Abstract
Background
Due to its variegated and colorful leaves, ornamental kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. acephala) has become a popular ornamental plant. In this study, we report the fine mapping and analysis of a candidate purple leaf gene using a backcross population and an F2 population derived from two parental lines: W1827 (with white leaves) and P1835 (with purple leaves).
Results
Genetic analysis indicated that the purple leaf trait is controlled by a single dominant gene, which we named BoPr. Using markers developed based on the reference genome ‘02–12’, the BoPr gene was preliminarily mapped to a 280-kb interval of chromosome C09, with flanking markers M17 and BoID4714 at genetic distances of 4.3 cM and 1.5 cM, respectively. The recombination rate within this interval is almost 12 times higher than the usual level, which could be caused by assembly error for reference genome ‘02–12’ at this interval. Primers were designed based on ‘TO1000’, another B. oleracea reference genome. Among the newly designed InDel markers, BRID485 and BRID490 were found to be the closest to BoPr, flanking the gene at genetic distances of 0.1 cM and 0.2 cM, respectively; the interval between the two markers is 44.8 kb (reference genome ‘TO1000’). Seven annotated genes are located within the 44.8 kb genomic region, of which only Bo9g058630 shows high homology to AT5G42800 (dihydroflavonol reductase), which was identified as a candidate gene for BoPr. Blast analysis revealed that this 44.8 kb interval is located on an unanchored scaffold (Scaffold000035_P2) of ‘02–12’, confirming the existence of assembly error at the interval between M17 and BoID4714 for reference genome ‘02–12’.
Conclusions
This study identified a candidate gene for BoPr and lays a foundation for the cloning and functional analysis of this gene.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12864-017-3613-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Ornamental kale, Purple leaf, Inheritance, Fine mapping, Candidate gene
Background
Ornamental kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. acephala) is a popular ornamental plant cultivated worldwide owing to its variegated, colorful leaves [1] and strong resistance to cold. The leaves of ornamental kale are diverse and colorful: the edges are emerald green, dark-green, gray-green, or yellow-green, and the center can be white, yellow, pink, red, purple or other complex color varieties. The leaf pattern of ornamental kale is classified as foliage leaves, round leaves, cracked leaves, wave leaves and other types. Furthermore, purple-leaf ornamental kale, which is mainly due to various anthocyanin components [2], is reported to possess strong antioxidant capacity and thus potential benefits to human health [3, 4].
Some leaf color genes have been mapped in Brassica crops. For example, the red leaf color trait is reportedly controlled by the single dominant gene Re in ornamental kale, which was mapped to C09 between SSR markers C9Z90 and C9Z94, with genetic distances of 0.3 cM and 2.0 cM, respectively [5]. In Brassica juncea, the purple leaf gene (PL) was mapped between SRAP markers ME7EM9 and ME2EM2, with genetic distances of 1.2 cM and 5.5 cM, respectively [6]. A purple leaf dominant gene (BrPur) in Brassica rapa was assigned to a locus between InDel markers BVRCPI613 and BVRCPI431, with a genetic interval of 0.6 cM [7]. An incomplete dominant gene (BnaA.PL1) for the purple leaf trait in Brassica napus has been mapped, and the possible candidate gene is predicted to encode adenosine 5’-phosphosulfate reductase [8]. Zhu et al. found the pink leaf color trait in ornamental kale to be controlled by a single semi-dominant gene mapped to C03 between SSR marker Ni2C12 and co-dominant SCAR marker Boac04, with genetic distances of 0.6 cM and 2.4 cM, respectively [9].
With the development of molecular biology and the release of the B. oleracea draft genome [10, 11], uncovering the genetic basis of important traits has become a focus of theoretical and applied studies in this species. To date, many genes/QTLs have been mapped in Brassica oleracea using InDel markers, including the Fusarium wilt resistance gene FOC1 [12, 13], the petal color gene cpc-1 [14], the yellow-green gene ygl-1 [15], and QTLs associated with heading traits [16], head-splitting resistance [17, 18], Diamondback (Plutella xylostella) moth resistance [19], and resistance to diseases such as Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [20], black rot [21, 22], and clubroot [23].
In this study, kale inbred line W1827 (with white leaves) was crossed to inbred line P1835 (with purple leaves) to construct F2 and backcross (BC) populations, which were used for genetic analysis and fine mapping of the gene for the purple leaf trait. Genes located within the fine-mapping region were analyzed. These findings will lay a foundation for the cloning and validation of BoPr and will facilitate elucidation of the molecular mechanism for purple leaf formation in B. oleracea L. var. acephala.
Methods
Plant materials
The female kale inbred line W1827 (P1, white leaf, Fig. 1a) was crossed with male kale inbred line P1835 (P2, purple color, Fig. 1b) to generate the F1 population. The F2 population was obtained via self-pollination of F1 plants; BC1P1 and BC1P2 populations were created by backcrossing of F1 × W1827 and F1 × P1835, respectively. All materials were from Cabbage and Broccoli Research Group, Institute of Vegetables and Flowers (IVF), Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS).
