC-1 72 h after transfection with miR-145-5p or miR-145-3p. GAPDH was used as a loading control. C. Cell proliferation was determined with the XTT assays 72 h after transfection with 10 nM si-MTDH-1 or si-MTDH-2. *P < 0.05. D. Cell migration activity was determined by wound healing assays. *P < 0.001. E. Cell invasion activity was determined using Matrigel invasion assays. *P < 0.001.
Cell proliferation was inhibited by si-MTDH transfectants in comparison with mock or si-control transfectants in EBC-1 cells (P < 0.05, Figure 4C). However in SK-MES-1 cells transfected with si-MTDH-1, proliferation was not inhibited in comparison with mock or si-control transfectants (Figure 4C).
Wound healing and Matrigel invasion assays showed significant inhibition of cell migration and invasion by si-MTDH transfectants (P < 0.001, Figures 4D and 4E).
Expression of MTDH in clinical lung SCC specimens
The mRNA expression levels of MTDH were significantly upregulated in lung SCC clinical samples (Figure 5A). As for MTDH copy number variation (CNV), our study showed that 60% of lung SCC patients had a genetic alteration (Figure 5B and 5C). The mRNA expression levels of MTDH significantly increased in accordance with the increase of MTDH gene copy number (Figure 5D). We assessed the Kaplan–Meier univariate survival of patients groups, comparing those with an MTDH alteration (CNV amplification or gain, or mRNA Z-score > 1.5) and those without an MTDH alteration (diploid or heterozygous loss, and mRNA Z-score equal or less than 1.5). The MTDH altered group had a significantly poorer overall survival [P = 0.0370] (Figure 5E).
Figure 5. Clinical significance of MTDH expression in lung SCC based on TCGA database.
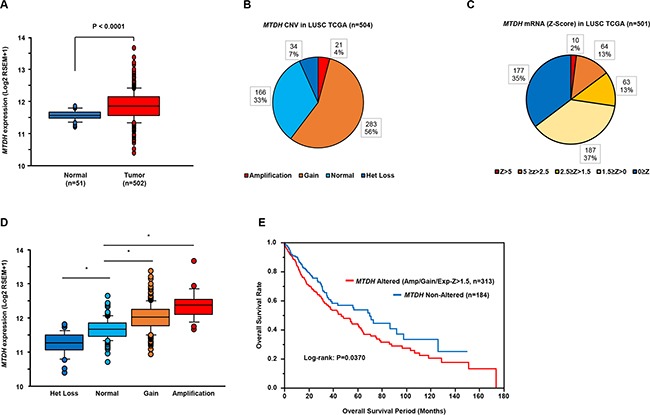
A. Comparison of MTDH mRNA expression levels between normal and tumor samples. B, C. The distribution of MTDH genomic copy number variation (n = 504) and mRNA Z-score (n = 501) in LUSCC TCGA. D. Box-and-whisker plots of MTDH mRNA expression with respect to genomic copy number *P < 0.0001. E. Clinical outcome for patients with altered MTDH (CNV, amplification or gain, or mRNA Z-score > 1.5) or non-altered MTDH (CNV, diploid or het loss, and mRNA Z-score ≤ 1.5) are displayed as Kaplan–Meier plots with log-rank tests.
Identification of MTDH-mediated downstream pathways in lung SCC cells
To identify the downstream genes regulated by MTDH, genome-wide gene expression analyses and in silico analyses were performed in lung SCC cells transfected with si-MTDH. Our present expression data using EBC-1 cells was deposited in GEO database (GEO accession number: GSE82108).
A total of 1,841 genes were reduced in si-MTDH transfected cells. Downregulated genes (top 40 genes) were listed in Supplementary Tables S1A and S1B. Furthermore, to investigate the functional roles of MTDH-mediated genes, we categorized these downregulated genes by KEGG pathways. Genes involved in these pathways are listed in Supplementary Table S2. Among these pathways, we focused on “Focal adhesion”, “Pathways in cancer” and “Endocytosis” pathways because MTDH contributed to cancer cell migration and invasion (Table 3).
