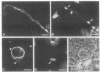
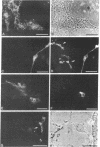
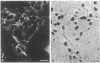
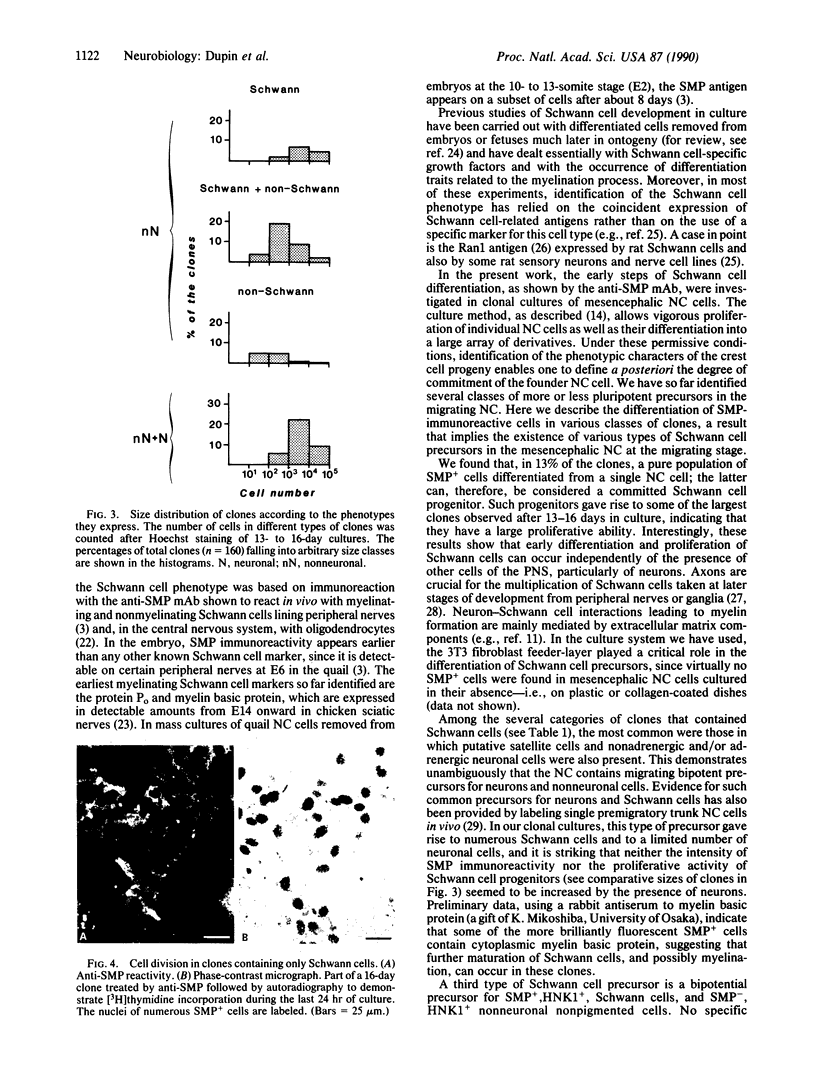
Abstract
In the vertebrate embryo, Schwann cells lining the peripheral nerves originate from the neural crest (NC), a structure that also gives rise to ganglion satellite cells, most of the neurons of the peripheral nervous system, melanocytes, and part of the cranial mesenchyme. We have studied the emergence of the Schwann cell lineage in vitro in clonal cultures of quail mesencephalic NC cells by using the Schwann cell myelin protein antigen as an early and specific marker for myelinating and nonmyelinating cells. After 13-16 days in culture, numerous clones contained Schwann cell myelin protein-positive cells, sometimes isolated and sometimes associated with other NC-derived cell types. Detailed phenotypic analysis of the clones allowed us to infer the presence of differently committed Schwann-cell ancestors in the NC during the migration stage. In particular, we found evidence for the existence of a bipotent precursor of Schwann cells and nonneuronal satellite cells; a common precursor of neurons, satellite cells, and Schwann cells; and a pluripotent precursor of Schwann cells, satellite cells, neurons, and melanocytes. These founder cell types coexist in the NC with a committed Schwann cell progenitor of high-proliferative potential that differentiates in vitro in the absence of other peripheral cells and axons.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguayo A. J., Charron L., Bray G. M. Potential of Schwann cells from unmyelinated nerves to produce myelin: a quantitative ultrastructural and radiographic study. J Neurocytol. 1976 Oct;5(8):565–573. doi: 10.1007/BF01175570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbury A. K. Schwann cell proliferation in developing mouse sciatic nerve. A radioautographic study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Sep;34(3):735–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.3.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroffio A., Dupin E., Le Douarin N. M. Clone-forming ability and differentiation potential of migratory neural crest cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5325–5329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Fields K. L., Raff M. C. A surface antigenic marker for rat Schwann cells. Nature. 1977 Mar 24;266(5600):364–366. doi: 10.1038/266364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner-Fraser M., Fraser S. E. Cell lineage analysis reveals multipotency of some avian neural crest cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):161–164. doi: 10.1038/335161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge M. B., Williams A. K., Wood P. M. Neuron-Schwann cell interaction in basal lamina formation. Dev Biol. 1982 Aug;92(2):449–460. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. J., Rafferty C. M., Todd M. S. Effects of inhibition of proteoglycan synthesis on the differentiation of cultured rat Schwann cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):1013–1021. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. J., Todd M. S., Rafferty C. M. Schwann cell myelination: induction by exogenous basement membrane-like extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2254–2263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. J., Todd M. S. Schwann cell myelination in a chemically defined medium: demonstration of a requirement for additives that promote Schwann cell extracellular matrix formation. Brain Res. 1987 Mar;429(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell L. A., Weston J. A. An analysis of melanogenesis in cultured chick embryo spinal ganglia. Dev Biol. 1970 Aug;22(4):670–697. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(70)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulac C., Cameron-Curry P., Ziller C., Le Douarin N. M. A surface protein expressed by avian myelinating and nonmyelinating Schwann cells but not by satellite or enteric glial cells. Neuron. 1988 May;1(3):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90141-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:81–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauquet M., Ziller C. A monoclonal antibody directed against quail tyrosine hydroxylase: description and use in immunocytochemical studies on differentiating neural crest cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Aug;37(8):1197–1205. doi: 10.1177/37.8.2569003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabella G. Ultrastructure of the nerve plexuses of the mammalian intestine: the enteric glial cells. Neuroscience. 