Fig. 1.

Phenotypes of the parental lines. a W1827. b P1835
Genetic analysis and InDel marker development
Leaf color was identified visually. The segregation ratios of the F2 and BC1 populations were analyzed using a Chi-square test with SAS software.
The ‘02–12’ reference genome of cabbage was downloaded from BRAD (http://brassicadb.org) [10]; the TO1000 sequence was obtained from the genome sequence (http://plants.ensembl.org/Brassica_oleracea) [11]. The sequencing-by-synthesis method was used to re-sequence the parents at approximately 10× coverage over the entire genome [24]. This work was completed at Beijing Genomics Institute (BGI) (Shenzhen, China). For preliminary mapping, the re-sequencing data for both parents was mapped to the ‘02–12’ reference genome of B. oleracea (http://brassicadb.org) to detect 3-5 bp insertion-deletion mutations between the parents. InDel primers were then designed. Due to the possible assembly error of the 02–12 reference genome, new primers in the preliminary mapping region were designed based on the TO1000 reference genome. Primers were designed to have amplicon lengths of 100–200 bp, GC contents of 40–50% and Tm values of 52–62 °C.
DNA extraction and bulked segregant analysis (BSA)
Genomic DNA was extracted from fresh leaves using a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) protocol [25]. The concentration of DNA was estimated using a spectrophotometer (BioDrop, UK) and diluted to 40–50 ng/μL.
Ten purple-leaf F2 individuals and ten white-leaf F2 individuals were selected to construct two pools using the BSA method [26]. Polymorphic InDel markers between the parents were used to screen these pools, and polymorphic markers between the pools were used to examine recombination with all white-leaf individuals in the F2 and BC1P1 populations.
The 20 μL PCR reaction mixture contained 4 μL DNA template (40–50 ng/μL), 2 μL 10× PCR buffer (Mg2+ included), 1.6 μL dNTPs (2.5 mM each), 0.8 μL forward primer (10 μM), 0.8 μL reverse primer (10 μM), 0.4 μL Taq DNA polymerase (2.5 U/μL) and 10.4 μL ddH2O. Reactions were performed in a thermal cycler as follows: 94 °C for 5 min; 35 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s and 72 °C for 45 s; 72 °C for 10 min. Amplicons were separated by 8% PAGE at 160 V for 1.5 h, followed by silver staining.
Data analysis
For each marker, individuals with the W1827 allele were categorized as ‘a’, and individuals with the P1835 allele were categorized as ‘b’; those with the F1 allele were categorized as ‘h’. The Kosambi mapping function was used to calculate genetic distances between markers [27], and the genetic map was constructed using MapDraw [28].
To identify probable genes associated with purple leaves, genes located within the candidate interval were analyzed based on annotations from the B. oleracea reference genome ‘TO1000’.
Analysis of the candidate gene
To amplify the candidate gene Bo9g058630, primers were designed in DNAMAN 7.0 using the sequence of Bo9g058630. PCR amplification was performed using the Q5 Ultra High Fidelity DNA polymerase. The PCR amplification conditions followed the manufacturer’s specifications. The annealing temperature was determined using the NEB Tm calculator (New England Biolabs, Inc.), and the elongation step was based on a rate of 30 s/kb. The candidate gene sequence was determined by Sanger sequencing of the PCR amplicons.
Results
Genetic analysis of leaf color of W1827 with P1835
Sixteen F1 individuals generated by crossing W1827 with P1835 exhibited purple leaves, indicating that the purple leaf color trait is dominant over the white-leaf trait. In the F2 population, 258 of 1008 individuals displayed white leaves and 750 purple leaves. The Chi-square test confirmed this segregation ratio to be 3:1. In the BC1P1 population, 1040 of 2034 individuals showed purple leaves and 994 white leaves, with the Chi-square test confirming the segregation ratio to be 1:1. The leaves of all 200 individuals in the BC1P2 population were purple (Table 1). These results indicated that the purple leaf trait is controlled by a single dominant gene, which we termed BoPr.
Table 1.
The Chi-square (χ 2) goodness-of-fit test ratios of leaf color segregation in BC and F2 populations
| Populations | Total plants number | Number of purple leaf individuals* | Number of white leaf individuals | Expected ratio | χ 2a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 16 | 16 | 0 | - | - |
| F2 | 1008 | 750 | 258 | 3:1 | 0.19 |
| BC1P1 | 2034 | 1040 | 994 | 1:1 | 0.52 |
| BC1P2 | 200 | 200 | 0 | - | - |
*Purple plants and white plants were determined by visual inspection
a χ 2 > χ2 0.05 = 3.84 was considered significant
Preliminary mapping of BoPr
Illumina paired-end sequencing generated reads of 9.2 Gb for kale inbred line W1827 and 9.9 Gb for line P1835. A total of 211 pairs of InDel marker primers were designed by comparing the whole-genome re-sequencing data with the sequence of the ‘02–12’ reference genome.
