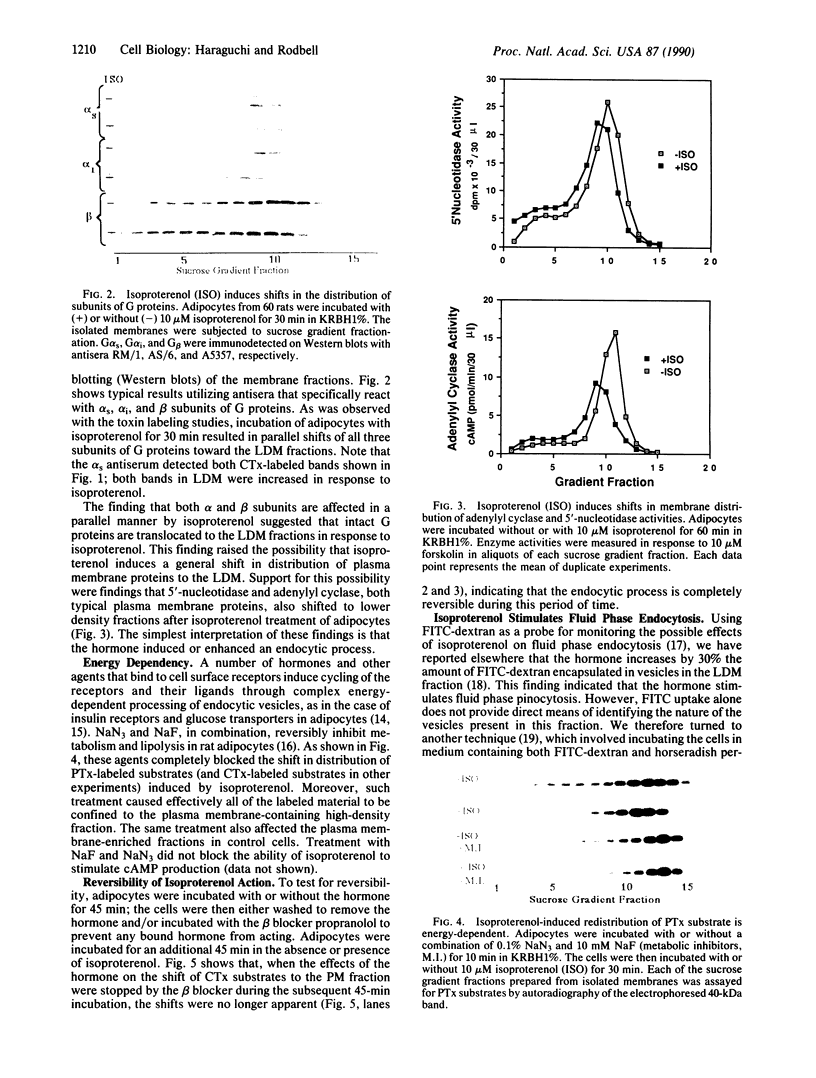
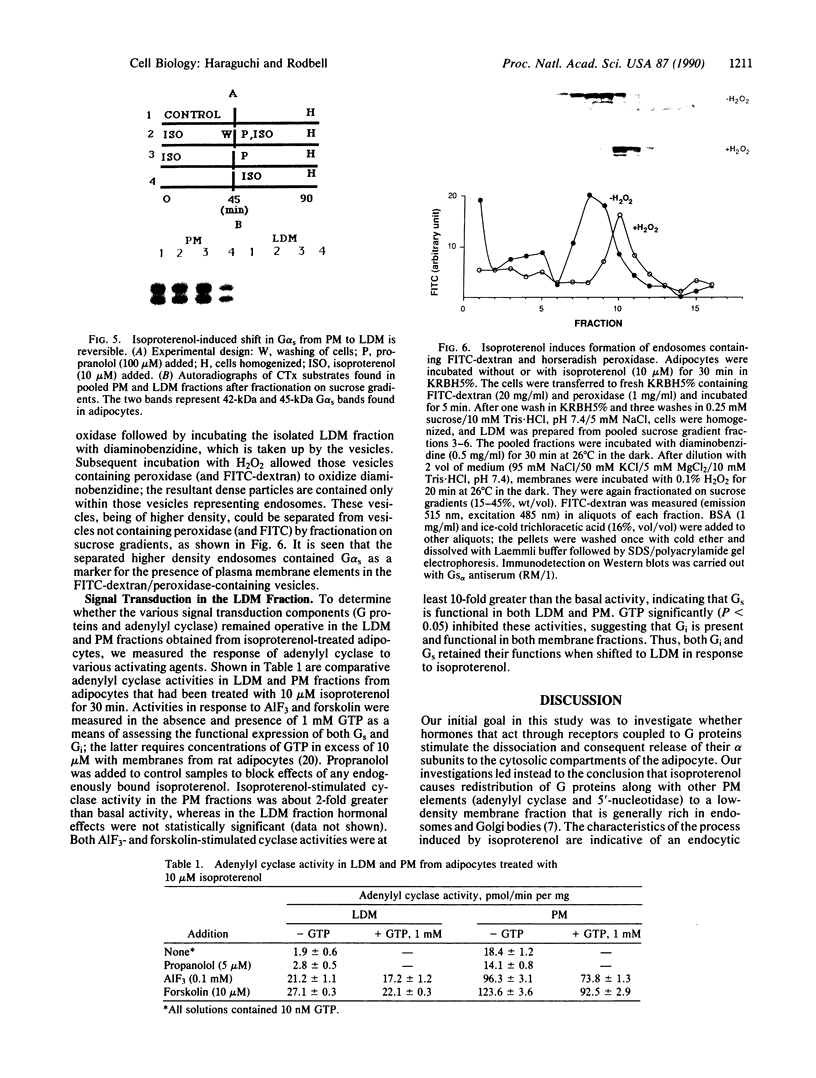
Abstract
Guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) are linked to a large number of surface membrane receptors and appear to regulate a variety of effector systems located both in the plasma membrane and in other parts of the cell. The mechanism of the disseminative actions of G proteins remains obscure. During an investigation of the fate of two types of G proteins, Gs and Gi, in rat adipocytes, we unexpectedly found that isoproterenol, which stimulates cAMP levels and lipolysis in these cells, induces parallel increases in both Gs and Gi in a low-density microsomal fraction rich in endosomes and Golgi bodies. Two plasma membrane constitutive enzymes, adenylyl cyclase and 5'-nucleotidase, are also elevated in this fraction. NaF and NaN3, metabolic inhibitors, block the redistribution process. The isoproterenol-stimulated shifts are completely reversible after removal of the hormone, indicating a recycling, endocytic process. The endocytic process seems to be fluid phase endocytosis, or pinocytosis, since isoproterenol stimulates the uptake of both fluorescent-labeled dextran and horseradish peroxidase into the same vesicles containing Gs. However, the vesicles that accumulate in response to isoproterenol seem heterogenous in properties that may reflect the lipolytic process induced by isoproterenol. It is speculated that the "pinosomes" formed in response to lipolytic hormones may continually produce signals within the cellular interior during their processing and cycling. Hence, signal production in response to hormones need not be confined to the cell membrane; circulating pinosomes may be responsible for some of the disseminative effects of hormones.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel A., Desai K., Halperin M. L. Free fatty acid and ATP levels in adipocytes during lipolysis. Metabolism. 1971 Jan;20(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey K. A., Maurey K. M., Storrie B. Characterization of early compartments in fluid phase pinocytosis: a cell fractionation study. J Cell Sci. 1986 Jul;83:119–133. doi: 10.1242/jcs.83.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. M., Schlegel W., Lin M. C., Rodbell M. The fat cell adenylate cyclase system. Characterization and manipulation of its bimodal regulation by GTP. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8927–8931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W. Structure-function relationships in the adipose cell. II. Pinocytosis and factors influencing its activity in the isolated adipose cell. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):342–353. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E. Fluid-phase endocytosis by isolated rat adipocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Dec;121(3):569–575. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honnor R. C., Dhillon G. S., Londos C. cAMP-dependent protein kinase and lipolysis in rat adipocytes. I. Cell preparation, manipulation, and predictability in behavior. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15122–15129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B. Molecular properties of the cGMP cascade of vertebrate photoreceptors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:793–812. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.004045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Pilch P. F. Fractionation of endocytic vesicles and glucose-transporter-containing vesicles in rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):725–732. doi: 10.1042/bj2560725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Sarver J. A., Vega F. V., Pointer R. H. Actions of insulin in fat cells. Effects of low temperature, uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation, and respiratory inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2226–2233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Suzuki K., Dansey L. E., Robinson F. W., Blevins T. L. Energy-dependent and protein synthesis-independent recycling of the insulin-sensitive glucose transport mechanism in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6400–6407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S., Pang I. H., Gilman A. G., Sternweis P. C. Chromatographic resolution and immunologic identification of the alpha 40 and alpha 41 subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2020–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Papahadjopoulos D., Nicolson G. L. Local anesthetics affect transmembrane cytoskeletal control of mobility and distribution of cell surface receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintart J., Courtoy P. J., Baudhuin P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis in rat liver: purification and enzymic characterization of low density organelles involved in uptake of galactose-exposing proteins. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):877–884. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F. A., Rodbell M. Pertussis toxin induces structural changes in G alpha proteins independently of ADP-ribosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2577–2581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F., Mattera R., Grenet D., Sekura R. D., Birnbaumer L., Field J. B. Adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of G proteins by pertussis and cholera toxin in isolated membranes. Different requirements for and effects of guanine nucleotides and Mg2+. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Jul;1(7):472–481. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-7-472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. Modulation of lipolysis in adipose tissue by fatty acid concentration in fat cell. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Oct 8;131(1):302–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb34798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler K. L., Rogus E., Klassen G. A., Rabinowitz D. Flux of palmitic acid across the adipose tissue membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Oct 8;131(1):78–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb34780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]