Abstract
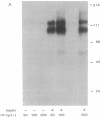
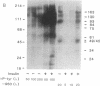
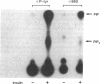
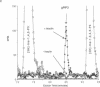
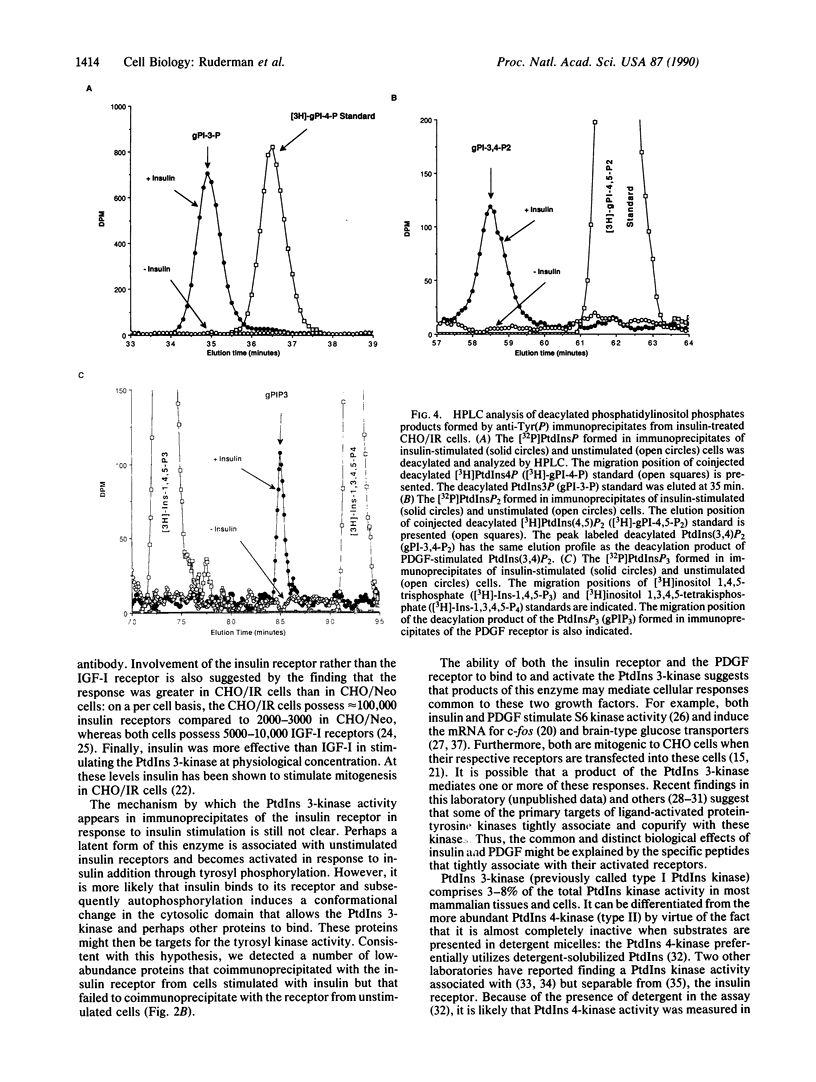
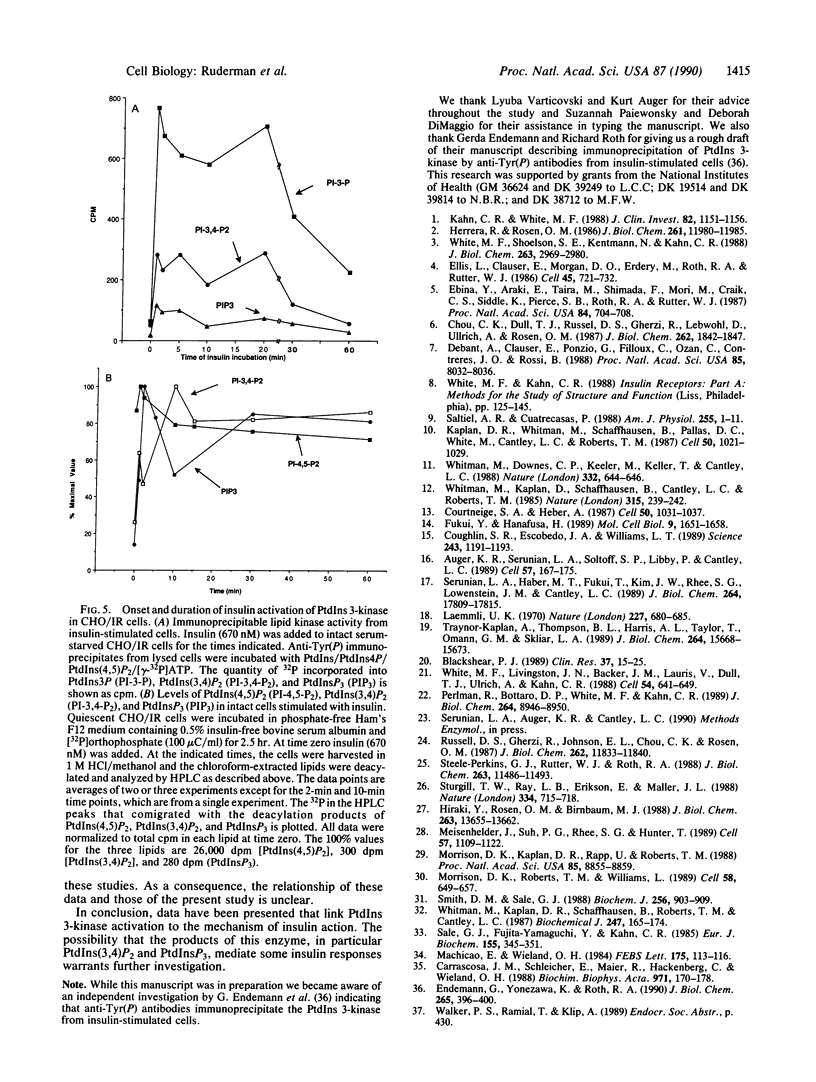
Insulin action appears to require the protein-tyrosine kinase domain of the beta subunit of the insulin receptor. Despite this, the identities and biochemical functions of the cellular targets of this tyrosine kinase are unknown. A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) that phosphorylates the D-3 position of the inositol ring associates with several protein-tyrosine kinases. Here we report that PI 3-kinase activity is immunoprecipitated from insulin-stimulated CHO cells by antiphosphotyrosine and anti-insulin receptor antibodies. Insulin as low as 0.3 nM increased immunoprecipitable PI 3-kinase activity within 1 min. Increases in activity were much greater in CHO cells expressing the human insulin receptor (100,000 receptors per cell) than in control CHO cells (2000 receptors per cell). During insulin stimulation, various lipid products of the PI 3-kinase either appeared or increased in quantity in intact cells, suggesting that the appearance of immunoprecipitable PI 3-kinase reflects an increase in its activity in vivo. These results indicate that insulin at physiological concentrations regulates the PI 3-kinase and suggest that this regulation involves a physical association between the insulin receptor and the PI 3-kinase and tyrosyl phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J. Insulin-stimulated protein biosynthesis as a paradigm of protein kinase C-independent growth factor action. Clin Res. 1989 Jan;37(1):15–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroscosa J. M., Schleicher E., Maier R., Hackenberg C., Wieland O. H. Separation of the protein-tyrosine kinase and phosphatidylinositol kinase activities of the human placental insulin receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 16;971(2):170–178. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Heber A. An 81 kd protein complexed with middle T antigen and pp60c-src: a possible phosphatidylinositol kinase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debant A., Clauser E., Ponzio G., Filloux C., Auzan C., Contreres J. O., Rossi B. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 does not alter the mitogenic effect of the hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8032–8036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endemann G., Yonezawa K., Roth R. A. Phosphatidylinositol kinase or an associated protein is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):396–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activity associates with viral p60src protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1651–1658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Rosen O. M. Autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor in vitro. Designation of phosphorylation sites and correlation with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11980–11985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraki Y., Rosen O. M., Birnbaum M. J. Growth factors rapidly induce expression of the glucose transporter gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13655–13662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., White M. F. The insulin receptor and the molecular mechanism of insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1151–1156. doi: 10.1172/JCI113711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machicao E., Wieland O. H. Evidence that the insulin receptor-associated protein kinase acts as a phosphatidylinositol kinase. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80581-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R., Bottaro D. P., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Conformational changes in the alpha- and beta-subunits of the insulin receptor identified by anti-peptide antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8946–8950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Johnson E. L., Chou C. K., Rosen O. M. The protein-tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor is necessary for insulin-mediated receptor down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11833–11840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. J., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Kahn C. R. Characterization of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity associated with the insulin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Mar 3;155(2):345–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. In search of a second messenger for insulin. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 1):C1–11. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serunian L. A., Haber M. T., Fukui T., Kim J. W., Rhee S. G., Lowenstein J. M., Cantley L. C. Polyphosphoinositides produced by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase are poor substrates for phospholipases C from rat liver and bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17809–17815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., Sale G. J. Evidence that a novel serine kinase catalyses phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in an insulin-dependent and tyrosine kinase-dependent manner. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):903–909. doi: 10.1042/bj2560903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele-Perkins G., Turner J., Edman J. C., Hari J., Pierce S. B., Stover C., Rutter W. J., Roth R. A. Expression and characterization of a functional human insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11486–11492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynor-Kaplan A. E., Thompson B. L., Harris A. L., Taylor P., Omann G. M., Sklar L. A. Transient increase in phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol trisphosphate during activation of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15668–15673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Livingston J. N., Backer J. M., Lauris V., Dull T. J., Ullrich A., Kahn C. R. Mutation of the insulin receptor at tyrosine 960 inhibits signal transmission but does not affect its tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):641–649. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Shoelson S. E., Keutmann H., Kahn C. R. A cascade of tyrosine autophosphorylation in the beta-subunit activates the phosphotransferase of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2969–2980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]