Abstract
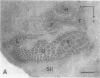
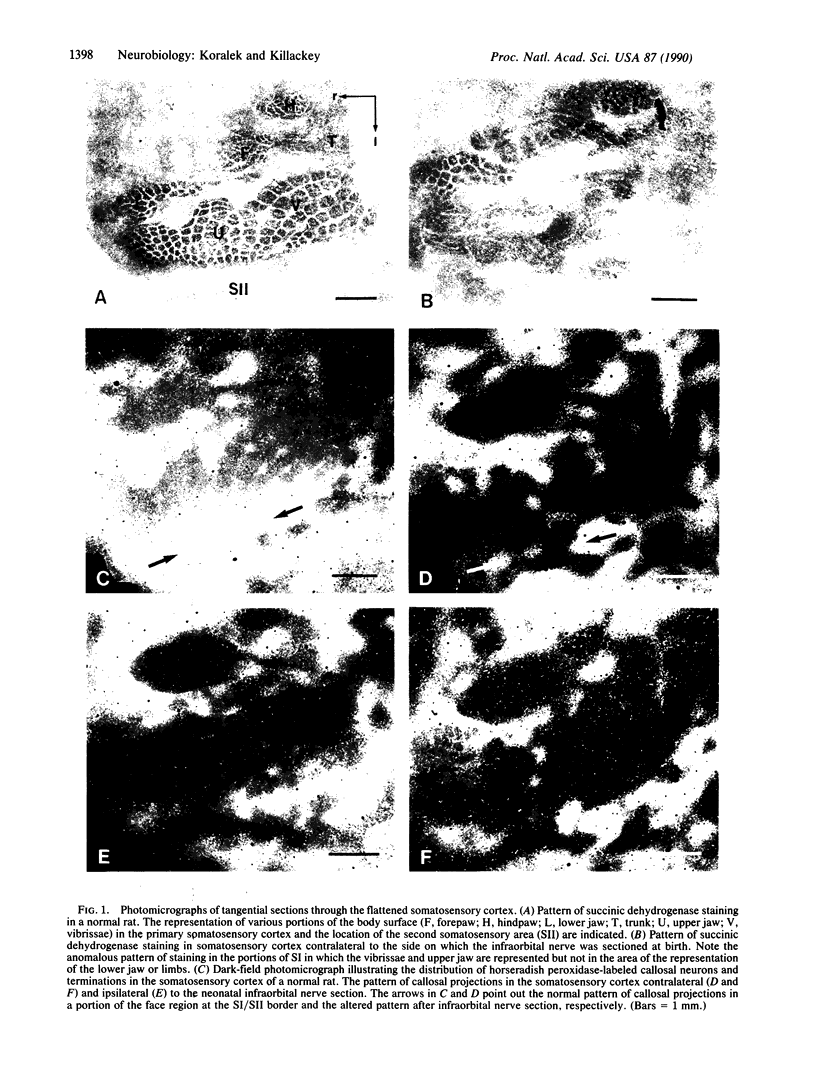
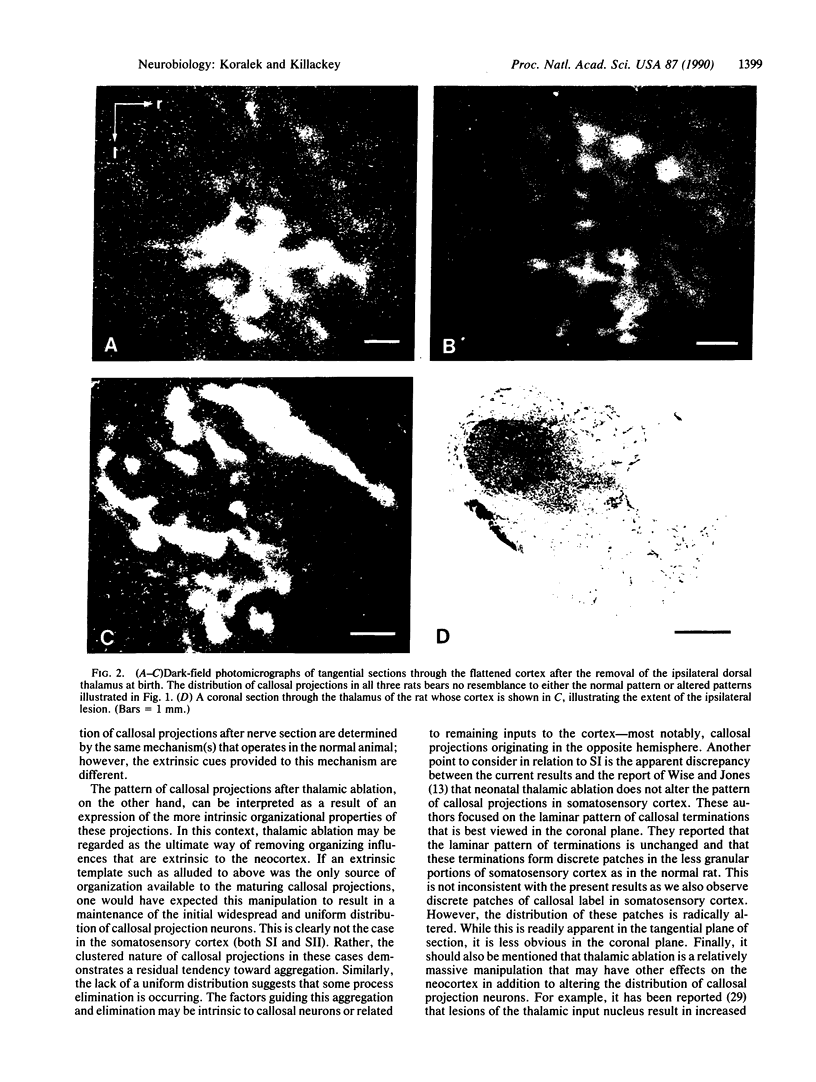
During the first postnatal week, the distribution of callosal projection neurons in the rat somatosensory cortex changes from a uniform to a discontinuous pattern. To determine if this change is influenced by afferent inputs to the somatosensory cortex, the effect of both early unilateral infraorbital nerve section and unilateral removal of the dorsal thalamus on the distribution of callosal projections in rat somatosensory cortex was examined. One month after either of the above manipulations at birth, the tangential distribution of callosal projections in the somatosensory cortex was examined using the combined retrograde and anterograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. Both manipulations alter the distribution of callosal projection neurons and terminations in the somatosensory cortex. After infraorbital nerve section, the distribution of callosal projections is altered in the contralateral primary somatosensory cortex. The abnormalities observed are consistent with the altered distribution of thalamocortical projections. In addition, consistent abnormalities were observed in the pattern of callosal projections of the second somatosensory area of both hemispheres. Most notably, they are absent in a portion of the region that contains the representation of the mystacial vibrissae and sinus hairs in this area. Thalamic ablation resulted in highly aberrant patterns of callosal projections in the somatosensory cortex on the operated side, where abnormal bands and clusters of callosal projections were observed in apparently random locations. These results are interpreted as evidence that both peripheral and central inputs influence the maturational changes in the distribution of callosal projection neurons.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates C. A., Erzurumlu R. S., Killackey H. P. Central correlates of peripheral pattern alterations in the trigeminal system of the rat. III. Neurons of the principal sensory nucleus. Brain Res. 1982 Sep;281(1):108–113. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(82)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates C. A., Killackey H. P. The organization of the neonatal rat's brainstem trigeminal complex and its role in the formation of central trigeminal patterns. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Oct 15;240(3):265–287. doi: 10.1002/cne.902400305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belford G. R., Killackey H. P. The sensitive period in the development of the trigeminal system of the neonatal rat. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Sep 15;193(2):335–350. doi: 10.1002/cne.901930203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvell G. E., Simons D. J. Somatotopic organization of the second somatosensory area (SII) in the cerebral cortex of the mouse. Somatosens Res. 1986;3(3):213–237. doi: 10.3109/07367228609144585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvell G. E., Simons D. J. Thalamic and corticocortical connections of the second somatic sensory area of the mouse. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Nov 15;265(3):409–427. doi: 10.1002/cne.902650309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusick C. G., Lund R. D. Modification of visual callosal projections in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Dec 20;212(4):385–398. doi: 10.1002/cne.902120406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. R., Killackey H. P. Distinguishing topography and somatotopy in the thalamocortical projections of the developing rat. Brain Res. 1985 Jan;349(1-2):309–313. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(85)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehay C., Horsburgh G., Berland M., Killackey H., Kennedy H. Maturation and connectivity of the visual cortex in monkey is altered by prenatal removal of retinal input. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):265–267. doi: 10.1038/337265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erzurumlu R. S., Killackey H. P. Development of order in the rat trigeminal system. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Feb 1;213(4):365–380. doi: 10.1002/cne.902130402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J. Extracellular current flow and the site of transduction by vertebrate hair cells. J Neurosci. 1982 Jan;2(1):1–10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-01-00001.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innocenti G. M., Frost D. O. Effects of visual experience on the maturation of the efferent system to the corpus callosum. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):231–234. doi: 10.1038/280231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy G. O., Akers R. M., Killackey H. P. Differential distribution of callosal projection neurons in the neonatal and adult rat. Brain Res. 1979 Sep 21;173(3):532–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy G. O., Killackey H. P. The ontogeny of the distribution of callosal projection neurons in the rat parietal cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Jan 20;195(3):367–389. doi: 10.1002/cne.901950302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Killackey H. P. Terminal arbors of axons projecting to the somatosensory cortex of the adult rat. I. The normal morphology of specific thalamocortical afferents. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3529–3543. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03529.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Killackey H. P. Terminal arbors of axons projecting to the somatosensory cortex of the adult rat. II. The altered morphology of thalamocortical afferents following neonatal infraorbital nerve cut. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3544–3553. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03544.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killackey H. P., Belford G. R. The formation of afferent patterns in the somatosensory cortex of the neonatal rat. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jan 15;183(2):285–303. doi: 10.1002/cne.901830206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killackey H. P., Fleming K. The role of the principal sensory nucleus in central trigeminal pattern formation. Brain Res. 1985 Sep;354(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(85)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killackey H. P., Shinder A. Central correlates of peripheral pattern alterations in the trigeminal system of the rat. II. The effect of nerve section. Brain Res. 1981 Jan;227(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(81)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M. Tetramethyl benzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry: a non-carcinogenic blue reaction product with superior sensitivity for visualizing neural afferents and efferents. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Feb;26(2):106–117. doi: 10.1177/26.2.24068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movshon J. A., Van Sluyters R. C. Visual neural development. Annu Rev Psychol. 1981;32:477–522. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.32.020181.002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary D. D., Stanfield B. B., Cowan W. M. Evidence that the early postnatal restriction of the cells of origin of the callosal projection is due to the elimination of axonal collaterals rather than to the death of neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Jul;227(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(81)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olavarria J., Malach R., Van Sluyters R. C. Development of visual callosal connections in neonatally enucleated rats. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jun 15;260(3):321–348. doi: 10.1002/cne.902600302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olavarria J., Van Sluyters R. C., Killackey H. P. Evidence for the complementary organization of callosal and thalamic connections within rat somatosensory cortex. Brain Res. 1984 Jan 23;291(2):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olavarria J., Van Sluyters R. C. Organization and postnatal development of callosal connections in the visual cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Sep 1;239(1):1–26. doi: 10.1002/cne.902390102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades R. W., Dellacroce D. D. Neonatal enucleation induces an asymmetric pattern of visual callosal connections in hamsters. Brain Res. 1980 Nov 24;202(1):189–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. M., Spear P. D. Organization of visual pathways in normal and visually deprived cats. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):738–855. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Sinha M. M. Somatotopic organization of Smll cerebral neocortex in albino rat. Brain Res. 1972 Feb 11;37(1):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise S. P., Jones E. G. Developmental studies of thalamocortical and commissural connections in the rat somatic sensory cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 15;178(2):187–208. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]