These InDel marker primers were used to screen for polymorphisms between the parents. Ultimately, 58 of the 211 pairs of primers revealed polymorphisms, with a polymorphic rate of 27.5%. The polymorphisms were further screened in two the bulks of the F2 population, and only BoID4814, BoID4826 and BoID4837 exhibited polymorphisms between the two bulks. The three markers were preliminarily located on chromosome C09 according to the marker location in the reference genome.
Subsequently, 41 new additional InDel markers near the three polymorphic primers were designed, 26 of which showed polymorphisms. Only co-dominant markers with clear and stable amplification were chosen for further analysis in the F2 and BC1P1 populations. A genetic map comprising 16 InDel markers (Table 2) was constructed using MapDraw [26] (Fig. 2a). InDel markers M17 and BoID4714 were found to be closest to BoPr, flanking the gene at genetic distances of 4.3 cM and 1.5 cM, respectively. Based on marker locations in the reference genome ‘02–12’, BoPr is located on chromosome C09. The interval between the two markers is 280 kb (6,312,350–6,592,994 bp).
Table 2.
The InDel primer sequences used in this study
| Primer name | Physical distance (bp) (02-12) | Forward primer sequence (5’-3’) | Reverse primer sequence (3’-5’) |
| BoID4673 | C09:4123400 | GAATCGAGACAGAACCGTAT | TAACGTTAACCGGATTGG |
| BoID4677 | C09:4347473 | TTAGCGTTTGTGTATTACCG | AAAGAACACAGAGGTTTGGA |
| BoID4697 | C09:5350367 | GGCTTTCTATCTGTCAAAAGG | GTTGGAGATTTTCTATCCGA |
| BoID4704 | C09:5830712 | TAATATTTGCGAGTGGAAGC | ATCCAGAACCGTCAATCTAA |
| BoID4707 | C09:5940678 | GTTTCACCCTTTGATCCTTT | TTCGCACCTTATCAAGTAGAG |
| M1 | C09:5943643 | TTGAGCTGCTTCCTTTAGTC | ACAGGAGTGGCATTTACATC |
| M15 | C09:6139366 | CTTACACGAACCTTCTCTCG | GGCCTGCATATAAACCTCTT |
| M17 | C09:6312350 | GAGGAGTCTACATGCGTTTC | TTGAGGGTAAAGTAGACGGA |
| BoID4714 | C09:6592994 | GCCTTAGCATCCAGAGATTA | ACGTCACAACGCTAATTACA |
| BoID4717 | C09:7100587 | TCCTGGATACGAAGTACCTG | TCCTAGAAACTTGTTGTCGC |
| BoID4794 | C09:13019067 | CATACTTGGAAGGAGCTTTG | CTCACAGTTTCTCCTTTTGG |
| BoID4798 | C09:13119313 | CGGATTAACACAGTGAAGAAG | AGATTTTGACCTTAGAAGCG |
| BoID4805 | C09:13318893 | ATATCGTCTGGCCCTCTATT | AGAACCCACAGAGACATCAC |
| BoID4814 | C09:14085188 | CCTTGGGATTTACAAGGTACT | GAGTAATCGAGAATTATGAGCC |
| BoID4837 | C09:18142750 | TGATACCTTTTGTCGAGCTT | ATTTGGGGTTGGTAGAAATC |
| BoID4863 | C09:20025875 | AGCAGTGCATGATACAAATG | CGGGCTGTCTAAATCATTA |
| Primer name | Physical distance (bp) (TO1000) | Forward primer sequence (5’-3’) | Reverse primer sequence (3’-5’) |
| BRID399 | C09:10788227 | GGTTGGATTTAGATTTGCTG | CTCCACCGTCATTGTATCAT |
| BRID471 | C09:16850910 | TCTAAAAGGAGAAGCCAGAA | GAGGGGAGATGAGGTTTACT |
| BRID472 | C09:16879357 | GTTTGAGTTTGTTTTGGGAG | GACTTGTAGCATTTGTCGTG |
| BRID482 | C09:17010450 | CATGCATTGAAAGTGTTGTC | AACTGAGCTTTCACACTGGT |
| BRID485 | C09:17102497 | CTTCTTGGAGGTCTCTTGTG | TGCACATTAAAACGGTAGG |
| BRID490 | C09:17147250 | TACTTGCATCAAATGTTGGG | GCACAGACTCATCTCCTTTC |
| BRID493 | C09:17167025 | AGCACTGAGACTACCCTTGA | CAGCTTTGTCTTGTGTCTGA |
| BRID494 | C09:17205726 | CGCCATATGAATAAAGGAAC | ACGAAGTCAACAAACAGCTT |
| BRID499 | C09:17500985 | ATGCGATGATGAGATAGCTT | AGATCCACTTCAATCCAATG |
| BRID505 | C09:17643567 | AACACATATTCCCGTCAAAC | GGAAAAGTGTGTTTTTGGG |
| BRID517 | C09:17879063 | AAATCATCCAAACCACTGTC | GTGCCTCTACTAGTTTTGGG |
| BRID530 | C09:18485633 | TTCAAGACTCTCCAGCTCAT | CAAGAGAAAGACTGGTTCGT |
Fig. 2.
