Figure 1. Characterization of acetate uptake in CRC cells.
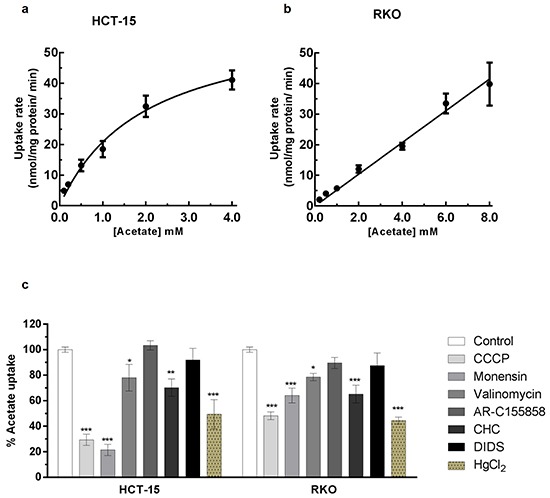
a, b. Plots of the initial uptake rates of labeled acetate, as a function of the acid concentration at pH 6.0 in HCT-15 (a) and RKO (b). Kinetic parameters, as affinity constant (Km) and transport capacity (Vmax) or Diffusion constant (Kd) for the uptake of acetate were based on the non-linear regression for the Michaelis-Menten equation f [V]=(Vmax x [Acetate])/(Km + [Acetate]) and Passive diffusion equation f[V] = Kd.[Acetate]. In HCT-15 the transporter system shows a Km of 1.97 ± 0.57 mM and a Vmax of 62 ± 9 nmol/ mg of protein/ min. In RKO acetate enters cells by passive diffusion with a Kd of 5.19 ± 0.16. (c) Effect of CCCP (100 μM), Monensin (100 μM), Valinomycin (100 μM), AR-C155858 (1 μM), CHC (10 mM), DIDS (1 mM) and HgCl2 (100 μM) in the uptake of 1 mM of acetate. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA: ***, ** and * indicate significant differences with a respective P-values of <0.001, <0.01 and <0.05 (n=3).
