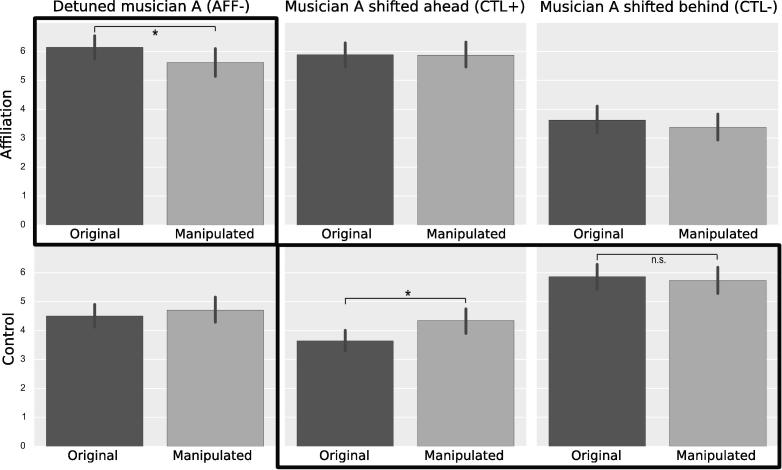
Fig. 5.
(Study 5) Affiliation and control judgements of the attitude of musician A with respect to musician B, before (“original”) and after (“manipulated”) three types of acoustic manipulations: decrease harmonic coordination (detuned musician A, AFF- condition), increased encoder-to-decoder causality (musician A shifted ahead, CTL+ condition), decreased encoder-to-decoder causality (musician A shifted behind, CTL− condition). Conditions enframed in dark lines correspond to predicted differences (e.g., AFF- on affiliation), and others to predicted nulls (e.g., AFF- on control). Hypothesis tests of paired difference with uncorrected t-tests, indicating significance at the p < .05 level, error bars represent 95% CI on the mean.