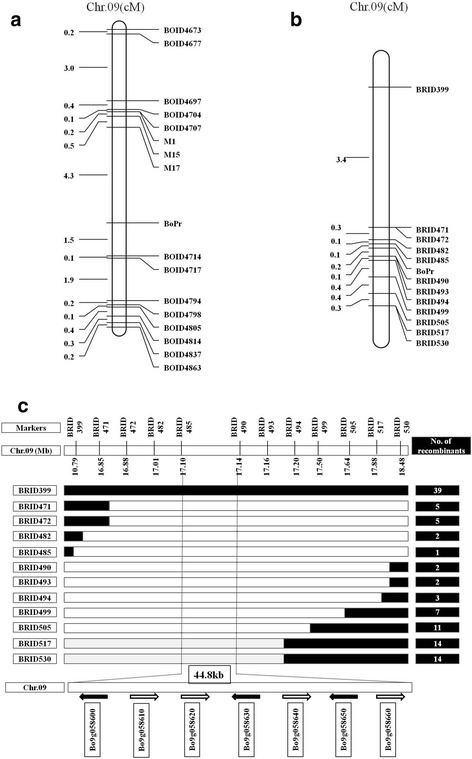
a Preliminary mapping of BoPr, units: cM. b Fine mapping of BoPr, units: cM. c Fine mapping using the BC1P1 population with 2034 plants. The BoPr gene was delimited to an interval between BRID485 and BRID490, with an estimated length of 44.8 kb, seven genes were annotated between markers BRID485 and BRID490 based on the reference genome sequence. The genetic structure for each recombinant type is depicted as white for homozygous white leaf alleles, black rectangles for heterozygous alleles, respectively. The relative positions of markers on C09 were determined according to the TO1000 genome sequence
Fine mapping of the purple leaf gene
The 280 kb interval spans two scaffolds (Scaffold000195_P2, Scaffold000050), and no polymorphic marker between the parents was found in this narrow interval. Moreover, the genetic distance for this 280 kb interval was calculated to be 5.8 cM, 12 times higher than the usual level (~600 kb/cM). Thus, another reference genome, ‘TO1000’ [11], was used to determine the accuracy of this interval. Blast alignment analysis showed the physical distance between markers M17 (7,590,215–7,590,234 bp) and BoID4714 (20,327,191–20,327,211 bp) to be approximately 12.73 Mb in the ‘TO1000’ reference genome, indicating possible assembly errors in the reference genome ‘02–12’ or ‘TO1000’. To determine whether this 12.73 Mb interval is linked to the BoPr gene, 70 pairs of InDel marker primers were designed based on the ‘TO1000’ reference genome. Polymorphisms between the two bulks were found for 12 of the 70 pairs, and these were used to analyze the BC1P1 and F2 populations. A genetic map comprising 12 InDel markers (Table 2) was constructed using MapDraw (Fig. 2b). InDel markers BRID485 and BRID490 were found to be the closest to BoPr, flanking the gene at genetic distances of 0.10 cM and 0.20 cM, respectively. Based on marker locations in the reference genome ‘TO1000’, the interval between BRID485 and BRID490 is 44.8 kb (17,102,497–17,147,250 bp).
Prediction and analysis of the candidate gene
Based on the ‘TO1000’ reference genome (http://plants.ensembl.org/Brassica_oleracea) (Parkin et al. 2014), seven genes were identified in the 44.8 kb region (Table 3). According to domain annotations from InterPro and BLASTX (best hit) analyses, four of these seven genes have not been annotated (Table 3). The other three genes are as follows: Bo9g058600 (homologous gene AT5G42790) encoding the largest proteasomal subunit; Bo9g058660 (homologous gene AT5G42810) encoding inositol tetra-pentaphosphate 2-kinase; Bo9g058630 (homologous gene AT5G42800) encoding dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR), which catalyzes conversion of dihydroquercetin to leucocyanidin in anthocyanin biosynthesis [29]. Thus, we tentatively designated Bo9g058630 as the candidate gene controlling the purple leaf color in ornamental kale.
Table 3.
