Abstract
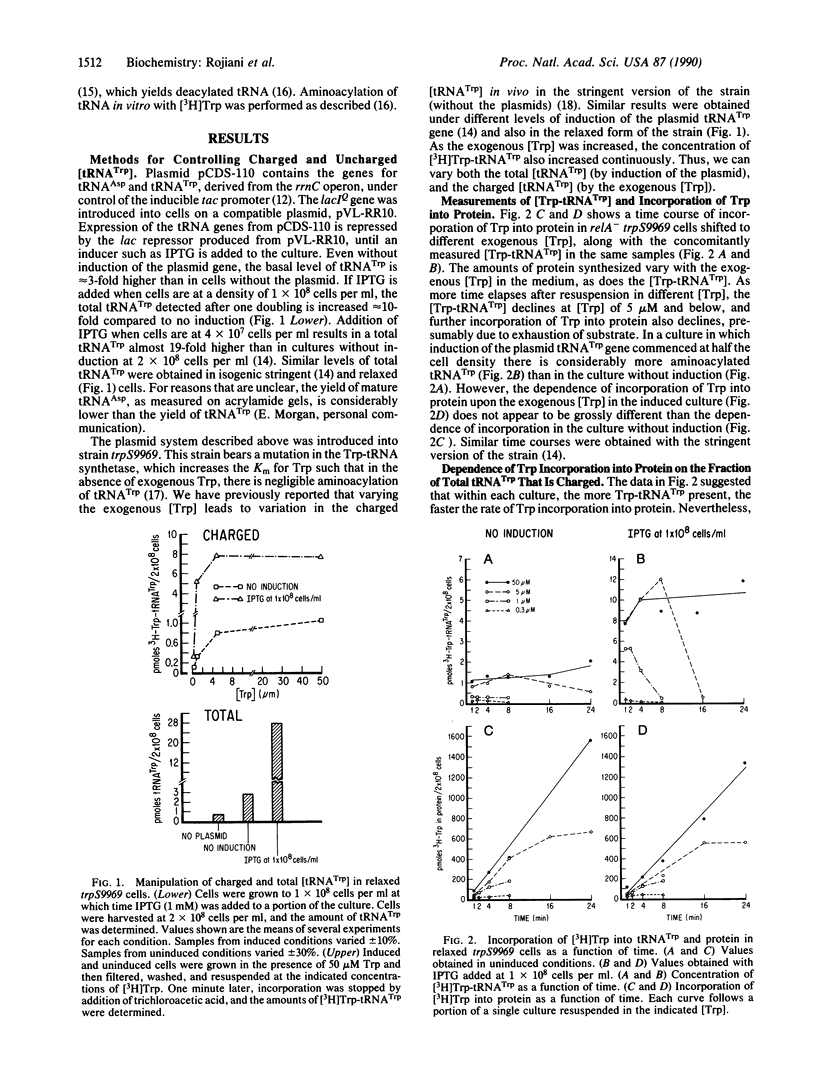
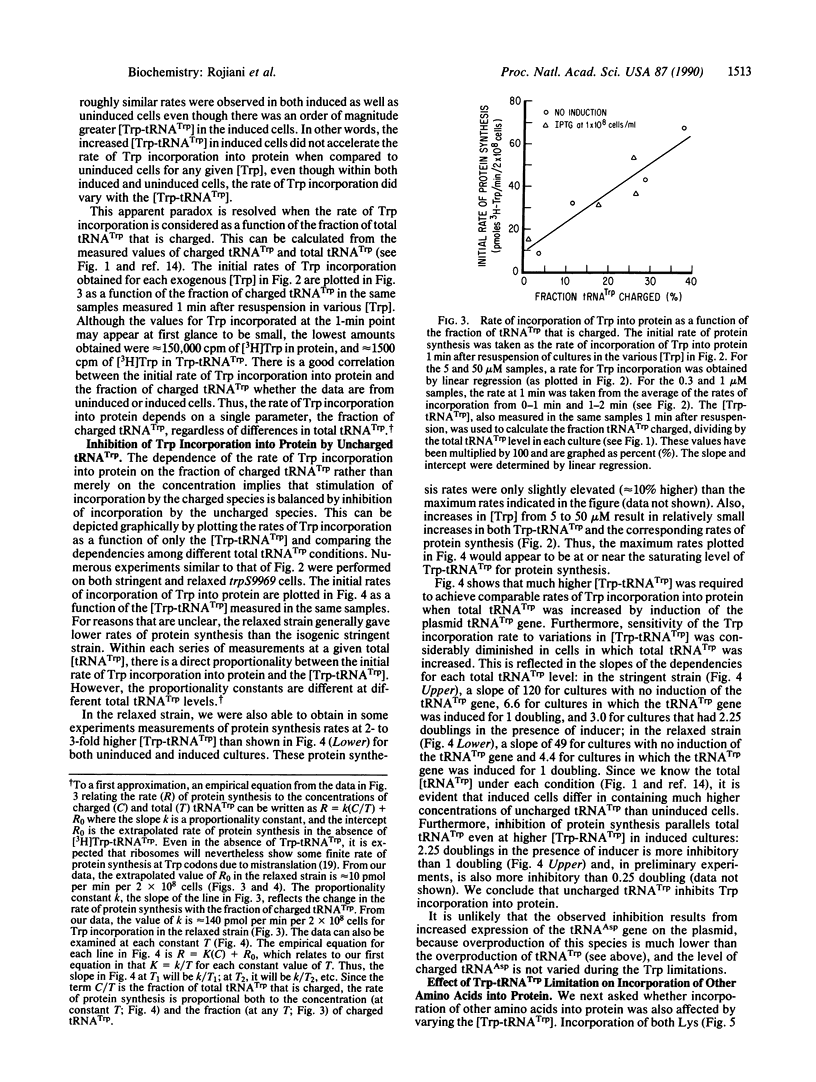
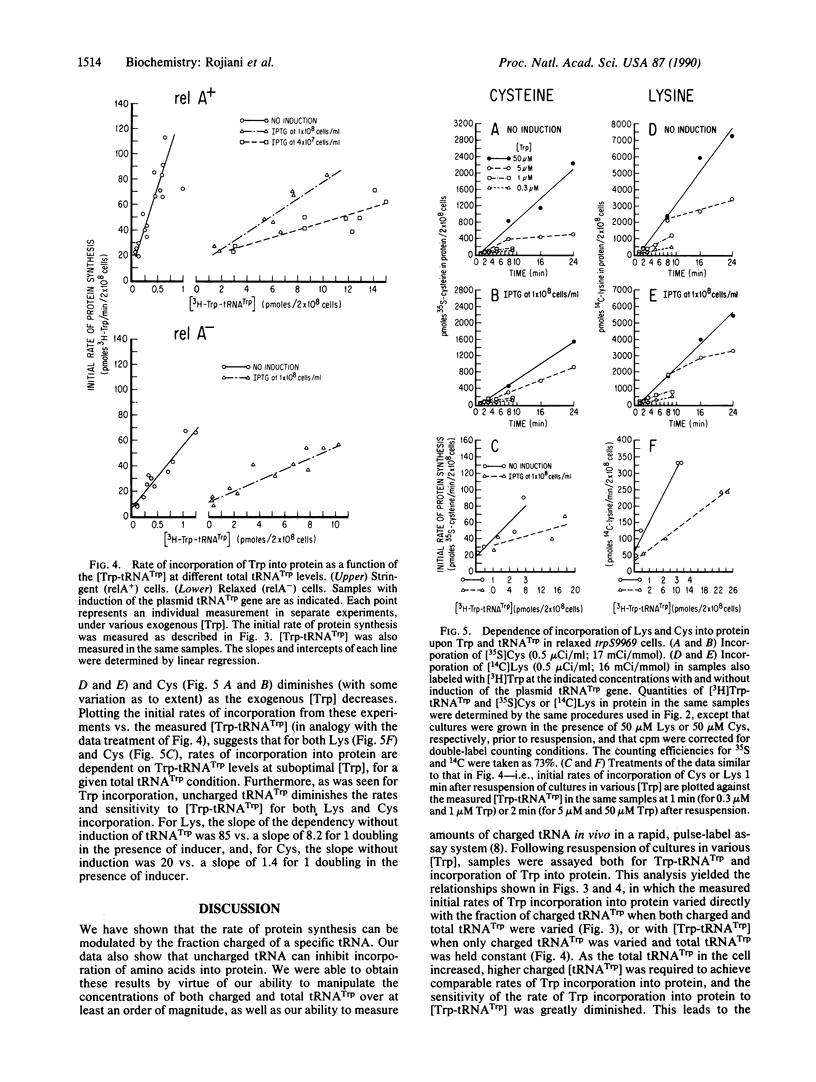
We have continuously monitored Trp-tRNA(Trp) concentrations in vivo and, in the same cultures, measured rates of protein synthesis in isogenic stringent and relaxed strains. We have also manipulated cellular charged and uncharged [tRNA(Trp)] by two means: (i) the strain used contains a Trp-tRNA synthetase mutation that increases the Km for Trp; thus, varying exogenous Trp varies cellular Trp-tRNA(Trp); and (ii) we have introduced into the mutant strain a plasmid containing the tRNA(Trp) gene behind an inducible promoter; thus, total [tRNA(Trp)] also can be varied depending on length of induction. The use of these conditions, combined with a previously characterized assay system, has allowed us to demonstrate that (i) the rate of incorporation of Trp into protein is proportional to the fraction of tRNA(Trp) that is charged; for any given total [tRNA(Trp)], this rate is also proportional to the [Trp-tRNA(Trp)]; (ii) uncharged tRNA(Trp) inhibits incorporation of Trp into protein; and (iii) rates of incorporation into protein of at least two other amino acids, Lys and Cys, are also sensitive to [Trp-tRNA(Trp)] and are inhibited by uncharged tRNA(Trp). Our results are consistent with models of translational control that postulate modulating polypeptide chain elongation efficiency by varying concentrations of specific tRNAs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. F. The effect of tRNA concentration on the rate of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):566–573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann J. E., Lodish H. F. A kinetic model of protein synthesis. Application to hemoglobin synthesis and translational control. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11927–11937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. F., Yarus M. Rates of aminoacyl-tRNA selection at 29 sense codons in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 5;209(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Yanofsky C. Mutants of Escherichia coli with an altered tryptophanyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1283–1294. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1283-1294.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant J. A. Stringent control in E. coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:393–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman E. Effect of rate-limiting elongation on bacteriophage MS2 RNA-directed protein synthesis in extracts of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):619–636. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Jacobzone M., Mercier R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r43–r74. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Block R. Synthesis of guanosine tetra- and pentaphosphate requires the presence of a codon-specific, uncharged transfer ribonucleic acid in the acceptor site of ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1564–1568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekema A., Kastelein R. A., Vasser M., de Boer H. A. Codon replacement in the PGK1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: experimental approach to study the role of biased codon usage in gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2914–2924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben W. E., Morgan E. A. Antitermination of transcription from an Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6789–6793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski H., Goldman E. Quantities of individual aminoacyl-tRNA families and their turnover in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):769–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.769-776.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski H. Incomplete aminoacylation of tRNALeu catalyzed in vitro by leucyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 27;518(2):345–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski H. Negative correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli aminoacyl-tRNA families and their affinities for elongation factor Tu-GTP. J Theor Biol. 1988 Aug 8;133(3):363–370. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koontz S. W., Jakubowski H., Goldman E. Control of RNA and protein synthesis by the concentration of Trp-tRNATrp in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage MS2. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):747–763. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G. Codon-specific binding of deacylated transfer ribonucleic acid to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3195–3202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lührmann R., Eckhardt H., Stöffler G. Codon-anticodon interaction at the ribosomal peptidyl-site. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):423–425. doi: 10.1038/280423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvel C. C., Arps P. J., Rubin B. C., Kammen H. O., Penhoet E. E., Winkler M. E. hisT is part of a multigene operon in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):60–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.60-71.