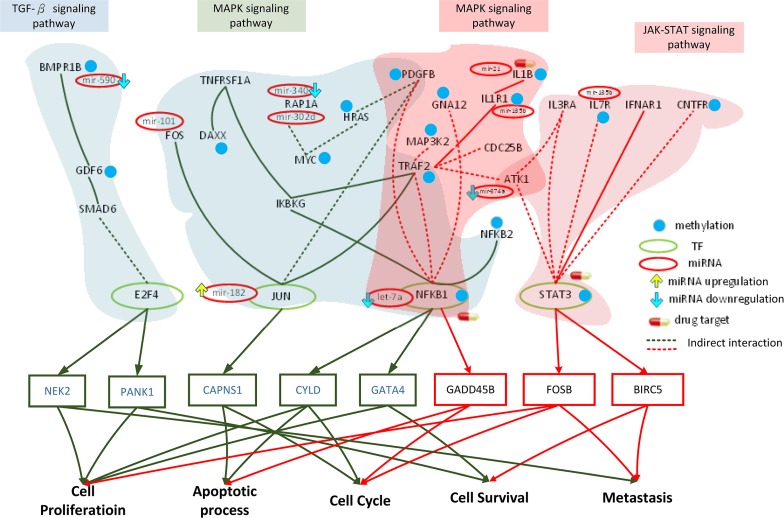
Figure 5. Role of miRNA regulation and DNA methylation on the mechanism of progression of HCC from stage III to stage IV.
The dark green frames and lines represent stage III HCC. The purple frames and lines represent stage IV HCC. Blue node represents DNA methylation of gene. The green and red ovals represent transcription factors (TFs) and miRNAs, respectively. The upward yellow arrowhead represents miRNA upregulation during stage IV HCC, compared to that in stage III. The downward blue arrowhead represents miRNA downregulation in stage IV compared to that in stage III. TRAF2, TNFRSF1A, FOS, HRAS, PDGFB, JUN, IKBKG, RAP1A, NFKB1, NFKB2, and DAXX are involved in the MAPK signaling pathway, while E2F4, GDF6, SMAD6, PPP2CB, and BMPR1B regulate the TGF-β pathway during stage III HCC. The transcription factors JUN, NFKB1, and E2F4 are activated by stress signals, including the MAPK signaling and TGF-β pathways, inducing cellular responses such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, cell survival, and metastasis. AKT1, TRAF2, IL1R1, PDGFB, MAP3K2, GNA12, IL1B, NFKB1, and CDC25B are involved in the MAPK signaling pathway, while AKT1, CNTFR, IL7R, IL3RA, STAT3, and IFNAR1 regulate the JAK-STAT signaling pathway during stage IV HCC. The transcription factors NFKB1 and STAT3 are activated by a number of stress signals, including the MAPK signaling and JAK-STAT pathways, inducing cellular responses, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, cell survival, and metastasis. miRNA and DNA methylation dysregulation may contribute to the perturbation of the MAPK and TGF-β pathways, resulting in aberrant cellular responses and HCC progression from stage III to stage IV. Obviously, the perturbation of the MAPK pathway and the shift from the TGF-β to JAK-STAT pathways caused by epigenetic miRNA regulation and DNA methylation may be the major mechanism of HCC progression from stage III to stage IV. STAT3, ILB, and NFKB1 were selected as potential drug targets to prevent the progression of HCC from stage III to stage IV.