Annotation of B. oleracea genes in the candidate region
| Bol IDa | E-value | Bo genesb | Gene position on C09c | AT IDd | E-value | AT GOe annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bol035270 | 0.0 | Bo9g058600 | 17102783–17104636 bp | AT5G42790 | 0.0 | the largest subunit of proteasome |
| - | - | Bo9g058610 | 17111283–17112572 bp | - | - | - |
| - | - | Bo9g058620 | 17113341–17114372 bp | - | - | - |
| Bol035269 | 0.0 | Bo9g058630 | 17116312–17117891 bp | AT5G42800 | 0.0 | dihydroflavonol reductase |
| - | - | Bo9g058640 | 17124223–17124381 bp | - | - | - |
| - | - | Bo9g058650 | 17137677–17138809 bp | - | - | - |
| Bol035268 | 0.0 | Bo9g058660 | 17145032–17147070 bp | AT5G42810 | 0.0 | Encodes an inositol tetra-/pentaphosphate 2-kinase |
a B. oleracea homologous genes in the candidate region (reference genome ‘02–12’)
bSeven B. oleracea genes in the candidate region. The likely leaf color genes and their information are indicated in bold (reference genome ‘TO1000’)
cThe physical position of seven B. oleracea genes on chromosome C09 (reference genome ‘TO1000’)
dThe best hits of the seven B. oleracea genes compared to A. thaliana (AT)
eGO annotations for seven Bo to AT best-hit genes obtained from TAIR
Primer pairs were designed spanning the full length of Bo9g058630 (Table 4), and PCR was performed using genomic DNA of W1827 and P1835 as the template. Based on agarose gel electrophoresis (Fig. 3), amplicons of approximately 4.0 kb for W1827 and approximately 2.0 kb for P1835 were obtained. Sequencing revealed that the full-length Bo9g058630 sequence in purple-leaf P1835 is 1580 bp, whereas that in white-leaf W1827 is 3856 bp. Compared with Bo9g058630 in P1835, a 124 bp deletion, a 2400 bp insertion at nucleotide 68 and four SNPs are present in W1827 (sequences of W1827 and P1835 are supplied in Additional file 1: Supplementary 1). Polymorphism of the candidate gene Bo9g058630 was further confirmed in the segregating population.
Table 4.
Primers used for full-length candidate gene cloning
| Primers | Primers sequences (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| Bo630 | GTCCACAACACTTTCATACAA//TTCCCAAAGCATAATCCATCT |
Fig. 3.
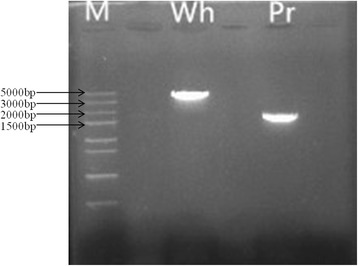
PCR products of amplicon Bo630 (isolated by agarose gel electrophoresis); M represents the DNA ladder, Pr is the inbred line P1835 with purple leaves, Wh is the inbred line W1827 with white leaves
Discussion
Mapping of the purple leaf gene
Purple-leaf traits have been studied in several species, such as rice [30, 31], tetraploid wheat [32], Brassica rapa [7], and carrot [9, 33]. Some genes related to anthocyanins, which might be responsible for purple leaf color, have been reported in Brassica, including BrPur in B. rapa [7], BnaA.PL1 in B. napus [8], and the Re and Pi genes in B. oleracea [5, 9].
Ren et al. [5] reported that markers C9Z90 (C09:18,377,796 bp) and C9Z94 (C09:6,872,051 bp) are tightly linked to Re, which controls the red-leaf phenotype in kale [5]. The red-leaf phenotype is similar with the purple phenotype of the parents used in the present study. Based on reference genome ‘TO1000’, our results show that C9Z90 is located between InDel markers BRID517 (17,879,063 bp) and BRID530 (18,485,633 bp) and that C9Z94 is located between InDel markers BoID4704 (6,418,130 bp) and BoID4707 (7,177,017 bp). This indicates that the mapping interval in Ren et al. [5] is larger than ours. Furthermore, the distance between the Re gene and the closest markers are 2.0 cM for C9Z94 and 0.3 cM for C9Z90 [5] but 6.1 cM for BoID4704 and 1.1 cM for BRID517 in our mapping population, which may be caused by different mapping populations. In our study, however, the BoPr gene was successfully fine mapped to a 44.8-kb interval based in the ‘TO1000’ reference genome.
For the mapping population, F2 and BC1 populations are usually constructed for mapping important agronomic traits. In this study, for markers far away from the candidate gene, the recombination rate of the F2 population was larger than that of the BC1P1 population; however, the opposite case was true for markers close to the candidate region (Additional file 2: Table S1). The closest flanking markers BRID485 and BRID490 were all screened from the BC1P1 population, with no recombinants in the F2 population. Furthermore, the rate of recessive individuals in the BC1P1 populations was 1/2, which was twice that of the F2 population. Therefore, we used the large BC1P1 population to fine map the candidate gene.
Possible assembly errors in cabbage reference genome ‘02–12’
With the development of technology, large amounts of data are produced by genome sequencing, though genome assemblies based on these data are often woefully incomplete. Although the Nipponbare reference sequence (RefSeq) exhibits the best quality among crop genomes, it still contains many assembly errors and gaps [34, 35]. Genome sequencing has been completed in three species of Brassica: B.napus [36], B. rapa [37] and B. oleracea [10, 11]. Some assembly problems have been reported. For example, Lee et al. [23] revised the ‘02–12’ reference genome assembly when they mapped clubroot resistance QTLs using genotyping-by-sequencing; new positions for 27 v-blocks and 10 s-blocks and several inversions of some alphabetically named blocks in reference genome ‘02–12’ and two mis-anchored sequence scaffolds in reference genome ‘TO1000’ were identified. In addition, Liu et al. [15] found possible assembly errors in ‘02–12’ while mapping a yellow-green leaf mutant.