Table 3A. Downregulated genes by si-MTDH in “Focal adhesion pathway”.
| Entrez gene ID | Gene symbol | Description | si-MTDH transfectant (fold-change) |
GSE19188 (fold-change) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| siRNA1 | siRNA2 | ||||
| 1290 | COL5A2 | collagen, type V, alpha 2 | 0.02 | −0.07 | 3.55 |
| 3688 | ITGB1 | integrin, beta 1 | −2.28 | −0.05 | 2.64 |
| 2317 | FLNB | filamin B, beta | −2.20 | −2.01 | 2.43 |
| 7422 | VEGFA | vascular endothelial growth factor A | −2.06 | 0.36 | 1.99 |
| 3915 | LAMC1 | laminin, gamma 1 (formerly LAMB2) | −3.22 | 0.18 | 1.61 |
| 1956 | EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor | −2.30 | −0.88 | 1.50 |
| 3371 | TNC | tenascin C | −4.17 | −0.37 | 1.46 |
| 5501 | PPP1CC | protein phosphatase 1, catalytic subunit, gamma isozyme | −0.60 | −2.04 | 1.42 |
| 5500 | PPP1CB | protein phosphatase 1, catalytic subunit, beta isozyme | −4.54 | −2.17 | 1.37 |
| 10000 | AKT3 | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 3 | −2.73 | −2.19 | 1.37 |
| 394 | ARHGAP5 | Rho GTPase activating protein 5 | −2.63 | 0.00 | 1.36 |
| 208 | AKT2 | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 2 | 0.22 | −2.70 | 1.34 |
| 5578 | PRKCA | protein kinase C, alpha | −0.26 | −3.17 | 1.30 |
| 3914 | LAMB3 | laminin, beta 3 | −2.31 | −0.20 | 1.04 |
Table 3B. Downregulated genes by si-MTDH in “Pathways in cancer”.
| Entrez gene ID | Gene symbol | Description | si-MTDH transfectant (fold-change) |
GSE19188 (fold-change) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| siRNA1 | siRNA2 | ||||
| 6513 | SLC2A1 | solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 1 | −2.02 | −0.30 | 6.34 |
| 112399 | EGLN3 | egl-9 family hypoxia-inducible factor 3 | −2.67 | −0.48 | 5.97 |
| 5888 | RAD51 | RAD51 recombinase | −1.08 | 1.16 | 4.24 |
| 4318 | MMP9 | matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase B, 92kDa gelatinase, 92kDa type IV collagenase) | −0.02 | −2.41 | 4.12 |
| 1163 | CKS1B | CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 1B | −2.27 | 0.87 | 3.42 |
| 5337 | PLD1 | phospholipase D1, phosphatidylcholine-specific | −0.82 | −2.39 | 2.83 |
| 3688 | ITGB1 | integrin, beta 1 | −2.28 | −0.05 | 2.64 |
| 5578 | PRKCA | protein kinase C, alpha | −0.26 | −3.17 | 2.08 |
| 7184 | HSP90B1 | heat shock protein 90kDa beta (Grp94), member 1 | −2.88 | 0.03 | 2.00 |
| 7422 | VEGFA | vascular endothelial growth factor A | −2.06 | 0.05 | 1.99 |
| 8030 | CCDC6 | coiled-coil domain containing 6 | −7.46 | 0.65 | 1.62 |
| 3915 | LAMC1 | laminin, gamma 1 (formerly LAMB2) | −3.22 | 0.18 | 1.61 |
| 54205 | CYCS | cytochrome c, somatic | −2.20 | 1.34 | 1.59 |
| 1956 | EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor | −2.30 | −0.88 | 1.50 |
| 613 | BCR | breakpoint cluster region | −2.43 | −0.76 | 1.28 |
| 208 | AKT2 | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 2 | 0.22 | −2.70 | 1.34 |
| 10000 | AKT3 | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 3 | −2.73 | −2.19 | 1.37 |
| 5728 | PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog | 0.13 | −3.01 | 1.26 |
| 861 | RUNX1 | runt-related transcription factor 1 | −3.21 | −3.90 | 1.26 |
| 3914 | LAMB3 | laminin, beta 3 | −2.31 | −0.20 | 1.04 |
Table 3C. Downregulated genes by si-MTDH in “Endcytosis pathway”.
