Abstract
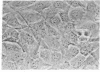
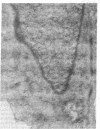
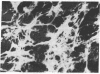
A cloned cell line of thymic origin has been characterized as epithelial in nature. A description of the procedures for derivation and cloning of the cell line includes use of epidermal growth factor. The thymic epithelial (TEPI) cell line is Ia antigen positive, forms desmosomes, and produces an extracellular fibronectin matrix. The supernatant from confluent monolayers of TEPI was tested for its ability to promote thymocyte functional activity. TEPI supernatant (TEPI SN) was demonstrated to greatly enhance the response of peanut agglutinin-positive thymocytes to alloantigen, as measured by cell-mediated lympholysis. Furthermore, preincubation of peanut agglutinin-positive thymocytes with TEPI SN prior to allostimulation resulted in marked enhancement, thus distinguishing it from interleukin 2. Finally, TEPI SN was demonstrated to induce interleukin 2 production by peanut agglutinin-positive thymocytes in the presence of concanavalin A. This activity was demonstrated not to be due to interleukin 1, which is absent in TEPI SN. Preliminary biochemical analysis indicates that the biological activity is associated with a Mr 50,000 entity. The data suggest that TEPI produces a soluble factor capable of inducing function of an immature thymocyte subpopulation into an IL 2 producer.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. Thymic macrophages modulate one stage of T cell differentiation in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1861–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. V., Nargang J. C., Loverde P. T., Golub E. S. The culture of mouse thymic reticulum cells: the effect of homologous serum on the establishment of primary cultures. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2738–2746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boniver J., Declève A., Dailey M. O., Honsik C., Lieberman M., Kaplan H. S. Macrophage and lymphocyte-depleted thymus reticuloepithelial cell cultures: establishment and functional influence on T-lymphocyte maturation, C-type virus expression and lymphomatous transformation in vitro. Thymus. 1981 Feb;2(4-5):193–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon P. J., Ramthun C. A., Henney C. S., Gillis S. Cytokine-dependent thymocyte responses. II. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes from immature thymocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Mizel S. B. T-Cell lymphoma model for the analysis of interleukin 1-mediated T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1133–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Scheid M., Watson J. Biochemical and biologic characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. III. The isolation and phenotypic characterization of Interleukin-2 producing T cell lymphomas. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2570–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays E. F. The role of thymus epithelial reticular cells in viral leukemogenesis. Cancer Res. 1968 Jan;28(1):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson E. J., Van Ewijk W., Owen J. J. Major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on the epithelium of the developing thymus in normal and nude mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):280–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan R. K., Crouse D. A. Studies on the thymic microenvironment: morphologic and functional characterization of thymic nonlymphoid cells grown in tissue culture. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Oct;26(4):385–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindred B. Functional activity of T cells which differentiate from nude mouse precursors in a congenic or allogeneic thymus graft. Immunol Rev. 1978;42:60–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klier F. G., Schubert D., Heinemann S. The ultrastructural differentiation of the clonal myogenic cell line L6 in normal and high K+ medium. Dev Biol. 1977 Jun;57(2):440–449. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruisbeek A. M., Astaldi G. C. Distinct effects of thymic epithelial culture supernatants on T cell properties of mouse thymocytes separated by the use of peanut agglutinin. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):984–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruisbeek A. M., Zijlstra J. J., Kröse T. J. Distinct effects of T cell growth factors and thymic epithelial factors on the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes by thymocyte subpopulations. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):995–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Osoba D. Current concepts of the immunological function of the thymus. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):437–520. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosentreich D. L. Characterization of lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) produced by a macrophage cell line, P388D1. II. Biochemical characterization of LAF induced by activated T cells and LPS. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1504–1508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Fibronectin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:111–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Pierce C. W. Functional maturation of thymic lymphocyte populations in vitro. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1484–1500. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paetkau V., Mills G., Gerhart S., Monticone V. Proliferation of murine thymic lymphocytes in vitro is mediated by the concanavalin A-induced release of a lymphokine (costimulator). J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1320–1324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. P., Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Initiation of 3T3 fibroblast cell division by epidermal growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Dec;86 (Suppl 2)(3 Pt 2):593–598. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040860504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman O. Cellular and humoral requirements for T-cell development. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979;332:123–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb47105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman O. Intrathymic and extrathymic T cell maturation. Immunol Rev. 1978;42:138–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dennert G., Warner J. F., Dutton R. W. Culture supernatants of a stimulated T-cell line have helper activity that acts synergistically with interleukin 2 in the response of B cells to antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2517–2521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksal S. D., Cohen I. R., Waksal H. W., Wekerle H., St Pierre R. L., Feldman M. Induction of T-cells differentiation in vitro by thymus epithelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:492–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei-Feng C., Scollay R., Shortman K. The functional capacity of thymus subpopulations: limit-dilution analysis of all precursors of cytotoxic lymphocytes and of all T cells capable of proliferation in subpopulations separated by the use of peanut agglutinin. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):18–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Ketelsen U. P., Ernst M. Thymic nurse cells. Lymphoepithelial cell complexes in murine thymuses: morphological and serological characterization. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):925–944. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A., Burton P. Isolation from human plasma of a protein fraction with thymic hormone-like activity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979;332:1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb47092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]