In this study, the recombination rate of markers M17 and BoID4714 in ‘02–12’ [10] (48 kb/cM) was found to be almost 12 times higher than the usual level in the cabbage genome (~600 kb/cM) in preliminary mapping. In ‘TO1000’, the primary mapping interval was found to be 12.7 Mb (~1760 kb/cM). Based on the ‘TO1000’ genome, the BoPr gene was fine mapped to a 44.8 kb interval, but according to primary mapping, this 44.8 kb is not located in the 280 kb region but is on an unanchored scaffold (Scaffold000035_P2) of ‘02–12’. Thus, the mapping results suggested possible assembly error and the potential location of the unanchored Scaffold000035_P2 in the 02–12 reference genome. However, this scaffold is only 1.5 Mb. More unanchored scaffolds could be detected within this interval in the future if PacBio, a third-generation sequencing platform, is applied to improve the reference genome of ‘02–12’. These results will contribute to the improvement of the cabbage genome and provide guidance for map-based cloning of other genes in this region.
The DFR gene in anthocyanin biosynthetic pathways
The biosynthetic pathways of anthocyanins and related genes have been well characterized, and DFR is a key enzyme in the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway [38]. In characterizing DFR genes, Ahmed et al. found that these genes are associated with cold and freezing stresses in B. rapa [39]. Guo et al. identified 73 anthocyanin biosynthetic genes, locating the DFR gene on chromosome A09, named BrDFR (Bra027457), in B. rapa [40].
In our study, Bo9g058630 was found to be homologous to Arabidopsis thaliana AT5G42800, which encodes DFR. DFRs utilizing the three primary dihydroflavonol substrates have been characterized. Expression of DFR clones together with plant-specific 4-coumaroyl: CoA ligase, chalcone synthase, chalcone isomerase, and flavanone 3-hydroxylase in E. coli resulted in the synthesis of various levels of pelargonidin and could be used for engineering of other bioactive flavonoids, such as flavan-3-ols [41]. The purple-leaf trait of ornamental kale is largely attributed to various anthocyanin components [2], and sequence alignment showed that the function of Bo9g058630 in the white-leaf line W1835 is disrupted by two InDels. Furthermore, we designed a co-dominant marker based on sequence differences between W1835 and P1827, and this marker co-segregated with the phenotype of all recessive individuals in the F2 and BC1 populations. Thus, we suggest that Bo9g058630 is the most likely candidate gene for the purple-leaf trait. However, further work involving transformation is needed to verify whether the function of this gene is responsible for purple leaves in kale.
Conclusions
Inheritance of purple leaves in kale was found to be controlled by a single dominant gene, BoPr, and this gene was mapped to a 44.8 kb interval (reference genome ‘TO1000’) on chromosome C09. InDel markers BRID485 and BRID490 are closest to BoPr, flanking the gene at genetic distances of 0.1 cM and 0.2 cM. In the fine-mapping region, only Bo9g058630 showed high homology to AT5G42800 (dihydroflavonol reductase), which was identified as a candidate gene for BoPr. This study lays a foundation for the cloning of the gene BoPr as well as further function analyses.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was financially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31572141), the Major State Research Development Program (2016YFD0101702), the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-IVFCAAS) and the earmarked fund for the Modern Agro-Industry Technology Research System, China (nycytx-35-gw01). This work was performed in the Key Laboratory of Biology and Genetic Improvement of Horticultural Crops, Ministry of Agriculture, Beijing 100081, People’s Republic of China.
Availability of data and materials
The reference B. oleracea genome sequence was obtained from Brassica Database (http://brassicadb.org); the reference TO1000 sequence was obtained from the genome sequence (http://plants.ensembl.org/Brassica_oleracea). As one of the data owners, we confirm that we have full permission to use the genome sequence for the purposes of this study (i.e., candidate gene identification and characterization). The use of the reference genome for these purposes was approved by all data owners.
Authors’ contributions
XL developed the F2 and BC populations and wrote and revised the manuscript. HY, FH, and ZL isolated the samples, performed the marker assays, and analyzed the marker data. FH, ZF, LY, MZ, HL, YL, ZL and YZ conceived the study and critically reviewed the manuscript. XL, CC and BG analyzed the sequencing data and designed the InDel primers. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- BRAD
Brassica Database
- BSA
Bulked segregant analysis
- InDel
Insertion/deletion
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
- QTL
Quantitative trait locus
- SNP
Single nucleotide polymorphism
Additional files
Supplementary 1. Sequences of W1827 and P1835. (DOC 29 kb)
The recombination rate of markers far away from the candidate gene in the F2 and BC1P1 population. (DOCX 13 kb)
Contributor Information
Xiao-ping Liu, Email: xiaopingliu0@163.com.
Bao-zhen Gao, Email: 18853812686@163.com.
Feng-qing Han, Email: feng857142@163.com.
Zhi-yuan Fang, Email: fangzhiyuan@caas.cn.
Li-mei Yang, Email: yanglimei@caas.cn.
