Abstract
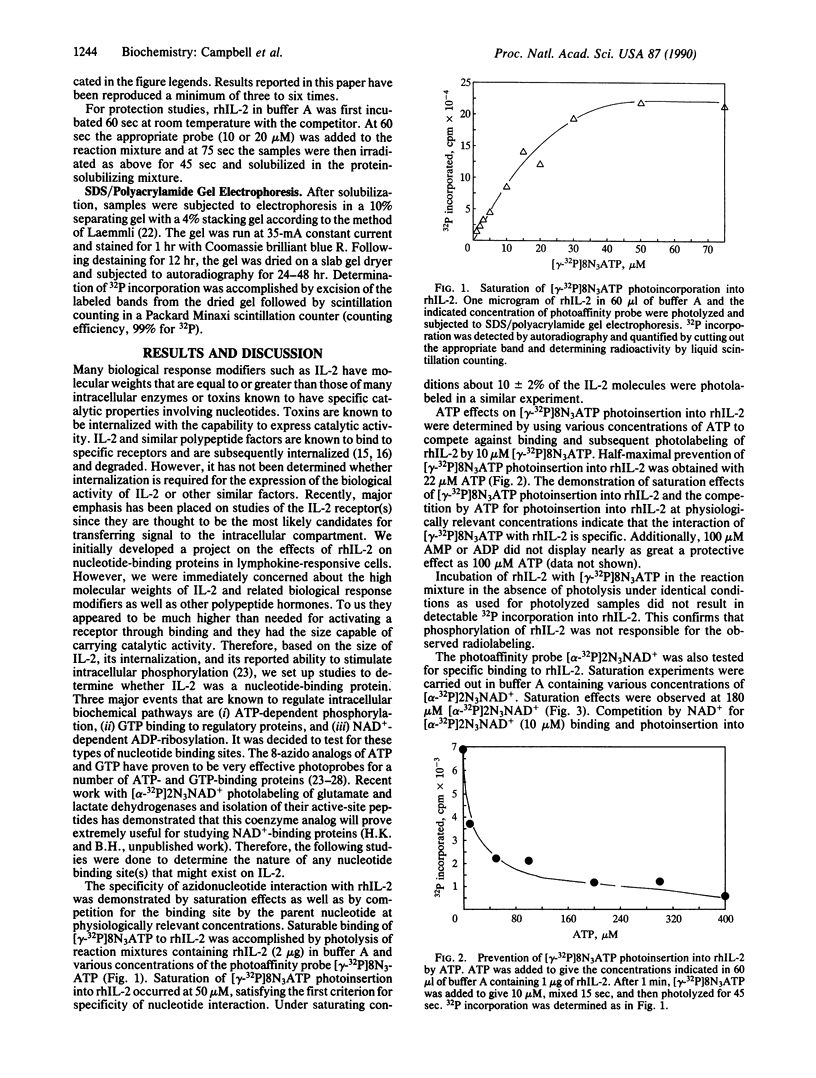
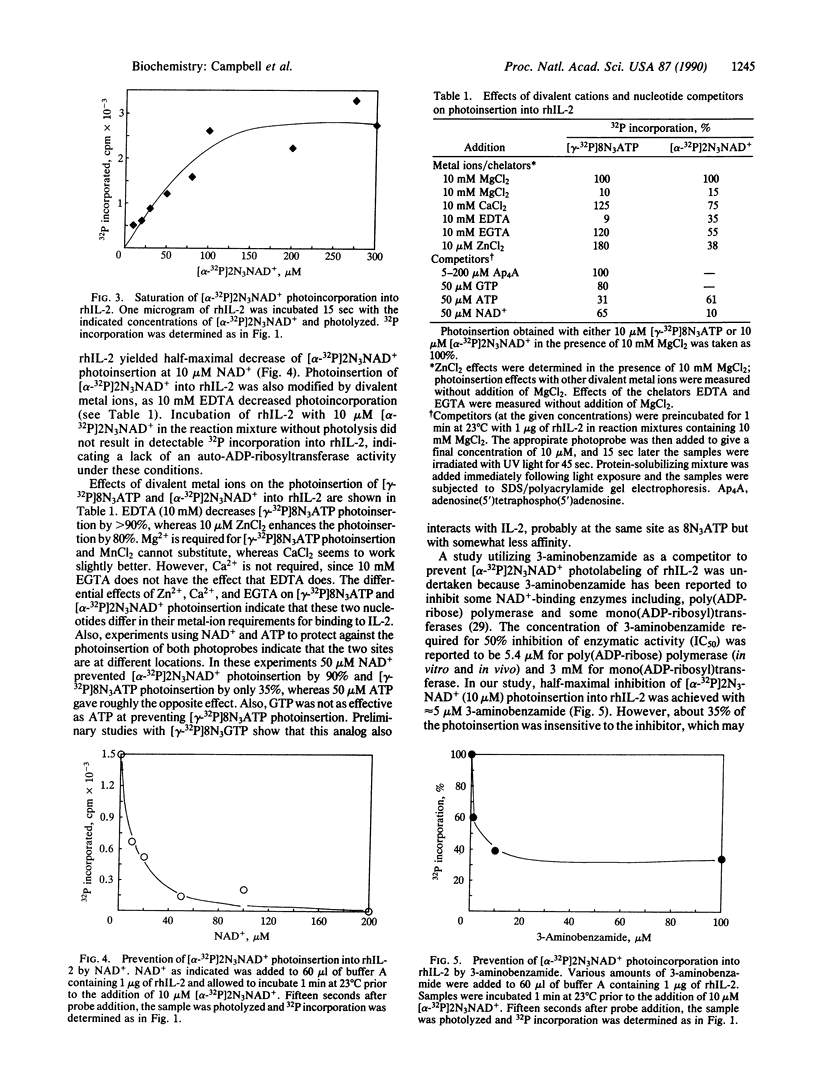
Interleukin 2 (IL-2) is a T-cell-derived lymphokine critical in the activation and proliferation of T cells, B cells, and lymphokine-activated killer cells. It is a glycoprotein of approximately 15,500 daltons that is synthesized and secreted after activation by antigen or mitogen. By using the analogs 8-azidoadenosine 5'-[gamma-32P]triphosphate [( gamma-32P]8N3ATP) and nicotinamide 2-azidoadenine [adenylate-32P]dinucleotide [( alpha-32P]2N3NAD+) as photoaffinity probes, we have detected specific, metal ion-requiring nucleotide binding sites on recombinant human IL-2 (rhIL-2). The specificity of these nucleotide interactions with rhIL-2 was demonstrated by saturation effects and by competition by the parent nucleotides at physiologically relevant concentrations. Saturation of photoinsertion into rhIL-2 occurred at 50 microM [gamma-32P]8N3ATP; a half-maximal decrease of its photoinsertion at 10 microM was obtained with 22 microM ATP. Saturation of photoinsertion with [alpha-32P]2N3NAD+ was observed at 180 microM; a half-maximal decrease of its photoinsertion at 10 microM was effected by 10 microM NAD+ and by 5 microM 3-aminobenzamide. The extent of photoinsertion of both photoprobes into rhIL-2 varied with the presence of different divalent metal ions. rhIL-2 photolabeling with [gamma-32P]8N3ATP appeared to be dependent on the presence of metal ion. It was effectively labeled in the presence of Mg2+ and photoinsertion was increased with the addition of Zn2+ at micromolar concentrations. Also, rhIL-2 underwent slow autophosphorylation by an intramolecular mechanism using [gamma-32P]8N3ATP as well as nonphotoactive nuceotide. The biological significance of these interactions is unknown, but their specificity suggests that nucleotide binding may be involved in the bioactivity of IL-2.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark S. C., Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Matsumoto-Kobayashi M., Kay R. M., Kaufman R. J., Brown E. L., Shoemaker C., Copeland T., Oroszlan S. Human T-cell growth factor: partial amino acid sequence, cDNA cloning, and organization and expression in normal and leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2543–2547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecki J. J., Abbott M. S., Selman B. R. Photoaffinity labeling with 2-azidoadenosine diphosphate of a tight nucleotide binding site on chloroplast coupling factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7744–7748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Plaetinck G., Cheroutre H., Simons G., Degrave W., Tavernier J., Remaut E., Fiers W. Molecular cloning of human interleukin 2 cDNA and its expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4307–4323. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domzig W., Stadler B. M., Herberman R. B. Interleukin 2 dependence of human natural killer (NK) cell activity. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1970–1973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard F., Corthesy P., Nabholz M., Lowenthal J. W., Zaech P., Plaetinck G., MacDonald H. R. Interleukin 2 is both necessary and sufficient for the growth and differentiation of lectin-stimulated cytolytic T lymphocyte precursors. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1644–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. W., Beckner S. K., Farrar W. L. Stimulation of specific GTP binding and hydrolysis activities in lymphocyte membrane by interleukin-2. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):166–168. doi: 10.1038/325166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Benjamin W. R., Hilfiker M. L., Howard M., Farrar W. L., Fuller-Farrar J. The biochemistry, biology, and role of interleukin 2 in the induction of cytotoxic T cell and antibody-forming B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:129–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg N., Welte K., Mertelsmann R., O'Reilly R., Dupont B. Interleukin 2-dependent natural killer (NK) cell lines from patients with primary T cell immunodeficiencies. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2635–2643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis B., Overmeyer J., John W., Marshall E., Haley B. Prevalence of nucleoside diphosphate kinase autophosphorylation in human colon carcinoma versus normal colon homogenates. Mol Carcinog. 1989;2(3):168–178. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940020310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Sugamura K., Sano K., Nakai M., Sugita K., Hinuma Y. High-affinity receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of interleukin 2 in human T cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):550–562. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulton G. N., Eardley D. D. Interleukin 2-dependent phosphorylation of interleukin 2 receptors and other T cell membrane proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2470–2477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geahlen R. L., Haley B. E. Use of a GTP photoaffinity probe to resolve aspects of the mechanism of tubulin polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11982–11987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Ramsey K. M., Mazumder A., Wilson D. J., Djeu J. Y., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. II. Precursor phenotype is serologically distinct from peripheral T lymphocytes, memory cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes, and natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):884–897. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley B. E. Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate binding sites. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:339–346. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley B. E. Photoaffinity labeling of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate binding sites of human red cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3852–3857. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefeneider S. H., Conlon P. J., Henney C. S., Gillis S. In vivo interleukin 2 administration augments the generation of alloreactive cytolytic T lymphocytes and resident natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):222–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julin D. A., Lehman I. R. Photoaffinity labeling of the recBCD enzyme of Escherichia coli with 8-azidoadenosine 5'-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9044–9051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merluzzi V. J., Savage D. M., Mertelsmann R., Welte K. Generation of nonspecific murine cytotoxic T cells in vitro by purified human interleukin 2. Cell Immunol. 1984 Mar;84(1):74–84. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. A., Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1007–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.181845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter R. L., Haley B. E. Photoaffinity labeling of nucleotide binding sites with 8-azidopurine analogs: techniques and applications. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:613–633. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin P. W., Jacobson E. L., Benjamin R. C., Moss J., Jacobson M. K. Quantitative studies of inhibitors of ADP-ribosylation in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4312–4317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C. Direct demonstration of the identity of T cell growth factor binding protein and the Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1332–1337. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J. Interleukin 2 and its cell-surface receptor. Behring Inst Mitt. 1985 Aug;(77):56–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Kutny R. M., Chowdhry V. Purification and partial sequence analysis of human T-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5990–5994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Grimm E. A., McGrogan M., Doyle M., Kawasaki E., Koths K., Mark D. F. Biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-2 produced in Escherichia coli. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6367046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suhadolnik R. J., Li S. W., Sobol R. W., Jr, Haley B. E. 2- and 8-azido photoaffinity probes. 2. Studies on the binding process of 2-5A synthetase by photosensitive ATP analogues. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8846–8851. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tigges M. A., Casey L. S., Koshland M. E. Mechanism of interleukin-2 signaling: mediation of different outcomes by a single receptor and transduction pathway. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):781–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2492678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman A. M., Harford J. B., Svetlik P. B., Leonard W. L., Depper J. M., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C., Klausner R. D. Only high-affinity receptors for interleukin 2 mediate internalization of ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1463–1466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