| Entrez gene ID | Gene symbol | Description | si-MTDH transfectant (fold-change) |
GSE19188 (fold-change) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| siRNA1 | siRNA2 | ||||
| 55040 | EPN3 | epsin 3 | 0.93 | −2.86 | 6.01 |
| 57154 | SMURF1 | SMAD specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 | −2.20 | −0.07 | 2.71 |
| 83737 | ITCH | itchy E3 ubiquitin protein ligase | −2.20 | −0.67 | 2.42 |
| 163 | AP2B1 | adaptor-related protein complex 2, beta 1 subunit | −2.28 | −0.99 | 1.76 |
| 9815 | GIT2 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting ArfGAP 2 | 0.06 | −2.30 | 1.53 |
| 51100 | SH3GLB1 | SH3-domain GRB2-like endophilin B1 | −3.11 | −2.15 | 1.11 |
| 9922 | IQSEC1 | IQ motif and Sec7 domain 1 | −0.14 | −2.90 | 1.35 |
| 2869 | GRK5 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 | −0.19 | −2.14 | 1.35 |
DISCUSSION
In miRNA biogenesis, processing of the pre-miRNA through Dicer1 generates a miRNA duplex (a passenger strand and a guide strand). The guide strand RNA from the duplex is retained and recruited to the RNA induced silencing complex (RISC) to target messenger RNAs, whereas the passenger strand has no regulatory activity and is degraded [27, 28]. Our recent studies showed that passenger strands of some miRNAs (miR-144-3p and miR-145-3p) have antitumor functions and directly target several oncogenic genes in BC cells [18, 20]. In this study, we demonstrated that miR-145-3p (passenger strand) had antitumor functions as did miR-145-5p (guide strand) in lung SCC cells. A large number of studies showed the antitumor function of miR-145-5p in several cancers, including lung cancer [21–26]. Based on previous studies and our data, both strands of pre-miR-145 (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p) act as antitumor miRNAs in cancer cells.
We hypothesized that miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p coordinately regulated target genes that significantly contributed to lung SCC pathogenesis. In this study, we applied in silico and gene expression analyses described in our previous studies [15–17, 18, 20]. Using that strategy, we previously found that ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 1 (UHRF1) was directly regulated by both miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in BC [18]. Moreover, we showed that UHRF1 was overexpressed in BC clinical specimens and that the high UHRF1 expression group had a significantly poorer cause-specific survival rate in comparison with the low expression group [18].
Here, we identified 7 putative candidate genes (MTDH, EPN3, TPD52, CYP27B1, LMAN1, STAT1 and TXNDC12) that were regulated by both miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in lung SCC cells. Several studies showed that TPD52 was overexpressed in several cancers, and function as an oncogenes [29, 30]. Recent study indicated that miR-145-5p and its target gene TPD52 contributed to malignancy progression and in metastasis of brain tumor [31]. In colon cancer cells, overexpression of miR-145-5p reduced STAT1 expression [32]. These facts suggest that list of candidate genes might be regulated by both miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in lung cancer cells. These genes mediated cancer pathways that are important for understanding lung SCC pathogenesis. We focused on MTDH in the present study and investigated its functional significance in lung SCC. MTDH is also termed astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) and lysine-rich CEACA-M1 co-isolated (LYRIC). It was initially cloned from human fetal astrocytes following HIV-1 infection or tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment [33]. The function of MTDH is a downstream mediator of several signal pathways, such as PI3K/AKT, NFκB, MAPK and Wnt/β-catenin [34, 35]. These activated pathways are deeply involved in cancer cells proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis [34, 35]. Our function assays showed that knockdown of MTDH inhibited cancer cell aggressiveness and affected downstream signal pathways under the following headings: “focal adhesion”, “pathways in cancer”, “endocytosis” and “cell cycle”. Our findings in this study support the oncogenic function of MTDH in lung SCC cells.