Mu Zhuang, Email: zhuangmu@caas.cn.
Hong-hao Lv, Email: lvhonghao@caas.cn.
Yu-mei Liu, Email: liuyumei@caas.cn.
Zhan-sheng Li, Email: lizhansheng@caas.cn.
Cheng-cheng Cai, Email: tsaicc@126.com.
Hai-long Yu, Email: 710512066@qq.com.
Zhi-yuan Li, Email: lizy1992@126.com.
Yang-yong Zhang, Phone: 0086-10-82108756, Email: zhangyangyong@caas.cn.
References
- 1.Schmidt S, Zietz M, Schreiner M, Rohn S, Kroh LW, Krumbein A. Genotypic and climatic influences on the concentration and composition of flavonoids in kale (Brassica oleracea var. sabellica) Food Chem. 2010;119:1293–9. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhang B, Hu ZL, Zhang YJ, Li YL, Zhou S, Chen GP. A putative functional MYB transcription factor induced by low temperature regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple kale. (Brassica oleracea var acephala f. tricolor) Plant Cell Rep. 2012;31:281–9. doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.de Gaulejac NSC, Glories Y, Vivas N. Free radical scavenging effect of anthocyanins in red wines. Food Res Int. 1999;32:327–33. doi: 10.1016/S0963-9969(99)00093-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yun JM, Afaq F, Khan N, Mukhtar H. Delphinidin, an anthocyanidin in pigmented fruits and vegetables, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human colon cancer HCT116 cells. Mol Carcinog. 2009;48:260–70. doi: 10.1002/mc.20477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ren J, Liu ZY, Niu RQ, Feng H. Mapping of Re, a gene conferring the red leaf trait in ornamental kale (Brassica oleracea. L. var. acephala). Plant Breed. 2015;134:494–500.
- 6.Luo YX, Du DZ, Fu G, Xu L, Li XP, Xing XR, Yao YM, Zhang XM, Zhao Z, Liu HD. Inheritance of leaf color and sequencerelated amplified polymorphic (SRAP) molecular markers linked to the leaf color gene in Brassica juncea. Afr J Biotechnol. 2011;10:14724–30. doi: 10.5897/AJB11.1107. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang WH, Zhang DS, Yu SC, Liu J, Wang D, Yu YJ, Zhao XY, Lu GX, Su TB, Zhang FL. Mapping the Br Pur gene for purple leaf color on linkage group A03 of Brassica rapa. Euphytica. 2014;199:293–302. doi: 10.1007/s10681-014-1128-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li HB, Zhu LX, Yuan GG, Heng SP, Yi B, Ma CZ, Shen JX, Tu JX, Fu TD, Wen J. Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of an anthocyanin-rich gene BnaA.PL1, conferring purple leaves in Brassica napus, L. Mol Genet Genomics. 2016;291:1523–34. doi: 10.1007/s00438-016-1199-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhu PF, Cheng MM, Feng X, Xiong Y, Liu C, Kang YH. Mapping of Pi, a gene conferring pink leaf in ornamental kale (Brassica oleracea, L. var. acephala, DC) Euphytica. 2016;207:377–85. doi: 10.1007/s10681-015-1555-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu S, Liu Y, Yang X, Tong C, Edwards D, Parkin IA, et al. The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3930. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Parkin IA, Koh C, Tang H, Robinson SJ, Kagale S, Clarke WE, et al. Transcriptome and methylome profiling reveals relics of genome dominance in the mesopolyploid Brassica oleracea. Genome Biol. 2014;15:R77. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-6-r77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lv HH, Yang LM, Kang JG, Wang QB, Wang XW, Fang ZY, et al. Development of InDel markers linked to Fusarium wilt resistance in cabbage. Mol Breed. 2013;32:961–7. doi: 10.1007/s11032-013-9925-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lv HH, Fang ZY, Yang LM, Zhang YY, Wang QB, Liu YM, et al. Mapping and analysis of a novel candidate Fusarium wilt resistance gene FOC1 in Brassica oleracea. BMC Genom. 2014;15:1094. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Han FQ, Yang C, Fang ZY, Yang LM, Zhuang M, Lv HH, Zhang YY, et al. Inheritance and InDel markers closely linked to petal color gene (cpc-1) in Brassica oleracea. Mol Breed. 2015;35:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s11032-015-0354-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu XP, Yang C, Han FQ, Fang ZY, Yang LM, Zhuang M, et al. Genetics and fine mapping of a yellow-green leaf gene (ygl-1) in cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) Mol Breed. 2016;36:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s11032-015-0425-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lv HH, Wang QB, Zhang YY, Yang LM, Fang ZY, Wang XW, et al. Linkage map construction using InDel and SSR markers and QTL analysis of heading traits in cabbage. Mol Breed. 2014;34:87–98. doi: 10.1007/s11032-014-0019-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pang WX, Li XN, Choi SR, Nguyen VD, Dhandapani V, Kim YY, et al. Mapping QTLs of resistance to head splitting in cabbage. (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.) Mol Breed. 2015;35:1–12. doi: 10.1007/s11032-015-0202-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Su YB, Liu YM, Li ZS, Fang ZY, Yang LM, Zhuang M, Zhang YY. QTL analysis of head splitting resistance in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata) using using SSR and InDel makers based on whole-genome Re-sequencing. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0138073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ramchiary N, Pang W, Nguyen VD, Li X, Choi SR, Kumar A, et al. Quantitative trait loci mapping of partial resistance to diamondback moth in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L) Theor Appl Genet. 