1981;6(3):425–436. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet M., Hoffman S., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Cytotactin, an extracellular matrix protein of neural and non-neural tissues that mediates glia-neuron interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen K. R., Mirsky R. Astrocyte-like glia in the peripheral nervous system: an immunohistochemical study of enteric glia. J Neurosci. 1983 Nov;3(11):2206–2218. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-11-02206.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse J., Keilhauer G., Faissner A., Timpl R., Schachner M. The J1 glycoprotein--a novel nervous system cell adhesion molecule of the L2/HNK-1 family. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):146–148. doi: 10.1038/316146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse J., Mailhammer R., Wernecke H., Faissner A., Sommer I., Goridis C., Schachner M. Neural cell adhesion molecules and myelin-associated glycoprotein share a common carbohydrate moiety recognized by monoclonal antibodies L2 and HNK-1. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):153–155. doi: 10.1038/311153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M., Teillet M. A. Experimental analysis of the migration and differentiation of neuroblasts of the autonomic nervous system and of neurectodermal mesenchymal derivatives, using a biological cell marking technique. Dev Biol. 1974 Nov;41(1):162–184. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moya F., Bunge M. B., Bunge R. P. Schwann cells proliferate but fail to differentiate in defined medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6902–6906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols D. H., Weston J. A. Melanogenesis in cultures of peripheral nervous tissue. I. The origin and prospective fate of cells giving rise to melanocytes. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANNESE E. Observations on the morphology, submicroscopic structure and biological properties of satellite cells (s.c.) in sensory ganglia of mammals. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1960;52:567–597. doi: 10.1007/BF00339847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner N., Hong D. M., Lieberman M. A., Bunge R. P., Glaser L. The neuronal cell-surface molecule mitogenic for Schwann cells is a heparin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6992–6996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Thomas L. C., Fawcett J. W. Expression of Schwann cell markers by mammalian neural crest cells in vitro. Development. 1989 Feb;105(2):251–262. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J., Fauquet M., Ziller C., Le Douarin N. M. Acetylcholine synthesis by mesencephalic neural crest cells in the process of migration in vivo. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):853–855. doi: 10.1038/282853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker G. C., Aoyama H., Lipinski M., Tursz T., Thiery J. P. Identical reactivity of monoclonal antibodies HNK-1 and NC-1: conservation in vertebrates on cells derived from the neural primordium and on some leukocytes. Cell Differ. 1984 Aug;14(3):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(84)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyemura K., Horie K., Kitamura K., Suzuki M., Uehara S. Developmental changes of myelin proteins in the chick peripheral nerve. J Neurochem. 1979 Mar;32(3):779–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Duband J. L., Thiery J. P. A cell surface determinant expressed early on migrating avian neural crest cells. Brain Res. 1983 Aug;285(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Thiery J. P. A cell surface marker for neural crest and placodal cells: further evolution in peripheral and central nervous system. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):468–481. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. M., Bunge R. P. Evidence that sensory axons are mitogenic for Schwann cells. Nature. 1975 Aug 21;256(5519):662–664. doi: 10.1038/256662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziller C., Dupin E., Brazeau P., Paulin D., Le Douarin N. M. Early segregation of a neuronal precursor cell line in the neural crest as revealed by culture in a chemically defined medium. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90482-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]