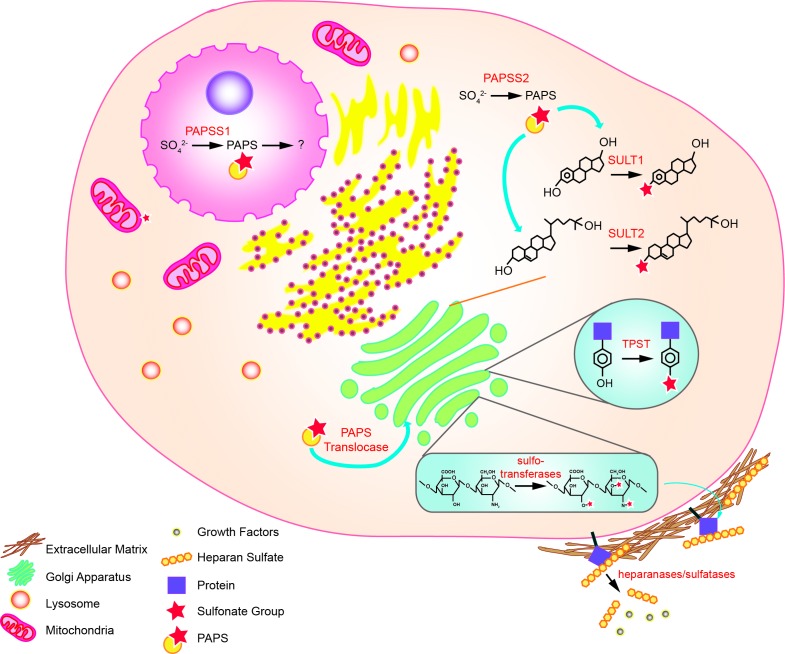
Figure 3. Sulfonation reactions in human cells.
In the nucleus, conversion of inorganic sulfate to PAPS is catalyzed by PAPSS1. In the cytoplasm, the same reaction is catalyzed by PAPSS2. The PAPS produced in the cytoplasm is used by cytosolic sulfotransferases to biotransform endo- and xeno-biotics. Cytosolic PAPS can also be transported to the golgi apparatus via the PAPS translocase, where tyrosine sulfation of proteins and sulfo-conjugation of polysaccharides occur. Sulfonated molecules such as heparan sulfates (HSs) may be secreted to the extracellular matrix or attached to cell surface proteins. Some of the HS may sequester growth factors that are released upon cleavage by heparanases and sulfatases.