The primary finding of the present study is the overexpression of MTDH, a gene that is involved in the pathogenesis of lung SCC. Our large cohort study indicated that expression of MTDH was upregulated in cancer tissues. Furthermore, Kaplan–Meier survival curves showed that high expression of MTDH predicted poorer survival of lung SCC patients. Our functional study showed that silencing of MTDH inhibited lung-SCC cell migration and invasion. Metastasis is responsible for most of the mortality in lung cancer. Other studies demonstrated that high level MTDH expression predicted poor survival of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and breast cancer [35–38].
Recent studies showed that several miRNAs control the expression of MTDH in multiple types of cancer, such as miR-375, miR-136, miR-26a and miR-145-5p [39–44]. Downregulation of these miRNAs enhanced the expression of MTDH in cancer cells. Several studies indicated that activation of H-Ras/PI3K signaling induce the expression of MYC, which binds to the MTDH promoter region and enhances its expression [34, 45]. Interestingly, p53 appears to transcriptionally regulate miR-145-5p by its interaction with a potential p53 response element in the pre-miR-145 promoter region and miR-145-5p directly targets oncogenic MYC [46, 47]. In the human genome, MTDH is located in 8q22. This area is associated with the center of activity for genomic amplification in multiple cancers [48]. Recent study showed that MTDH and MYC cooperate to promote hepatic cancer [49]. Thus, it appears that overexpression of MTDH in cancer cells enhances its aggressiveness.
In conclusion, downregulation of dual strand pre-miR-145 (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p) was detected in lung SCC clinical specimens. Both miR-145-3p and miR-145-5p act as antitumor miRNAs in lung SCC cells. Oncogenic MTDH was directly regulated by these miRNAs. Expression of MTDH is involved in lung SCC pathogenesis and its high expression predicts poorer survival of lung SCC patients. Elucidation of miR-145-5p/miR-145-3p/MTDH-mediated molecular networks may lead to a better understanding of lung SCC pathogenesis and the development of new treatment protocols.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Clinical specimens, cell culture and RNA extraction
From 2010 to 2013, Kagoshima University Hospital collected 33 lung SCCs and 22 noncancerous lung specimens from patients who underwent pneumonectomy. Our study was approved by the Institutional Review Board for Clinical Research of Kagoshima University School of Medicine. Each patient gave us prior written informed consent and approval.
We used the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer TNM classification system to stage the samples. All samples were histologically graded [50].
Archival formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) samples were used for qRT-PCR analysis. Eight FFPE tissue sections (10-μm) were used for extraction of total RNA, using Recover All™ Total Nucleic Acid Isolation kits Ambion (Texas, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocols.
Two human lung SCC cell lines (SK-MES-1 and EBC-1) were obtained from Japanese Cancer Research Resources Bank (JCRB) and the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA), respectively.
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
PCR quantification was carried out essentially as previously described [12–17]. TaqMan probes and primers for MTDH (assay ID: Hs00757841_m1, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), EPN3 (HS00978957_m1), TPD52 (Hs00893105_m1), CYP27B1 (Hs01096154_m1), LMAN1 (Hs01557542), STAT1 (Hs01013996_m1) and TXNDC12 (Hs00210841_m1) were assay-on-demand gene expression products. To quantify the expression level of miRNAs, we utilized stem-loop RT-PCR for miR-145-5p (assay ID: 002278, Applied Biosystems) and miR-145-3p (assay ID: 002149, Applied Biosystems) following the manufacturer's protocol. mRNA and miRNA data were normalized to human GUSB (assay ID: Hs99999908_m1; Applied Biosystems) and RNU48 (assay ID: 001006; Applied Biosystems), respectively. The fold-change was calculated using the delta–delta Ct method.
