Abstract
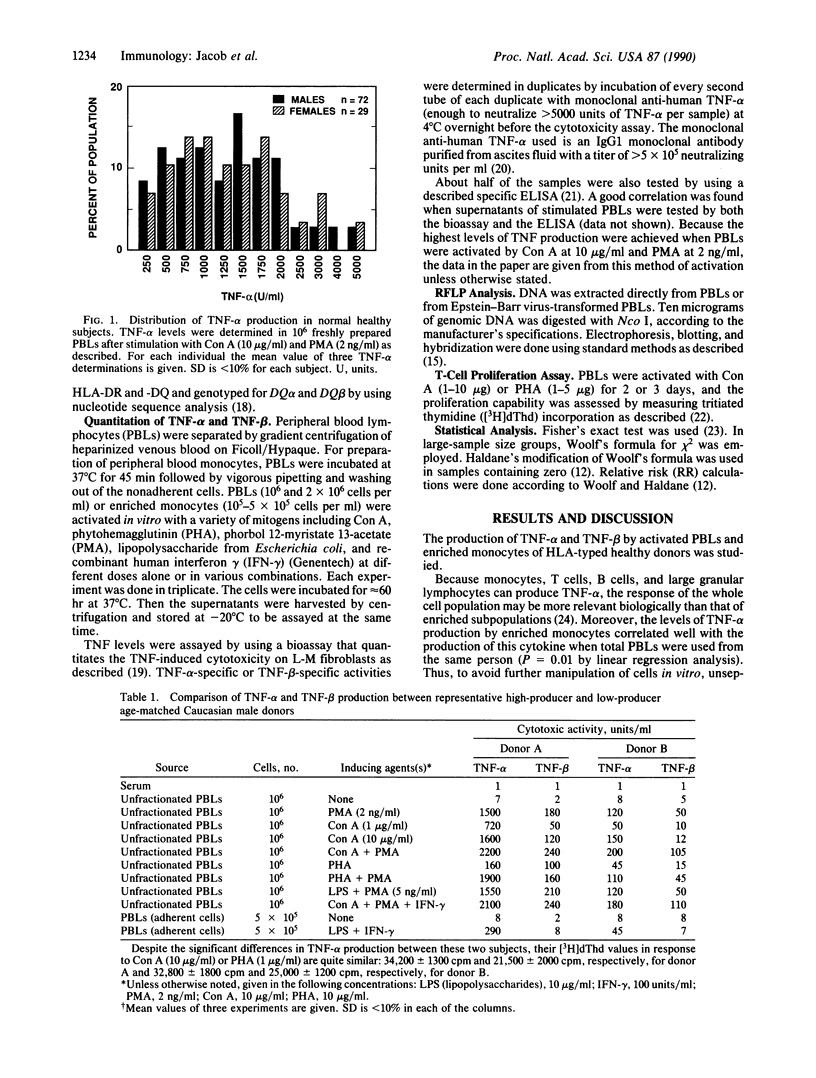
We report on the production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and TNF-beta by mitogen-activated peripheral blood lymphocytes or enriched monocyte subpopulations from human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-typed healthy subjects. The results indicate that HLA-DR2- and DQw1-positive donors frequently exhibit low production of TNF-alpha, whereas DR3- and DR4-positive subjects show high levels of TNF-alpha production. No correlation between TNF-alpha levels and HLA-A, -B, and -C genotype was found. The relevance of this quantitative polymorphism to the genetic predisposition to lupus nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients was investigated. DR2, DQw1-positive SLE patients show low levels of TNF-alpha inducibility; this genotype is also associated with an increased incidence of lupus nephritis. DR3-positive SLE patients, on the other hand, are not predisposed to nephritis, and these patients have high TNF-alpha production. DR4 haplotype is associated with high TNF-alpha inducibility and is negatively correlated with lupus nephritis. These data may help explain the strong association between HLA-DR2, DQw1 in SLE patients and their susceptibility to nephritis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringman T. S., Aggarwal B. B. Monoclonal antibodies to human tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta: application for affinity purification, immunoassays, and as structural probes. Hybridoma. 1987 Oct;6(5):489–507. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1987.6.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham I., Sargent C. A., Trowsdale J., Campbell R. D. Molecular mapping of the human major histocompatibility complex by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7237–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres S., Ghorbani R., Kelley V. E., Georgilis K., Lonnemann G., van der Meer J. W., Cannon J. G., Rogers T. S., Klempner M. S., Weber P. C. The effect of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by mononuclear cells. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 2;320(5):265–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902023200501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fronek Z., Timmerman L. A., Alper C. A., Hahn B. H., Kalunian K., Peterlin B. M., McDevitt H. O. Major histocompatibility complex associations with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1988 Dec 23;85(6A):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Aggarwal B. B., Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Nedwin G. E., Palladino M. A., Patton J. S., Pennica D., Shepard H. M., Sugarman B. J. Tumor necrosis factors: gene structure and biological activities. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):597–609. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., McDevitt H. O. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha in murine autoimmune 'lupus' nephritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):356–358. doi: 10.1038/331356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer S. M., Carver M. E. Serum-free in vitro bioassay for the detection of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Jongeneel C. V., Nedospasov S. A., Lindahl K. F., Steinmetz M. Tumour necrosis factor and lymphotoxin genes map close to H-2D in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):265–267. doi: 10.1038/325265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Smith D., Jarrett-Nedwin J., Pennica D., Goeddel D. V., Gray P. W. Human lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor genes: structure, homology and chromosomal localization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6361–6373. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumour necrosis factor. Polypeptide mediator network. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):330–331. doi: 10.1038/326330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince W. S., Harder K. J., Saks S., Reed B. R., Chen A. B., Jones A. J. ELISA for quantitation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in serum. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1987;5(8):793–802. doi: 10.1016/0731-7085(87)80097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Waksman B. H. Cytotoxicity mediated by soluble antigen and lymphocytes in delayed hypersensitivity. 3. Analysis of mechanism. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1267–1279. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Morton C. C., Nedospasov S. A., Fiers W., Pious D., Strominger J. L. Genes for the tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta are linked to the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8699–8702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Klinman D. M. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1988 Apr;14(1):25–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Bjorndahl J. M., Wang C. Y., Kao H. T., Fu S. M. Production of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin by human T cell lines and peripheral blood T lymphocytes stimulated by phorbol myristate acetate and anti-CD3 antibody. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):937–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Jung L. K., Walters J. A., Chen W., Wang C. Y., Fu S. M. Production of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin by human B cell lines and tonsillar B cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1539–1551. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsinger P. D., Yount W. J. Phytohemagglutinin response in systemic lupus erythematosus. Reconstitution experiments using highly purified lymphocyte subpopulations and monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):626–638. doi: 10.1172/JCI108814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Bakke O. Glucocorticoids suppress the production of tumour necrosis factor by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Immunology. 1988 Feb;63(2):299–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodrow J. C. Immunogenetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1988 Feb;15(2):197–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