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menninger J. R. Computer simulation of ribosome editing. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 25;171(4):383–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinberger H. J., Sternbach H., Nierhaus K. H. Three tRNA binding sites on Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Lilley R., Little S., Emtage J. S., Yarranton G., Stephens P., Millican A., Eaton M., Humphreys G. Codon usage can affect efficiency of translation of genes in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6663–6671. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojiani M. V., Jakubowski H., Goldman E. Effect of variation of charged and uncharged tRNA(Trp) levels on ppGpp synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6493–6502. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6493-6502.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd K. E., Bochner B. R., Cashel M., Roth J. R. Mutations in the spoT gene of Salmonella typhimurium: effects on his operon expression. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):534–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.534-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. Codon usage in regulatory genes in Escherichia coli does not reflect selection for 'rare' codons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7737–7749. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siehnel R. J., Morgan E. A. Unbalanced rRNA gene dosage and its effects on rRNA and ribosomal-protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):476–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.476-486.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C. L., Rose J. K., Yanofsky C., Yang H. L., Zubay G. Tryptophanyl-tRNA and tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase are not required for in vitro repression of the tryptophan operon. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 3;245(144):131–133. doi: 10.1038/newbio245131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen M. A., Kurland C. G., Pedersen S. Codon usage determines translation rate in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):365–377. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich A. K., Parker J. Strains overproducing tRNA for histidine. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):540–545. doi: 10.1007/BF00338095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Comstock L. J., Vasser M. The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



