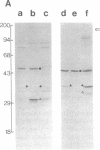
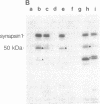
Abstract
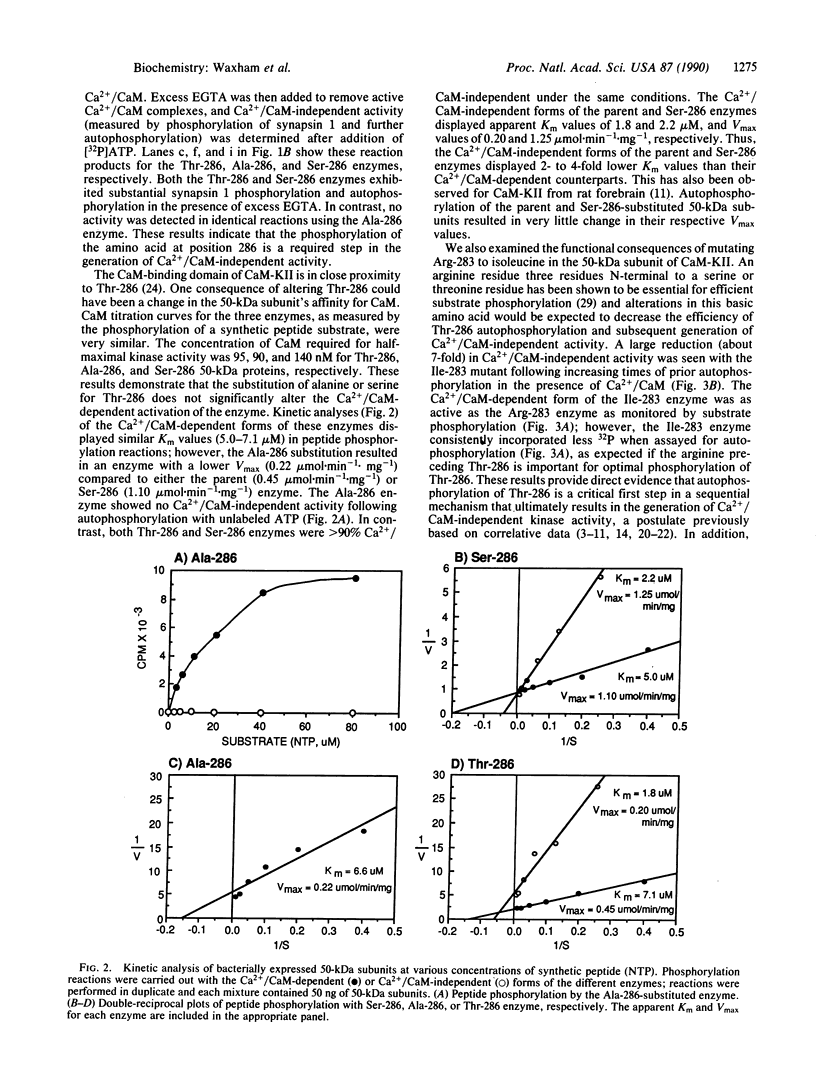
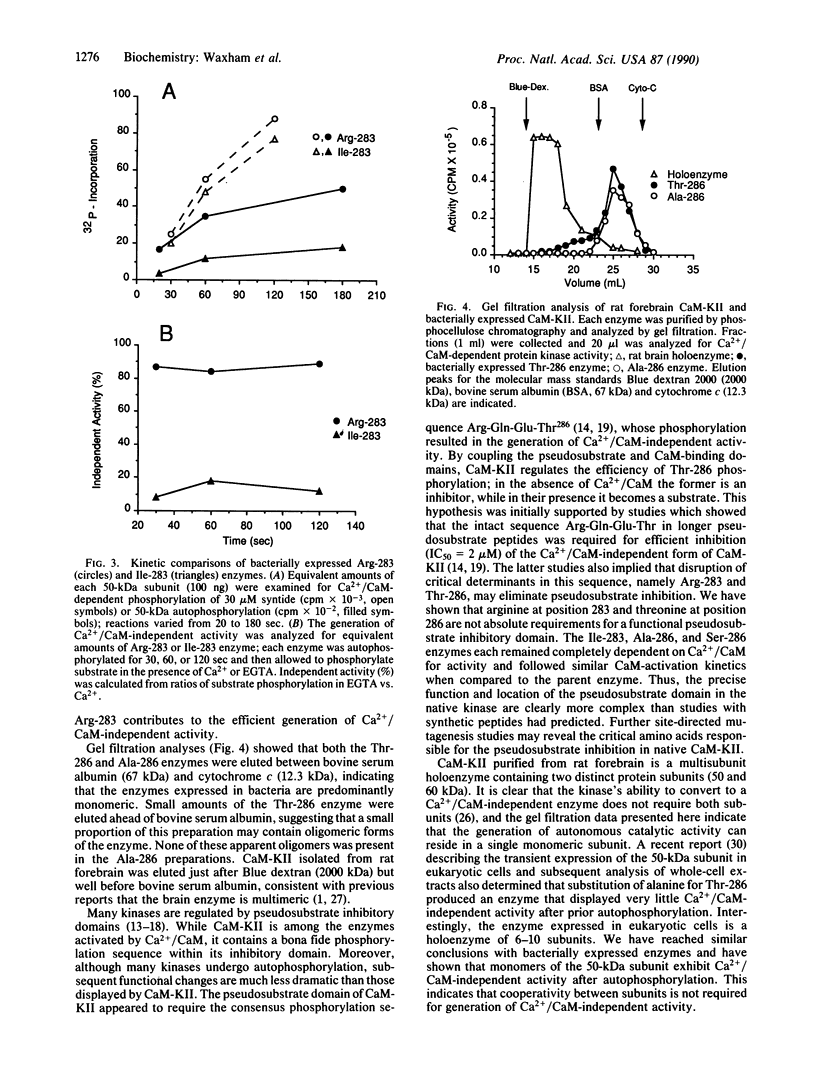
We have examined the role of Thr-286 autophosphorylation in the autoregulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we have substituted alanine or serine for Thr-286, or isoleucine for Arg-283, in the 50-kDa subunit of the kinase and expressed each protein in bacteria. Activation and autophosphorylation of all four enzymes were stringently dependent on Ca2+/calmodulin, indicating that neither Arg-283 nor Thr-286 is an absolute requirement for the pseudosubstrate inhibition of the enzyme. Autophosphorylation of the Ile-283 or Ala-286 enzyme generated little, if any, Ca2+/calmodulin-independent kinase activity, unlike the parent (Thr-286) or Ser-286 enzyme. The enzymes expressed in bacteria are predominantly monomeric, indicating that the generation of Ca2+/calmodulin-independent activity does not require the cooperative interactions of subunits normally present in the brain holoenzyme.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett M. K., Kennedy M. B. Deduced primary structure of the beta subunit of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase determined by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1794–1798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran R. J., Fong Y. L., Schworer C. M., Soderling T. R. Regulatory interactions of the calmodulin-binding, inhibitory, and autophosphorylation domains of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18145–18151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley R. M., Means A. R., Ono T., Kemp B. E., Burgin K. E., Waxham N., Kelly P. T. Functional analysis of a complementary DNA for the 50-kilodalton subunit of calmodulin kinase II. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):293–297. doi: 10.1126/science.3037704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Kapiloff M. S., Lou L. L., Rosenfeld M. G., Schulman H. Expression of a multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase and mutational analysis of its autoregulation. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie G. Pseudosubstrates turn off protein kinases. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):592–593. doi: 10.1038/335592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., McGuinness T. L., Greengard P. Evidence that the major postsynaptic density protein is a component of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):945–949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., Shenolikar S. Role of autophosphorylation in regulating calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1987;139:690–714. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)39121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., Weinberger R. P., Waxham M. N. Active site-directed inhibition of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II by a bifunctional calmodulin-binding peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):4991–4995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., Yip R. K., Shields S. M., Hay M. Calmodulin-dependent protein phosphorylation in synaptic junctions. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1620–1634. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Guerriero V., Jr, Bagchi I. C., Means A. R. The calmodulin binding domain of chicken smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase contains a pseudosubstrate sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2542–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B., Bennett M. K., Erondu N. E. Biochemical and immunochemical evidence that the "major postsynaptic density protein" is a subunit of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7357–7361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Rabbit skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. The calmodulin binding domain as a potential active site-directed inhibitory domain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11958–11963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Y., Nairn A. C., Gorelick F., Greengard P. