Abstract
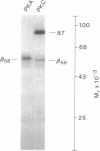
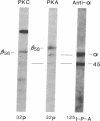
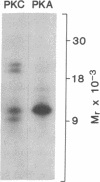
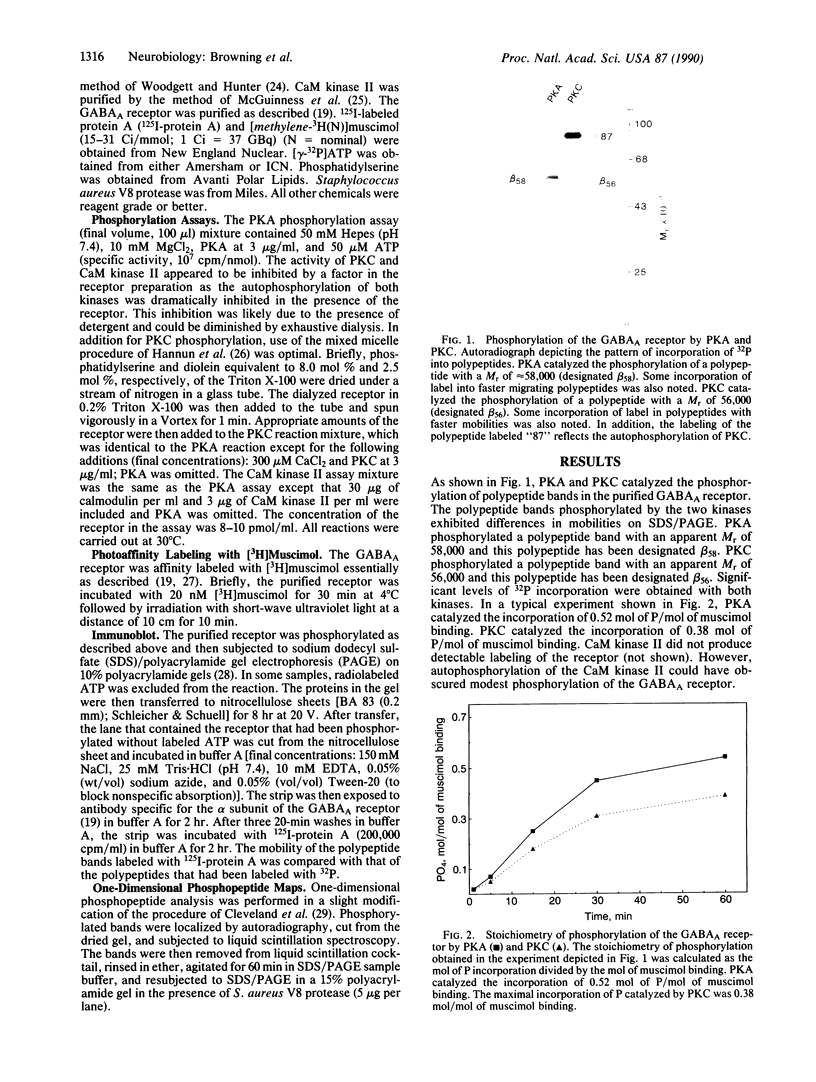
A number of recent studies have suggested that phosphorylation of the gamma-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) receptor could modulate receptor function. Activators of protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase have been shown to influence GABAA receptor function. In addition, Sweetnam et al. [Sweetnam, P. M., Lloyd, J., Gallombardo, P., Malison, R. T., Gallager, D. W., Tallman, J. F. & Nestler, E. J. (1988) J. Neurochem. 51, 1274-1284] have reported that a kinase associated with a partially purified preparation of the receptor could phosphorylate the alpha subunit of the receptor. Moreover, Kirkness et al. [Kirkness, E. F., Bovenkerk, C. F., Ueda, T. & Turner, A. J. (1989) Biochem. J. 259, 613-616] have recently shown that cAMP-dependent protein kinase could phosphorylate a muscimol binding polypeptide of the GABAA receptor. To explore the issue further, we have examined the ability of specific kinases to catalyze significant phosphorylation of the GABAA receptor that has been purified to near homogeneity. The GABAA receptor was purified as previously described using benzodiazepine affinity chromatography. The purified receptor possessed no detectable kinase activity. Protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalyzed the phosphorylation of the beta and alpha subunits of the receptor. However, most of the phosphate incorporation was associated with the beta subunit. Two muscimol binding polypeptides designated beta 58 (Mr 58,000) and beta 56 (Mr 56,000) were present in the preparation. The higher molecular weight polypeptide, beta 58, was phosphorylated specifically by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. beta 56 was phosphorylated specifically by protein kinase C. beta 58 and beta 56 gave distinct patterns in a one-dimensional phosphopeptide analysis. The stoichiometry of phosphorylation (mol of phosphate/mol of muscimol binding) catalyzed by cAMP-dependent protein kinase was 0.52 and that catalyzed by protein kinase C was 0.38. Taken together these data confirm that there are two forms of the beta subunit of the GABAA receptor and suggest that these two forms of the beta subunit are phosphorylated by distinct kinases.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M. [3H]Propyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate as a selective radioligand for the BZ1 benzodiazepine receptor subclass. J Neurochem. 1981 Aug;37(2):333–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bureau M., Olsen R. W. gamma-Aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptor protein carries binding sites for both ligands on both two major peptide subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1006–1011. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng L., Ransom R. W., Olsen R. W. [3H]muscimol photolabels the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding site on a peptide subunit distinct from that labeled with benzodiazepines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1308–1314. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi F., Molinaro M., Zani B. M. Agents that activate protein kinase C reduce acetylcholine sensitivity in cultured myotubes. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1339–1342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs K., Sieghart W. Evidence for the existence of several different alpha- and beta-subunits of the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor complex from rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Feb 27;97(3):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90619-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyenes M., Farrant M., Farb D. H. "Run-down" of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor function during whole-cell recording: a possible role for phosphorylation. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):719–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M. Activation of protein kinase C by Triton X-100 mixed micelles containing diacylglycerol and phosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10039–10043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuschneider G., Schwartz R. D. cAMP and forskolin decrease gamma-aminobutyric acid-gated chloride flux in rat brain synaptoneurosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2938–2942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. F., Tank D. W., Greengard P., Huganir R. L. Functional modulation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by tyrosine phosphorylation. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):677–680. doi: 10.1038/336677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Delcour A. H., Greengard P., Hess G. P. Phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor regulates its rate of desensitization. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):774–776. doi: 10.1038/321774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Greengard P. cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1130–1134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkness E. F., Bovenkerk C. F., Ueda T., Turner A. J. Phosphorylation of gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA)/benzodiazepine receptors by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):613–616. doi: 10.1042/bj2590613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippa A. S., Beer B., Sano M. C., Vogel R. A., Meyerson L. R. Differential ontogeny of type 1 and type 2 benzodiazepine receptors. Life Sci. 1981 May 21;28(21):2343–2347. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maelicke A. Structural similarities between ion channel proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Jun;13(6):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness T. L., Lai Y., Greengard P. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Isozymic forms from rat forebrain and cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1696–1704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Sontheimer H., Shivers B. D., Ymer S., Kettenmann H., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H. Importance of a novel GABAA receptor subunit for benzodiazepine pharmacology. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):582–585. doi: 10.1038/338582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safran A., Sagi-Eisenberg R., Neumann D., Fuchs S. Phosphorylation of the acetylcholine receptor by protein kinase C and identification of the phosphorylation site within the receptor delta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10506–10510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T. N., Neale J. H. Type I and type II gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptors: purification and analysis of novel receptor complex from neonatal cortex. J Neurochem. 1989 Apr;52(4):1114–1122. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb01855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R. Activation of protein kinase C differentially modulates neuronal Na+, Ca2+, and gamma-aminobutyrate type A channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6192–6196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber G. B., Ransom R. W., Dilber A. I., Olsen R. W. The gamma-aminobutyric-acid/benzodiazepine-receptor protein from rat brain. Large-scale purification and preparation of antibodies. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 17;167(1):125–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelzer A., Kay A. R., Wong R. K. GABAA-receptor function in hippocampal cells is maintained by phosphorylation factors. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):339–341. doi: 10.1126/science.2455347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson F. A., Duggan M. J., Casalotti S. O. Identification of the alpha 3-subunit in the GABAA receptor purified from bovine brain. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 30;243(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetnam P. M., Lloyd J., Gallombardo P., Malison R. T., Gallager D. W., Tallman J. F., Nestler E. J. Phosphorylation of the GABAa/benzodiazepine receptor alpha subunit by a receptor-associated protein kinase. J Neurochem. 1988 Oct;51(4):1274–1284. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tehrani M. H., Hablitz J. J., Barnes E. M., Jr cAMP increases the rate of GABAA receptor desensitization in chick cortical neurons. Synapse. 1989;4(2):126–131. doi: 10.1002/syn.890040206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Hunter T. Isolation and characterization of two distinct forms of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4836–4843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Schofield P. R., Draguhn A., Werner P., Köhler M., Seeburg P. H. GABAA receptor beta subunit heterogeneity: functional expression of cloned cDNAs. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1665–1670. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]