Abstract
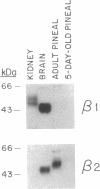
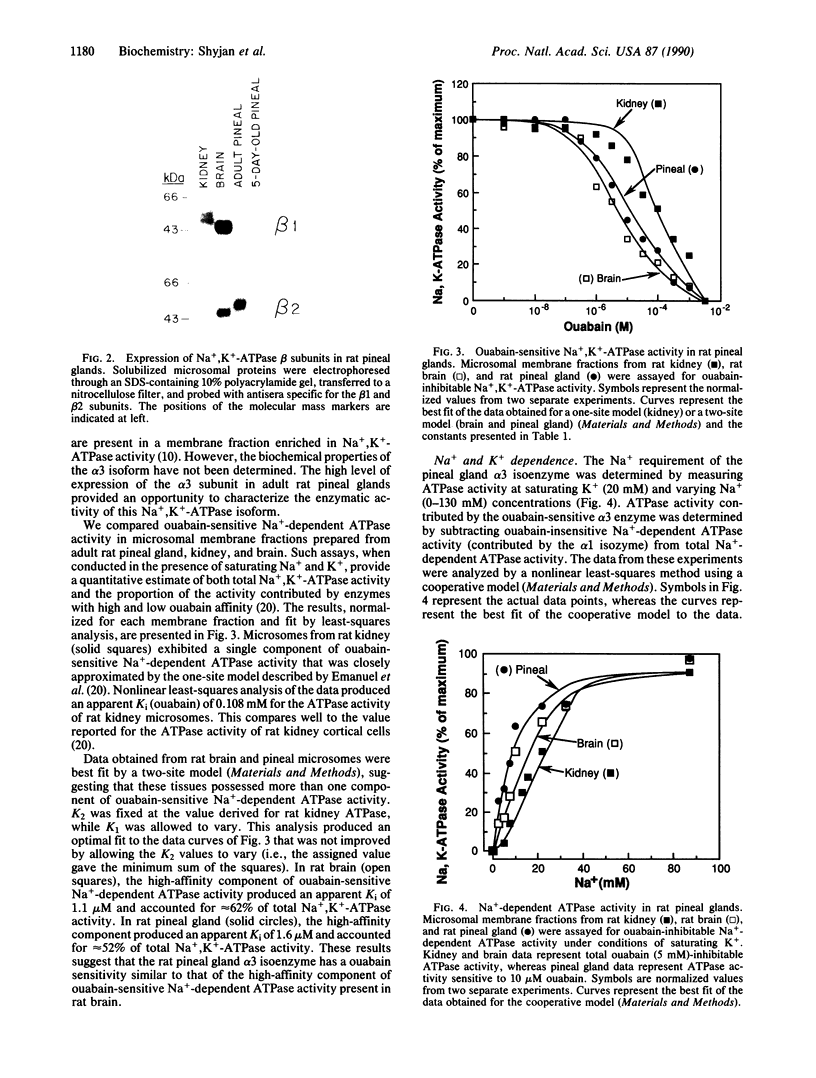
We have used immunoblotting and biochemical techniques to analyze expression of Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha and beta subunits in rat pineal glands. Western blot analysis of pineal microsomal membrane fractions with antisera specific for each of the three rat alpha and two rat beta subunits revealed similar levels of expression of alpha 1 and alpha 3 subunits in pineal glands of 5-day-old rats. High levels of alpha 3 and beta 2 subunits and low levels of alpha 1 subunits were detected in adult glands. No alpha 2 or beta 1 subunits were detectable at either developmental stage. Examination of the enzymatic properties of the pineal gland alpha 3 isoform suggests that this enzyme is a ouabain-sensitive ATPase whose activity is dependent upon Na+ and K+. This ATPase exhibited a lower apparent Km for Na+ than the kidney alpha 1 isoenzyme and did not show positive cooperative Na+ activation. Our results suggest that the activity of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 3 isoenzyme may be adapted to function under conditions of hyperpolarizing transmembrane potentials.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Josephson L. A slow interconversion between active and inactive states of the (Na-K)ATPase. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 30;15(24):5280–5287. doi: 10.1021/bi00669a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspers M. L., Schwartz R. D., Labarca R., Paul S. M. Autoradiographic visualization and characterization of [3H]ouabain binding to the Na+,K+-ATPase of rat brain and pineal. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 21;409(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90719-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceña V., González-García C., Svoboda P., Weller J. L., Klein D. C. Developmental study of ouabain inhibition of adrenergic induction of rat pineal serotonin N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.87). J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14467–14471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel J. R., Garetz S., Stone L., Levenson R. Differential expression of Na+,K+-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunit mRNAs in rat tissues and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9030–9034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel J. R., Schulz J., Zhou X. M., Kent R. B., Housman D., Cantley L., Levenson R. Expression of an ouabain-resistant Na,K-ATPase in CV-1 cells after transfection with a cDNA encoding the rat Na,K-ATPase alpha 1 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7726–7733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M. ATPase and phosphatase activity of Na+,K+-ATPase: molar and specific activity, protein determination. Methods Enzymol. 1988;156:105–115. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)56013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-García C., Ceña V., Klein D. C. Characterization of the alpha +-like Na+,K+-ATPase which mediates ouabain inhibition of adrenergic induction of N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.87) activity: studies with isolated pinealocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;32(6):792–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Nikamoto A., Kojima T., Matsumoto A., Nakao M. Expression of sodium pump activities in BALB/c 3T3 cells transfected with cDNA encoding alpha 3-subunits of rat brain Na+,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 26;238(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. 3. Purification from the outer medulla of mammalian kidney after selective removal of membrane components by sodium dodecylsulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):36–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent R. B., Fallows D. A., Geissler E., Glaser T., Emanuel J. R., Lalley P. A., Levenson R., Housman D. E. Genes encoding alpha and beta subunits of Na,K-ATPase are located on three different chromosomes in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5369–5373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R., Hesse J. E., Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. The mechanism of osmotic transfection of avian embryonic erythrocytes: analysis of a system for studying developmental gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1055–1065. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J. Insulin affects the sodium affinity of the rat adipocyte (Na+,K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10075–10080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Vasallo P., Dackowski W., Emanuel J. R., Levenson R. Identification of a putative isoform of the Na,K-ATPase beta subunit. Primary structure and tissue-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4613–4618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer R. W., Schneider J. W., Savitz A., Emanuel J., Benz E. J., Jr, Levenson R. Rat-brain Na,K-ATPase beta-chain gene: primary structure, tissue-specific expression, and amplification in ouabain-resistant HeLa C+ cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3884–3890. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J., Lingrel J. B. Tissue-specific and developmental regulation of rat Na,K-ATPase catalytic alpha isoform and beta subunit mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10436–10442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt A., Weller J. L., Klein D. C., Sakai K. K., Marks B. H. Blockade by ouabain or elevated potassium ion concentration of the adrenergic and adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate-induced stimulation of pineal serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 May;11(3):241–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K. K., Marks B. H. Adrenergic effects on pineal cell membrane potential. Life Sci I. 1972 Mar 15;11(6):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(72)90231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Mercer R. W., Gilmore-Hebert M., Utset M. F., Lai C., Greene A., Benz E. J., Jr Tissue specificity, localization in brain, and cell-free translation of mRNA encoding the A3 isoform of Na+,K+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):284–288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of three distinct forms of the Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8125–8132. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyjan A. W., Levenson R. Antisera specific for the alpha 1, alpha 2, alpha 3, and beta subunits of the Na,K-ATPase: differential expression of alpha and beta subunits in rat tissue membranes. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4531–4535. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Zinn K., Cantley L. C. A study of the vanadate-trapped state of the (Na,K)-ATPase. Evidence against interacting nucleotide site models. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9852–9859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Enzymatic properties of separated isozymes of the Na,K-ATPase. Substrate affinities, kinetic cooperativity, and ion transport stoichiometry. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11508–11513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Isozymes of the Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 9;988(2):185–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Two molecular forms of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated ATPase in brain. Separation, and difference in affinity for strophanthidin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6060–6067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urayama O., Sweadner K. J. Ouabain sensitivity of the alpha 3 isozyme of rat Na,K-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):796–800. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. M., Shull G. E., Lingrel J. B. Multiple mRNAs from rat kidney and brain encode a single Na+,K+-ATPase beta subunit protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4905–4910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]