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: identification of autophosphorylation sites responsible for generation of Ca2+/calmodulin-independence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5710–5714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Y., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Autophosphorylation reversibly regulates the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependence of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4253–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lickteig R., Shenolikar S., Denner L., Kelly P. T. Regulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by Ca2+/calmodulin-independent autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19232–19239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Kapiloff M. S., Durgerian S., Tatemoto K., Russo A. F., Hanson P., Schulman H., Rosenfeld M. G. Molecular cloning of a brain-specific calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5962–5966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisman J. E., Goldring M. A. Feasibility of long-term storage of graded information by the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase molecules of the postsynaptic density. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5320–5324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou L. L., Lloyd S. J., Schulman H. Activation of the multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase by autophosphorylation: ATP modulates production of an autonomous enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9497–9501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Kennedy M. B. Regulation of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase by autophosphorylation: a Ca2+-triggered molecular switch. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Patton B. L., Kennedy M. B. Sequences of autophosphorylation sites in neuronal type II CaM kinase that control Ca2(+)-independent activity. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):593–604. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne M. E., Fong Y. L., Ono T., Colbran R. J., Kemp B. E., Soderling T. R., Means A. R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Characterization of distinct calmodulin binding and inhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7190–7195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Woodgett J. R., Cohen P., Kemp B. E. Substrate specificity of a multifunctional calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14471–14476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Schwartz J. H. Phosphorylation-dependent subcellular translocation of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase produces an autonomous enzyme in Aplysia neurons. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):835–842. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schworer C. M., Colbran R. J., Keefer J. R., Soderling T. R. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Identification of a regulatory autophosphorylation site adjacent to the inhibitory and calmodulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13486–13489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schworer C. M., Colbran R. J., Soderling T. R. Reversible generation of a Ca2+-independent form of Ca2+(calmodulin)-dependent protein kinase II by an autophosphorylation mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8581–8584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields S. M., Vernon P. J., Kelly P. T. Autophosphorylation of calmodulin-kinase II in synaptic junctions modulates endogenous kinase activity. J Neurochem. 1984 Dec;43(6):1599–1609. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel G., Czernik A. J., Gorelick F., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: identification of threonine-286 as the autophosphorylation site in the alpha subunit associated with the generation of Ca2+-independent activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6337–6341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxham M. N., Aronowski J., Kelly P. T. Functional analysis of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II expressed in bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7477–7482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]