Transfection with mature miRNA and small interfering RNA (si-RNA) by transfection of lung SCC cells
Here, we used the following miRNA species: Pre-miR™ miRNA precursors (hsa-miR-145-5p, assay ID: PM 11480; hsa-miR-145-3p, assay ID: PM 13036; negative control miRNA; assay ID: AM 17111) (Thermo Fisher). We also purchased the following from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA): Stealth Select RNAi siRNA, si-MTDH (assay ID: HSS 150644, and P/N: HSS 150646. Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA USA) provided negative-control siRNA (D-001810-10). For transfection, RNAs were incubated with OPTI-MEM (Invitrogen) and Lipofectamine RNAiMax reagent (Invitrogen) as previously studies [12–17].
Cell proliferation, migration, and invasion assays
XTT assays were used to assess cell proliferation (Cell Proliferation Kit II, Roche Applied Sciences, Tokyo, Japan). Cell migration was analysed with wound healing assays. Modified Boyden chambers containing Transwell-precoated Matrigel membrane filter inserts were used to quantitate cellular invasion. Details of these assays were described as previously [12–17].
Use of total genome expression and in silico analyses to identify genes regulated by miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p in lung SCC cells
Specific genes affected by miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p were identified by a combination of in silico and genome-wide gene expression analyses. Genes regulated by miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p were listed using the TargetScan database. We then attempted to identify targets using the EBC-1 cell line transfected with these miRNAs. A Sure Print G3 Human GE 8 × 60K Microarray (Agilent Technologies) was used for expression profiling of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p transfectants. The microarray data were deposited into GEO (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/), accession number GSE77790. Genes upregulated in NSCLC were obtained from publicly available data sets in GEO (accession numbers: GSE19188). The overall strategy is outlined in Figure 2.
Regulation of targets downstream from MTDH in lung SCC
We investigated lung SCC cells to identify pathways regulated by MTDH. We analyzed gene expression using si-MTDH-transfected EBC-1 cells. Microarray data were used for expression profiling of si-MTDH transfectants. The microarray data were deposited into GEO (accession number: GSE77790). We analyzed common down- or upregulated genes using the GEO dataset.
Western blotting
Protein lysates (50 μg) were obtained 96 h after transfection. Proteins were separated by NuPAGE on 4–12% bis-tris gels (Invitrogen) and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. Membranes were immunoblotted with diluted polyclonal MDTH antibody (1:200; HPA 015104; Sigma-Aldrich, St Lois, MO, USA) and GAPDH antibody (1:100; MAB374; Chemicon, Temecula, CA, USA). The procedure of Western blotting was described previously [12–17].
Plasmid construction and dual-luciferase reporter assay
The partial wild-type sequence of the MTDH 3′-untranslated region (UTR) was inserted between the XhoI–PmeI restriction sites in the 3′-UTR of the hRluc gene in the psiCHECK-2 vector (C8021; Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Alternatively, we used sequences that were missing the miR-145-5p target sites (position 3151-3157 or position 3503-3510) or the miR-145-3p target site (position 147-153). The synthesized DNA was cloned into the psiCHECK-2 vector. EBC-1 cells were transfected with 20 ng of the vector, 20 nM microRNAs, and 1 μL Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) in 100 μL Opti-MEM (Invitrogen). The procedure of dual-luciferase reporter assay was described previously [12–17].
TCGA database analysis of lung SCC specimens
The clinical significance of MTDH in lung SCC was assessed by RNA sequencing and a putative CNV database (predicted by a GISTIC algorithm) in LUSCC TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas: https://tcga-data.nci.nih.gov/). The genomic and clinical data were retrieved from cBioportal (http://www.cbioportal.org/) or UCSC Cancer Browser (https://genome-cancer.ucsc.edu/proj/site/hgHeatmap/). The normalized mRNA expression values in the RNA sequencing data were processed and distributed in log2 transformed RSEM (RNA-Seq by Expectation Maximization) values (cBioportal) or log2 transformed (RSEM+1) (UCSC Cancer Browser). The Z-scores of MTDH mRNA expression data and clinical sample information corresponding to LUSCC patients were collected from cBioportal. The MTDH altered group (CNV = amplification or gain, or mRNA Z-score > 1.5, total 313 cases) and the MTDH non-altered group (CNV = diploid or heterozygous loss, and mRNA Z-score ≤ 1.5, total 184 cases) were analyzed by Kaplan–Meier survival curves and log-rank statistics.
