Abstract
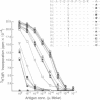
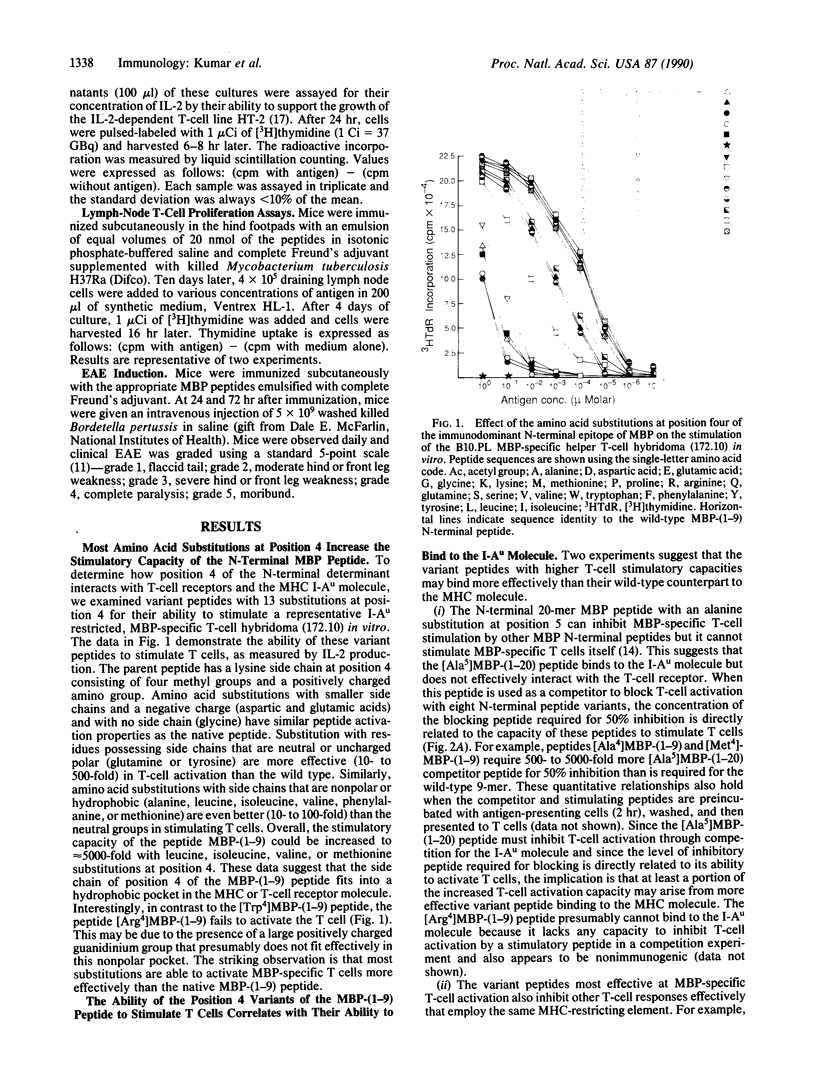
Myelin basic protein (MBP) or helper T cells reactive against MBP induce an autoimmune disease, experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, in B10.PL and PL/J inbred mice. In both strains, virtually the entire repertoire of MBP-specific T cells recognize an N-terminal peptide fragment in the context of the I-Au molecule encoded by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and utilize a very limited set of T-cell receptor genes. To delineate the nature of the trimolecular complex, consisting of the T-cell receptor, MBP-peptide fragment, and MHC molecule (I-Au), we have synthesized 13 variants of the 9-mer N-terminal immunodominant peptide differing at residue 4 and studied their immune recognition in vitro and in vivo. These substitutions have a striking range of effects on T-cell activation, ability to bind to the MHC molecule, and initiation of immune responses in vivo. An understanding of the autoimmune peptide/MHC/T-cell receptor interactions allowed us to design variant 9-mer peptides that have high affinity for an MHC molecule and are effective in blocking experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, possibly through two distinct mechanisms, peripheral T-cell tolerance and the inhibition of binding of the encephalitogenic peptide to the MHC molecules.