2015;128:1209–18. doi: 10.1007/s00122-015-2501-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mei J, Ding Y, Lu K, Wei D, Liu Y, Disi JO, et al. Identification of genomic regions involved in resistance against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum from wild Brassica oleracea. Theor Appl Genet. 2013;126:549–56. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-2000-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kifuji Y, Hanzawa H, Terasawa Y, Nishio T. QTL analysis of black rot resistance in cabbage using newly developed EST-SNP markers. Euphytica. 2013;190:289–95. doi: 10.1007/s10681-012-0847-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lee J, Izzah NK, Jayakodi M, Perumal S, Joh HJ, Lee HJ, et al. Genome-wide SNP identification and QTL mapping for black rot resistance in cabbage. BMC Plant Biol. 2015;15:32. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0424-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee J, Izzah NK, Choi BS, Joh HJ, Lee SC, et al. Genotyping-by-sequencing map permits identification of clubroot resistance QTLs and revision of the reference genome assembly in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) DNA Res. 2015;14:S113. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsv034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ronaghi M, Uhlén M, Nyrén P. A sequencing method based on real-time pyrophosphate. Science. 1998;281:363–5. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5375.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Murray MG, Thompson WF. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980;8:4321–5. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88:9828–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kosambi DD. The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen. 1943;12:172–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1943.tb02321.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Liu RH, Meng JL. MapDraw: a microsoft excel macro for drawing genetic linkage maps based on given genetic linkage data. Hereditas. 2003;25:317–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shirley BW, Hanley S, Goodman HM. Effects of ionizing radiation on a plant genome: analysis of two Arabidopsis transparent testa mutations. Plant Cell. 1992;4:333–47. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kinoshita T, Takamure I. Gene mapping of the first and second linkage groups in rice. Journal Faculty of Agriculture Hokkaido University. 1990;64:208–17
- 31.Sakamoto W, Murata M, Maekawa M. Complex organization of the rice purple leaf locus involved in tissue-specific accumulation of anthocyanin. In: Kush GS, Brar DS, Hardy B, editors. Advances in rice genetics. Supplement to Rice Genetics IV. Proceedings of the Fourth International Rice Genetics Symposium, 22–27 Oct 2000, Los Banos: International Rice Research Institute; 2003. p. 475–7.
- 32.Khlestkina EK, Röder MS, Börner A. Mapping genes controlling anthocyanin pigmentation on the glume and pericarp in tetraploid wheat (Triticum durum L.) Euphytica. 2010;171:65–9. doi: 10.1007/s10681-009-9994-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Simon PW. High-resolution mapping of root and leaf anthocyanin pigmentation QTL in carrot. Proceedings, Plant & Animal Genome, January 10–14, 2015
- 34.Deng Y, Pan Y, Luo M. Detection and correction of assembly errors of rice Nipponbare reference sequence. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 2014;16:643–50. doi: 10.1111/plb.12090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Denton JF, Lugo-Martinez J, Tucker AE, Schrider DR, Warren WC, Hahn MW. Extensive error in the number of genes inferred from draft genome assemblies. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014;10:e1003998. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu S, Parkin IA, Tang H, Wang X, et al. Plant genetics. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science. 2014;345:950–3. doi: 10.1126/science.1253435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang X, Wang H, Wang J, Sun R, Wu J, Liu S, et al. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat Genet. 2011;43:1035–9. doi: 10.1038/ng.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Holton TA, Cornish EC. Genetics and biochemistry of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Cell. 1995;7:1071–83. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.7.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ahmed NU, Park JI, Jung HJ, Yang TJ, Hur Y, Nou IS. Characterization of dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR) genes and their association with cold and freezing stress in Brassica rapa. Gene. 2014;550:46–55. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Guo N, Cheng F, Wu J, Liu B, Zheng S, Liang J, Wang XW. Anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in Brassica rapa. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:426. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Leonard E, Yan Y, Fowler ZL, Li Z, Lim CG, Lim KH, Koffas MAG. Strain improvement of recombinant Escherichia coli for efficient production of plant flavonoids. Mol Pharm. 2008;5:257–65. doi: 10.1021/mp7001472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The reference B. oleracea genome sequence was obtained from Brassica Database (http://brassicadb.org); the reference TO1000 sequence was obtained from the genome sequence (http://plants.ensembl.org/Brassica_oleracea). As one of the data owners, we confirm that we have full permission to use the genome sequence for the purposes of this study (i.e., candidate gene identification and characterization). The use of the reference genome for these purposes was approved by all data owners.