Statistical analysis
The relationships between 2 groups and the numerical values obtained by RT-qPCR were analysed using Mann-Whitney U-tests. Spearman's rank test was used to evaluate the correlations between the expression of miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p. The relationships among more than 3 variables and numerical values were analysed using the Bonferroni-adjusted Mann-Whitney U-test. Survival analysis was analysed by the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test, using Stat Mate software (version 4.01, ATMS Co., Tokyo, Japan). All other analyses were performed using Expert StatView (version 5, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the KAKENHI, grant numbers (C) 15K10801 and (C) 16K19458.
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2015;65:87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Travis WD. Pathology of lung cancer. Clinics in chest medicine. 2011;32:669–692. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2011.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, Soria JC, Rabe KF. Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: recent developments. Lancet (London, England) 2013;382:709–719. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61502-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nature reviews Genetics. 2008;9:102–114. doi: 10.1038/nrg2290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Singh SK, Pal Bhadra M, Girschick HJ, Bhadra U. MicroRNAs--micro in size but macro in function. The FEBS journal. 2008;275:4929–4944. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Iorio MV, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in cancer: small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5848–5856. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.0317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nature reviews Cancer. 2006;6:259–269. doi: 10.1038/nrc1840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wiemer EA. The role of microRNAs in cancer: no small matter. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43:1529–1544. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2007.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kikkawa N, Hanazawa T, Fujimura L, Nohata N, Suzuki H, Chazono H, Sakurai D, Horiguchi S, Okamoto Y, Seki N. miR-489 is a tumour-suppressive miRNA target PTPN11 in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC) Br J Cancer. 2010;103:877–884. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Itesako T, Seki N, Yoshino H, Chiyomaru T, Yamasaki T, Hidaka H, Yonezawa T, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M, Enokida H. The microRNA expression signature of bladder cancer by deep sequencing: the functional significance of the miR-195/497 cluster. PLoS One. 2014;9:e84211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fukumoto I, Kinoshita T, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Yamamoto N, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Nakagawa M, Okamoto Y, Seki N. Identification of tumour suppressive microRNA-451a in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma based on microRNA expression signature. Br J Cancer. 2014;111:386–394. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fukumoto I, Hanazawa T, Kinoshita T, Kikkawa N, Koshizuka K, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Okamoto Y, Seki N. MicroRNA expression signature of oral squamous cell carcinoma: functional role of microRNA-26a/b in the modulation of novel cancer pathways. Br J Cancer. 2015;112:891–900. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goto Y, Kojima S, Nishikawa R, Kurozumi A, Kato M, Enokida H, Matsushita R, Yamazaki K, Ishida Y, Nakagawa M, Naya Y, Ichikawa T, Seki N. MicroRNA expression signature of castration-resistant prostate cancer: the microRNA-221/222 cluster functions as a tumour suppressor and disease progression marker. Br J Cancer. 2015;113:1055–1065. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mataki H, Enokida H, Chiyomaru T, Mizuno K, Matsushita R, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Higashimoto I, Samukawa T, Nakagawa M, Inoue H, Seki N. Downregulation of the microRNA-1/133a cluster enhances cancer cell migration and invasion in lung-squamous cell carcinoma via regulation of Coronin1C. J Hum Genet. 2015;60:53–61. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2014.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mataki H, Seki N, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Goto Y, Kumamoto T, Machida K, Mizuno K, Nakagawa M, Inoue H. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-206 as a dual inhibitor of MET and EGFR oncogenic signaling in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2015;46:1039–1050. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mizuno K, Seki N, Mataki H, Matsushita R, Kamikawaji K, Kumamoto T, Takagi K, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Kato M, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Inoue H. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-29 family inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion directly targeting LOXL2 in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2016;48:450–460. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Matsushita R, Yoshino H, Enokida H, Goto Y, Miyamoto K, Yonemori M, Inoguchi S, Nakagawa M, Seki N. Regulation of UHRF1 by dual-strand tumor-suppressor microRNA-145 (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p): inhibition of bladder cancer aggressiveness. Oncotarget. 2016;7:28460–87. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Matranga C, Tomari Y, Shin C, Bartel DP, Zamore PD. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell. 2005;123:607–620. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Matsushita R, Seki N, Chiyomaru T, Inoguchi S, Ishihara T, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Mataki H, Tatarano S, Itesako T, Nakagawa M, Enokida H. Tumour-suppressive microRNA-144-5p directly targets CCNE1/2 as potential prognostic markers in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015;113:282–289. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kano M, Seki N, Kikkawa N, Fujimura L, Hoshino I, Akutsu Y, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Matsubara H. miR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b: Tumor-suppressive miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2804–2814. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Tatarano S, Kawahara K, Uchida Y, Nishiyama K, Fujimura L, Kikkawa N, Seki N, Nakagawa M. miR-145 and miR-133a function as tumor suppressors and directly regulate FSCN1 expression in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:883–891. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yoshino H, Enokida H, Itesako T, Kojima S, Kinoshita T, Tatarano S, Chiyomaru T, Nakagawa M, Seki N. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-143/145 cluster targets hexokinase-2 in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2013;104:1567–1574. doi: 10.1111/cas.12280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kojima S, Enokida H, Yoshino H, Itesako T, Chiyomaru T, Kinoshita T, Fuse M, Nishikawa R, Goto Y, Naya Y, Nakagawa M, Seki N. The tumor-suppressive microRNA-143/145 cluster inhibites cell migration and invasion by targeting GOLM1 in prostate cancer. J Hum Genet. 2014;59:78–87. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2013.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sachdeva M, Mo YY. miR-145-mediated suppression of cell growth, invasion and metastasis. Am J Transl Res. 2010;2:170–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kent OA, McCall MN, Cornish TC, Halushka MK. Lessons from miR-143/145: the importance of cell-type localization of miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:7528–7538. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gregory RI, Chendrimada TP, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R. Human RISC couples microRNA biogenesis and posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell. 2005;123:631–640. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ahmed F, Ansari HR, Raghava GP. Prediction of guide strand of microRNAs from its sequence and secondary structure. BMC bioinformatics. 2009;10:105. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Kojima S, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Inoguchi S, Kinoshita T, Fuse M, Sakamoto S, Nakagawa M, Naya Y, Ichikawa T, Seki N. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-224 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion via targeting oncogenic TPD52 in prostate cancer. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:1973–1982. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Byrne JA, Frost S, Chen Y, Bright RK. Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) and cancer-oncogene understudy or understudied oncogene? Tumour Biol. 2014;35:7369–7382. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Donzelli S, Mori F, Bellissimo T, Sacconi A, Casini B, Frixa T, Roscilli G, Aurisicchio L, Facciolo F, Pompili A, Carosi MA, Pescarmona E, Segatto O, Pond G, Muti P, Telera S, Strano S, Yarden Y, Blandino G. Epigenetic silencing of miR-145-5p contributes to brain metastasis. Oncotarget. 2015;6:35183–35201. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gregersen LH, Jacobsen AB, Frankel LB, Wen J, Krogh A, Lund AH. MicroRNA-145 targets YES and STAT1 in colon cancer cells. PLoS One. 2010;5:e8836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Noch EK, Khalili K. The role of AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC in the pathogenesis of central nervous system disease. Advances in cancer research. 2013;120:159–192. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-401676-7.00006-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hu G, Wei Y, Kang Y. The multifaceted role of MTDH/AEG-1 in cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:5615–5620. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Huang Y, Li LP. Progress of cancer research on astrocyte elevated gene-1/Metadherin. Oncol Lett. 2014;8:493–501. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Brown DM, Ruoslahti E. Metadherin, a cell surface protein in breast tumors that mediates lung metastasis. Cancer cell. 2004;5:365–374. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(04)00079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liang Y, Hu J, Li J, Liu Y, Yu J, Zhuang X, Mu L, Kong X, Hong D, Yang Q, Hu G. Epigenetic Activation of TWIST1 by MTDH Promotes Cancer Stem-like Cell Traits in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75:3672–3680. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yu C, Chen K, Zheng H, Guo X, Jia W, Li M, Zeng M, Li J, Song L. Overexpression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression and pathogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:894–901. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, Mutallip M, Sakurai D, Fujimura L, Kawakami K, Chiyomaru T, Yoshino H, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Okamoto Y, Seki N. Tumor suppressive microRNA-375 regulates oncogene AEG-1/MTDH in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) J Hum Genet. 2011;56:595–601. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2011.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hui AB, Bruce JP, Alajez NM, Shi W, Yue S, Perez-Ordonez B, Xu W, O'sullivan B, Waldron J, Cummings B, Gullane P, Siu L, Liu FF. Significance of dysregulated metadherin and microRNA-375 in head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:7539–7550. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.He XX, Chang Y, Meng FY, Wang MY, Xie QH, Tang F, Li PY, Song YH, Lin JS. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 2012;31:3357–3369. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhao J, Wang W, Huang Y, Wu J, Chen M, Cui P, Zhang W, Zhang Y. HBx elevates oncoprotein AEG-1 expression to promote cell migration by downregulating miR-375 and miR-136 in malignant hepatocytes. DNA and cell biology. 2014;33:715–722. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang B, Liu XX, He JR, Zhou CX, Guo M, He M, Li MF, Chen GQ, Zhao Q. Pathologically decreased miR-26a antagonizes apoptosis and facilitates carcinogenesis by targeting MTDH and EZH2 in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:2–9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dong R, Liu X, Zhang Q, Jiang Z, Li Y, Wei Y, Li Y, Yang Q, Liu J, Wei JJ, Shao C, Liu Z, Kong B. miR-145 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting metadherin in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5:10816–10829. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lee SG, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Sarkar D, Franke TF, Fisher PB. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 activates cell survival pathways through PI3K-Akt signaling. Oncogene. 2008;27:1114–1121. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sachdeva M, Zhu S, Wu F, Wu H, Walia V, Kumar S, Elble R, Watabe K, Mo YY. p53 represses c-Myc through induction of the tumor suppressor miR-145. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:3207–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808042106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Suzuki HI, Yamagata K, Sugimoto K, Iwamoto T, Kato S, Miyazono K. Modulation of microRNA processing by p53. Nature. 2009;460:529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature08199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Anttila V, Stefansson H, Kallela M, Todt U, Terwindt GM, Calafato MS, Nyholt DR, Dimas AS, Freilinger T, Muller-Myhsok B, Artto V, Inouye M, Alakurtti K, et al. Genome-wide association study of migraine implicates a common susceptibility variant on 8q22. 1. Nature genetics. 2010;42:869–873. doi: 10.1038/ng.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Srivastava J, Siddiq A, Gredler R, Shen XN, Rajasekaran D, Robertson CL, Subler MA, Windle JJ, Dumur CI, Mukhopadhyay ND, Garcia D, Lai Z, Chen Y, Balaji U, Fisher PB, Sarkar D. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 and c-Myc cooperate to promote hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. Hepatology. 2015;61:915–929. doi: 10.1002/hep.27339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shepherd FA, Crowley J, Van Houtte P, Postmus PE, Carney D, Chansky K, Shaikh Z, Goldstraw P. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer lung cancer staging project: proposals regarding the clinical staging of small cell lung cancer in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the tumor, node, metastasis classification for lung cancer. Journal of thoracic oncology. 2007;2:1067–1077. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31815bdc0d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