Full text
PDF
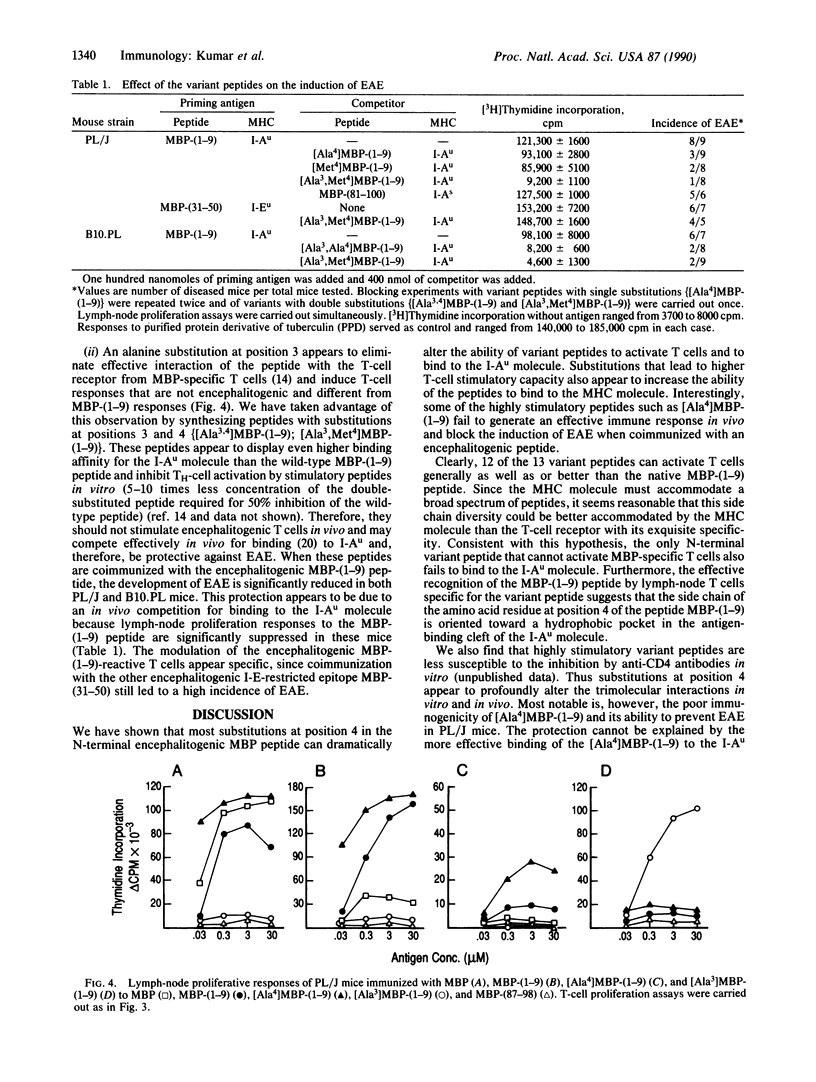

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., Mitchell D. J., Timmermann L., Wraith D. C., Tausch G. S., Waldor M. K., Zamvil S. S., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. Limited heterogeneity of T cell receptors from lymphocytes mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis allows specific immune intervention. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90558-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adorini L., Muller S., Cardinaux F., Lehmann P. V., Falcioni F., Nagy Z. A. In vivo competition between self peptides and foreign antigens in T-cell activation. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):623–625. doi: 10.1038/334623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Sleckman B. P., Ratnofsky S. E., Burakoff S. J. The biologic roles of CD2, CD4, and CD8 in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:579–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. A hypothetical model of the foreign antigen binding site of class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):845–850. doi: 10.1038/332845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Colon S., Smith C., Freed J. H., Miles C., Grey H. M. Interaction between a "processed" ovalbumin peptide and Ia molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3968–3971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Aebersold R., Ziltener H., Schrader J. W., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Automated chemical synthesis of a protein growth factor for hemopoietic cells, interleukin-3. Science. 1986 Jan 10;231(4734):134–139. doi: 10.1126/science.3079915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Carding S., Jones B., Murray J., Portoles P., Rasmussen R., Rojo J., Saizawa K., West J., Bottomly K. CD4+ T cells: specificity and function. Immunol Rev. 1988 Jan;101:39–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono D. H., Urban J. L., Horvath S. J., Ando D. G., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. Two minor determinants of myelin basic protein induce experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in SJL/J mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):213–227. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Kono D. H., Urban J. L., Hood L. The T-cell receptor repertoire and autoimmune diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:657–682. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Endres R., Shimonkevitz R., Zlotnik A., Dialynas D., Fitch F., Kappler J. The major histocompatibility complex-restricted antigen receptor on T cells. II. Role of the L3T4 product. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1077–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinelli C. B., McFarlin D. E. Adoptive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in SJL/J mice after in vitro activation of lymph node cells by myelin basic protein: requirement for Lyt 1+ 2- T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1420–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammensee H. G., Kroschewski R., Frangoulis B. Clonal anergy induced in mature V beta 6+ T lymphocytes on immunizing Mls-1b mice with Mls-1a expressing cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):541–544. doi: 10.1038/339541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E. An in vitro system for the study of myelin synthesis. J Neurochem. 1969 Jan;16(1):83–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. T cell subsets and the recognition of MHC class. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:129–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Horvath S. J., Hood L. Autoimmune T cells: immune recognition of normal and variant peptide epitopes and peptide-based therapy. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90288-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Kumar V., Kono D. H., Gomez C., Horvath S. J., Clayton J., Ando D. G., Sercarz E. E., Hood L. Restricted use of T cell receptor V genes in murine autoimmune encephalomyelitis raises possibilities for antibody therapy. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):577–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., Smilek D. E., Mitchell D. J., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. Antigen recognition in autoimmune encephalomyelitis and the potential for peptide-mediated immunotherapy. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Powell M. B., Sakai K., Rothbard J. B., Steinman L. Multiple discrete encephalitogenic epitopes of the autoantigen myelin basic protein include a determinant for I-E class II-restricted T cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1181–1186. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S., Nelson P., Trotter J., Mitchell D., Knobler R., Fritz R., Steinman L. T-cell clones specific for myelin basic protein induce chronic relapsing paralysis and demyelination. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):355–358. doi: 10.1038/317355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]